Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shannon RW
Uploaded by
Beverly Aguirre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Shannon Rw
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesShannon RW
Uploaded by
Beverly AguirreCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Cailean Shannon M.
Doñasales
Gr11 STEM F-Recognition
1.Identify the information about Kate M. Cronan, MD
When you click the hyperlink, Kate Coran, MD there is no information about her, however, the link discusses
the rank among the hospital, the Life-changing Research, and the donation and volunteering. What I
observe and see about the link burns Kate Cronan reviewed the article.
2.Write the meaning of each word below
Hot bath water
Hot water can be dangerous, particularly for kids younger than 5. Their skin is thinner than older kids' and a
dults', so can burn more easily. Just 3 seconds of exposure to tap water that's 140°F (60°C) can cause a thir
d-degree burn. Hot bath water typically refers to water that has been heated to a temperature that is
comfortable for soaking in a bathtub
Sunburn
Sunburn can happen being in the sun, the symptoms can see the skin of redness and discomfort. Sunburn
typically appears as red, swollen and painful skin that may feel warm or hot to the touch. In more severe
cases, blisters or peeling may also occur.
Button Batteries
Button batteries are small, shiny, coin-shaped batteries
Electrical current
Electrical current, also known as electric current, refers to the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
Acetaminophen
Is an over-the-counter medicine taken to relieve fever and pain. It's a safe drug when used correctly for a
wide variety of problems.
Ibuprofen
is an over-the-counter medicine taken to relieve aches and pain and reduce fever.
3.Answer the following Question by summarizing the information text:
What are the common causes of burns?
Thermal Burns: Burns caused by contact with flames, hot surfaces, hot liquids, and other sources of high
heat.
Radiation burns: Burns caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.
Chemical burns: Burns caused by contact with chemicals, such as acids, bleach, and other household
cleaning products.
Electrical burns: Burns caused by rubbing against a hard surface, such as a carpet or road, or due to
excessive rubbing or friction between two body parts.
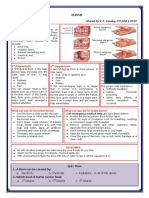
What are the types of burns?
First-degree burns: These burns affect the top layer of skin (epidermis) and usually cause redness, pain,
and mild swelling. They can be caused by brief exposure to heat, sunburn, or a mild chemical burn. First-
degree burns generally heal on their own within a few days without leaving scars.
Second-degree burns: These burns affect the epidermis and the layer beneath it (dermis) and can cause
blisters, severe pain, redness, and swelling. Second-degree burns can be caused by exposure to hot
liquids, flames, or chemicals. They generally take longer to heal and may require medical attention to
prevent infection and scarring.
Third-degree burns: These burns are the most severe and affect all layers of skin, as well as the tissues
underneath. Third-degree burns can cause the skin to appear white or blackened, and they may not be
painful due to nerve damage. They can be caused by prolonged exposure to flames, hot liquids, or
electricity. Third-degree burns require immediate medical attention and may require skin grafting to promote
healing.
What should we do for burns?
For first-degree burns: Remove the person from the source of heat or stop the burning process. Run cool
water over the burned area or apply a clean, damp cloth to the area to relieve pain and reduce swelling.
Cover the burn with a clean, dry bandage or dressing.
For second-degree burns: Follow the same steps as for first-degree burns, but do not break any blisters that
may have formed. Seek medical attention if the burn covers a large area, affects a sensitive area (such as
the face or genitals), or is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, chills, or severe pain.
For third-degree burns: Call for emergency medical assistance immediately. Do not remove any clothing that
may be stuck to the burned area, and do not apply any ointments or other substances to the burn. Cover the
burn with a clean, dry cloth or dressing to protect it from contamination and reduce the risk of infection.
