Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gestational Conditions
Uploaded by
Hyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gestational Conditions
Uploaded by
Hyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasCopyright:
Available Formats
..
CARE OF MOTHER, CHILD AT RISK OR WITH PROBLEMS ……………………
GESTATIONAL CONDITIONS SPONTANEOUS ABORTION or MISCARRIAGE
● Hyperemesis Gravidarum Abortion- is the medical term for any interruption of a pregnancy before a
● Ectopic Pregnancy fetus is viable.
● Gestational Trophoblastic disease (Hmole) ● Viable Fetus- more than 20-24 weeks of gestation or weighs at
● Incompetent Cervix least 500 g.
● Spontaneous Abortion ● Miscarriage- occurs spontaneously
● Placenta Previa - Early Miscarriage - before 16 weeks
● Abruptio Placenta - Late Miscarriage - happens after 16 weeks (16-24 weeks AOG)
● Premature Rupture of Membrane
● Pregnancy Induced Hypertension CAUSES OF SPONTANEOUS MISCARRIAGE
- Abnormal fetal development
HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM: - Immunologic factor
- known as Pernicious vomiting - Implantation abnormalities
- nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (past week 12 AOG) - Insufficient levels of progesterone
- severe that dehydration, ketonuria, and significant weight loss - Systemic infection
occurs - Ingestion of a teratogenic drug
- Cause: unknown - Ingestion of alcohol
SUGGESTED CAUSATIVE FACTORS Assessment
1. High levels of HCG in early pregnancy ● Vaginal spotting with slight cramping – the presenting symptom
2. Metabolic or nutritional deficiencies ● Assessment factor
3. Thyroid dysfunction 1. Confirmation of pregnancy
4. Ambivalence toward pregnancy and family-related stress 2. Pregnancy length in weeks
5. Most common in primigravid clients 3. Duration of bleeding
4. Intensity (amount of bleeding that occurred)
HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM ASSESSMENT: 5. Frequency
1. Nausea is most pronounced on arising; however, can occur at other 6. Associated symptoms
times during the day 7. Action
2. Persistent vomiting 8. Blood type
3. Weight loss
4. Dehydration (↓ urinary output, rapid PR, ↓ grade fever, dry skin, TYPES OF MISCARRIAGE:
sunken eyes, dry lips) I. Threatened Miscarriage
5. Electrolyte imbalances (↓ Na, K, chloride; hypokalemic alkalosis) S/S:
6. Ketonuria - vaginal spotting w/ slight cramping (scanty at first,
7. Increased hematocrit levels bright red)
- no cervical dilation
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & LAB Actions/Implementation:
1. Hematocrit, hemoglobin 1. Assess fetal viability (FHR, ultrasound)
2. Electrolytes 2. Test blood for HCG level ( a double result means the placenta is
3. Urine protein and acetone still intact)
3. Avoidance of strenuous activity for 24-48 hours.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: 4. Complete bed rest may not be necessary
● Imbalance nutrition 5. Offer emotional support
● Risk for deficient fluid volume r/t vomiting secondary to 6. A woman can resume her activities once the bleeding stops after 48
hyperemesis gravidarum hours. Coitus is restricted for 2 weeks after the bleeding episode.
THERAPEUTIC NURSING MANAGEMENT I. Imminent (Inevitable) Miscarriage
Goal: Hospitalization is required for severe symptoms o/w intravenous (A threatened miscarriage becomes imminent if uterine contractions and
hydration and correction of metabolic imbalances needed. cervical dilation occur.)
a. Implement common N/V nursing interventions S/S:
- Recommend smaller, frequent meals; include salty foods - vaginal spotting with cramping
- Suggest crackers before arising - positive uterine contraction
- Avoid spicy and fried foods - cervical dilation
- Advice remaining upright for 30 min after eating - loss of some tissues (products of conception)
- Discuss the use of antacids with a primary care provider Action/Implementation:
b. Treatments & goals for a hospitalized px 1. Advise the woman to come to the hospital if uterine contractions
- Control vomiting ( anti-emetics i.e. Reglan) and cramping happen.
- NPO 2. Assess/Monitor spontaneous vaginal bleeding and cramping
- Progress to small feedings every 2-3 hours, then advanced to a soft 3. Save expelled tissues/clots.
diet, then to a normal diet. 4. Count perineal pads to evaluate blood loss
- Quiet environment 5. Monitor vital signs
- Intake & Output 6. Provide IV fluids
- Adequate nutrition-nasogastric tube feeding may be necessary 7. Prepare the client for dilatation and evacuation as prescribed.
