Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydro
Uploaded by
羅伊約翰0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesInfiltration is the process by which water enters the soil. It is important in civil engineering fields like hydrology and irrigation design because it impacts the water budget and how concentrated solutes are in runoff. Factors that affect infiltration include soil type, vegetation cover, slope, rainfall intensity, and initial soil moisture. Infiltration is measured using methods like flooding basins or using infiltrometer rings, and classified based on the rate of water sinking or flow needed to maintain a constant water level. Understanding infiltration is crucial for modeling overheating risks in buildings and for ensuring proper soil conditions for vegetation in construction projects.
Original Description:
Original Title
hydro
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfiltration is the process by which water enters the soil. It is important in civil engineering fields like hydrology and irrigation design because it impacts the water budget and how concentrated solutes are in runoff. Factors that affect infiltration include soil type, vegetation cover, slope, rainfall intensity, and initial soil moisture. Infiltration is measured using methods like flooding basins or using infiltrometer rings, and classified based on the rate of water sinking or flow needed to maintain a constant water level. Understanding infiltration is crucial for modeling overheating risks in buildings and for ensuring proper soil conditions for vegetation in construction projects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesHydro
Uploaded by
羅伊約翰Infiltration is the process by which water enters the soil. It is important in civil engineering fields like hydrology and irrigation design because it impacts the water budget and how concentrated solutes are in runoff. Factors that affect infiltration include soil type, vegetation cover, slope, rainfall intensity, and initial soil moisture. Infiltration is measured using methods like flooding basins or using infiltrometer rings, and classified based on the rate of water sinking or flow needed to maintain a constant water level. Understanding infiltration is crucial for modeling overheating risks in buildings and for ensuring proper soil conditions for vegetation in construction projects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name:
Tionko, John Roy F. Date: March 12, 2023
Section: CE410 CEC41S1 Instructor: Engr. Given Dave P. Layos
Assignment 3.1
Infiltration, Percolation, and Ground Storage
1. What is infiltration and why is it important in civil engineering?
Hydrology, agricultural and civil engineering, irrigation design, and soil and water conservation
all depend on the process of infiltration. It is complicated and depends on the beginning and
boundary circumstances inside the flow domain as well as the soil and rainfall parameters. A
crucial factor in the water budget calculation is infiltration. In hydrology, agricultural and civil
engineering, irrigation design, and soil and water conservation, an accurate estimation of the
infiltration rate is essential. Solutes enter the soil profile through infiltration, which also affects
how concentrated they are in the runoff.
2. What factors affect infiltration and how does it impact hydrology?
the type of soil (texture, structure, hydrodynamic characteristics). Capillary forces and
adsorption are influenced by the properties of the soil.
the area of the soil. By lengthening the time it takes for water to penetrate the soil, vegetation
has a favorable impact on infiltration.
the morphology and topography of slopes
the flow supply (rain intensity, irrigation flow)
the original humidity level of the soil. A key component of the infiltration regime is soil
dampness. For wet or dry soils, the infiltration regime develops throughout time differently.
soil compaction due to rain drop impact and other effects. The surface soil layer may be
affected if heavy agricultural machinery is used.
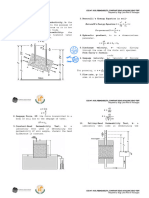
3. What methods are used to measure infiltration capacity and how are they classified?
Field data are typically used to calculate infiltration rate. The main techniques for measuring
infiltration rate include flooding basins or furrows, sprinkling (to simulate rain), and measuring
water entering from cylinders, although many various techniques and equipment types have
been employed (infiltrometer rings). The rate of water surface sinking, the rate of flow needed
to keep a big basin's level constant, or the size of a very large ring infiltrometer are used as
indicators of the infiltration rate. The rate of flow or subsidence for the time that the wetting
front is passing through the enclosed area of the soil column is taken as the infiltration rate if
smaller infiltrometer rings are utilized.
4. What are the practical applications of infiltration in civil engineering projects?
The future of the built environment depends critically on the rising problem of building
overheating. It has previously been understated or neglected how crucial it is to comprehend
infiltration pathways when evaluating and modeling the overheating risks associated with
apartments and other multi-residential buildings. Examples that show the need for a deeper
understanding of internal air circulation are provided in this study when precise estimates of
interior temperatures are needed. The issue is now being concealed by widespread building
simulation procedures and current technical memorandum standards, which do not offer a
solid foundation from which average or worst-case scenarios can be effectively taken into
account.
5. How is infiltration capacity measurement and classification used in civil engineering design and
construction?
At least two weeks before planting soil is delivered to the site, the designer should be given
the findings of the soil test. Test findings that have been submitted should include a grade and
a USDA categorization of the soil texture or a statement indicating the soil mix complies with
MnDOT regulations or other requirements. Two weeks before the media is delivered to the
site, samples of the mixed product should be sent to the designer as well. If the first submittal
doesn't satisfy requirements, the designer should analyze the materials as soon as possible to
avoid any potential delays in the acquisition and assessment of another media source.
References:
Infiltration into soils: Conceptual approaches and solutions (2013),
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/wrcr.20155#:~:text=Accurate
%20estimate%20of%20infiltration%20rate,their%20concentration%20in%20the%20runoff.
INFILTRATION (2001), https://echo2.epfl.ch/VICAIRE/mod_1a/chapt_5/main.htm#:~:text=The
%20main%20factors%20that%20influence,the%20soil%20coverage.
