Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 1.3
Chapter 1 1.3
Uploaded by
Aqiena BalqisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 1.3
Chapter 1 1.3
Uploaded by
Aqiena BalqisCopyright:
Available Formats
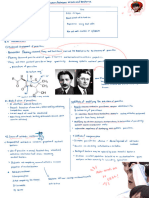
1.
3 Prokaryotes by Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes C simple all )
living organisms multicellular Bacteria is unicellular
unicellular or
organism
•
- ~
simple organisms such as bacteria , Have DNA
single
•
cell
-
→
Plants
by animals made
up of many Genome of
•
cells E. Coli is about
are 1.5 millimeters in
length
•
,
.
Each cell has but the
length of
•
a
particular the bacterium is about 1000 times shorter
share character
membrane
.
1- cell
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes 2- DNA
3- - free
↳ all unicellular ribosome
organisms ↳
most are multicellular
except for c. site of
\ bound
protein synthesis)
archae bacteria
plant 4- cytosol
-
-
en bacteria M m
protists plants
-
-
cyanobacteria *
fungi animals
living cell
reproduce
-
-
can
-
↳ Bacteria have to divide too
Types of prokaryotes * Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission ,
budding
Arcnae bacteria Ancient bacteria ↳ divide half Cnot )
in as
organized eukaryotes
• -
as
Enbacteria Gram
positively Exchange of genetic material ( v)
•
gram negative
-
Nostocs
cyanobacteria eg Photosynthetic Exchange of by female gamete 1×1
•
:
-
male .
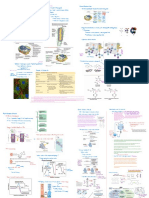
* The size of prokaryotic cells are much smaller than Comparison . . .
eukaryotic cells .
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
simple in structure
highly structured
-
-
Prokaryotic cells -
have a
variety of
shapes
-
no
recognizable organelles
-
developed specialized packaging
Most and
gives them shape transport
have cell wall that mechanisms that
common
shapes
-
: -
•
Coccus spherical UH wall is the more fluid all be to
eg Streptococcus may necessary support
-
: :
Bacillus shaped
rod eg Escherichia their larger size
•
: :
coli membrane .
.
Spin Ilium spiral Spiro chaeta
• -
eg
Cytoplasm enclosed within all
: : -
,
•
Comma forms :
eg : Vibrio membrane does not exhibit much
structure
-
One long strand chromosomes
-
Many chromosomes
You might also like
- A Guide To Field Identification: Birds of North AmericaDocument346 pagesA Guide To Field Identification: Birds of North AmericaMomzy Moo100% (10)
- Houseplant ListDocument1 pageHouseplant Listelvis prestlyNo ratings yet
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterDocument1 pageBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Practocal Manual On Plant Tissue CultureDocument130 pagesPractocal Manual On Plant Tissue CultureĐương Anh CaoNo ratings yet
- Branches of GeneticsDocument3 pagesBranches of Geneticskevin maravilla100% (3)
- The Serious GooseDocument21 pagesThe Serious GooseOlga MGNo ratings yet
- StarCity Company ProfileDocument8 pagesStarCity Company ProfileStar CityNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Nature & Variety of Living OrganismsDocument2 pages1 - The Nature & Variety of Living OrganismsStudy with ShayaNo ratings yet
- 4b89c76031f763b4941ae95569111b5aDocument252 pages4b89c76031f763b4941ae95569111b5aIon NasarauNo ratings yet
- Propagation by Grafting and BuddingDocument20 pagesPropagation by Grafting and BuddingȘtefan Nicu BuzucNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science Iv I. Lesson ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science Iv I. Lesson ObjectivesKim Rose BorresNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument9 pagesBiologyvibesatevenNo ratings yet
- L1 - Gene ExpressionDocument5 pagesL1 - Gene Expressiontowalovesports920No ratings yet
- Antibacterial and Anti ViralsDocument2 pagesAntibacterial and Anti ViralsKinley YangzomNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Bio Notw NewDocument19 pagesCell and Molecular Bio Notw NewPASSORN SAE JEWNo ratings yet
- Super NotesDocument18 pagesSuper NotesYasir Kamal 13No ratings yet
- Animalsk-2 QR Grab Food HighDocument1 pageAnimalsk-2 QR Grab Food HighLola LolaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 What Is A Ce!? 8.2 Ce! Theory 8.3 An Overview of Ce! 8.4 Prokaryotic Ce!s 8.5 Eukaryotic Ce!sDocument2 pages8.1 What Is A Ce!? 8.2 Ce! Theory 8.3 An Overview of Ce! 8.4 Prokaryotic Ce!s 8.5 Eukaryotic Ce!ssrishtiNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom FlowchartDocument11 pagesPlant Kingdom FlowchartVaibhav Chauhan100% (1)