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT II. Complete Miscarriage
● PHARMACOLOGY (The uterine products of conception are expelled spontaneously without any
1. Sedatives assistance.)
2. Antiemetics S/S:
3. Correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalances - vaginal spotting and cramping
4. IV Lactated Ringers - the bleeding slows within 2 hours and stops within a few days after
the passage of the uterine products
● COMPLICATIONS - cervical dilation
1. Dehydration - uterine contractions
2. Electrolyte imbalance - passage of complete uterine contents (fetus, membranes &
3. Severe Weight loss placenta)
4. Metabolic alkalosis
III. Incomplete Miscarriage
(A part of the conceptus is expelled (usually the fetus), but the membrane or
placenta is retained in the uterus.)
BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCY ● Complication: Maternal Hemorrhage
● Spontaneous Abortion/Miscarriage ● The physician usually will prescribe dilatation and curettage
● Ectopic Pregnancy evacuate the placental remains, clots, and other tissues.
● Gestational Trophoblastic Disease ● Do not give false hopes, the woman has to know that her
● Premature Cervical Dilation pregnancy is already lost.
● Placenta Previa
● Abruptio Placenta IV. Missed Miscarriage
(Otherwise called Early Pregnancy Failure)
…………………………….………RAGANAS, HYACINTH MAE V. BSN-2D………………………………….
.. CARE OF MOTHER, CHILD AT RISK OR WITH PROBLEMS ……………………
(The fetus dies in the uterus but is not expelled) ● Common site:
S/S: A. Fallopian Tube (95%) – tubal rupture occurs before 12
- the absence of fetal heart sound weeks
- no increase in size AEB no increase in fundal height 1. Ampulla (80%)
- painless vaginal bleeding 2. Isthmus (12%)
Action/Implementation: 3. Interstitial or fimbrial (8%)
1. Ultrasound has to be performed B. CERVICAL
2. Prepare client for D & E C. ABDOMINAL
3. Prepare the client for labor if the pregnancy is over 14 weeks. D. OVARIAN
Misoprostol (Cytotec) and oxytocin for elective termination of ● 2% of pregnancies are ectopic
pregnancy. ● The second most frequent cause of bleeding early in pregnancy
4. Provide IV fluids 5. Offer emotional support/counseling
PREDISPOSING FACTORS:
COMPLICATIONS OF MISCARRIAGE 1. Adhesion of the fallopian tube caused by chronic salpingitis or
1. Hemorrhage Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Not serious and fatal with complete spontaneous 2. Congenital malformations such as webbing in the fallopian tube
miscarriage 3. Scars from tubal surgery
- Major hemorrhage is possible for incomplete 4. A uterine tumor pressing on the proximal end of tube
miscarriage with accompanying coagulation defect 5. IUD
(DIC)
Implementation: ASSESSMENT FINDINGS
1. Monitor vital signs to detect possible hypovolemic shock. - No unusual symptoms at the time of implantation.
2. Position the woman flat and massage the uterine fundus. 1. amenorrhea or abnormal menstrual period/ spotting
3. Prepare patient for D & C. 2. nausea & vomiting
4. Administer BT as prescribed. 3. + pregnancy test
5. Prepare replacement of fibrinogen or another clotting factor as 4. tubal rupture signs: sudden, acute low abdominal pain radiating to
required/prescribed. the shoulder- Kehr’s sign (referred shoulder pain)
6. Teach the patient the importance of taking methylergonovine 5. Bluish navel (Cullen’s sign) d/t to blood accumulated in the
