Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extrinsic Motivation Intrinsic Motivation: A. GLOW (Consistency, Interest, Joy)
Uploaded by
erickson hernanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Extrinsic Motivation Intrinsic Motivation: A. GLOW (Consistency, Interest, Joy)
Uploaded by
erickson hernanCopyright:
Available Formats
MOTIVATION TECHNIQUES
1. Extrinsic Motivation is the type which is originating primarily from the individual's outside self. It
is not permanent. This needs some sort of continuous reinforcement
2. Intrinsic Motivation is a self-driven type of motivation that lasts for a long time. The learners
themselves are driven by their own goals, dreams and ambitions. This is the kind of motivation
that must be developed among the learners.
1. GO DEEPLY
a. GLOW ( Consistency, Interest, Joy)
- A teacher who most of the time exhibits a frowning face is not a pleasant sight to behold.
Too many students feel disappointed and demoralized when teachers cast a dagger look
on them when their performance falls short of the teacher's expectations.
b. OBSERVE ( Focus, Vigilance, Visibility )
- Take extra effort to be very vigilant of whether the students perform positively or
negatively. If the students are performing well, recognize their efforts so they will be more
inspired to work.
c. DEMONSTRATE (Caution, Approachability, Autonomy)
- Teachers do not project an image of "In-approachability" due to his or her high standard
of compelling the students to perform excellently, thereby creating an environment of
compulsion and fear. It will be a beautiful scenario if students are given the freedom to be
themselves. Decision making should be the sole task of the teacher.
d. ENGAGE ( ActiveParticipation, Involvement, Collaboration)
- Students should be involved in academic learning activities which they could do
meaningfully and successfully. The construction of meaning to the activities p inside and
outside the class is a motivating factor for the students to be involved in different tasks
provided by the teacher.
e. EMBRACE (Acceptance, Positive Approach, Communication)
- Every student should be embraced as your own despite their weaknesses, limitations. A
negative remark on a student's poor performance in class is a "sin" motivation. A hurting
comment demoralizes a student.
f. PRAISE ( Appreciation, Confirmation, Sincerity )
- It should be given spontaneously genuinely as an expression of the teachers'
confirmation and appreciation of a task well done by the students. They should never be
wanting in praising their students' positive change behavior.
g. LISTEN ( Attentiveness, Openness, Patience )
- This should be coupled with a desire to find out what a student is trying to drive at every
time he or she is called to recite or share in the class. Effective listening is synonymous
with taking the students' responses without interruption, displaying impatience or
rushing the learner just because the teacher is not pleased with the students' feedback.
h. YIELD ( Affirmation, Agreement, Alliance )
- Synonymous with the objective acceptance of the students' feedback or answers. In a
while the teacher must learn how to give way to the demands of the students. The wisdom
of the young should not be underestimated.
