Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stat 101 Nonlinear Regression
Uploaded by
Kshitij PalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stat 101 Nonlinear Regression
Uploaded by
Kshitij PalCopyright:
Available Formats
Aspire Mountain Academy
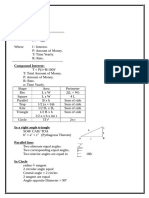
Stat 101 Introduction to Statistics Nonlinear Regression Reference Sheet
General Models
Model General Form Example Applications
Tobacco smoking deaths, capital asset pricing, labor demand and supply, cost of landscaping
Linear y = a +bx
mulch, effect of pulp mill or mine effluent on aquatic ecosystems
Falling objects, projectile motion, car crash deaths, stock market index, concentration of
Quadratic y = ax2 + bx + c
certain medications in blood, general human population growth
x Subway fare in certain cities, bacteria growth, natural temperature drop of many materials,
Exponential y = ab
many component and system failures (especially electronics), radioactive decay
Shock wave from explosions, localized population growth (of both people and animals),
Logarithmic y = a + b(ln x)
principal remaining on a mortgage loan
b Bone length and diameter, metabolic rate and body size, new movie ticket sales,
Power y = ax
temperature-based energy consumption
Data Transformations Table
Some models require transformations. Use the table below to know what needs transforming for your model and how to get the correct coefficients for
your regression model.
StatCrunch Data Transformation
Model General Form Regression
Option In Options Window In Results Window
a = Intercept
Linear y = a +bx Simple Linear X: None Y: None
b = Slope
a = X^2
2 [None, but make sure
Quadratic y = ax + bx + c Polynomial b=X
Poly. Order = 2]
c = Intercept
Intercept
x Transform Intercept in results window with a = e .
Exponential y = ab Simple Linear X: None Y: log(y) Slope
Transform Slope in results window with b = e .
a = Intercept
Logarithmic y = a + b(ln x) Simple Linear X: log(x) Y: None
b = Slope
Intercept
Transform intercept in results window with a = e .
Power y = axb Simple Linear X: log(x) Y: log(y)
Take exponent directly from results window (b = Slope).
You might also like
- ACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Document6 pagesACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Waheed ShaabanNo ratings yet
- 31 Least SquaresDocument39 pages31 Least SquaresgariNo ratings yet
- Stats FormulaDocument2 pagesStats FormulaNam TranNo ratings yet
- Exponents/Logs/Complex NumbersDocument2 pagesExponents/Logs/Complex Numbersmishi19No ratings yet
- MIT6 011s18lec15Document11 pagesMIT6 011s18lec15Patrick NgakouNo ratings yet
- 01 Uic - Algebra 1 - 2017 KeyDocument3 pages01 Uic - Algebra 1 - 2017 KeyJazyl PeralesNo ratings yet
- 01 Uic Algebra 1 2017Document3 pages01 Uic Algebra 1 2017Jazyl PeralesNo ratings yet
- Functions and Graphs Grade 11Document23 pagesFunctions and Graphs Grade 11Reitumetse MolefeNo ratings yet
- GR 12 - Maths - Winter Revision Document - 2023-1Document47 pagesGR 12 - Maths - Winter Revision Document - 2023-1vanessamahlatse81No ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form4Document11 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form4THINES REVI100% (12)
- C21507Document11 pagesC21507alrakevolnivekNo ratings yet
- Ch10 - Curve FittingDocument157 pagesCh10 - Curve FittingshvdoNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formulas CheatsheetDocument3 pagesStatistics Formulas CheatsheetCarmen Bl100% (1)
- Chap - 05 - P1 Sequential Synchronous AnalysisDocument31 pagesChap - 05 - P1 Sequential Synchronous AnalysisTakudzwa KowoNo ratings yet
- 4-Simple Banget Linear RegressionnDocument8 pages4-Simple Banget Linear RegressionnWiga Maulana BaihaqiNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 MIT HSE ResearchDocument21 pagesLecture4 MIT HSE Researchameeque khaskheliNo ratings yet
- Output Feedback and State FeedbackDocument9 pagesOutput Feedback and State FeedbackSteve DemirelNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument26 pagesLinear RegressionPrashant SahuNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesPhysics Formula (AutoRecovered)John Paull CuaNo ratings yet
- Mathimatics - Foundations of Seismic ProcessingDocument16 pagesMathimatics - Foundations of Seismic ProcessingsolomonNo ratings yet
- Engineering FormulasDocument6 pagesEngineering FormulasgkdimpuNo ratings yet
- Session 19-20 - ANT 5001 - 2019-21Document42 pagesSession 19-20 - ANT 5001 - 2019-21Praveen DwivediNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 1DDocument94 pagesKinematics 1DGeethika gorakalaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Formula SheetDocument2 pagesAlgebra Formula Sheettishaoppong452No ratings yet