maleate, including the dosage. peritoneal cavity
7. Offer/Provide emotional support. 6. Rectal pressure because of blood in the cul-de-saC
7. Sharp localized pain when the cervix is touched.
2. Infection 8. Signs of shock/circulatory collapse
- Its possibility is minimal if pregnancy loss occurs over a short LABORATORY FINDINGS
time, bleeding is self-limiting, and instrumentation is less. 1. Low hemoglobin count, low hematocrit level d/t bleeding process
- Increased possibility may happen for women who have lost large or loss of blood
amounts of blood. 2. Low HCG indicates that the pregnancy has ended
S/S: 3. Elevated WBC d/t to trauma
- fever (38ºC), abdominal pain or tenderness, and foul vaginal
discharge DIAGNOSIS
Infectious Organism: 1. Pelvic Ultrasonography – no embryonic sac in the uterine cavity
- Escherichia coli 2. Culdocentesis – aspiration of non-clotting blood from the
Implementation: cul-de-sac of Douglas (positive tubal rupture)
1. Teach women the danger signs of infection. 3. Laparoscopy – not common; requires direct visualization
2. Instruct the woman to wipe her perineal area from front to back ● therapy for a ruptured ectopic pregnancy which is to ligate the
after voiding and after defecation. bleeding vessels and to remove or repair the damaged fallopian
3. Caution her not to use tampons to control vaginal discharge. tube
4. Encourage more intake of fluids.
5. Provide IV if required/as prescribed. TREATMENT
1. Methotrexate - indicated for unruptured ectopic (mass) smaller
3. Septic Abortion than 4 cm - to induce labor and preserve fallopian tube
- An abortion that is complicated with infection. 2. Surgical removal of ruptured tube: SALPINGECTOMY
- Infection occurs more frequently in women who have tried to 3. Management of Profound shock if ruptured: blood replacement and
self-abort or were aborted illegally using a nonsterile instrument. IVF
- Septic abortion may lead to INFERTILITY d/t uterine scarring or 4. Antibiotics
fibrotic scarring of the fallopian tube
S/S: COMPLICATIONS
- fever, crampy abdominal pain, & tender uterus 1. Hemorrhage
Complications: 2. Infection
- Toxic Shock Syndrome, Septicemia, Kidney Failure, and Death 3. Rh sensitization. RhoGAM prevents isoimmunization; given to
Management: Rh-negative mothers with Rh-positive ectopic pregnancy
1. CBC, serum electrolytes, serum creatinine, blood type & cross
match, cervical, vaginal, & urine cultures. COMMON NURSING Dx
2. I & O q hourly. - Powerlessness related to early loss of pregnancy secondary to
3. IVF administration. ectopic pregnancy
4. CVP or Pulmonary artery catheterization
5. D&C ● Nursing Implementation
6. Oxygen and other ventilatory support 1. Obtain assessment data rapidly, especially for
7. Pharmacology: anticipatory shock
a. Antibiotics (Penicillin, Gentamicin, clindamycin) 2. Implement measures for a shock as soon as possible.
b. Tetanus toxoid 3. Position patient on Modified Trendelenburg (shock)
c. Dopamine & Digitalis 4. Start IVF, and D5LR for plasma administration, blood
transfusion, or drug administration as ordered.
4. Isoimmunization 5. Monitor V/S, bleeding, I & O
- The woman is Rh-negative against Rh-positive fetal blood which 6. Provide physical & psychological support.
may enter the maternal circulation - anticipate grief
- The production of maternal antibodies against Rh-positive blood. - anticipate possible guilt responses
Management: - anticipate fear related to a potential
- After a miscarriage, all women with Rh-negative blood should disturbance in childbearing capacity in the
receive Rh (D antigen) immune globulin (RhIG) – to prevent future
building-up antibodies in the event the conceptus was Rh positive
GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASE (HMOLE) (2nd
NURSING PROBLEM: TRIMESTER)
● Powerlessness or Anxiety related to loss of pregnancy. ● Abnormal proliferation and then degeneration of the trophoblastic
● Sadness or Grief villi (Gang & Guintoli,2007)
● A developmental anomaly of the placenta that changes chorionic
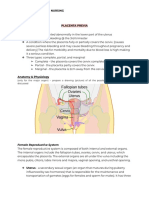
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY (1st Trimester Bleeding) villi into a mass of clear vesicles.
Main Problem: Implantation occurs outside the uterine cavity.
…………………………….………RAGANAS, HYACINTH MAE V. BSN-2D………………………………….