- The 5 KingdomsDocument1 pageThe 5 KingdomsCharlotte FranklinNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Untrastructure of CellsDocument2 pages1.2 Untrastructure of CellskwonghyunparkNo ratings yet
- Bio411 C1Document1 pageBio411 C1Aqiena BalqisNo ratings yet
- Act 4. Book Pages 29, 30, 31Document4 pagesAct 4. Book Pages 29, 30, 31liliangiselle8No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDocument12 pagesChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellhuy luongNo ratings yet
- Tips For Locating Old Immunization Records: When You Find Your RecordsDocument1 pageTips For Locating Old Immunization Records: When You Find Your Recordsetio basseyNo ratings yet
- C 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of MeiosisDocument2 pagesC 10.1 Cell Cycle 10.2 M Phase 10.3 Significance of Mitosis 10.4 Meiosis 10.5 Significance of MeiosissrishtiNo ratings yet
- A Little Chick Gets HelpDocument4 pagesA Little Chick Gets Helpapi-441976119No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom ?Document20 pagesPlant Kingdom ?avika guptaNo ratings yet
- Concept and Use of A Classification SystemDocument12 pagesConcept and Use of A Classification SystemChai MingzeNo ratings yet
- Language 1 Language 2: Taboos and /ssues The Sale of Human Organs 18Document2 pagesLanguage 1 Language 2: Taboos and /ssues The Sale of Human Organs 18Варя АлфёроваNo ratings yet
- Biology IADocument20 pagesBiology IAVenice LoNo ratings yet
- Paudel TB Threat in Asin Elephants 2019 PDFDocument3 pagesPaudel TB Threat in Asin Elephants 2019 PDFKamal100% (1)
- PublicationDocument222 pagesPublicationThyagoNo ratings yet
- Stat 494 HW5Document1 pageStat 494 HW5JohnNo ratings yet
- Immune-And-Endocrine-System (Notes)Document22 pagesImmune-And-Endocrine-System (Notes)Jenn CaoNo ratings yet
- Amplifying DNA Fragments - FactRecallDocument2 pagesAmplifying DNA Fragments - FactRecallsabinaNo ratings yet
- 3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Document10 pages3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Sasuke UchihaNo ratings yet
- Sample PosterDocument1 pageSample PosterAlrayyan RashidNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument26 pagesCell BiologyAya OkumuraNo ratings yet
- Biology O Level Summary NotesDocument1 pageBiology O Level Summary NotesAdriana MuzfirahNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Class 7 - SCIENCEDocument3 pagesConcept Map - Class 7 - SCIENCEgotafryNo ratings yet
- Instrumnets For KTDocument2 pagesInstrumnets For KTKousik AmancharlaNo ratings yet
- Poster Caitlin BrennanDocument1 pagePoster Caitlin Brennansagun maharjanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Summary Notes For Topics Listed in DescriptionDocument1 pageIGCSE Biology Summary Notes For Topics Listed in DescriptionskyeNo ratings yet
- 2023 ResumeDocument1 page2023 Resumeapi-663098440No ratings yet
- Biochem Lab (Act 1)Document29 pagesBiochem Lab (Act 1)56bmkkn2rnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology by 6Document8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology by 6Emmanuel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument2 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesRalf FiedalinoNo ratings yet
- Guide Gi CancerDocument1 pageGuide Gi Cancerapi-446887131No ratings yet
- Epidemiological Studies: Example AdvantagesDocument1 pageEpidemiological Studies: Example Advantagesطفوف محمد.No ratings yet
- 01 Bio 3Document1 page01 Bio 3LovialNo ratings yet
- Prevention of CSADocument1 pagePrevention of CSAsushantkalraNo ratings yet
- Genome Projects - FactRecallDocument1 pageGenome Projects - FactRecallsabinaNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay Proposal Form 2Document3 pagesExtended Essay Proposal Form 2Aarush khannaNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms WorksheetDocument1 pageLiving Organisms Worksheetbecky.brownu746No ratings yet
- 10th Tamil Unit 2 One Mark Questions and Answers Download PDFDocument46 pages10th Tamil Unit 2 One Mark Questions and Answers Download PDFPOKE TUBERNo ratings yet
