Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Term 1 Science Notes Year 10
Term 1 Science Notes Year 10
Uploaded by
chloeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Term 1 Science Notes Year 10
Term 1 Science Notes Year 10
Uploaded by
chloeCopyright:
Available Formats
Term 1 Science notes
Glossary
Ionic compound: compounds consisting of ions, formed because of the electrostatic attraction between
anions and cations
Compound: substance formed from two or more chemical elements chemically bonded together
Ion: an atom or molecule that carries a electric charge
Anion: negatively charged ions (non-metals)
- Cation: positively charged ions (metals)
G: gas
L: liquid
Aq: aqueous
S: solid
Spectator ion: an ion involved in the chemical reaction but is not changed throughout the reaction staying
the same before and after the reaction
Net ionic equation: a chemical equation that shows only those elements, compounds and ions that are
directly involved in the chemical equation
Formula writing examples (cross method)
NH41+ and CO32- --> (NH4)2CO3 (ammonium carbonate)
Need to balance equation (same quantities on each side)
Like maths you can simplify (if all of the numbers are
same can simplify to 1 therefore don’t need to write
numbers)
Solubility table (provided)
Solubility table is used to predict whether a precipitate will be formed
Polyatomic ions (provided)
Nitrate: NO31- (CHARGE OF 1-)
Hydroxide: OH1-(CHARGE OF 1-)
Sulfate: SO42-(CHARGE OF 2-)
Carbonate: CO32-(CHARGE OF 2-)
Phosphate: PO43-(CHARGE OF 3-)
Ammonium: NH41+(CHARGE OF 1+)
Chemical reactions
Reaction Example
acid + metal → a salt + hydrogen Word equation: Sulfuric acid + Magnesium --> Magnesium
sulfate + hydrogen
Chemical equation: H2SO4 + Mg (s) --> MgSO4 (aq) +
H2 (g)
acid + carbonate → a salt+ carbon Word equation: Hydrochloric acid + magnesium carbonate
dioxide + water --> magnesium chloride + carbon dioxide + water
Chemical equation: 2HCl (aq) + MgCO3 (aq) --> MgCl2 (aq)
+ CO2 +H2O
acid + base → a salt + water Word equation: Sulfuric acid + sodium hydroxide -->
sodium sulfate + water
Chemical equation: H2SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH --> Na2SO4 +
2H2O
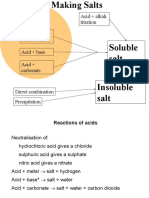
Acids and Bases
pH = 7 (neutral)
ways to identify pH level: litmus paper, universal indicator
Acids Bases
pH < 7 pH > 7
corrosive corrosive
Sour taste Sour taste
Vinegar, citric acid, carbonic acid Toothpaste, soap, ammonia
Combustion
Combustion is the rapid reaction of a substance usually a fuel, with oxygen gas to produce heat
3 things needed for combustion to occur
- fuel
- Oxygen
- Activation energy
Complete combustion
fuel + oxygen -------- > carbon dioxide + water
Example: methane + oxygen ----- > carbon dioxide + water
CH4 (g) + O2 (g) ______ > CO2 (g) = H2O (l)
Incomplete combustion
Methane + oxygen -> carbon monoxide + water
Ethanol + oxygen -> carbon monoxide + water
Octane (in petrol) + oxygen -> carbon monoxide + water
Cellulose )wood) + oxygen -> carbon monoxide + carbon soot + water
Decomposition
Decomposition reactions are the process in which a chemical break up into simpler parts
General form: AB -> A + B
Elements: CO -> C + O
Compounds: Ca(OH) ₂ -> CaO + H₂O
Respiration
Respiration is the process in living organisms involving the production of energy
Speed, distance and time
Speed:
- SI unit: m/s, m s−1
- Scalar
- Speed it the time rate at which an object is moving along a path
Distance
- SI unit: m (meters)
- Scalar
- Distance refers to how much ground an object had covered during its motion
Time:
- SI unit: s (seconds)
- scalar
- Time is the progression of events from the past to the present into the future
Speed, time, distance triangle (STD!!)