.. CARE OF MOTHER, CHILD AT RISK OR WITH PROBLEMS ……………………
● Presents as an edematous grapelike cluster that may be ● A cervix that dilates prematurely and therefore cannot hold a fetus
nonmalignant or may develop in choriocarcinoma. until term
● It occurs in about 1 % of women
Incidence: ● This commonly occurs at approximately week 20 of pregnancy
- 1:1500 pregnancies ● The cervical dilation is painless
- common in the Orient and in people of low socioeconomic status
Cause: UNKNOWN MANIFESTATIONS:
Risk Factors: ➢ Show, a pink-stained vaginal discharge (first symptom)
- Increased maternal age ( women older than 35 years) ➢ Increased pelvic pressure
- low socioeconomic status: low protein intake ➢ Rupture of membranes and discharge of amniotic fluid
- blood group A women who marry blood group O men ➢ (+) uterine contractions
TWO TYPES OF MOLAR GROWTH ASSOCIATED FACTORS
● Complete Mole ● Increased maternal age
- all trophoblastic villi swell and become cystic. ● Congenital structural defects
- embryo forms, it dies early at 1-2 mm in size; no fetal ● Trauma to the cervix occurring after repeated D & C
blood in the villi
- karyotype is normal 46 XY or 46 XX, chromosome DIAGNOSIS:
component was contributed only by the father, or an - Usually diagnosed only after the pregnancy is lost
“empty ovum” was fertilized and was duplicated - Can be detected early before the symptoms occur by SONOGRAM
● Partial Mole
- some of the villi form normally TREATMENT
- has 69 chromosomes ● Cervical Cerclage
- A surgical procedure is performed by suturing the
ASSESSMENT FINDINGS cervix using purse-string technique by the vaginal route
1. Brownish or reddish, intermittent or profuse vaginal bleeding by under regional anesthesia
16 weeks with clear-fluid-filled vesicles - Usually performed at weeks 12-14 of pregnancy after
2. Rapid uterine enlargement is inconsistent with the age of gestation. confirming by sonogram that the fetus of a 2nd
3. Symptoms of PIH before 20 weeks (↑BP, edema, proteinuria) pregnancy is healthy
4. Excessive nausea and vomiting d/t elevated HCG (1-2 M IU/L/24 - Its purpose of the suture is to strengthen the cervix and
hours) prevent if from dilating
5. Positive pregnancy test - the sutures are removed at weeks 37-38 of pregnancy
6. No fetal signs – heart tones, parts, movements
7. Abdominal pain Cervical Cerclage (80%-90% success rate)
● Mcdonald Procedure
DIAGNOSIS - nylon sutures are placed horizontally and vertically
a. Passage of clear-fluid-filled vesicles – the first sign that aids across the cervix and pulled tight to reduce the cervical
diagnosis canal to few millimeters in diameter
b. TRIAD SIGNS: ● Shirodkar Procedure
- Big uterus - Sterile tape is threaded in a cervix and sutured in place
- Vaginal bleeding: brownish and intermittent to achieve a closed cervix
- HCG greater than 1 million (Normal Value: 400,000
IU/L/24 hrs) CONDITIONS ASSOCIATED WITH THIRD TRIMESTER BLEEDING
c. Ultrasound ● Placenta Previa
d. Flat plate of the abdomen done after 15 weeks – no fetal skeleton ● Abruptio Placenta
● Premature rupture of membrame or preterm labor
PROGNOSIS
- 80% remission after D & C; may progress to cancer of the chorion PLACENTA PREVIA
- CHORIOCARCINOMA - Low implantation of the placenta
TREATMENT: Four Degrees
a. Evacuation by D & C or hysterectomy if no spontaneous A. Low-lying Placenta Previa
evacuation a.1. the implantation is lower rather than in the upper portion of the
b. Hysterectomy if above 45 years old and no future pregnancy is uterus (low - lying)
desired, or with increased chorionic gonadotropin after D & C a.2. Marginal Implantation - the placenta edge approaches the
c. HCG titer monitoring for one year – NO PREGNANCY for 1 year cervical os
(use contraception) because signs of pregnancy can mask early B. Partial Placenta Previa
signs of choriocarcinoma - implantation of the placenta occludes a portion of the
d. Medical replacement: blood, fluid, plasma cervical os
e. Chemotherapy for malignancy: METHOTREXATE is the drug of C. Total Placental Previa
choice - Implantation of the placenta totally occludes the
f. Chest X-ray to detect early lung metastasis cervical os
COMPLICATIONS ASSOCIATED FACTORS
a. Choriocarcinoma: most dreaded complication ● Increased parity
b. Hemorrhage: most serious during the early treatment phase ● Advanced maternal age