- Exponents: Saw Wati Hnin (Victoria) Aung Khant Moe (Daniel)Document33 pagesExponents: Saw Wati Hnin (Victoria) Aung Khant Moe (Daniel)Victoria .1117No ratings yet
- Parent Function ReviewDocument2 pagesParent Function ReviewnahjauneeNo ratings yet
- NCM 2nd 4b08 Supplementary Examples Exercise On Logarithmic Transformation eDocument13 pagesNCM 2nd 4b08 Supplementary Examples Exercise On Logarithmic Transformation eapi-517118868No ratings yet
- Stats Cheatsheet FinalDocument2 pagesStats Cheatsheet FinalThulasi KumarNo ratings yet
- Stat 151 - Final ReviewDocument15 pagesStat 151 - Final ReviewHo Uyen Thu NguyenNo ratings yet
- 04 Logistic RegressionDocument46 pages04 Logistic RegressionKHUSHI JAINNo ratings yet
- Derivative and Antiderivative Shortcuts: NotesDocument1 pageDerivative and Antiderivative Shortcuts: NotesyaaapNo ratings yet
- UPenn Intro To Models - Lect 1Document1 pageUPenn Intro To Models - Lect 1SicklesNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetVien LaCroseNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument27 pagesLinear RegressionAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Loglog Equation For HurstDocument22 pagesLoglog Equation For HurstManuel HerreraNo ratings yet
- DF FormulaeDocument7 pagesDF FormulaeBentojaNo ratings yet
- 10 RDDocument16 pages10 RDGing lonmnNo ratings yet
- General Linear Model & Classical Inference: London, SPM-M/EEG CourseDocument24 pagesGeneral Linear Model & Classical Inference: London, SPM-M/EEG CourserkNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear Regression & Nonlinear Regression ModelsDocument51 pagesMultiple Linear Regression & Nonlinear Regression Modelsxiaohui qiNo ratings yet
- Economic Maths Lesson Summary Fall 2020Document15 pagesEconomic Maths Lesson Summary Fall 2020Nabeel AdilNo ratings yet
- Tute1 QuestionsDocument4 pagesTute1 QuestionsLucas BakkerNo ratings yet
- Functions (Algebraic) Summary MAT1510Document1 pageFunctions (Algebraic) Summary MAT1510heathercollins203No ratings yet
- Presentation - COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY FOR MACHININGDocument28 pagesPresentation - COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY FOR MACHININGMuhammad Atif Qaim KhaniNo ratings yet
- Algebra I - GA Milestones Formulas PDFDocument1 pageAlgebra I - GA Milestones Formulas PDFAlexander Roman SichNo ratings yet
- Qm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dDocument13 pagesQm Summary Final: h μ x σ σ s s σ s ρ δ dJan BorowskiNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods in Economics Panel Data and Generalized Least SquaresDocument24 pagesQuantitative Methods in Economics Panel Data and Generalized Least SquaresWazzupWorldNo ratings yet
- A2T Final Exam 11 FormulaeDocument2 pagesA2T Final Exam 11 FormulaeNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Essential Mathematics For Economics and Business Teresa Bradley Paul PattonDocument5 pagesSolution Manual For Essential Mathematics For Economics and Business Teresa Bradley Paul PattonKAFIL KANWER50% (2)
- Jacobian MethodsDocument23 pagesJacobian MethodsOdhieNo ratings yet
- ZTZMGob JDocument7 pagesZTZMGob JObert MupomokiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01 - Functions, Notation, Domain, Range 2022Document8 pagesLesson 01 - Functions, Notation, Domain, Range 2022h6p4jbtpysNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 2DRV2Document9 pagesUnit 3 2DRV2sajalsinghal1512No ratings yet
- State Feedback (Continued), Optimal Control: Morten O. Alver (Based On Slides by Morten D. PedersenDocument43 pagesState Feedback (Continued), Optimal Control: Morten O. Alver (Based On Slides by Morten D. PedersenWiccy IhenaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Runoff Modelling Production Function 2023 2024Document50 pagesSession 3 Runoff Modelling Production Function 2023 2024Tiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- AmathDocument9 pagesAmathAnnette ChiangNo ratings yet
- Review All Chapters Prob-Stats 2022 - PRINTDocument26 pagesReview All Chapters Prob-Stats 2022 - PRINTLe Tran Vu HoangNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics - Session 9Document60 pagesBusiness Statistics - Session 9caprolactamcl4571No ratings yet
- 09 Num-Lin-Alg NewDocument38 pages09 Num-Lin-Alg NewGandNo ratings yet
- OU Classroom PoliciesDocument3 pagesOU Classroom PoliciesKshitij PalNo ratings yet
- Sri InternationalDocument46 pagesSri InternationalKshitij PalNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel PollutoinDocument10 pagesFossil Fuel PollutoinKshitij PalNo ratings yet
