Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec04 - Lab Management Transes
Lec04 - Lab Management Transes
Uploaded by
HANNAH N. RULIDA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesThe document discusses laboratory staffing and scheduling. It addresses factors in staffing like the types of personnel needed based on workload and complexity. Job analysis and design are important for developing job descriptions that outline tasks, duties and reporting relationships. Scheduling aims to match personnel with fluctuating workload by considering availability, skills, qualifications, and type and volume of work. Different schedule categories and Philippine labor laws on work hours are reviewed. The goal is to staff at appropriate levels using floaters and extenders to fill gaps and cover absences.
Original Description:
Original Title
LEC04_LAB MANAGEMENT TRANSES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses laboratory staffing and scheduling. It addresses factors in staffing like the types of personnel needed based on workload and complexity. Job analysis and design are important for developing job descriptions that outline tasks, duties and reporting relationships. Scheduling aims to match personnel with fluctuating workload by considering availability, skills, qualifications, and type and volume of work. Different schedule categories and Philippine labor laws on work hours are reviewed. The goal is to staff at appropriate levels using floaters and extenders to fill gaps and cover absences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesLec04 - Lab Management Transes
Lec04 - Lab Management Transes
Uploaded by
HANNAH N. RULIDAThe document discusses laboratory staffing and scheduling. It addresses factors in staffing like the types of personnel needed based on workload and complexity. Job analysis and design are important for developing job descriptions that outline tasks, duties and reporting relationships. Scheduling aims to match personnel with fluctuating workload by considering availability, skills, qualifications, and type and volume of work. Different schedule categories and Philippine labor laws on work hours are reviewed. The goal is to staff at appropriate levels using floaters and extenders to fill gaps and cover absences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
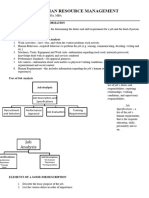
SUBJECT: LABORATORY MANAGEMENT
TOPIC: STAFFING AND SCHEDULING
organization so that job description, work standards and
STAFFING performance appraisal systems can be developed.
The setting of long-term goals and objectives for the FACTORS IN JOB ANALYSIS
number and types of personnel needed to meet labor
requirements of the laboratory 1. Working condition
2. Technology
FACTORS IN STAFFING 3. Job specifications
TYPES OF PERSONNEL NEEDED 4. Availability of labor
5. Personal interaction
- Depends of complexity of procedures, amount of 6. Legal aspects
supervision and support for the person, 7. Work flow
workload, turnaround time, testing 8. Work itself
methodology 9. Work process
STAFFING LEVELS FUNCTIONAL JOB ANALYSIS
- Level of service expected from each unit and the ➢ Employees are assigned to jobs for which they
workload have appropriate training and competence, a
major factor in assuring quality health care
PERFORMANCE TRAINING
services.
- Make sure employees are properly trained
JOB DESCRIPTION
starting from orientation
➢ A written statement that designates the tasks,
WORKLOAD PROJECTIONS
duties, working conditions and reporting
- Anticipating needs and matching the right relationships for a specific job.
people with the workload ➢ A tool that provides a means of communication
between the staff and the organization.
JOB ➢ A tool for assuring that the employee, supervisor
A collection of tasks, duties and responsibilities assigned and organization understand the duties of the
to an individual worker position.
JOB DESIGN BASIN INFORMATION IN THE JOB DESCRIPTION
▪ The process of organizing work into jobs Identification and headings
✓ Name of the facility
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE THE MAKEUP OF A JOB ✓ Location of the work
▪ Organizational factors ✓ Short descriptive title of the position
▪ People issues (POSITION SUMMARY)
▪ Legal and union requirements Job specification
- A summary in abridged form of the formal
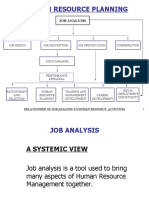
JOB ANALYSIS education skills and experience required to
perform the duties of the job and also included
➢ The process of collecting and analyzing
are any unusual physical requirements or
information about the tasks work flow and jobs
working conditions.
being done in an
Reporting Relationships ISSUES AND FACTORS INFLUENCING SCHEDULE
- The person to whom the employee’s reports, DECISIONS
supervises
1. AVAILABILITY OF STAFF
Duties
▪ Skills of each worker (generalists/ specialist)
- List of the duties, tasks and responsibilities and
▪ Qualifications (license)
functions that define the job with the authority
▪ Flexibility (shift assignments)
scale.
