Professional Documents
Culture Documents
345 - Hematology Physiology) Polycythemias
Uploaded by
Aro DanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
345 - Hematology Physiology) Polycythemias
Uploaded by
Aro DanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 8/21/2021
1. POLYCYTHEMIA
Hematology: Polycythemia Medical Editor: Dr. Sofia Suhada M.Uzir
OUTLINE
I) INTRODUCTION
II) ERYTHROPOIETIN (EPO)
III) POLYCYTHEMIA VERA
IV) BLOOD DOPING
V) SECONDARY POLYCYTHEMIA
VI) SUMMARY
VII) REVIEW QUESTIONS
VIII) REFERENCES
I) INTRODUCTION
Polycythemia is an abnormally increased concentration of
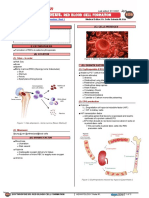
RBCs in the blood, either through reduction of plasma Figure 2. JAK STAT pathway [ResearchGate]
volume or increase in red cell numbers. [Oxford Languages]
There are two types:
o Polycythemia vera (primary) (A) EFFECTS OF POLYCYTHEMIA
o Secondary polycythemia Polycythemia causes:
o Increase RBC to water ratio
II) ERYTHROPOIETIN (EPO) Viscosity of blood will increase → thicker blood
EPO is made by the kidneys at the distal convoluted Increase incidence of clot formations
tubules (thrombi/emboli)
o It stimulates myeloid stem cells and proerythroblasts • In veins → deep vein thrombosis (DVT) may
into erythropoietic process Figure 1 develop
o EPO increases RBCs through JAK STAT pathway • In coronary artery → myocardial infarction
• In pulmonary arteries → pulmonary embolism
In the proximal convoluted tubules, there are also cells
• In cerebrum → stroke
that are constantly secreting EPO
o Increase bleeding → longer prothrombin time
Note:
JAK STAT IV) BLOOD DOPING
o Janus Kinase and Signal Transducer and Activator of
Transcription Causes transient polycythemia
For example, in the Olympics (non-ethical!)
o Athletes take their blood out and store it to be
reinserted into the circulatory system a day before
their event
Figure 1. EPO stimulating proerythroblast in erythropoiesis
[Science Direct]
Figure 3. Summary blood doping [Sports247]
III) POLYCYTHEMIA VERA (1) Why blood doping?
Increase in RBC production primarily due to hyper Blood doping helps to increase in the number of RBCs in
functional JAK STAT pathway in the bone marrow the body
There is a problem in the receptor in which EPO binds to o Increases oxygen carrying capacity
o Causes increased in functions of JAK STAT pathway More blood oxygen supply to the muscle
Signal nucleus for proliferations More endurance
Activating genes to undergo transcription and
translations (2) Drawbacks
o Hyperfunctioning → amplified effects → increase in Increase in viscosity
erythropoiesis = increase in the RBCs o Thicker blood → increase incidence clot formation,
Remember: thrombi/emboli especially if not properly hydrated
Polycythemia = abnormal increase in production of o Increase peripheral resistance → increase in the
RBCs blood pressure (may cause hypertension)
Dizziness
Headaches
Polycythemia HEMATOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 3
V) SECONDARY POLYCYTHEMIA The following may be caused by polycythemia
except
Due to the enhance of EPO production a. Thrombi formation
Causes: b. Decrease in functioning RBCs
o Hypoxia/low amount of oxygen c. Stroke
High altitudes d. DVT
Cardiovascular diseases
• Decrease oxygen carrying capacity What causes secondary polycythemia?
Renal cancer a. Low oxygen levels
• Enhance production of EPO b. Renal cancer
Increase EPO → increase JAK STAT pathway → c. Heart diseases
increase erythropoiesis → increase in RBCs d. All of the above
The following typically distinguishes polycythemia
vera from other causes of erythrocytosis
a. Massive splenomegaly
b. Aquagenic pruritis
c. High hematocrit
d. High hemoglobin
The following cause microcytic erythrocytosis
Figure 4. Number of cells producing erythropoietin a. Beta thalassemia trait
[Vivo Pathophysiology] b. Hypoxic erythrocytosis
c. Polycythemia vera
d. All of the above
VI) SUMMARY
Polycythemia is primarily due to hyper functional JAK Regarding polycythemia vera all are true except
STAT pathway in the bone marrow. a. Erythroid progenitor cells are resistant to apoptosis
o This triggers more erythropoiesis hence, more RBCs b. Autonomous clonal form of erythrocytosis
formation. c. Elevated plasma erythropoietin level excludes
polycythemia vera as the cause for erythrocytosis
Secondary polycythemia is caused by the increase in d. Abundant bone marrow iron
production of EPO → Increases the JAK STAT pathway
and RBCs
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
VII) REVIEW QUESTIONS VIII) REFERENCES
Regarding polycythemia, which is correct? ● Oxford Languages (2021) https://languages.oup.com/google-
dictionary-en/
a. There are 2 types ● NatBoardMCQ (2015) [Quiz]
b. There are 3 types http://www.natboardmcqs.com/hematology-mcq-exercise-19/
c. There are 4 types ● Hong-MouShih Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.
