Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HMole Handouts
Uploaded by
martirezdawnceline0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesHMole Handouts
Uploaded by
martirezdawncelineCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
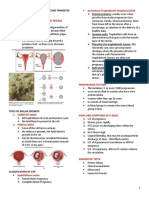
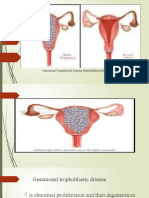
H-MOLE/GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC DISEASE No FHR or palpation of fetal parts
S/Sx of preeclampsia before usual time of onset such as
(HYDATIDIFORM OR H-MOLE)/MOLAR PREGNANCY
elevated BP edema and proteinuria
Abnormal proliferation and degeneration of the
High level of HCG with excessive N/V before 20th week of
trophoblastic villi.
gestation
As the cell degenerate, they become filled with fluid and
Anemia often accompanies bleeding
appears grapelike vesicles per vagina with soft abdomen
Maybe bright red and Dark red to brownish vaginal
and absent fetal parts on palpation
bleeding with 12 weeks
Ultrasound showing a characteristic snowstorm pattern.
Two Distinct types:
1. Complete molar pregnancy
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT:
• Have only placental parts, forms when a sperm fertilizes an
1. Suction Curettage or dilatation and curettage to remove
empty egg
mole
• The chromosome are either 46XX or 46XY but are
2. Serum hCG monitoring − HCG should be monitored for
contributed by only one parent and the chromosome material
1 year and should be negative 2−8 weeks after removal of
is duplicated.
mole. It is monitored every 2 weeks until normal then
• It usually leads to carcinoma
monthly for 6 months then every 2 months for the next 6
2. Partial Mole
months.
• It has 69 chromosome in which there are three
3. Chest x ray may also be done every 3 months for 6
chromosomes for every pair instead of two. 23 from the
months because H− mole cancer cells can metastasize to
mother and 2 sets from the father. This could occur when two
lungs.
cells fertilize one egg.
4. Oral Contraceptive use for 1 year− the woman is
• It rarely leads to carcinoma
advised not to get pregnant yet and pills should not
contain estrogen
Risk factors:
5. Methotrexate − anti cancer drug for one year to prevent
1. Higher occurrence in asian
development of malignancy
2. Women below 18 and above 40 years old
6. Hysterectomy
3. Women with low socioeconomic status who have low protein
intake
NURSING CARE:
4. History of molar pregnancy
Health education about contraceptives and rusks of future
pregnancies; pregnancy is delayed for at least 1 year.
ASSESSMENT:
Updated laboratory examinations to detect rising of HCG
Size of uterus is disproportionate to length of pregnancy
levels
UTZ shows no fetal skeleton /parts
Assess V/S, I/O
Provide emotional support
You might also like
- Gestational Conditions HandoutDocument17 pagesGestational Conditions HandoutFilamae Jayahr Caday100% (4)
- Hydatidiform Mole OutlineDocument3 pagesHydatidiform Mole Outlineyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- 3RD TrimesterDocument7 pages3RD TrimesterAmethystNo ratings yet
- Beige and Brown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation - 20240208 - 104844 - 0000Document10 pagesBeige and Brown Aesthetic Group Project Presentation - 20240208 - 104844 - 0000Romm JacobNo ratings yet
- High Risk Ob Notes 1Document20 pagesHigh Risk Ob Notes 1pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- H MolepcdplDocument55 pagesH MolepcdplCrisha SaguidNo ratings yet
- Definitions of AbortionDocument4 pagesDefinitions of AbortionhfcxtshhfcNo ratings yet
- Beige and Brown Aesthetic Group Project PresentationDocument9 pagesBeige and Brown Aesthetic Group Project PresentationRomm JacobNo ratings yet
- Cryptorchidism: A Concise Guide to Undescended TestesDocument14 pagesCryptorchidism: A Concise Guide to Undescended TestesMutiara Prima DianaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophic Disease & Placental DisordersDocument4 pagesGestational Trophic Disease & Placental DisordersJannen CasasNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Testing - AUBFDocument6 pagesPregnancy Testing - AUBFMitch IbayNo ratings yet
- Care of High-Risk Pregnant WomenDocument7 pagesCare of High-Risk Pregnant WomenJenny Agustin FabrosNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Early Pregnancy: Causes and ManagementDocument177 pagesBleeding in Early Pregnancy: Causes and ManagementPriscilla Sarah PayneNo ratings yet
- M3 - ReviewerDocument8 pagesM3 - ReviewerKristine KimNo ratings yet
- GYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument21 pagesGYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaElaine Marie Rendon PalmejarNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother With High-Risk Pregnancy ProblemsDocument4 pagesCare of Mother With High-Risk Pregnancy ProblemsHyacinth Mae Virtudazo RaganasNo ratings yet