You might also like
- First Aid for Burns GuideDocument21 pagesFirst Aid for Burns Guidegashbin MahdyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document27 pagesPresentation 1krpNo ratings yet
- Types and Treatment of Burn InjuriesDocument2 pagesTypes and Treatment of Burn InjuriesJohn Paolo OrioNo ratings yet
- Burns and ScaldsDocument14 pagesBurns and ScaldsMuhamad IqbalNo ratings yet
- P.E First Aid Treatment For Burns (ISABEDRA)Document13 pagesP.E First Aid Treatment For Burns (ISABEDRA)Reycard IsabedraNo ratings yet
- BurnDocument4 pagesBurnCatiereign VerdeNo ratings yet
- Burns 1Document24 pagesBurns 1Suhas BanpurkarNo ratings yet
- First - Degree BurnDocument5 pagesFirst - Degree BurnOctooberNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument24 pagesBurnsMutaz MandilNo ratings yet
- 3.2. First Aid-BurnsDocument31 pages3.2. First Aid-BurnsParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Causes, Types and Treatment of BurnsDocument5 pagesCauses, Types and Treatment of BurnsPooja ChapdiNo ratings yet
- First Aid For BurnsDocument10 pagesFirst Aid For BurnsRalc Retsel AtadNo ratings yet
- Burns: What Are The Categories of Burns?Document8 pagesBurns: What Are The Categories of Burns?Marco1998No ratings yet
- Burn First Aid: Dr. Nawal Alghareeb Done By: - Mashael AlsaediDocument7 pagesBurn First Aid: Dr. Nawal Alghareeb Done By: - Mashael AlsaedikymoNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument11 pagesBurnssomnathNo ratings yet
- Burns and Firs AidDocument6 pagesBurns and Firs AidNarmin AlievaNo ratings yet
- How to Treat Burns in 40 StepsDocument12 pagesHow to Treat Burns in 40 Stepshany winihastutiNo ratings yet
- BurnDocument5 pagesBurnpallaviNo ratings yet
- First Aid for Burns: Thermal, Chemical and ElectricalDocument21 pagesFirst Aid for Burns: Thermal, Chemical and ElectricalJanine SarzaNo ratings yet
- Burns and ScaldsDocument9 pagesBurns and Scaldsesmangmaybel814No ratings yet
- BURNSDocument16 pagesBURNSRegina KadenyiNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument6 pagesBURNSJerona AyongNo ratings yet
- Burn and FractureDocument30 pagesBurn and FractureJalouis GabalfinNo ratings yet
- By: Aileen C. Contreras-Limjoco M.DDocument48 pagesBy: Aileen C. Contreras-Limjoco M.Dclara jocomilNo ratings yet
- First Aid: BY Prof. A. Emad Omar ZakiDocument31 pagesFirst Aid: BY Prof. A. Emad Omar ZakiMohamedNo ratings yet
- Burns 2Document28 pagesBurns 2Suhas BanpurkarNo ratings yet
- Burns & ScoldsDocument3 pagesBurns & Scoldsdeneucy juniorNo ratings yet
- U2L1.First Aid For BurnsDocument2 pagesU2L1.First Aid For BurnsNaveen KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument58 pagesBurnsMarie MayNo ratings yet
- Nama: Nurhalisah Kelas: A2/2018 NIM: NH0118058Document2 pagesNama: Nurhalisah Kelas: A2/2018 NIM: NH0118058nurhalisah nurhalisahNo ratings yet
- Burns and ScaldsDocument6 pagesBurns and ScaldsApril BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Burns Guide: Causes, Types, TreatmentDocument4 pagesBurns Guide: Causes, Types, TreatmentMartin KoaNo ratings yet
- Burns: Burn and Its CausesDocument1 pageBurns: Burn and Its CausesRanjan MehrotraNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument1 pageBurnsapi-518183280No ratings yet
- Burn Types and TreatmentDocument19 pagesBurn Types and Treatmentnoviember0% (1)
- Adult 2Document5 pagesAdult 2Arwa HakamiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Burns Based On Depth CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesClassification of Burns Based On Depth CharacteristicsmexelleNo ratings yet
- Burn Injury Causes, Types, First Aid & When to Seek Medical HelpDocument19 pagesBurn Injury Causes, Types, First Aid & When to Seek Medical HelpAhmad JoiyaNo ratings yet
- Home Medical Reference Complementary Medicine: Center For Integrative Medicine Audio/Video Library Physicians and StaffDocument5 pagesHome Medical Reference Complementary Medicine: Center For Integrative Medicine Audio/Video Library Physicians and Stafflordofdragon100% (2)
- BASIC FA. BurnsDocument5 pagesBASIC FA. BurnsNicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- Burns !burnDocument13 pagesBurns !burnXTREME_10No ratings yet
- Burns: Burns Are Types of Injuries To Flesh Caused by Heat, Electricity, Chemicals, LightDocument3 pagesBurns: Burns Are Types of Injuries To Flesh Caused by Heat, Electricity, Chemicals, LightrbalayantoNo ratings yet
- Provide Steps On Performing First Aid For Burns IncidentDocument2 pagesProvide Steps On Performing First Aid For Burns IncidentDhona Mae FidelNo ratings yet
- BurnDocument10 pagesBurnMS AntikaNo ratings yet
- Burns ReportDocument9 pagesBurns ReportLia-Jy SanoanNo ratings yet
- Burn in Children: Smriti Poudel LecturerDocument58 pagesBurn in Children: Smriti Poudel Lecturersmriti sharmaNo ratings yet
- BurnDocument7 pagesBurnpatlekhilesh8No ratings yet
- Introduction To Burns: Bacteria VirusesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Burns: Bacteria Virusesanon-50728No ratings yet
- Burns Etiology & ClassificationDocument31 pagesBurns Etiology & Classificationahmedzakaria0No ratings yet