▪ Number of persons available
▪ Priorities of duties – ranked according
2. TYPE AND VOLUME OF WORK PERFORMED
to their performance
▪ Tests offered, timing elements (hat tests will be
▪ Format of duty descriptions
performed during what period)
▪ Authority scale
3. THE WORKPLACE
▪ Performance and evaluation criteria
PHILIPPINE WORK SCHEDULES LAW
According to Philippine Labor Code:
▪ Normal work hours = not > 8 hrs./day (40
hrs./week)
▪ < 8 hours = part-time (in proportion to number
of hours worked)
▪ Overtime is work rendered beyond 8 hours
BASIC INFORMATION IN THE JOB DESCRIPTION o Exception: government employees,
managerial personnel, house-helpers
▪ Date of preparation and activation
and piece rate worker
▪ Approval signatures
STEPS IN MAKING A SCHEDULE
JOB DESCRIPTION AND EVALUATION CRITERIA
1. Select type of schedule
▪ Knowledge parameters – trainings and
2. Establish staffing levels
education requirements, quality
3. Develop staffing personnel pools
▪ Technical abilities – hands-on experience,
4. Determine format, terminology and schedule
physical skills and talents, quantity
keys
▪ Judgment factors – degree of autonomy in
5. Set posting time frame
decision making
6. Prepare skeleton stage
▪ Relationships – communication routes,
7. Complete routine scheduling stage
supervision status
8. Fill in gaps
▪ Attendance and reliability expectations
9. Post schedule
regarding technical and physical demands of the
workload CATEGORIES OF SCHEDULES
SCHEDULING ▪ Simply lists of attendance
▪ Work assignments
“Matching the people presently working in the ▪ Combination
laboratory with current workload requirement.”
Builds on staffing information and focuses on matching
people on a day-to-day basis with the fluctuating work
load of the laboratory.
STAFFING LEVELS
The staffing requirements for a shift
STAFFING PERSONNEL POOLS
▪ Senior MedTechs (specialists) – 2
▪ MedTechs (generalists – 8
▪ Laboratory technicians – 2 FLOATERS
▪ Phlebotomists -5 - A person who is able to work in many sections of
▪ MedTech - Phlebotomists -4 the laboratory and is assigned according to
▪ Receptionists -3 fluctuating daily and hourly workload needs.
▪ Histopathology technicians -2
PROFESSIONAL EXTENDERS
SCHEDULE TERMINOLOGY AND KEYS
- Technical and clerical assistants who do tasks
C = Chemistry traditionally performed by a professional
U Urinalysis (Clinical Microscopy)
ABSENCE AND ABSENTEEISM
H = Hematology - Occurs any time a person is not at work when
P= Phlebotomists scheduled.
- Occurrence of an unscheduled absence
OL = On leave
ABSENTEEISM
TIME FRAME
- A failure to meet the standard for attendance set
▪ Schedules are frequently posted for either 1 by the laboratory
month or 4 weeks
▪ Final schedule should be posted at least 2 MANAGEMENT OF ABSENTEEISM
weeks prior to the end of current cycle - Clearly defined policy on when absenteeism
SKELETON STAGE becomes a corporate problem
- Measurable and objective criteria for monitoring
A working draft that includes weekends and requested attendance
time off - Plan for following and correcting a problem at its
earliest stage.
You might also like
- OQ45 ScoringDocument2 pagesOQ45 ScoringDaniel MellaNo ratings yet
- The Karachi Residents Directory 1932 Pages 1-27 - OCRDocument27 pagesThe Karachi Residents Directory 1932 Pages 1-27 - OCRRishi100% (1)
- Carousel PDFDocument44 pagesCarousel PDFEduardo100% (5)
- 4 Job Description of Lab StaffDocument2 pages4 Job Description of Lab StaffPORTUGAL JUSTINE ALLYSANo ratings yet
- Job Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsDocument28 pagesJob Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsSyrah Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Job AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Job AnalysisAlthea GacilanNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT 4 in Human Resource ManagementDocument4 pagesHANDOUT 4 in Human Resource ManagementsumandaymattgianNo ratings yet
- Job Design Job DescriptionDocument13 pagesJob Design Job DescriptionSiddharth TewariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Job AnalysisDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Job AnalysisNorjiella Binti Mohd NurdinNo ratings yet
- LAbMan 2.2 Reviewer 1Document2 pagesLAbMan 2.2 Reviewer 1Alondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Job AnalysisDocument18 pagesChapter 4-Job AnalysisRahat JamilNo ratings yet
- Io PsychDocument7 pagesIo PsychPrecious KayeNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis, Job Description and Job Specification SummaryDocument6 pagesJob Analysis, Job Description and Job Specification SummaryRille Ephreim AsisNo ratings yet
