Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GSB
Uploaded by
bsudhareddyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GSB
Uploaded by
bsudhareddyCopyright:
Available Formats
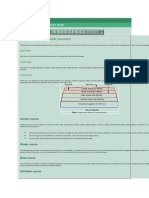
GSB - Granular Sub Base is the layer in road foundation just above the compacted soil layer
(the compacted soil layer is called subgrade).
Many times, when the road passes through an area where there are changes of water trying to
cross the road through its foundation, or where the road foundation is liable to be submerged
in water, it is desirable to have a layer of special material in foundation which prevents natural
ground water to reach the upper layers of road (which are top wearing course and other base
layers of bitumen).
GSB or granular sub base is typically a material which prevents capillary water to rise to top
road layers as its particle size is planned in such a way that the capillary action stops and can’t
go beyond GSB. Secondly it has to act as a medium where water can pass through without
damaging other road layers. The particles of GSB even in compacted form have sufficient voids
in between so that water from one side of road can seep through and reach the other side of
road without damaging any other layers which would otherwise lead to rutting in road due to
foundation (base) failure, or give rise to problems like erosion.
Coming on to property of GSB, the GSB material is expected to have two main properties.
1. Strength to act as a good base for road foundation where no settlement can
happen even on heavy loading by traffic.
2. IT should have such a distribution of particles (Gradation) that even after full
compaction when it is tightly packed, there are sufficient small voids between
particles to allow water to pass through and simultaneously discourage
capillary rise.
The above two properties are controlled by certain tests whose limits are defined for various
roads in text books and quality control manuals published by various agencies.
As GSB is required in bulk quantity in road construction commercially speaking one more
property it should have is to be cheap. The GSB material is normally available from dry river
beds as coarse pebbles left once sand is taken away by water. In some places where river
mining is not allowed, such material is not naturally available nearby crushed stones as per
required gradation is used which is relatively costly.
To adjust the gradation of GSB so that mix has required proportion of each size of particles
sometimes sandy soil id also mixed in pebbles obtained from river bed and thoroughly mixed
by Loader or excavator machine. Often to increase the yield of mixed material contractors try
to add more soil than required as per design. This act is very dangerous as the entire purpose
of laying GSB layer would be beaten if proper gradation of particles as per design or
specifications is not maintained.
GSB thickness is at least 200 mm. Ideally the bottom 100 mm is to act as filter layer so that
rainwater does not enter the subgrade. The top 100 mm is supposed to act as a drainage layer
so that water is drained out horizontally into the earthen shoulder and away from the
pavement.
You might also like
- Group 4 PresentationDocument96 pagesGroup 4 PresentationClarenz BragaNo ratings yet
- Pavement Materials and SpecificationsDocument16 pagesPavement Materials and Specificationsjun jun100% (2)
- Footing - ChecklistDocument2 pagesFooting - ChecklistbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Cycles WorksheetanswersDocument2 pagesCycles WorksheetanswersRaheem Don Breedz Phillips0% (1)
- Road StructureDocument10 pagesRoad StructureMohammed NawzanNo ratings yet
- Typical Crossection of Road: Engineering Practice and Construction ManagementDocument8 pagesTypical Crossection of Road: Engineering Practice and Construction ManagementSyed Waseem AbbasNo ratings yet
- Sub GradeDocument6 pagesSub GradeIra AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Highway ConstructionDocument80 pagesHighway Constructionsarat100% (1)
- 1.construction of W.B.M RoadsDocument12 pages1.construction of W.B.M RoadsRubel RanaNo ratings yet