2. ARCS c. CONFIDENCE
- Learning Requirements
a. ATTENTION - Success opportunities
- Perceptual Arousal - Personal Control
- Inquiry Arousal d. SATISFACTION
- Variability - Intrinsic Reinforcement
b. RELEVANCE - Extrinsic Rewards
- Goal Orientation - Equity
- Motive Matching
- Familiarity
You might also like
- Why Do We Learn - 3Document1 pageWhy Do We Learn - 3api-371832017No ratings yet
- Jonathan Porro Folder of WisdomDocument4 pagesJonathan Porro Folder of Wisdomapi-437415281100% (1)
- Roles of A TeacherDocument3 pagesRoles of A TeacherPauline BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2analysis Module (Idt Ho)Document11 pages2analysis Module (Idt Ho)dan cosmiNo ratings yet
- Batonlapoc, Botolan, Zambales: Polytechnic College of BotolanDocument3 pagesBatonlapoc, Botolan, Zambales: Polytechnic College of BotolanShairra AbdonNo ratings yet
- Handouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportDocument5 pagesHandouts From Week 10 To Week 12 Summation of ReportAkoni si ARARNo ratings yet
- What Is MOTIVATIONDocument3 pagesWhat Is MOTIVATIONAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fs 1 - Midterm NotesDocument4 pagesFs 1 - Midterm NotesJERRICK P. ARMECINNo ratings yet
- Self ConceptDocument8 pagesSelf ConceptsunshinesunshineNo ratings yet
- Lipardo - Learning Task 3Document2 pagesLipardo - Learning Task 3Giuseppe LipardoNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode 2: GUIDING PRINCIPLES in The ASSESSMENT ofDocument3 pagesLearning Episode 2: GUIDING PRINCIPLES in The ASSESSMENT ofELIZABETH SILLANo ratings yet
- Educ104 4-5 Week UlobDocument6 pagesEduc104 4-5 Week UlobNorienne TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LearningDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Learningsohini bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Educ 211 - Torralba - MotivationDocument19 pagesEduc 211 - Torralba - MotivationFaye Abegail TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management in The 21st Century ClassroomDocument6 pagesClassroom Management in The 21st Century ClassroomJan Christian C. BarcelaNo ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument6 pagesHealth Educationkhayceemeade2No ratings yet
- Inclusive Educ PDFDocument12 pagesInclusive Educ PDFHannahNo ratings yet
- SSE 122 - Teaching in The Specialized FieldDocument18 pagesSSE 122 - Teaching in The Specialized FieldMeliza Casipit100% (2)
- Educ213 Activity 3 - Into The FutureDocument2 pagesEduc213 Activity 3 - Into The FutureCelineNo ratings yet
- 330 Motivation NotesDocument1 page330 Motivation NotesStacy LieutierNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Approaches of Teaching and Learning - July - 2013 - 9611000004 - 9602226Document2 pagesHumanistic Approaches of Teaching and Learning - July - 2013 - 9611000004 - 9602226Cristiana GrozavescuNo ratings yet
- Teaching Proffesion: What Is Classroom Management?Document3 pagesTeaching Proffesion: What Is Classroom Management?Angelo NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Ten Ways To Give Better FeedbackDocument2 pagesTen Ways To Give Better Feedbackapi-467854007No ratings yet
- Determinants of LearningDocument4 pagesDeterminants of LearningLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesMaybza ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Associate Degree in Education Cyril Potter College of Education Science 155Document3 pagesAssociate Degree in Education Cyril Potter College of Education Science 155Ravin RagbeerNo ratings yet
- Session3 CoT 5ExpectationsThatHelpShapeACultureOfThinkingV2Document1 pageSession3 CoT 5ExpectationsThatHelpShapeACultureOfThinkingV2Julissa GomezNo ratings yet
- Field StudyDocument22 pagesField StudyLorjen Fernandez RetanalNo ratings yet
- Management DisciplineDocument17 pagesManagement DisciplineJaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document7 pagesLesson 1Mary Ann Andes CaruruanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Ed-102 (FINAL DRAFT)Document9 pagesReviewer-In-Ed-102 (FINAL DRAFT)eurekadeverliebasilioNo ratings yet
- Assessment:: Name of Student: Course Code: Module #: Course Title: TopicDocument3 pagesAssessment:: Name of Student: Course Code: Module #: Course Title: TopicrhemA PuguonNo ratings yet
- Servidad - Educ 112 Lesson 2.6Document1 pageServidad - Educ 112 Lesson 2.6Sophia Ivy E. ServidadNo ratings yet