- Slaid Chapter 2Document22 pagesSlaid Chapter 2nurin natasyaNo ratings yet
- HRM 2022 Ch04Document45 pagesHRM 2022 Ch04Nivi MiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Job Analysis & Job DesignDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - Job Analysis & Job Designsukoyo100% (1)
- Job Analysis (Chap 3)Document24 pagesJob Analysis (Chap 3)NehaAsif100% (1)
- Chap 3 HRMDocument8 pagesChap 3 HRMK59 HOANG THANH THUYNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Analyzing Work and Designing JobsDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 4 Analyzing Work and Designing JobsMa Faith Angelica MoralesNo ratings yet
- HRM Uint 2Document61 pagesHRM Uint 2Nazir Ahmed100% (1)
- Io Psych Chap2Document3 pagesIo Psych Chap2Gela FabianiaNo ratings yet
- HRM - 02 - HR Planning & Diversity Management PDFDocument23 pagesHRM - 02 - HR Planning & Diversity Management PDFmikaNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis: Presented By: FSZDocument28 pagesJob Analysis: Presented By: FSZTaraa HoqueNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis & Job DesignDocument19 pagesJob Analysis & Job DesignwardhantpeNo ratings yet
- Jeraldine B. SantiagoDocument31 pagesJeraldine B. SantiagoDine WilNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument12 pagesJob AnalysisrashritNo ratings yet
- 04 Job AnalysisDocument34 pages04 Job AnalysisFarhan NurhadianaNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis (HRM)Document16 pagesJob Analysis (HRM)Manaal HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Job AnalysisDocument18 pagesUnit 2 - Job Analysisparika khannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Job AnalysisDocument18 pagesUnit 2 - Job Analysisparika khannaNo ratings yet
- Job and JOB AnalysisDocument38 pagesJob and JOB Analysisebrar totoNo ratings yet
- Hres MidtermDocument8 pagesHres MidtermYOSHIKI SHIMIZUNo ratings yet
- Humres ReviewerDocument6 pagesHumres ReviewerIrene LadesmaNo ratings yet
- Managing People Slides Chap 4 Designing JobsDocument19 pagesManaging People Slides Chap 4 Designing JobsShaun LewNo ratings yet
- PDF document-A7376F0D6B53-1Document12 pagesPDF document-A7376F0D6B53-1Sharwin .No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - HRMDocument25 pagesChapter 3 - HRMHạnh HồngNo ratings yet
- MGMT312 Human Resources Management: Topic 3: Job Analysis (Book A: Chapter 4) Lecturer: June YANGDocument29 pagesMGMT312 Human Resources Management: Topic 3: Job Analysis (Book A: Chapter 4) Lecturer: June YANG韩意颜No ratings yet
- Review Class Part 2 For Industrial Psychology JOB ANALYSIS and EVALUATION - AdditionalDocument47 pagesReview Class Part 2 For Industrial Psychology JOB ANALYSIS and EVALUATION - AdditionalMary Ann AmbitaNo ratings yet
- Indus Psych Chapter 2Document6 pagesIndus Psych Chapter 2Academics PurposesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 I O PsychDocument4 pagesChapter 2 I O Psychchristineruthfare03No ratings yet
- Chapter 3.0 Job AnalysisDocument42 pagesChapter 3.0 Job AnalysisDeadLy PerformersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Job Analysis A N D Job Design: Maria Saeed KhattakDocument47 pagesChapter 3: Job Analysis A N D Job Design: Maria Saeed KhattakMaria Saeed KhattakNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Job Desing Job Analysis - 5f41fd2b91c2eDocument27 pagesSession 2 - Job Desing Job Analysis - 5f41fd2b91c2eIreshaNadeeshaniNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Job Analysis and Talent ManagementDocument14 pagesCH 4 - Job Analysis and Talent ManagementAhlam AliNo ratings yet
- L2 3-JobAnalysisTalentManagementDocument57 pagesL2 3-JobAnalysisTalentManagementChíi KiệttNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and Talent ManagementDocument19 pagesJob Analysis and Talent ManagementNaimmul FahimNo ratings yet
- Lab MNGT 3Document6 pagesLab MNGT 3Cejay Erl MagnoNo ratings yet
- 02 Job AnalysisDocument37 pages02 Job AnalysisKian LaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Job AnalysisDocument18 pagesUnit 2 - Job Analysisvrukshani channeNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and Job DesignDocument33 pagesJob Analysis and Job DesignAshutosh GhadaiNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning: Job AnalysisDocument34 pagesHuman Resource Planning: Job AnalysisaidushNo ratings yet
- HRM - PPT - Ch. 04Document33 pagesHRM - PPT - Ch. 04Hannan KhanNo ratings yet
- Dessler CHPTR 4Document35 pagesDessler CHPTR 4Mugheera AhmedNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument19 pagesJob AnalysisMarium ShabbirNo ratings yet