- Constipation RemediesDocument2 pagesConstipation RemediesconstipationremedyNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument41 pagesBiologySecret of friendship Go GoNo ratings yet
- Core and Advance JavaDocument6 pagesCore and Advance JavaSantosh KARNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub - Gospel Chord Progressions KeyboardDocument6 pagesEdoc - Pub - Gospel Chord Progressions KeyboardPolce Rafael TalahatuNo ratings yet
- FYJC 2022 23 Question Bank BiologyDocument33 pagesFYJC 2022 23 Question Bank BiologyJainamNo ratings yet
- SOAL MID SEMESTER 2 (Jawaban)Document1 pageSOAL MID SEMESTER 2 (Jawaban)ArdiantoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering NotedDocument17 pagesBiochemical Engineering NotedRUANGLADDA LIMPONGSAWATNo ratings yet
- IONIX ModelDocument6 pagesIONIX ModelTrường Bửu TrầnNo ratings yet
- G8 - Sci SLM Q4 Wk1 Corrfor QADocument15 pagesG8 - Sci SLM Q4 Wk1 Corrfor QACristy VillamorNo ratings yet
- 2c MembranesDocument10 pages2c Membranesmonishamonisha224yNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - Micronotes by Seep PahujaDocument2 pagesTransport in Plants - Micronotes by Seep PahujamanojchodharyhathrasNo ratings yet
- It's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentFrom EverandIt's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- First Reporters Ppt. What Are The Major Components of An EcosystemDocument14 pagesFirst Reporters Ppt. What Are The Major Components of An EcosystemMaryshamea MamacNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Genetics Combined PowerpointsDocument49 pagesMeiosis and Genetics Combined Powerpointsapi-242405009No ratings yet
- Bio2581 Syllabus 2018Document6 pagesBio2581 Syllabus 2018api-389173677No ratings yet
- HAN - 2022 - Bacterial Rather Than Fungal Diversity and Community Assembly Drive SoilDocument11 pagesHAN - 2022 - Bacterial Rather Than Fungal Diversity and Community Assembly Drive SoilJenickson CostaNo ratings yet
- Abstracts-Indian Biodiversity Congress-2010-PAGES-96-to-237Document142 pagesAbstracts-Indian Biodiversity Congress-2010-PAGES-96-to-237Sreejith AravindakshanNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument8 pagesCulture MediaHershey BaconNo ratings yet
- HAREPRIYAN.M - NNEET-G1-CH1-Living WorldDocument7 pagesHAREPRIYAN.M - NNEET-G1-CH1-Living WorldSachithananthanNo ratings yet
- FlowersDocument10 pagesFlowersAmina Zeghar BNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan: Lyceum-Northwestern University Urdaneta CampusDocument24 pagesLearning Plan: Lyceum-Northwestern University Urdaneta CampusJohnson FernandezNo ratings yet
- Importance of Biotechnology in AgricultureDocument4 pagesImportance of Biotechnology in AgricultureVinu Nair100% (4)
- Topic:: Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, QuezonDocument3 pagesTopic:: Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, QuezonOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Plant Pathology MSTDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Plant Pathology MSTAshutosh Prakash ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- The History of Animal EvolutionDocument11 pagesThe History of Animal EvolutionMong GulongNo ratings yet
- 97213-Article Text-253451-1-10-20131118Document7 pages97213-Article Text-253451-1-10-20131118Fauziah MustafaNo ratings yet
- Animal Behavior Study GuideDocument6 pagesAnimal Behavior Study Guideapi-595420397No ratings yet
- Fungal and Viral ReplicationDocument22 pagesFungal and Viral ReplicationAbigail Mayled LausNo ratings yet
- LSM1102 Cyh Lecture 2 FaqDocument5 pagesLSM1102 Cyh Lecture 2 FaqtxNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Gram Positif Dan NegatifDocument3 pagesBakteri Gram Positif Dan NegatifVenna MelindaNo ratings yet
- Topics From Botany: Kvpy Analysis: Sa StreamDocument12 pagesTopics From Botany: Kvpy Analysis: Sa StreamAnonymous EyhxoejNo ratings yet
- Brucella PDFDocument2 pagesBrucella PDFhca_12No ratings yet
- Reference Books For CSIR-NET - BioTecNikaDocument11 pagesReference Books For CSIR-NET - BioTecNikaDr-Katari VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Filamentous Fungi and YeastDocument26 pagesFilamentous Fungi and Yeastማላያላም ማላያላምNo ratings yet