c. Uterine perforation ● Past cesarean births
d. Infection ● Past uterine curettage
● Multiple pregnancy
NURSING IMPLEMENTATION Incidence Rate: 5:1000 pregnancies
1. Advise bed rest Outcome: Increase in congenital fetal anomalies
2. Monitor VS, blood loss, molar/tissue passage, I & O
3. Maintain fluid & electrolyte balance, plasma, and blood volume ASSESSMENT FINDINGS
through replacements as ordered
● Painless vaginal bleeding (fresh, bright red and sudden) in the third
4. Prepare for D & C, hysterotomy, or hysterectomy as indicated
trimester approximately week 30/7th month
5. Provide psychological support; anticipate
● Uterine soft/flaccid or intermittent hardening if in labor
- Fear related to the potential development of cancer
● Intermittent pain if it happens in labor secondary to uterine
- Disturbance in self-esteem for carrying an abnormal
contractions
pregnancy
6. Prepare for discharge.
● Bleeding may be slight or profuse which may come after an
- Emphasize the need for follow-up HCG titer
activity, coitus or internal examination
determination for 1 year
- Reinforce instructions on NO PREGNANCY FOR
DIAGNOSIS
ONE YEAR; give instructions related to contraception.
Ultrasonography gives 95% ACCURATE RESULT
- detects site of placental implantation
PREMATURE CERVICAL DILATATION (INCOMPETENT CERVIX)
● Previously termed as incompetent cervix TREATMENT
…………………………….………RAGANAS, HYACINTH MAE V. BSN-2D………………………………….
.. CARE OF MOTHER, CHILD AT RISK OR WITH PROBLEMS ……………………
A. Watchful waiting: EXPECTANT MANAGEMENT, conservative if b. Rigid, boardlike, and painful abdomen
any c. Enlarged uterus d/t concealed bleeding; signs of shock not
● the mother is not in labor proportional to the degree of external bleeding (classic type)
● Fetus is premature, stable, and not in distress d. If in labor: tetanic contractions with the absence of alternating
● Bleeding is not severe contraction and relaxation of the uterus
B. AMNIOTOMY
● artificial rupture of the bag of waters DIAGNOSIS:
● Causes fetal head to descend causing mechanical a. Clinical diagnosis – signs and symptoms
pressure at placental site controlling bleeding b. Ultrasound – detects the retroplacental bleeding
C. DOUBLE SET UP (One set for vaginal delivery and another for c. Clotting studies – reveal DIC, clotting defects
classical CS):prepared for IE in suspected placenta previa in the
following conditions: The thromboplastin from retroplacental clot enters maternal circulation and
● Term gestation consumes maternal free fibrinogen resulting in:
● Mother in labor and progressing well 1. DIC (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation): small fibrin clots
● Mother and fetus are stable in circulation
- If the woman is not in labor or in shock, 2. Hypofibrinogemia: decrease normal fibrinogen results in the
and/or fetus is distressed, only one set-up is absence of normal blood coagulation
to be prepared, an emergency CLASSICAL
cesarean section set up COMPLICATIONS:
D. DELIVERY: If conditions for watchful waiting are absent: a. Hemorrhagic shock
● Vaginal delivery if birth canal is bot obstructed b. COUVELAIRE UTERUS: The bleeding behind the placenta may
● Cesarean section if placental placement prevents cause some of the blood to enter the uterine musculature causing
vaginal birth. In previa, CLASSICAL CS is indicated as the uterine muscles not to contract well once the placenta is
the lower uterine segment is occupied by the placenta. delivered.