- Infertility: PGI Ira Mikkaella GenobisDocument49 pagesInfertility: PGI Ira Mikkaella GenobisIra Mikkaella GenobisNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document7 pagesMCN 2GabNo ratings yet
- Types and Management of AbortionDocument6 pagesTypes and Management of AbortionJan Vincent BallesterosNo ratings yet
- GYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument21 pagesGYN Module 3 Case 1: Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaElaine Marie Rendon PalmejarNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancyDocument6 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancykirbsNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Well-Being 1. Fetal MovementDocument6 pagesAssessment of Fetal Well-Being 1. Fetal MovementClaire Julianne CapatiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Abnormal Ob High Risk PregnancyDocument13 pagesNCM 109 Abnormal Ob High Risk PregnancyMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- 2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Document75 pages2F Compiled Oral Revalida 1Mary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Oup 2Document72 pagesOup 2John Christian LasalitaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Summary NotesDocument14 pagesUnit 2 Summary NotesQuesyNo ratings yet
- 2C-OREV-COMPILATION-TOPICDocument56 pages2C-OREV-COMPILATION-TOPICPaolo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Anenorrhea 2016-2017Document24 pagesPrimary and Secondary Anenorrhea 2016-2017zianab ali100% (1)
- AbortionDocument14 pagesAbortionyt2zkpkphqNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Molar Pregnancy - Case PresentationDocument7 pagesMolar Pregnancy - Case Presentationアンナドミニク100% (1)
- NCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3Document17 pagesNCM 109 (PRELIMS) - Lesson 3nianNo ratings yet
- Obg AbortionDocument62 pagesObg Abortionkashyap priyankaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (Hydatidiform Mole)Document4 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease (Hydatidiform Mole)Zhane Inamac CezarNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease WordDocument3 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease WordsahaniNo ratings yet
- OSCE Revision OBG DocumentDocument60 pagesOSCE Revision OBG DocumentshreyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107Document83 pagesNCM 107Jan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Topic:: "Gestational Conditions Affecting Pregnancy Outcomes"Document29 pagesTopic:: "Gestational Conditions Affecting Pregnancy Outcomes"Marie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Lecture MidtermsDocument9 pagesMaternal Lecture MidtermsFreema FloresNo ratings yet
- INFERTILITYDocument2 pagesINFERTILITYyxly imperialNo ratings yet
- ABORTIONDocument3 pagesABORTIONAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- H MoleDocument7 pagesH MoleRaymond Christopher LimNo ratings yet
- MCN2 Prelim-NotesDocument4 pagesMCN2 Prelim-NotesChris AnnNo ratings yet
- Vesicular Mole: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Egypt, Domiat G. HospitalDocument32 pagesVesicular Mole: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Egypt, Domiat G. HospitalPrathibha GuruguriNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bassem W. Yani, MD Diploma of Urology, FEBU, FCS, Cairo, EGYPT Consultant Urologist Uth Lusaka ZambiaDocument43 pagesDr. Bassem W. Yani, MD Diploma of Urology, FEBU, FCS, Cairo, EGYPT Consultant Urologist Uth Lusaka ZambiaMohammed AadeelNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Bleeding in PregnancyDocument4 pagesVaginal Bleeding in PregnancyAra BaltarNo ratings yet
- Pcos VictoriaDocument4 pagesPcos VictoriaAgustina S. SelaNo ratings yet
- OB - Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (JCR)Document5 pagesOB - Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (JCR)gellie gellesNo ratings yet
- Mullerian Duct Abnormalities, Hirsutism, Bacterial Vaginosis & IUCDsDocument4 pagesMullerian Duct Abnormalities, Hirsutism, Bacterial Vaginosis & IUCDsrohitNo ratings yet
- High Risk Prenatal CareDocument4 pagesHigh Risk Prenatal CareKatherine Gayle GuiaNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument9 pagesAbortionmendato marcabanNo ratings yet
- ABORTIONDocument2 pagesABORTION2AAQUINO, PRECIOUS ANGEL F.No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Maternal TransesDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Maternal TransesCarl UyNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Diagnosis Pathophysio Etiology Signs Management/ConsiderDocument4 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Diagnosis Pathophysio Etiology Signs Management/ConsiderTin AteliagaNo ratings yet
- Twin Pregnancy with Complete Hydatidiform Mole and HELLP SyndromeDocument3 pagesTwin Pregnancy with Complete Hydatidiform Mole and HELLP SyndromeGEAMH OBGYNNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Lab Tests ExplainedDocument55 pagesPregnancy Lab Tests ExplainedJoseph DusichNo ratings yet