- Unds Reviewer Finals PDFDocument3 pagesUnds Reviewer Finals PDFShane SaynoNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument53 pagesMotivationIrsh ThoushNo ratings yet
- Emotional DisturbanceDocument2 pagesEmotional Disturbanceapi-341965740No ratings yet
- Module 4-Growth MindsetDocument26 pagesModule 4-Growth MindsetRyan Negad100% (1)
- Acilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusDocument25 pagesAcilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusClara ArejaNo ratings yet
- Human Learning 6Document3 pagesHuman Learning 6Janee JaneNo ratings yet
- Motivation Group 4Document35 pagesMotivation Group 4Regine Natali FarralesNo ratings yet
- Program: 1. Research Output Assessment: Direction:: Action Research Outpu TDocument8 pagesProgram: 1. Research Output Assessment: Direction:: Action Research Outpu TRose Ailyn Panelo CalongeNo ratings yet
- Part2 Exam, Navarez, ResponsoDocument1 pagePart2 Exam, Navarez, Responsomariejanine navarezNo ratings yet
- PST - MLS ActivityDocument3 pagesPST - MLS ActivityGwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 103 ReportDocument4 pagesProf Ed 103 ReportDave Matthew LibiranNo ratings yet
- Developing, Monitoring and Maintaining Productive Pupil BehaviourDocument18 pagesDeveloping, Monitoring and Maintaining Productive Pupil BehaviourSiti Noor WahidaNo ratings yet
- Learning Process Faculty GuidedlDocument38 pagesLearning Process Faculty GuidedlHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Teaching Is A Complex Human Activity - ItDocument2 pagesTeaching Is A Complex Human Activity - Itarnold john boniteNo ratings yet
- 203Document9 pages203Lyza Rhane LapastoraNo ratings yet
- High School: Curriculum OverviewDocument13 pagesHigh School: Curriculum Overviewshidik BurhaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 ReportDocument19 pagesLesson 8 ReportMaam NikkiNo ratings yet
- "Without The Foundation of The Old One, You Cannot Make An AuthenticDocument3 pages"Without The Foundation of The Old One, You Cannot Make An AuthenticBams PadillaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Metacognitive Factors Motivational and Affective Factors Individual Differences Factors Developmental and Social FactorsDocument5 pagesCognitive and Metacognitive Factors Motivational and Affective Factors Individual Differences Factors Developmental and Social Factorsapi-535082025No ratings yet
- Philosophical MatrixDocument3 pagesPhilosophical MatrixIvy Jean Amadora FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Standard 6 Lesson 4Document40 pagesStandard 6 Lesson 4Abdul Ghafoor ChhachharNo ratings yet
- PmtaDocument4 pagesPmtaDaphne Rhed A. BaticanNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - SummaryDocument3 pagesGroup 2 - SummaryPitche RUSILNo ratings yet
- Health L5Document5 pagesHealth L5cuteathena11No ratings yet
- Motivating Our Students: Wei-Chien Lee, Ph.D. Counseling Services 924-5910Document28 pagesMotivating Our Students: Wei-Chien Lee, Ph.D. Counseling Services 924-5910Prasad ShahNo ratings yet
- Self-Paced Learning Module: Evelyn C. Casareno Instructor IDocument11 pagesSelf-Paced Learning Module: Evelyn C. Casareno Instructor IEliNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Life Exile Trial and DeathDocument9 pagesRizal's Life Exile Trial and Deatherickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Industry AnalysisDocument2 pagesIndustry Analysiserickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 12 Questionserickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Characters in NoliDocument39 pagesCharacters in Nolierickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Concept of A System and The Issues of GoalDocument1 pageDiscuss The Concept of A System and The Issues of Goalerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- 2960Document3 pages2960erickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Post-Test Answer Sheets: F F T T TDocument4 pagesPost-Test Answer Sheets: F F T T Terickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appreciation: Darryl PagpagitanDocument8 pagesCertificate of Appreciation: Darryl Pagpagitanerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Virtual KUMU A Psycho Social and Mental Health KumustahanDocument2 pagesVirtual KUMU A Psycho Social and Mental Health Kumustahanerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Implementation-Report Virtual-KUMU-A-Psycho-Social-and-Mental-Health-KumustahanDocument10 pagesImplementation-Report Virtual-KUMU-A-Psycho-Social-and-Mental-Health-Kumustahanerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- An Inconvenient Truth WorksheetDocument7 pagesAn Inconvenient Truth Worksheeterickson hernanNo ratings yet