Future pregnancies will be terminated by another CS c. DIC
because the presence of a classical CS scar is a d. CVA is secondary to DIC
CONTRAINDICATION to vaginal delivery; it is the e. Hypofibrinogenemia
leading cause of UTERINE RUPTURE. f. Renal failure
g. Infection h. Prematurity, fetal distress/demise (IUFD)
COMPLICATIONS
● Hemorrhage NURSING IMPLEMENTATIONS
● Prematurity a. Maintain bedrest, LLR
● Obstruction of the birth canal b. Careful monitoring:
- Maternal VS
NURSING IMPLEMENTATION - FHT
a. Maintain bedrest – left lateral recumbent with a head pillow - Labor onset/progress
b. DO NOT PERFORM an IE or vaginal examination - I & O, oliguria/anuria
c. Careful assessment: VS, bleeding, onset/progress of labor, FHT - Uterine pain
d. Prepare client for diagnostic ultrasonography - bleeding (not proportional to the degree of shock)
e. Institute shock measures as necessary. Initially, bleeding in previa c. Administer intravenous fluid, plasma, or blood as ordered
is rarely life-threatening but may become profuse with internal d. Prepare for diagnostic exams – explain results
examination e. Provide psychological support by preparing the patient for all
f. Provide psychological and physical support examinations, explaining what is happening, and
g. Prepare for conservative management, double setup, or a classical informing/explaining the results
CS f. Prepare for emergency birth either per vagina or CS
h. Observe for bleeding after delivery: The lower uterine segment, the g. Observe for ASSOCIATED PROBLEMS AFTER DELIVERY
site of placental detachment, is not as contractile as the upper - Poorly contracting uterus (Couvelaire uterus) leading to
fundal portion post-partal hemorrhage
- Disseminated Intravascular coagulation (DIC) leads to
ABRUPTIO PLACENTA hemorrhage and possibly CVA
● A complication of late pregnancy or labor characterized by - Hypofibrinogenemia leads to post-partal hemorrhage
premature partial or complete separation of a normally implanted - Prematurity, neonatal distress that will lead to neonatal
placenta. morbidity and mortality
● also termed ACCIDENTAL HEMORRHAGE / ABLATIO
PLACENTA
● INCIDENCE: 2nd leading cause of bleeding in the 3rd trimester;
occurs in 1: 300 pregnancies
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
● Maternal Hypertension: PIH, renal disease
● Sudden uterine decompression as in multiple
pregnancy and polyhydramnios
● Advance age
● Multiparity
● Short umbilical cord
● Trauma: fibrin defects
TYPES OF ABRUPTIO PLACENTA
● TYPE I: Concealed, covert, or central type; the classic type
- Placenta separates at the center causing blood to
accumulate behind the placenta
- External bleeding not evident
- Signs of shock not proportional to the amount of
external bleeding
● TYPE II: Marginal, overt, or external bleeding type
- Placenta separates at the margins
- Bleeding is external, usually proportional to the amount
of internal bleeding
- May be complete or incomplete depending on the
degree of detachment
ASSESSMENT FINDINGS:
a. Painful vaginal bleeding in the 3rd-trimester
…………………………….………RAGANAS, HYACINTH MAE V. BSN-2D………………………………….
You might also like
- NCM 109 MCN Semifinals Gestational ConditionsDocument6 pagesNCM 109 MCN Semifinals Gestational ConditionsQUEZON, BRITNEY KIM E.No ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocument17 pagesGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Pregnancy Testing - AUBFDocument6 pagesPregnancy Testing - AUBFMitch IbayNo ratings yet
- MCN Spontaneous MiscarriageDocument2 pagesMCN Spontaneous MiscarriageBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument36 pagesAbortionAnjali Rahul AjmeriNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Maternal TransesDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Maternal TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- Gestational 1Document8 pagesGestational 1RoseAngelyne VicenteNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Maternal TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Maternal TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pre Gestational ConditionDocument11 pages2 - Pre Gestational ConditionAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- HypertensiveDocument2 pagesHypertensiveJhon Mhark GarinNo ratings yet
- Abortion: DEFINITION-Abortion Is The Separation Partial orDocument77 pagesAbortion: DEFINITION-Abortion Is The Separation Partial orPadmaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions 1Document14 pagesGestational Conditions 1Fatima TañedoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Abnormal Ob High Risk PregnancyDocument13 pagesNCM 109 Abnormal Ob High Risk PregnancyMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Abn. PregnancyDocument177 pagesAbn. PregnancyPriscilla Sarah PayneNo ratings yet