Physiology and pathophysiology of renal erythropoietin-producing
d. There are 5 types cells (2018)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S09296646183006
In polycythemia vera, which is true? 39
● VIVO Pathophysiology (2018) [digital image]
a. There is hyper functionality of erythropoiesis in the http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/endocrine/otherend
liver o/epo.html
b. There is hyper functionality of JAK STAT pathway in ● Blood doping (2017) [digital image]
the liver https://www.sports247.my/blood-doping-doesnt-work-least-not-
amateurs-study/
c. There is hyper functionality of erythroblasts in the ● JAK STAT pathway [digital image]
bone marrow https://www.researchgate.net/figure/JAK2-receptor-signaling-and-
d. There is hyper functionality of JAK STAT pathway in activation-of-STAT-pathway-The-binding-of-
erythropoietin_fig1_261957679
the bone marrow ● Le T, Bhushan V, Sochat M, Chavda Y, Zureick A. First Aid for
the USMLE Step 1 2018. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2017
In secondary polycythemia, which is false? ● Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Anatomy & Physiology. Hoboken, NJ:
Pearson; 2020.
a. It is due to enhance of EPO production ● Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical Physiology.; 2017.
b. It can be seen in certain renal cancers ● Urry LA, Cain ML, Wasserman SA, Minorsky PV, Orr RB,
c. It decreases the oxygen carrying capacity Campbell NA. Campbell Biology. New York, NY: Pearson; 2020.
● Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL,
d. Hypoxia is one of the main causes Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. New York
etc.: McGraw-Hill Education; 2018.
Thrombosis in polycythemia vera is due to ● Sabatine MS. Pocket Medicine: the Massachusetts General
Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine. Philadelphia: Wolters
a. Erythrocytosis
Kluwer; 2020.
b. Leukocytosis
c. Thrombocytosis
d. all of the above
True regarding pathogenesis of polycythemia vera
a. erythropoietin independent erythroid colony
formation
b. hypersensitivity of polycythemia vera erythroid
progenitor cells to EPO
c. resistance of polycythemia vera progenitor cells to
apoptosis
d. all of the above
2 of 3 HEMATOLOGY: Note #1. Polycythemia
Polycythemia HEMATOLOGY: Note #1. 3 of 3
You might also like
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutDocument16 pagesFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- Khan Academy DNA Technology QuestionsDocument4 pagesKhan Academy DNA Technology QuestionsLoraNo ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 002) CBC - Approach To Polycythemia (Notes)Document4 pagesHematology Pathology - 002) CBC - Approach To Polycythemia (Notes)Aro DanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 Blood MariebDocument30 pagesChapter17 Blood MariebMario AndersonNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Quiz ResultsNicoleNo ratings yet
- Cell TestttDocument22 pagesCell TestttMark Soto100% (2)
- Bio Exam ZsmuDocument84 pagesBio Exam ZsmuManthan Patil100% (1)
- AP Biology: Cell CommunicationDocument20 pagesAP Biology: Cell CommunicationJiwon Shin100% (1)
- Biocomp Exam 2013Document11 pagesBiocomp Exam 2013e100% (1)
- 6.6.Q BANK SLdocxDocument20 pages6.6.Q BANK SLdocxNaz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- How genetics explains evolution of complex traitsDocument8 pagesHow genetics explains evolution of complex traitsLim YH100% (1)
- MCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Document27 pagesMCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Leen Alodat100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle & CANCERDocument17 pagesThe Cell Cycle & CANCERjesuslovers100% (1)
- Aerobic respiration diagram outlineDocument80 pagesAerobic respiration diagram outlineTori Hop Along Clinch100% (1)
- L Energy and Respiration I PDFDocument12 pagesL Energy and Respiration I PDFMichelle Yeap67% (3)
- MT Sep 2021-22 XII Bio QP 004 FinalDocument10 pagesMT Sep 2021-22 XII Bio QP 004 FinalKalpna Rani100% (1)
- Problem Set 1 Introduction and Cell SignalingDocument9 pagesProblem Set 1 Introduction and Cell SignalingPreston Adhikari100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration GuideDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration GuideL Chan100% (1)