- By Intern Dr. Borhan UddinDocument12 pagesBy Intern Dr. Borhan UddinmanjuNo ratings yet
- 2nd Trimester BleedingDocument50 pages2nd Trimester BleedingRaiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform Mole-Is A Type of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasm ThatDocument4 pagesHydatidiform Mole-Is A Type of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasm ThatjhelabooNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument10 pagesSpina BifidamartirezdawncelineNo ratings yet
- Edited Reaction Paper 1ST Seminar Jay C. CamachoDocument29 pagesEdited Reaction Paper 1ST Seminar Jay C. CamachomartirezdawncelineNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 1Document97 pagesNCM 109 1martirezdawncelineNo ratings yet
- Activity No.2 EntrepDocument3 pagesActivity No.2 EntrepmartirezdawncelineNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Dini Preeklampsia Dan Eklampsia Dan Pencegahan Preeklampsia Dan EklampsiaDocument22 pagesDiagnosis Dini Preeklampsia Dan Eklampsia Dan Pencegahan Preeklampsia Dan EklampsiaAbigail Bl SiagianNo ratings yet
- Managing Antepartum HemorrhageDocument6 pagesManaging Antepartum HemorrhageNurul SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Cooper - Domestic Violence & Pregnancy - A Literature Review PDFDocument5 pagesCooper - Domestic Violence & Pregnancy - A Literature Review PDFpoetry2proseNo ratings yet
- Abortion Pro Life Vs Pro ChoiceDocument6 pagesAbortion Pro Life Vs Pro Choiceapi-356865000No ratings yet
- Antenatal Fetal MonitoringDocument28 pagesAntenatal Fetal MonitoringchestersudhakarNo ratings yet
- Total ProteinDocument3 pagesTotal ProteinTriRatnaFauziah50% (2)
- PhilHealth Coverage for Pregnant WomenDocument20 pagesPhilHealth Coverage for Pregnant WomenErnest Jerome MalamionNo ratings yet
- Bonnie - Tam - 22S2 NUR2029 Teaching Schedule - Rev (1) (2) (3) - 5-1-23Document9 pagesBonnie - Tam - 22S2 NUR2029 Teaching Schedule - Rev (1) (2) (3) - 5-1-23Seokjin RJNo ratings yet
- NOELLE® S554.100: Childbirth and Neonatal Resuscitation Patient SimulatorDocument4 pagesNOELLE® S554.100: Childbirth and Neonatal Resuscitation Patient SimulatorAna Diana DucaNo ratings yet
- MOLAR Pregnancy V2 2021Document5 pagesMOLAR Pregnancy V2 2021CassNo ratings yet
- Gynecology and Obstetrics Unit Space ProximityDocument10 pagesGynecology and Obstetrics Unit Space ProximitySheryl ShekinahNo ratings yet
- Expanded Programme For Free Maternity: Package BenefitsDocument2 pagesExpanded Programme For Free Maternity: Package BenefitsQuentene odongoNo ratings yet
- ICOEDocument2 pagesICOEmeutia wardhanie ganieNo ratings yet
- Ob Post TestDocument11 pagesOb Post TestAlexNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Handbook: "Am I Pregnant?" All B-HCG Levels ExplainedDocument74 pagesPregnancy Handbook: "Am I Pregnant?" All B-HCG Levels ExplainedDr0Web100% (1)
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord ProlapseYwagar Ywagar100% (1)
- Cord ProlapseDocument3 pagesCord ProlapseNise Mon KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Blighted OvumDocument33 pagesBlighted Ovumamirz_4100% (1)
- Restrictia de Crestere FetalaDocument7 pagesRestrictia de Crestere FetalaBianca MariaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics & Gynecologyc MnemonicsDocument12 pagesObstetrics & Gynecologyc MnemonicsMuhammad Luqman Nul HakimNo ratings yet
- Municipal Ordinance No. 04-2012Document6 pagesMunicipal Ordinance No. 04-2012JayPardinianNuyda100% (1)
- Faktor - Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Pengeluaran ASI Pada Ibu Post PartumDocument14 pagesFaktor - Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Pengeluaran ASI Pada Ibu Post Partumnovriyana saniNo ratings yet
- Obstetric - OB Ultrasound Made Easy - Step-By-Step Guide - POCUS 101Document42 pagesObstetric - OB Ultrasound Made Easy - Step-By-Step Guide - POCUS 101skype72214100% (1)
- Pathogenesis of Preterm LaborDocument14 pagesPathogenesis of Preterm LaborAgung Sunarko PutraNo ratings yet
- Management Placenta PreviaDocument24 pagesManagement Placenta PreviaMuhammad RifaldiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Why, When, What Is FoundDocument15 pagesUltrasound-Why, When, What Is FoundDyAnna Williams GordonNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Birth After Previous Caeserian SectionDocument18 pagesVaginal Birth After Previous Caeserian SectionSky JuiceNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Bleeding in Pregnancy - Teaching Care PlanDocument3 pagesVaginal Bleeding in Pregnancy - Teaching Care PlannajmulNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Actions - Monika MakwanaDocument10 pagesAbnormal Uterine Actions - Monika Makwanamonika makwanaNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Placenta and CordDocument47 pagesAbnormalities of Placenta and CordShrooti Shah75% (4)