- ABORTIONDocument6 pagesABORTIONJan Vincent BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Physiologic SignsDocument59 pagesPhysiologic SignsChari RivoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - MCN TransesDocument7 pagesModule 3 - MCN TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- High Risk Ob Notes 1Document20 pagesHigh Risk Ob Notes 1pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- Puerperum Notes 1Document7 pagesPuerperum Notes 1Google SecurityNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionDocument55 pagesNursing Care of The High Risk Pregnant Client With Gestational ConditionMarc FresNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument8 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyDeniel Ivan MasangcayNo ratings yet
- 27-Normal and Abnormal PuerperiumDocument29 pages27-Normal and Abnormal PuerperiumSu OoNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy CasiaDocument16 pagesEctopic Pregnancy CasiaMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Maternal MidtermDocument253 pagesMaternal MidtermTrishaNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter 21 Pregnancy Complication BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCYDocument76 pages1 Chapter 21 Pregnancy Complication BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCYCAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.No ratings yet
- Module 2 - MCN TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - MCN TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataDocument9 pagesCase Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataImee JenNo ratings yet
- Signs Indicating Possible Complications of PregnancyDocument6 pagesSigns Indicating Possible Complications of Pregnancygerald polopotNo ratings yet
- OBGYN TransDocument6 pagesOBGYN TransanonymousNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Prelims ReviewerDocument2 pagesNCM 109 Prelims ReviewerReyna Chame GarcinezNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Well-Being 1. Fetal MovementDocument6 pagesAssessment of Fetal Well-Being 1. Fetal MovementClaire Julianne CapatiNo ratings yet
- Multiple GestationDocument4 pagesMultiple GestationCHRISNA AMMANG PASPASANNo ratings yet
- High Risk Prenatal CareDocument4 pagesHigh Risk Prenatal CareKatherine Gayle GuiaNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRICS - Midterms - 1.1 - Diagnosis of Pregnancy - TRANSDocument5 pagesOBSTETRICS - Midterms - 1.1 - Diagnosis of Pregnancy - TRANSAi Gutierrez100% (1)
- Puerperium ManagementDocument19 pagesPuerperium ManagementDavina DakapNo ratings yet
- 1st Trimester ScansDocument36 pages1st Trimester ScansJANE 7117No ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument4 pagesMCN ReviewerMaria Arabella LanacaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document8 pagesCase Study 1inspire.nacNo ratings yet
- Complications of Intrapartum and Post PartumDocument8 pagesComplications of Intrapartum and Post PartumMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Theme:: Early Gestosis. Late GestosisDocument17 pagesTheme:: Early Gestosis. Late GestosisPoisonIvyyyNo ratings yet
- Study ThisDocument30 pagesStudy ThisKamva DukadaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive State of Pregnancy-Ready ToDocument2 pagesHypertensive State of Pregnancy-Ready ToEdmund Lominoque LamelaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Bleeding in PregnancyDocument4 pagesVaginal Bleeding in PregnancyAra BaltarNo ratings yet
- 68 Abnormal PeuperiumDocument44 pages68 Abnormal PeuperiumGodsonYeboah-AwudziNo ratings yet
- The Infant Should Always Be in A Rear-Facing Car Seat From Birth To 9.1 KGDocument7 pagesThe Infant Should Always Be in A Rear-Facing Car Seat From Birth To 9.1 KGSabhi Sandhu100% (1)
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancyDocument6 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancykirbsNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3Document17 pagesNCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3nianNo ratings yet
- Definitions of AbortionDocument4 pagesDefinitions of AbortionhfcxtshhfcNo ratings yet
- HMole HandoutsDocument2 pagesHMole HandoutsmartirezdawncelineNo ratings yet
- COURSE in The WARD Interhospital FinalDocument8 pagesCOURSE in The WARD Interhospital Finalkimadlo656No ratings yet
- Pre-Eclampsia and EclampsiaDocument19 pagesPre-Eclampsia and EclampsiaBiscuits and milkNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice Disease Infographics by SlidesgoDocument42 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Disease Infographics by Slidesgoshahedshaderma15No ratings yet
- CME Miscarriages Combined 1Document76 pagesCME Miscarriages Combined 1syawal zulfitriNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument14 pagesAbortionyt2zkpkphqNo ratings yet
- 4 - 5 Weeks AOG 3 Trimester: PeriodDocument4 pages4 - 5 Weeks AOG 3 Trimester: PeriodRojales FrancisNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument14 pagesNeonatal Jaundicewewewwe memeNo ratings yet
- GynaecologyDocument158 pagesGynaecologySyahrul ShaaraniNo ratings yet