Displacement
- SI unit: m/s
- vector
- Displacement refers to how far out of place an object it from the original position
Displacement / time graphs
Displacement time graph Distance time graph
- can reach negative points (moved past - can’t reach negative points (can’t have
original point) negative distance)
- Shows the displacement of a moving - Shows the distance and speed of an object
object changed through time changed with time
Acceleration
Acceleration: the rate of change of velocity with respect to time
Symbol: a
SI unit: ms-2 (m/s/s)
Acceleration = Change in Velocity
Change in time
a = v = v-u
t t
where a = acceleration in ms-2
v = change in velocity (ms-1)
t = change in time (s)
v = final velocity (ms-1)
u = initial velocity (ms-1)
Velocity:
- SI unit: m/s
- Vector
- Velocity is the measure of level and direction of movement
Acceleration and Velocity / time graphs
You might also like
- WPS D1.6 Annex m1 PDFDocument1 pageWPS D1.6 Annex m1 PDFbollascribdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSC FormulasDocument6 pagesChemistry HSC Formulashpgc101100% (1)
- Redox and Electrode PotentialsDocument21 pagesRedox and Electrode PotentialsAaron Joshua AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Sharma Science Classes: Science Notes Chapter 1 (Chemical, Reaction and Equations)Document7 pagesSharma Science Classes: Science Notes Chapter 1 (Chemical, Reaction and Equations)Aman YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations ReactionsDocument57 pagesChemical Equations ReactionsCacey Daiwey CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument32 pagesBalancing Chemical EquationsAple RigorNo ratings yet
- 1103 SpringShorts PatternDocument19 pages1103 SpringShorts PatternKlaudia LewickaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Chemical Reactions and EquationsgustafNo ratings yet
- 432 eDocument404 pages432 eIJAZ M RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Academic Science Notes Exam, Course ReviewDocument23 pagesGrade 10 Academic Science Notes Exam, Course ReviewJermaine Mercado100% (1)
- Chapter 11 - Chemical Reactions PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 11 - Chemical Reactions PDFapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Math EE IBDocument16 pagesMath EE IBCalc girl ReddingtonNo ratings yet
- Ut ThicknessDocument130 pagesUt Thicknessjar_2100% (3)
- Loading and Unloading of LPG Tanker ShipDocument13 pagesLoading and Unloading of LPG Tanker ShipMohammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Md310 Quick ManualDocument55 pagesMd310 Quick ManualHitesh PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Final Intro To Chemical ReactionsDocument52 pagesFinal Intro To Chemical ReactionsGerma Comanda100% (1)
- Chemical ReactionsDocument52 pagesChemical ReactionsDella Fajar PNo ratings yet
- EPB Short Course 2010Document94 pagesEPB Short Course 2010sCoRPion_trNo ratings yet
- Describing Chemical ReactionsDocument42 pagesDescribing Chemical ReactionshypezakramNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Asam BasaDocument5 pagesReaksi Asam BasaHendra SaputraNo ratings yet
- CHEM (1st Topic)Document6 pagesCHEM (1st Topic)Lyanna VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chem121-Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument87 pagesChem121-Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsberkitenberkanNo ratings yet
- Colin Murray 18.2 Balancing Oxidation Reduction EquationsDocument49 pagesColin Murray 18.2 Balancing Oxidation Reduction EquationsDrive Baiq Nila Sari NingsihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesChapter 7 Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsKhara TeanoTanNo ratings yet
- N (A) Science (Chem) CHP 7b Writing Chemical EquationsDocument13 pagesN (A) Science (Chem) CHP 7b Writing Chemical EquationshamsterishNo ratings yet
- Chemistry E2B (Formulae and Equations)Document9 pagesChemistry E2B (Formulae and Equations)Mable MoeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions in Aqueous Solutioniam_crazii_4_mhe100% (2)
- Kinetics NotesDocument19 pagesKinetics NotesMichaela ZanetteNo ratings yet
- RedoxreactionDocument11 pagesRedoxreactionWindows AjsNo ratings yet
- 0 0 +1 - 1 Oss of Lectron, Xidation, Educing Gent Ain of Lectron, EductionDocument6 pages0 0 +1 - 1 Oss of Lectron, Xidation, Educing Gent Ain of Lectron, EductionTheresaNo ratings yet
- HTTPWWW - occc.edukmbaileyChem1115TutorialsNet Ionic Eqns Answers - HTMDocument1 pageHTTPWWW - occc.edukmbaileyChem1115TutorialsNet Ionic Eqns Answers - HTMVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2024Document62 pagesElectrochemistry 2024shellodkomaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 5 - Double Displacement Reactions: Report FormDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT 5 - Double Displacement Reactions: Report FormNguyễn Hoàng ĐăngNo ratings yet
- RedOx Rxns PDFDocument31 pagesRedOx Rxns PDFRileShampionNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry NotesDocument57 pagesIndustrial Chemistry NotesPatricia de LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equi StationDocument18 pagesChemistry Equi StationSALSABILA SALSABILANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1928 Electrochemistry 29Document76 pagesChapter 1928 Electrochemistry 29Kent NguyenNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument5 pagesStoichiometryZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- Half and Ionic Equations (GCSE)Document31 pagesHalf and Ionic Equations (GCSE)william.ongeri.tutoringNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations: Preparation For College Chemistry Columbia University Department of ChemistryDocument31 pagesChemical Equations: Preparation For College Chemistry Columbia University Department of ChemistryLakshmi SinghNo ratings yet