- 500 MctheoriesDocument81 pages500 Mctheorieserickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Badminton CompilationDocument58 pagesBadminton Compilationerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Basic/ Fundamental Skills and Drills in Badminton (Written Report)Document4 pagesBasic/ Fundamental Skills and Drills in Badminton (Written Report)erickson hernan100% (1)
- Badminton: Facilities, Equipment & Playing AreaDocument13 pagesBadminton: Facilities, Equipment & Playing Areaerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument59 pagesClimate Changeerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Mathnd Mod World Mod 4Document5 pagesMathnd Mod World Mod 4erickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern Worldmod5Document8 pagesMathematics in The Modern Worldmod5erickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World-Module7Document8 pagesMathematics in The Modern World-Module7erickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 ParcorDocument5 pagesModule 4 Parcorerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Girls Template - Endah ListaDocument5 pagesGirls Template - Endah Listaerickson hernanNo ratings yet
- Applied Entreprenuership DLL Week2Document5 pagesApplied Entreprenuership DLL Week2Roden Son100% (1)
- Sample Recognition For Teachers in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesSample Recognition For Teachers in The Philippinesrachel maravilla100% (2)
- Change or Die - DessyDocument43 pagesChange or Die - DessyZulkifli MansurNo ratings yet
- Cunoasterea Mediului PDFDocument236 pagesCunoasterea Mediului PDFMihaela GuritaNo ratings yet
- Counseling ResumeDocument1 pageCounseling Resumeapi-452946482No ratings yet
- Question For Test Paper M1DDocument22 pagesQuestion For Test Paper M1DArjun DeoreNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Circular MotionDocument35 pagesDynamics of Circular MotionEmmaren SabridoNo ratings yet
- Purposeful Community Reflection ToolDocument5 pagesPurposeful Community Reflection Toolapi-418757774No ratings yet
- Modern Synthetic Methods - 1Document64 pagesModern Synthetic Methods - 1Sankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- ADDIE ModelDocument24 pagesADDIE Modelhaziq iskandarNo ratings yet
- Tonganoxie Usd 464 Strat Plan DetailedDocument6 pagesTonganoxie Usd 464 Strat Plan Detailedapi-405695853No ratings yet
- Resume For Betsie Counts BaraczDocument2 pagesResume For Betsie Counts BaraczBetsie Counts BaraczNo ratings yet
- Artikel Proses Asimilasi Dan Akomodasi Dalam MemDocument7 pagesArtikel Proses Asimilasi Dan Akomodasi Dalam Memdinda permata hatiNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument29 pagesProjectile MotionLeague of Individuals for Environment SBCNo ratings yet
- NSTP-CWTS2-EFG5 - Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesNSTP-CWTS2-EFG5 - Reflection PaperRose Ulyshier AreolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On PE Swimming3Document2 pagesLesson Plan On PE Swimming3Igorota SheanneNo ratings yet
- SHDP Foundation Course Application Project PlanDocument9 pagesSHDP Foundation Course Application Project PlanNestorJepolanCapiñaNo ratings yet
- The Application of Testing ACROSS CULTURESDocument3 pagesThe Application of Testing ACROSS CULTURESBrighton MarizaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Practice SheetDocument5 pagesKinematics Practice SheetAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Theme-Based Assessment OverviewDocument19 pagesTheme-Based Assessment OverviewCarl CorreosNo ratings yet
- F Dt. 04.03.2018 Social Entrepreneurship in IndiaDocument8 pagesF Dt. 04.03.2018 Social Entrepreneurship in IndiaAshish NandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6.problem Set 2Document5 pagesUnit 6.problem Set 2Aryaa KapilNo ratings yet
- Summary-of-Introduction-to-HOTS-SOLO-PLP, Summarized by Elinita C. ManaloDocument2 pagesSummary-of-Introduction-to-HOTS-SOLO-PLP, Summarized by Elinita C. Manalojoel manalo100% (1)
- IPCRF Development PlanDocument2 pagesIPCRF Development PlanMaryknoll PonceNo ratings yet