- 2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Document75 pages2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Mary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Puerperium NotesDocument5 pagesPuerperium NotesCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- How Lupang Hinirang Ought To Be Sung by Joey AyalaDocument1 pageHow Lupang Hinirang Ought To Be Sung by Joey AyalaHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Gowning and Gloving The SurgeonDocument2 pagesGowning and Gloving The SurgeonHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 7 2022 Older AdultDocument16 pagesPharma Unit 7 2022 Older AdultHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Dependable Systems For Quality Care - Hammerton-RaganasDocument2 pagesDependable Systems For Quality Care - Hammerton-RaganasHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- MED AD and NGTDocument3 pagesMED AD and NGTHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Perineal CareDocument12 pagesPerineal CareHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Updated - Handling and Assisting DeliveriesDocument49 pagesUpdated - Handling and Assisting DeliveriesHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- 5 Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument24 pages5 Pregnancy Induced HypertensionHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Rules For WFRP 2eDocument2 pagesPregnancy Rules For WFRP 2eKenneth Fergus Benjamin McNishNo ratings yet
- Case Reports in Women's Health: Ying Ju, Xu Liu, Huiling Wang, Jun YangDocument4 pagesCase Reports in Women's Health: Ying Ju, Xu Liu, Huiling Wang, Jun YangHanizahnwNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Hyperemesis Gravidarum Maricar Abonado Midwifery IIDocument27 pagesCase Presentation Hyperemesis Gravidarum Maricar Abonado Midwifery IIMaricar Crescini AbonadoNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Is An Extreme, Persistent Nausea and Vomiting During PregnancyDocument1 pageHyperemesis Gravidarum: Is An Extreme, Persistent Nausea and Vomiting During PregnancyDarren RobertoNo ratings yet
- Anc 1Document128 pagesAnc 1Naila OmerNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument3 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumAldrece Castroverde100% (1)
- Hiperemesis Gravidarum Dan Kehamilan EktopikDocument17 pagesHiperemesis Gravidarum Dan Kehamilan EktopikNovia RizqiNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument9 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumChyank Qu SaddamNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders: Recessive Disorders (Homozygous) Description Cases Per Birth Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)Document18 pagesGenetic Disorders: Recessive Disorders (Homozygous) Description Cases Per Birth Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)tango0385100% (1)
- Minor Disorders Content.....Document12 pagesMinor Disorders Content.....Pabhat Kumar80% (5)
- Nausea, Vomiting in Pregnancy & Hyperemesis Gravidarum, UPDATE 2024Document30 pagesNausea, Vomiting in Pregnancy & Hyperemesis Gravidarum, UPDATE 2024patsilwalNo ratings yet
- A CASE REPORT: Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyDocument46 pagesA CASE REPORT: Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyIrma Permata sariNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Practice IDocument23 pagesMaternal and Child Health Practice Igaea_myzticmoonNo ratings yet
- Maternal Medical Disorders: SBA QuestionsDocument11 pagesMaternal Medical Disorders: SBA QuestionsBernardo Daniel Lawrencius100% (2)
- 2017-10-23 New Zealand Woman's WeeklyDocument96 pages2017-10-23 New Zealand Woman's WeeklyMitch YeohNo ratings yet
- NCM 109-Module 1 Lesson 2Document31 pagesNCM 109-Module 1 Lesson 2MARY ROSE DOLOGUINNo ratings yet
- 1Document25 pages1Harvey Cj NarvasaNo ratings yet
- Vomiting in PregnancyDocument13 pagesVomiting in PregnancyPriyanka John100% (4)
- ANC ModuleDocument103 pagesANC ModulePreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hiperemesis GravidarumDocument6 pagesJurnal Hiperemesis GravidarumArief Tirtana PutraNo ratings yet
- Pathologic Obstetrics, Care of Infants and Children and Family Planning TechnologyDocument118 pagesPathologic Obstetrics, Care of Infants and Children and Family Planning TechnologylovelyNo ratings yet
- Management of Hyperemesis Gravidarum PDFDocument10 pagesManagement of Hyperemesis Gravidarum PDFResi Lystianto PutraNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: By: Solomon Berhe OBGYN ResidentDocument73 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: By: Solomon Berhe OBGYN Residentmuleget haileNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Diet Sebelum Kehamilan Dan Risiko Hiperemesis GravidarumDocument23 pagesJournal Reading Diet Sebelum Kehamilan Dan Risiko Hiperemesis GravidarumNalendra Tri WidhianartoNo ratings yet
- Pasar p1 Exam CutieDocument10 pagesPasar p1 Exam CutieLeevine DelimaNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Brief ReviewDocument8 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Brief ReviewMISSLADYTIGNERNo ratings yet
- ATI Maternal Newborn Chapter 1-ContraceptionDocument23 pagesATI Maternal Newborn Chapter 1-ContraceptionVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (4)
- Midwife Prometric Test1Document17 pagesMidwife Prometric Test1Nesrine TrabelsiNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument16 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumKristine Alejandro80% (5)
- Nur 145 Answer KeyDocument36 pagesNur 145 Answer KeyJhoanna Marie VillaverdeNo ratings yet