- Chemiosmosis ExplainedDocument4 pagesChemiosmosis Explainedramloghun veer100% (1)
- Chapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Document6 pagesChapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Rafael G. Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge AS Level Biology Enzymes Section C Initial Rate GraphDocument18 pagesCambridge AS Level Biology Enzymes Section C Initial Rate Graphlucifer100% (1)
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerAimee PascualNo ratings yet
- Sat II Real Evolution QuestionsDocument3 pagesSat II Real Evolution QuestionsMido MidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - Questions中华雅思王No ratings yet
- BIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewDocument45 pagesBIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewNigel Zhang100% (1)
- MCQ RespirationDocument28 pagesMCQ RespirationBonifacius Budi Nugroho100% (1)
- Plant Cell and Organelle FunctionsDocument79 pagesPlant Cell and Organelle Functionsrachit100% (2)
- GametogenesisDocument10 pagesGametogenesisalivirgo90No ratings yet
- Exam Questions Aqa Trilogy Bioenergetics: Q1-6 Foundaton Q3-9 HigherDocument28 pagesExam Questions Aqa Trilogy Bioenergetics: Q1-6 Foundaton Q3-9 Higherapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument60 pagesCell DivisionCharmaineNo ratings yet
- Topic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNDocument11 pagesTopic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNliang yi choo100% (1)
- Cell Struc (Q)Document26 pagesCell Struc (Q)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates NotesWutWut100% (1)
- TOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)Document6 pagesTOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)L Chan100% (1)
- Enzyme ReviewDocument2 pagesEnzyme ReviewSamura HasibNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions 1. A Level Biology, AQA, Unit 2, June 2015Document19 pagesExam Questions 1. A Level Biology, AQA, Unit 2, June 2015Ryan JamesNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ProtocolDocument6 pagesEnzyme Protocoltapas kunduNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Classification and EvolutionDocument109 pages4.3 Classification and Evolutiontaaniya sadiq100% (1)
- Lab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFDocument4 pagesLab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFBeth RobeliaNo ratings yet
- 2009 Year 11 Biology ExamDocument11 pages2009 Year 11 Biology ExamJay Li100% (1)
- Cell Communication Packet 1Document20 pagesCell Communication Packet 1jade20090106100% (1)
- Past Questions Cells N Biomolecules A Level BiologyDocument32 pagesPast Questions Cells N Biomolecules A Level BiologyZak berry100% (1)
- Solan Bab 3 StrukturDocument5 pagesSolan Bab 3 StrukturMuhammad Amir100% (1)
- Cell Organelles and StructuresDocument39 pagesCell Organelles and StructuresHarshad Gadhvi100% (1)
- 22 10 Human Genetics CIBID 2014Document98 pages22 10 Human Genetics CIBID 2014Малиша МанићNo ratings yet
- Mock FinalDocument19 pagesMock Finalbuddybbuddy100% (1)
- Q1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeDocument56 pagesQ1.The Diagram Shows A Mitochondrion.: Feversham CollegeZaksd100% (1)
- Bio October 2107 QP Unit 3Document16 pagesBio October 2107 QP Unit 3clyde100% (1)
- Calculating Water Potential Worksheet-2012 2Document4 pagesCalculating Water Potential Worksheet-2012 2aemilianne100% (1)
- 16 Microscopy ReviewDocument12 pages16 Microscopy Reviewapi-300931855100% (1)
- Classification and Keys Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesClassification and Keys Exam QuestionsIlincaVasilescuNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules Qs and MSDocument112 pagesBio Molecules Qs and MSAmaan Ahmed100% (1)
- Microscopy & Cell Structure AS Biology 9700Document9 pagesMicroscopy & Cell Structure AS Biology 9700Asif Ayaz100% (1)
- Cell Signaling Problem SetDocument7 pagesCell Signaling Problem SetJohn WangNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument34 pagesQ1. The Diagram Shows A Summary of The Light-Independent Reaction of PhotosynthesisChee Beng Yeap100% (1)