- Typical Layers of A Flexible PavementDocument5 pagesTypical Layers of A Flexible Pavementruel galutanNo ratings yet
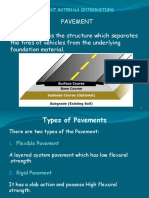
- Pavement The Pavement Is The Structure Which Separates The Tires of Vehicles From The Underlying Foundation MaterialDocument23 pagesPavement The Pavement Is The Structure Which Separates The Tires of Vehicles From The Underlying Foundation MaterialSmart EngineerNo ratings yet
- Road LayersDocument6 pagesRoad LayersNecmi HocaNo ratings yet
- Components of Road StructureDocument13 pagesComponents of Road StructureAmanuel AzemeteNo ratings yet
- Earthworks1 (1) .PDF - Adobe Acrobat ProDocument6 pagesEarthworks1 (1) .PDF - Adobe Acrobat ProPeolebleNo ratings yet
- HWAYDocument2 pagesHWAYMarc Anthony de Villa100% (1)
- Construction of Embankment and Sub-GradeDocument63 pagesConstruction of Embankment and Sub-Gradeਸੁਖਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਾਂਗਟ100% (1)
- Conceptual Questions: and Gradation. Drainage Requirements Often Conflict With Separation andDocument2 pagesConceptual Questions: and Gradation. Drainage Requirements Often Conflict With Separation andEDEN2203No ratings yet
- Water Bound MacadamDocument4 pagesWater Bound MacadamAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering Lab Assignment#03Document73 pagesHighway Engineering Lab Assignment#03tayyabNo ratings yet
- 3.5 RoadDocument6 pages3.5 RoadMohammad Abid YusofNo ratings yet
- Geofabrics Track Design Guide - 1 PDFDocument12 pagesGeofabrics Track Design Guide - 1 PDFRavi SalimathNo ratings yet
- Structural Components of A Flexible PavementDocument8 pagesStructural Components of A Flexible Pavementragunas tatyaNo ratings yet
- Desirable Characteristics: Module 1: Introduction Introduction To Pavement DesignDocument21 pagesDesirable Characteristics: Module 1: Introduction Introduction To Pavement DesignBharath SpidyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Highway PavementsDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Highway PavementsAmith SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement Techniques: Figure 1. Preloading of SoilDocument10 pagesGround Improvement Techniques: Figure 1. Preloading of Soilgel prelligeraNo ratings yet
- Typical Road Structure Cross Section PDFDocument5 pagesTypical Road Structure Cross Section PDFbilalNo ratings yet
- A Mini Project On Bituminous Road LayersDocument20 pagesA Mini Project On Bituminous Road Layersapi-1988935887% (39)
- An Overview To The Construction of Road PavementsDocument21 pagesAn Overview To The Construction of Road PavementsliuhoyinNo ratings yet
- Additional GuideDocument82 pagesAdditional GuideObsinet ObsinetNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Unpaved SurfacesDocument10 pagesPreparation of Unpaved SurfacesKathleen Faith TibonNo ratings yet
- Cc302 Highway Engineering: Razif Fitri Bin Radzwan 06DKA12F1097Document44 pagesCc302 Highway Engineering: Razif Fitri Bin Radzwan 06DKA12F1097Ruzengulalebih ZEta's-Listik100% (1)
- California Bearing RatioDocument13 pagesCalifornia Bearing RatioGABRIELNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Lecture1 CIV241Document64 pagesUnit2 - Lecture1 CIV241Soumya MishraNo ratings yet
- Pavement and It's TypesDocument46 pagesPavement and It's TypesWazeer HosseinNo ratings yet
- 15cv833-Pavement DesignDocument90 pages15cv833-Pavement DesignMEHRAN KAPRANo ratings yet
- 3.1 DCC30103 - Chapter 3.1 Construction of Flexible PavementDocument56 pages3.1 DCC30103 - Chapter 3.1 Construction of Flexible PavementFATIN NABILA100% (1)
- Session 6 - DeJulio Compatibility Mode PDFDocument32 pagesSession 6 - DeJulio Compatibility Mode PDFCE PassajNo ratings yet
- Document Siri 2Document65 pagesDocument Siri 2Hema Chandra Reddy KarimireddyNo ratings yet
- Poor DraingeDocument3 pagesPoor DraingeDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pavement DesignDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Pavement DesignPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Highway & Railroad Engineering: 2 Trimester - Second Half SY 2020 - 2021Document34 pagesHighway & Railroad Engineering: 2 Trimester - Second Half SY 2020 - 2021usernotfound404No ratings yet