- HRM - PPT - Ch. 04Document33 pagesHRM - PPT - Ch. 04Sidra SwatiNo ratings yet
- 03 Job AnalysisDocument27 pages03 Job AnalysisAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and Design 1Document23 pagesJob Analysis and Design 1Dhearly NaluisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Part 1Document21 pagesChapter 02 Part 1Qasim Jahangir WaraichNo ratings yet
- MGT-351 Human Resource Management Chapter-04 Job Analysis and The Talent Management ProcessDocument16 pagesMGT-351 Human Resource Management Chapter-04 Job Analysis and The Talent Management ProcessShadman Sakib FahimNo ratings yet
- CH-3 HRMDocument57 pagesCH-3 HRMwww.dha1988No ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Work Study [Revised Edition]From EverandPractical Guide To Work Study [Revised Edition]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- D Defia Ance Ein PHL Lan: Adventure Code: DDEX X1 1Document32 pagesD Defia Ance Ein PHL Lan: Adventure Code: DDEX X1 1C_rovereNo ratings yet
- Reading Text Answer KeyDocument4 pagesReading Text Answer KeyJuna AlgonesNo ratings yet
- The Comparative MethodDocument20 pagesThe Comparative MethodRamjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Kill CurveDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Kill CurveEdvinasStankūnasNo ratings yet
- Rami Hameed CV PDFDocument2 pagesRami Hameed CV PDFramihameed2000No ratings yet
- Budget 2024-25Document34 pagesBudget 2024-25anuragaryan666No ratings yet
- Chapter II Nailatul Khasanah Biologi'15Document10 pagesChapter II Nailatul Khasanah Biologi'15Denima HuluNo ratings yet
- 040 SEUMAL in Re CunananDocument2 pages040 SEUMAL in Re CunananCarissa CruzNo ratings yet
- Arduino For Arduinians - Copyright PageDocument1 pageArduino For Arduinians - Copyright PageabdelbadiebekkoucheNo ratings yet
- Midtern PR 1Document20 pagesMidtern PR 1Kristina PabloNo ratings yet
- Ecofeminism Thoughts: The Effective Analysis Based On Mother ArchetypeDocument6 pagesEcofeminism Thoughts: The Effective Analysis Based On Mother ArchetypereviewjreNo ratings yet
- Chatting About A Series ListeningDocument3 pagesChatting About A Series ListeningIvan CruzNo ratings yet
- Heroism: A Conceptual Analysis and Differentiation Between Heroic Action and Altruism - Franco, Blau & Zimbardo 2011Document15 pagesHeroism: A Conceptual Analysis and Differentiation Between Heroic Action and Altruism - Franco, Blau & Zimbardo 2011Zeno FrancoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Management in Project-Based OrganizationsDocument23 pagesKnowledge Management in Project-Based OrganizationsADB Knowledge Solutions100% (1)
- Ascia Action Plan Anaphylaxis Epipen Personal 2014Document1 pageAscia Action Plan Anaphylaxis Epipen Personal 2014api-247849891No ratings yet
- Ethics in The Practice of Petroleum Engineering: Denver Chapter of SPEEDocument27 pagesEthics in The Practice of Petroleum Engineering: Denver Chapter of SPEEMuhak1No ratings yet
- Service ChargeDocument3 pagesService ChargeGiovanne GonoNo ratings yet
- 10 Meaningful Ways To Get More Twitter Followers - Sprout SocialDocument1 page10 Meaningful Ways To Get More Twitter Followers - Sprout SocialLKMs HUBNo ratings yet
- Script Tea - Callum Turner CompleteDocument4 pagesScript Tea - Callum Turner Completeapi-529320728No ratings yet
- Body WieghtsDocument25 pagesBody WieghtsmgharrierNo ratings yet
- Site Visit ReportDocument13 pagesSite Visit ReportadilNo ratings yet
- School of Accounting and Finance: Sample ExaminationDocument4 pagesSchool of Accounting and Finance: Sample ExaminationChenyu HuangNo ratings yet
- #Myproject FINALDocument24 pages#Myproject FINALAarti YewrikarNo ratings yet
- Development of Instant Fish Soup PowdertDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Instant Fish Soup PowdertSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Evola, Benoist and ViolenceDocument30 pagesEvola, Benoist and ViolenceAN NXNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Xlpe Using in Cable ExtrudingDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Xlpe Using in Cable ExtrudingRoza FirdausNo ratings yet
- Bhoogol Se Samabandhit Kuchh Samany Gyan Padhie: Not: Ek Achchha Blog Jisaka Link HaiDocument13 pagesBhoogol Se Samabandhit Kuchh Samany Gyan Padhie: Not: Ek Achchha Blog Jisaka Link Haigirish___88No ratings yet




























































![Practical Guide To Work Study [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/245836753/149x198/e8597dfaef/1709916910?v=1)


