- AN 3110 Internet PowerPoint LectureDocument135 pagesAN 3110 Internet PowerPoint LectureKshitij PalNo ratings yet
- AN 3110 Computer Tech PowerPoint LectureDocument61 pagesAN 3110 Computer Tech PowerPoint LectureKshitij PalNo ratings yet
- RC Shear Wall Analysis and DesignDocument24 pagesRC Shear Wall Analysis and DesignGifari ZulkarnaenNo ratings yet
- The Generalized Spectral Radius and Extremal Norms: Fabian WirthDocument24 pagesThe Generalized Spectral Radius and Extremal Norms: Fabian WirthMohammad SoroushNo ratings yet
- Determining of Planck'S Constant Using Leds: The Physics Teacher January 2008Document4 pagesDetermining of Planck'S Constant Using Leds: The Physics Teacher January 2008Rahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Aristo Science Workbook 1A (Answer) PDF Solubility EvaporationDocument1 pageAristo Science Workbook 1A (Answer) PDF Solubility Evaporationntlroblox870% (1)
- Hunting The Elements Video QuestionsDocument4 pagesHunting The Elements Video Questionsapi-26400457150% (4)
- Maths Form ThreeDocument184 pagesMaths Form ThreeAgustino WaitihacheNo ratings yet
- Kokusho 2004Document9 pagesKokusho 2004Hưng Huỳnh TấnNo ratings yet
- Good Practice Guide For Strategic Noise MappingDocument129 pagesGood Practice Guide For Strategic Noise Mappingromina_cmbNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity and Half LifeDocument5 pagesRadioactivity and Half LifeMaria Sol LambertNo ratings yet
- How To Download Notes Guides Past PapersDocument33 pagesHow To Download Notes Guides Past PapersHassan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 2019 2020Document67 pagesFluid Mechanics 2019 2020basic langNo ratings yet
- Implosions For The Wiki PagesDocument3 pagesImplosions For The Wiki PagesnoNo ratings yet
- 5 Physics Light Test Name: For The Multiple Choice Questions CIRCLE The Letter of The BEST Answer 1Document11 pages5 Physics Light Test Name: For The Multiple Choice Questions CIRCLE The Letter of The BEST Answer 1Rafael Marco ManubayNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics With Lab Flumec1: School of Engineering and ArchitectureDocument134 pagesFluid Mechanics With Lab Flumec1: School of Engineering and ArchitectureSamantha SamanthaNo ratings yet
- Aditya College of Engineering & Technology (A), Surampalem Course End Survey Form-CSE-DSDocument4 pagesAditya College of Engineering & Technology (A), Surampalem Course End Survey Form-CSE-DSahmedali51367No ratings yet
- Is 3075Document12 pagesIs 3075rajeevkumarrajeevNo ratings yet
- Waves II: 5.1 Reflection & Transmission of WavesDocument21 pagesWaves II: 5.1 Reflection & Transmission of WavesMatias BatallaNo ratings yet
- 02 Mvax 12Document1 page02 Mvax 12sikander843562No ratings yet
- Acs Jcim 0c00285Document5 pagesAcs Jcim 0c00285hightower3No ratings yet
- Modelling, Simulation and Monitoring of IM For EMU TrainDocument6 pagesModelling, Simulation and Monitoring of IM For EMU Trainjaroldane1000No ratings yet
- A) B) C) D) E) : Thermodynamics Technical AptitudeDocument11 pagesA) B) C) D) E) : Thermodynamics Technical AptitudeAvinash GateNo ratings yet
- Test-Summary Formation FactorDocument15 pagesTest-Summary Formation FactorWanucy Barroso RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Propagation and Attenuation Characteristics of Various Ground VibrationsDocument12 pagesPropagation and Attenuation Characteristics of Various Ground VibrationsTony Christian Canahua ChoquezaNo ratings yet
- Lectures - of - Polygons - BG - 1997Document164 pagesLectures - of - Polygons - BG - 1997ah.sooriNo ratings yet
- Smoke Detector Testing: Allen Hess - CFAA Presentation April 2011Document36 pagesSmoke Detector Testing: Allen Hess - CFAA Presentation April 2011parallax1957No ratings yet
- Actuator Instruction Manual - RCEL006-009Document2 pagesActuator Instruction Manual - RCEL006-009Josue Reyes GironNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer (SHMT) : CHE-402 Date: 08/11/2016Document23 pagesSimultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer (SHMT) : CHE-402 Date: 08/11/2016Atif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Application of Geophysical Methods in Civil Engineering: January 2011Document13 pagesApplication of Geophysical Methods in Civil Engineering: January 2011Abubakar Ibrahim DayyabuNo ratings yet
- Removal of Impurities in Aluminum by Use of FluxesDocument5 pagesRemoval of Impurities in Aluminum by Use of FluxesLilian Jefferson MalavaziNo ratings yet
- Final Paper Automatic Sortingmachineusing Conveyor Belt 170386Document6 pagesFinal Paper Automatic Sortingmachineusing Conveyor Belt 170386Nedaa AbboushiNo ratings yet