- Sub BaseDocument5 pagesSub BaseKrugerNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Types of Pavements & Load Distribution UpdatedDocument12 pagesModule-1 Types of Pavements & Load Distribution UpdatedHuzaifa ZafarNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement Design and Its Coast Elevation: J.Venkata Sai Sumanth, G.Nirmala, P.Pradeep KumarDocument6 pagesFlexible Pavement Design and Its Coast Elevation: J.Venkata Sai Sumanth, G.Nirmala, P.Pradeep KumarAyanwale-cole pelumi AkeemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pavement DesignDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Pavement DesignChris EminentNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement 1Document3 pagesFlexible Pavement 1Jakinur HossainNo ratings yet
- Typical Layer of Flexible PavementDocument2 pagesTypical Layer of Flexible PavementrubydelacruzNo ratings yet
- (نسخة) (نسخة) Eighth Lecture Pavement TypesDocument11 pages(نسخة) (نسخة) Eighth Lecture Pavement Typesحميد مجيدNo ratings yet
- Permeable Pavements: New Technique For Construction of Road Pavements in IndiaDocument7 pagesPermeable Pavements: New Technique For Construction of Road Pavements in IndiaSALIL GUPTANo ratings yet
- RoadsDocument35 pagesRoadssalahudinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pavement DesignDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Pavement DesignDaniel Berhane100% (1)
- Introduction To Pavement DesignDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Pavement Designmvap2856No ratings yet
- Typical Road Structure Cross Section DetailsDocument4 pagesTypical Road Structure Cross Section DetailsDipankar OkayNo ratings yet
- FW Terram Roadhighway Brochure 1 PDFDocument32 pagesFW Terram Roadhighway Brochure 1 PDFCarmen Law NtNo ratings yet
- Earthworks-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesEarthworks-WPS OfficeMichelle Awa-aoNo ratings yet
- Steps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsDocument13 pagesSteps To Improve Roads On Black Cotton SoilsPerkresht PawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Highway Materials-TerminologiesDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Highway Materials-TerminologiesSolomon MugeraNo ratings yet
- General IntroductionDocument12 pagesGeneral IntroductionKanimozhi SNo ratings yet
- Constructing The RoadbedDocument28 pagesConstructing The RoadbedYedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Selection of Soil and Drinage System in RailwaysDocument21 pagesSelection of Soil and Drinage System in RailwaysVetri VelNo ratings yet
- Structural Abstract (2C+G+10 Floors)Document5 pagesStructural Abstract (2C+G+10 Floors)bsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- PREETI IKSA OPTION - 1-ModelDocument1 pagePREETI IKSA OPTION - 1-ModelbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Workorder Format-OrisiDocument8 pagesWorkorder Format-OrisibsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- TC For MSR CONCREDocument1 pageTC For MSR CONCREbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Preeti New SiteDocument2 pagesPreeti New SitebsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Geto Aluminium Formwork User ManualDocument35 pagesGeto Aluminium Formwork User ManualbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- RIDDLES ON REPUBLIC DAY - PranavDocument12 pagesRIDDLES ON REPUBLIC DAY - PranavbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Heritage Items OrdersDocument76 pagesHeritage Items OrdersbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Goa Visiting PlacesDocument19 pagesGoa Visiting PlacesbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Aravali Institute of Management, Jodhpur Local Industry ProjectDocument12 pagesAravali Institute of Management, Jodhpur Local Industry ProjectbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Pranav 5F Computers ACTIVITYDocument1 pagePranav 5F Computers ACTIVITYbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Fnedb V2.0Document59 pagesFnedb V2.0bsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Domestic Products Export ProductsDocument36 pagesDomestic Products Export ProductsbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- OrderDocument10 pagesOrderbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- 