- Trauma and Emergecny Nursing: Course TittleDocument64 pagesTrauma and Emergecny Nursing: Course TittleAbdisamed AllaaleNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid - ToPIC 4 (Burns)Document33 pagesBasic First Aid - ToPIC 4 (Burns)Karl James RetaNo ratings yet
- Burns and InjuryDocument27 pagesBurns and InjuryJane Ann Alolod100% (1)
- Burn Injury Case Study: Understanding Causes, Degrees and TreatmentDocument21 pagesBurn Injury Case Study: Understanding Causes, Degrees and TreatmentPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- Explain Actions Performed To Handle An Injury in The English Language (Burns)Document4 pagesExplain Actions Performed To Handle An Injury in The English Language (Burns)Sukma WulandariNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument37 pagesBurnskint100% (2)
- Burns (ALS) History of Present IllnessDocument12 pagesBurns (ALS) History of Present IllnessIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Burns 2Document4 pagesBurns 2Charmae NaveaNo ratings yet
- Safety MeasureDocument2 pagesSafety MeasureMari OpocNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandContact Dermatitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review of Current Treatments For Granulomatous Cheilitis (British Journal of Dermatology, Vol. 166, Issue 5) (2012)Document4 pagesA Comprehensive Review of Current Treatments For Granulomatous Cheilitis (British Journal of Dermatology, Vol. 166, Issue 5) (2012)Padmapriya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage and Shock PresentationDocument33 pagesHemorrhage and Shock PresentationJoy JoycNo ratings yet
- AMH Talk MH Workplace FINAL Oct 2014Document38 pagesAMH Talk MH Workplace FINAL Oct 2014Princess RanyNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Diagnosis Celiac DiseaseDocument16 pagesApproaches To Diagnosis Celiac DiseaseJunior GrobeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Presentation (General Surgery) - 1Document29 pagesClinical Case Presentation (General Surgery) - 1Siddiqur Rahman AkashNo ratings yet
- TQ Q2 Hope1Document6 pagesTQ Q2 Hope1PrudevenoNo ratings yet
- Argumentitive Essay About Bariatric SurgeryDocument2 pagesArgumentitive Essay About Bariatric SurgeryNourNo ratings yet
- Sections of Lab - EssayDocument3 pagesSections of Lab - EssayhalamanNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Parritz-Troy - PPTDocument21 pagesCH 12 Parritz-Troy - PPTTeeng BadimalboNo ratings yet
- HypokalemiaDocument4 pagesHypokalemiaFani Dapa TakaNo ratings yet
- ATI RN Mental Health Online Practice BDocument38 pagesATI RN Mental Health Online Practice Bseansdrew2No ratings yet
- Oet Writing Nurse 4Document2 pagesOet Writing Nurse 4Janine Joson SalvaniaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Spina BifidaDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Spina BifidaSham ObaidatNo ratings yet
- Shin SplintsDocument2 pagesShin SplintsBen K.No ratings yet
- Commentary "Incidence of Total Thyroidectomy and Lobectomy"Document2 pagesCommentary "Incidence of Total Thyroidectomy and Lobectomy"Cristina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Emergency CT Scans Requiring IV Iodinated Contrast 230602 195353Document4 pagesEmergency CT Scans Requiring IV Iodinated Contrast 230602 195353bharatNo ratings yet
- P.A. Tool (Case Pres FINAL.)Document23 pagesP.A. Tool (Case Pres FINAL.)Crystal Ann TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Neadyuvancia Cancer de Pene 1Document5 pagesNeadyuvancia Cancer de Pene 1Ivan Perez NestaresNo ratings yet
- J Jacc 2023 02 011Document3 pagesJ Jacc 2023 02 011Evania BeatriceNo ratings yet
- Curs 10-Pulp Pathology II-1Document32 pagesCurs 10-Pulp Pathology II-1Bianca BurcăNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Related Emergencies (ALS)Document10 pagesAlcohol Related Emergencies (ALS)Ilyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Service: Medicine Attending Physician: Dr. Santos Date/Time 06/10/21 1400Document4 pagesService: Medicine Attending Physician: Dr. Santos Date/Time 06/10/21 1400Andrea Kyla Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Dating ViolenceDocument3 pagesDating Violenceapi-490237409No ratings yet
- Social Studies SbaDocument26 pagesSocial Studies SbaKeasha Jones100% (1)
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of Nurses on MI CareDocument32 pagesKnowledge, Attitude and Practices of Nurses on MI CareM.TennekoonNo ratings yet
- Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses: Osha Forms For RecordingDocument12 pagesWork-Related Injuries and Illnesses: Osha Forms For RecordingCollin GrayNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Health Screening Form for Vaccinated StaffDocument2 pagesCoronavirus Health Screening Form for Vaccinated StaffSharjeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Gradenigos Syndrome A ReviewDocument5 pagesGradenigos Syndrome A ReviewPaola SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMark John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dyspepsia in Children IFFGDDocument2 pagesDyspepsia in Children IFFGDNorman Alexander TampubolonNo ratings yet