- H2 Evolution QuestionsDocument27 pagesH2 Evolution QuestionsWesley Tan100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Document6 pagesProtein Synthesis Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwk100% (1)
- CH 7 Blood Disorders F FF FDocument75 pagesCH 7 Blood Disorders F FF FZainab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Ap2 Chapter18 Powerpoint Blood SU21Document37 pagesAp2 Chapter18 Powerpoint Blood SU21btheresakNo ratings yet
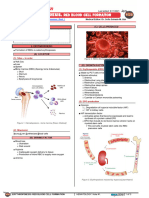
- 342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument6 pages342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell Formationhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 342 Hematology Physiology Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument3 pages342 Hematology Physiology Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Brosur Humasrate enDocument8 pagesBrosur Humasrate enandi takwaNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab ManualDocument104 pagesHistology Lab ManualBanyu علي تقويم Biru33% (3)
- PhysioEx Exercise 2 Activity 2Document11 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 2 Activity 2villanuevaparedesaracely4No ratings yet
- Blood Typing LabDocument3 pagesBlood Typing Labapi-279500653No ratings yet
- ADD-00064731 White Paper MAPSSDocument6 pagesADD-00064731 White Paper MAPSSFouad RahiouyNo ratings yet
- 1 Unit Three - Excitable Tissues (Nerve)Document38 pages1 Unit Three - Excitable Tissues (Nerve)tadele1067% (3)
- Emergency and Critical Care Procedures in Small AnimalsDocument9 pagesEmergency and Critical Care Procedures in Small AnimalsTessaNo ratings yet
- Lasercyte DX Message Codes enDocument1 pageLasercyte DX Message Codes enSpital Veterinar AndivetNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - RLE 1 Significance of Laboratory ResultsDocument9 pagesWorksheet - RLE 1 Significance of Laboratory Results1H - Althea VestilNo ratings yet
- Gregory McKay PHD Thesis CompressedDocument174 pagesGregory McKay PHD Thesis Compressedsondoshagag311No ratings yet
- Jurnal Daun SalamDocument10 pagesJurnal Daun SalamTianaNo ratings yet
- #Davidson - Review #HematologyDocument23 pages#Davidson - Review #Hematologyemtiaz zamanNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion ReactionsDocument3 pagesBlood Transfusion ReactionsANDREW MWITINo ratings yet
- Massive Transfusion and Massive Transfusion ProtocolDocument9 pagesMassive Transfusion and Massive Transfusion ProtocolRamachandran SundararamanNo ratings yet
- Clasificacion AnemiaDocument11 pagesClasificacion AnemiaclaudiaNo ratings yet
- 04 Periodontal Morphology Components of The Alveolar BoneDocument7 pages04 Periodontal Morphology Components of The Alveolar BoneNaufal ThufailNo ratings yet
- 8 Types of Blood Cells and Their FunctionsDocument5 pages8 Types of Blood Cells and Their FunctionsKimberly Bundley-JohnsonNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Activity 7Document8 pagesPhysioEx Activity 7i1011221013No ratings yet
- Coagulação Na GravidezDocument14 pagesCoagulação Na GravidezblefariNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9: Study of StomataDocument10 pagesExperiment 9: Study of StomatajasmitaadodhiaNo ratings yet
- The 3 Types of Joints in The BodyDocument3 pagesThe 3 Types of Joints in The BodyLhyn Liam-LameraNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy BasicsDocument40 pagesPhlebotomy BasicsbiffdoggieNo ratings yet
- Werlhof's Disease, Von Willebrand DiseaseDocument19 pagesWerlhof's Disease, Von Willebrand DiseaseBeulah AlexNo ratings yet
- Hypophthalmus: Studi Kondisi Darah Ikan Patin Siam (Di Sungai Tapung Kiri Dan Sungai Sail Provinsi RiauDocument13 pagesHypophthalmus: Studi Kondisi Darah Ikan Patin Siam (Di Sungai Tapung Kiri Dan Sungai Sail Provinsi RiauRyzki Nur PratamaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis - Hematology BlockDocument40 pagesHemostasis - Hematology BlockamandaNo ratings yet
- RH Isoimmunization 2021Document24 pagesRH Isoimmunization 2021Muhammad Omar Wasim AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisordersDocument197 pagesHematologic DisordersDanica Mae BianitoNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) PretestDocument13 pagesComplete Blood Count (CBC) Pretestjai2xNo ratings yet