2 ConcreteDocument41 pages2 ConcretebsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- 38 39052ncrace13-001mct-01 1Document12 pages38 39052ncrace13-001mct-01 1bsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Ijsrp p1041Document7 pagesIjsrp p1041bsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Construction Wastes by Efficient Site Practices: Abhijith Harikumar, Sreejith M H, Priya A.Jacob, Aiswarya SDocument3 pagesMinimizing Construction Wastes by Efficient Site Practices: Abhijith Harikumar, Sreejith M H, Priya A.Jacob, Aiswarya SbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- 174 - Raavela Interiors PVT-VDocument3 pages174 - Raavela Interiors PVT-VbsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- 291-R1-Offer For Transformer Erection and Related Work. DT 30-08-2016Document3 pages291-R1-Offer For Transformer Erection and Related Work. DT 30-08-2016bsudhareddyNo ratings yet
- Soil Consistency (Plasticity) : (Das, Chapter 4) Sections: All Except 4.8Document28 pagesSoil Consistency (Plasticity) : (Das, Chapter 4) Sections: All Except 4.8sazwan2No ratings yet
- Plant Needs and Growing Conditions: Give It ADocument30 pagesPlant Needs and Growing Conditions: Give It AAdyangNo ratings yet
- Advantages of HydroponicsDocument2 pagesAdvantages of HydroponicsKartik KarthikNo ratings yet
- Five Factors of CleaningDocument2 pagesFive Factors of CleaningKimberly Bruce De CastroNo ratings yet
- Problems On Plasticity of SoilsDocument2 pagesProblems On Plasticity of SoilsHemam Prasanta0% (1)
- Landscape ConservationDocument16 pagesLandscape ConservationParthiban RajendranNo ratings yet
- Notif CSP 22 Engl 020222FDocument123 pagesNotif CSP 22 Engl 020222FHarshvardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Suka Foundation: Water Table Improvement ProceduresDocument4 pagesSuka Foundation: Water Table Improvement ProceduresMuthuNagarajanNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks-Ut-1 2Document30 pages2 Marks-Ut-1 2rohit2425No ratings yet
- Kuliah Ke 3.2 Pile Foundation PDFDocument54 pagesKuliah Ke 3.2 Pile Foundation PDFAlbert Wilson MarbunNo ratings yet
- Soil Biology and BiochemistryDocument3 pagesSoil Biology and BiochemistryS AbdNo ratings yet
- Defects in Building:: A) Structural DefectDocument12 pagesDefects in Building:: A) Structural DefectkalimNo ratings yet
- Sts PPT PresentationDocument11 pagesSts PPT PresentationVENA LANDERONo ratings yet
- Garbage EnzymeDocument6 pagesGarbage Enzymefaiez100% (1)
- Biology Grade 7Document153 pagesBiology Grade 7ConsistencyNo ratings yet
- DeforestationDocument10 pagesDeforestationNitesh Kotian100% (2)
- Helminthostachys Zeylanica (L.) Hook., Kamraj, Tukod LangitDocument7 pagesHelminthostachys Zeylanica (L.) Hook., Kamraj, Tukod LangitNature Herbs100% (1)
- Soil 3 - Soil CompositionDocument24 pagesSoil 3 - Soil CompositionLoveroop Singh100% (1)
- Contact PressureDocument2 pagesContact PressurerpkodamNo ratings yet
- Tree Spade ManualDocument28 pagesTree Spade ManualJuan Eduardo PFNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Permability Settlement of SoilDocument58 pagesRelation Between Permability Settlement of SoilAshok DasariNo ratings yet
- Saving The PlanetDocument2 pagesSaving The PlanetNatasha KHNo ratings yet
- Application of Process Simulation Software METSIMDocument7 pagesApplication of Process Simulation Software METSIMBart FrienderNo ratings yet
- Basics of LandfillsDocument24 pagesBasics of LandfillsManinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Building ConstructionDocument3 pagesEarthquake Resistant Building ConstructionKristine SantosNo ratings yet
- 2019-Agrawal-Thermal Performance SlinkyDocument33 pages2019-Agrawal-Thermal Performance SlinkyKamal Kumar AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Assignment EntrepreneurDocument38 pagesAssignment EntrepreneurAnonymous RWngbvaNo ratings yet
- Soil Testing Lab: K.R. Soil Foundation & EngineersDocument2 pagesSoil Testing Lab: K.R. Soil Foundation & EngineersMd SohagNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary - Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocument6 pagesExecutive Summary - Pseudomonas Aeruginosaapi-537754056No ratings yet