- Definitions 12Document37 pagesDefinitions 12YEUNG WAN CHUEN ANGELIQUENo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Part 2: Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument37 pagesUnit 5 - Part 2: Redox Reactions and ElectrochemistryBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- 03 Volumetric AnalysisDocument8 pages03 Volumetric AnalysisRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 4Andrea PerezNo ratings yet
- SHS Gr.12 Chap 5Document25 pagesSHS Gr.12 Chap 5Harold BunnydotNo ratings yet
- Writing Balancing and Predicting Products of ChemicalDocument6 pagesWriting Balancing and Predicting Products of ChemicalRonald Anthony Gebilaguin BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Half and Ionic Equations (GCSE)Document31 pagesHalf and Ionic Equations (GCSE)william.ongeri.tutoringNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outline: 8.6 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDocument13 pagesChapter Outline: 8.6 Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsNurudin ForzaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: The Periodic Table and ChargesDocument4 pagesStoichiometry: The Periodic Table and ChargesLei YinNo ratings yet
- Lec 02Document17 pagesLec 02zgazga amirNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8.3 (Ionic Equation Step by Step) SolutionsDocument3 pagesWorksheet 8.3 (Ionic Equation Step by Step) SolutionsChantoni50% (2)
- ELETROCHEMISTRYDocument42 pagesELETROCHEMISTRYSomayya AnsaryNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument30 pagesRedoxMelanie perez cortezNo ratings yet
- Xi Redox Reaction HoDocument7 pagesXi Redox Reaction Homanishkushwah640No ratings yet
- Chem 115: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesChem 115: Types of Chemical ReactionsJhin KhadaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument33 pagesOxidation Reduction ReactionsSaeful Ghofar100% (2)
- Chemical Kinetics Cinetica ChimicaDocument42 pagesChemical Kinetics Cinetica Chimicalavinia diaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions LectureDocument5 pagesRedox Reactions LectureKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document44 pagesChapter 11Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Salts FormationDocument19 pagesSalts FormationUrwa Abdul MannanNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical EquationsDocument66 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical EquationsanacercetNo ratings yet
- Chem 26 3rd LE NotesDocument18 pagesChem 26 3rd LE NotesYshaReyesNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument56 pagesMetalsTariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic 1 IALDocument22 pagesChemistry Topic 1 IALLong YipNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Balancing by Half Reaction 2020Document30 pages10.3 Balancing by Half Reaction 2020Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 10-11 ch05 - Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument40 pagesPertemuan 10-11 ch05 - Oxidation Reduction ReactionsArifah YumnaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReviewDocument20 pagesRedox Reviewapi-3706290100% (1)
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Interface Sai-Sp User GuideDocument88 pagesStructural Analysis Interface Sai-Sp User GuideThanga PandiNo ratings yet
- Apparel Iii To Viii PDFDocument53 pagesApparel Iii To Viii PDFRaja Prabhu100% (1)
- Demand & Consumer Behaviour - ppt3Document31 pagesDemand & Consumer Behaviour - ppt3Prerna MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Cim NotesDocument30 pagesCim NotesS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- Softy Ice Cream Machine Prices Call: 91-9899332022Document2 pagesSofty Ice Cream Machine Prices Call: 91-9899332022Brand PNo ratings yet
- C Program To Find The TraceDocument2 pagesC Program To Find The TraceRohit SidNo ratings yet
- TR 9000 Series BrochureDocument2 pagesTR 9000 Series BrochureSreejith SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- PQR - WPS Review 2021Document21 pagesPQR - WPS Review 2021problematic NymphNo ratings yet
- Quiz - RAC Part Two Sp19c (Logan Malone 2018)Document10 pagesQuiz - RAC Part Two Sp19c (Logan Malone 2018)Martha Treviño100% (1)
- Siebel 8.1 Certifications Question AnswersDocument33 pagesSiebel 8.1 Certifications Question AnswersSweta SinghNo ratings yet
- WCN3-1056SR-A11R Rev.A0Document4 pagesWCN3-1056SR-A11R Rev.A0BlablacarNo ratings yet
- Peer-to-Peer File Sharing SystemDocument7 pagesPeer-to-Peer File Sharing SystemakanshaNo ratings yet
- WebandsocialDocument6 pagesWebandsocialDheeraj JakkuvaNo ratings yet
- 12.03.22 & 14.03.22 - JR - STAR CO SUPER CHAINA (MODEL-A&B) - SYLLABDocument2 pages12.03.22 & 14.03.22 - JR - STAR CO SUPER CHAINA (MODEL-A&B) - SYLLABsriNo ratings yet
- Current Flow and Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesCurrent Flow and Ohm's LawJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Overview of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine VAWT Is OneDocument6 pagesOverview of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine VAWT Is OneAjeem DurraniNo ratings yet
- 2 - Data TransferDocument22 pages2 - Data TransferRazinR8No ratings yet
- BSC Itim May 2013BSC IT Prevoues Question PaperDocument28 pagesBSC Itim May 2013BSC IT Prevoues Question PaperPurushothama KilariNo ratings yet
- Learning Reinforcement 6 J.villanueva Gmath 2567Document4 pagesLearning Reinforcement 6 J.villanueva Gmath 2567Sittie Ainna Acmed UnteNo ratings yet
- Doec Question Bank: Ut 2 and Yt 2)Document4 pagesDoec Question Bank: Ut 2 and Yt 2)Aditya DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Problems Involving Polynomial FunctionsDocument16 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Problems Involving Polynomial FunctionsRIZAL ZANORTE0% (1)
- MinitabDocument30 pagesMinitabAruni JayathilakaNo ratings yet