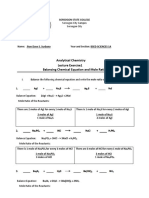
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise1 Balancing Chemical Equation and Mole RatioDocument3 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Exercise1 Balancing Chemical Equation and Mole RatioJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- WebquestDocument3 pagesWebquestapi-402685678No ratings yet
- Philosophic Inventory 1Document4 pagesPhilosophic Inventory 1api-450536386No ratings yet
- Errata Second EditionDocument2 pagesErrata Second EditionBsbsbaNo ratings yet
- Updated Inventory of LR TemplateDocument4 pagesUpdated Inventory of LR TemplateErika Kristina MortolaNo ratings yet
- Visual RepresentationDocument2 pagesVisual Representationapi-405690949No ratings yet
- The Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsFrom EverandThe Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- ESL Reading Activities For Kids (6-13): Practical Ideas for the ClassroomFrom EverandESL Reading Activities For Kids (6-13): Practical Ideas for the ClassroomRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsFrom EverandThe Read-Aloud Family: Making Meaningful and Lasting Connections with Your KidsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (205)
- Uncovering the Logic of English: A Common-Sense Approach to Reading, Spelling, and LiteracyFrom EverandUncovering the Logic of English: A Common-Sense Approach to Reading, Spelling, and LiteracyNo ratings yet
- The Artful Read-Aloud: 10 Principles to Inspire, Engage, and Transform LearningFrom EverandThe Artful Read-Aloud: 10 Principles to Inspire, Engage, and Transform LearningRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reading Comprehension Practice, Grades 7 - 8From EverandReading Comprehension Practice, Grades 7 - 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reading Comprehension, Grade 7From EverandReading Comprehension, Grade 7Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Alphabet Phonics Flashcards: Preschool and Kindergarten Letter-Picture Recognition, Word-Picture Recognition Ages 3-6From EverandAlphabet Phonics Flashcards: Preschool and Kindergarten Letter-Picture Recognition, Word-Picture Recognition Ages 3-6Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Teach Reading with Orton-Gillingham: 72 Classroom-Ready Lessons to Help Struggling Readers and Students with Dyslexia Learn to Love ReadingFrom EverandTeach Reading with Orton-Gillingham: 72 Classroom-Ready Lessons to Help Struggling Readers and Students with Dyslexia Learn to Love ReadingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Differentiated Reading for Comprehension, Grade 1From EverandDifferentiated Reading for Comprehension, Grade 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phonics Pathways: Clear Steps to Easy Reading and Perfect SpellingFrom EverandPhonics Pathways: Clear Steps to Easy Reading and Perfect SpellingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Accelerated Learning: Accelerated Learning Strategies to Master Skill Acquisition and Boost Productivity With a Step by Step BlueprintFrom EverandAccelerated Learning: Accelerated Learning Strategies to Master Skill Acquisition and Boost Productivity With a Step by Step BlueprintNo ratings yet
- The Book Whisperer: Awakening the Inner Reader in Every ChildFrom EverandThe Book Whisperer: Awakening the Inner Reader in Every ChildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Goo Goo, Ga Ga! Baby's Babble to Baby's First Words. - Baby & Toddler First Word BooksFrom EverandGoo Goo, Ga Ga! Baby's Babble to Baby's First Words. - Baby & Toddler First Word BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Reading Comprehension Practice, Grade 5From EverandReading Comprehension Practice, Grade 5Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Reading Mind: A Cognitive Approach to Understanding How the Mind ReadsFrom EverandThe Reading Mind: A Cognitive Approach to Understanding How the Mind ReadsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mommy, Teach Me to Read!: A Complete and Easy-to-Use Home Reading ProgramFrom EverandMommy, Teach Me to Read!: A Complete and Easy-to-Use Home Reading ProgramRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Guided Word Building: Systematic, Sequential Phonics LessonsFrom EverandGuided Word Building: Systematic, Sequential Phonics LessonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)