A Field Method for Measurement of Infiltration (1963),
https://pubs.usgs.gov/wsp/1544f/report.pdf
The importance of infiltration pathways in assessing and modelling overheating risks in multi-
residential buildings (2020), https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0143624420906765
Construction specifications for infiltration (2022),
https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Construction_specifications_for_infiltration
You might also like
- CE410 Assignment3.1 Tionko JohnRoy FDocument2 pagesCE410 Assignment3.1 Tionko JohnRoy F羅伊約翰No ratings yet
- Shrinkage-Swelling Potential of SoilDocument70 pagesShrinkage-Swelling Potential of SoilNoraima EdrisNo ratings yet
- Effective Ways of Erosion Control On High Way ConstructionDocument49 pagesEffective Ways of Erosion Control On High Way ConstructionLaison GodloveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1amkDocument13 pagesChapter 1amkAung Kaung MyatNo ratings yet
- G3 Revised ManuscriptDocument26 pagesG3 Revised ManuscriptJulysa CasanguanNo ratings yet
- JGEET - Jounal - Putera Agung Et Al - 2024Document9 pagesJGEET - Jounal - Putera Agung Et Al - 2024mardianaNo ratings yet
- Founationsonexpansivesoils AreviewDocument8 pagesFounationsonexpansivesoils Areview153-B RAKSHITHANo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Subsurface Soil Investigation and Repor2Document12 pagesGeotechnical Subsurface Soil Investigation and Repor2briggsqueen11No ratings yet
- Group 1 - Section 4 - Full ReportDocument18 pagesGroup 1 - Section 4 - Full ReportEliya AiyaniNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Section 4 - Full ReportDocument18 pagesGroup 1 - Section 4 - Full ReportEliya AiyaniNo ratings yet
- Lec01 Fundamentals PDFDocument14 pagesLec01 Fundamentals PDFRaja GNo ratings yet
- GEOENVIRONMENTAL Introduction PDFDocument151 pagesGEOENVIRONMENTAL Introduction PDFHari RamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Geoenvironmental EngineeringDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Geoenvironmental EngineeringkrupaNo ratings yet
- Sensors 20 03585 PDFDocument14 pagesSensors 20 03585 PDFZhraa NorNo ratings yet
- Unit - III - Procurement of Revelant Soil Quality1Document22 pagesUnit - III - Procurement of Revelant Soil Quality1Anusha PenchalaNo ratings yet
- Effect Desicaation CrackingDocument11 pagesEffect Desicaation CrackingRyan RahdianaNo ratings yet
- Robert Pitt Article On Clay Soil InfiltrationDocument22 pagesRobert Pitt Article On Clay Soil InfiltrationEdmar CardenasNo ratings yet
- Bfc43103 Project Report - Group2 - Section 4Document44 pagesBfc43103 Project Report - Group2 - Section 4Juraini Binti Abdul SaadNo ratings yet
- Water: Determination of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity For Urban RunoDocument15 pagesWater: Determination of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity For Urban RunoAnusia ThevendaranNo ratings yet
- Article 92Document7 pagesArticle 92Raj KishorNo ratings yet
- Paper PrePrintDocument6 pagesPaper PrePrintAbdulkarim AliNo ratings yet
- GEOENVIRONMENTAL EnginneringDocument151 pagesGEOENVIRONMENTAL EnginneringAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Foundation DesignFrom EverandSoil Investigation and Foundation DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Settlements Induced by Tunneling in Soft GroundDocument31 pagesSettlements Induced by Tunneling in Soft GroundAdrian Liviu BugeaNo ratings yet
- Founationsonexpansivesoils AreviewDocument8 pagesFounationsonexpansivesoils Areviewravikarkar2224No ratings yet
- PPT-2 Site InvestigationDocument22 pagesPPT-2 Site InvestigationSaurabh YeleNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Text DocumentWatchItWithKobbyNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Analysis and Solution of Waterlogging in Kothrud Region, PuneDocument11 pagesStormwater Analysis and Solution of Waterlogging in Kothrud Region, PuneIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Soil Water ConservationDocument43 pagesSoil Water ConservationK.P BHOGAYATANo ratings yet
- Lucrare Cristescu, ManDocument6 pagesLucrare Cristescu, MannistoraliNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mohan, Et Al - Design and Construction Considerations For Wetland Restoration Using Dredged MaterialDocument14 pages5 - Mohan, Et Al - Design and Construction Considerations For Wetland Restoration Using Dredged MaterialsiskaapNo ratings yet
- Engineering Considerations in Folds, Faults, and JointsDocument2 pagesEngineering Considerations in Folds, Faults, and JointsSlasher FloresNo ratings yet
- Review of Causes of Foundation Failures and Their Possible Preventive and Remedial Measures - KKUDocument6 pagesReview of Causes of Foundation Failures and Their Possible Preventive and Remedial Measures - KKUPUNITHNo ratings yet
- #7817693 FinalDocument22 pages#7817693 FinalFantastic WriterNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study of The Mechanical Behavior of A Foundation Raft Under The Hydrodynamic Influence of The Mechanical Characteristics of Clay SoilsDocument15 pagesNumerical Study of The Mechanical Behavior of A Foundation Raft Under The Hydrodynamic Influence of The Mechanical Characteristics of Clay SoilsTsangaNo ratings yet
- Philips & Kitch 2011Document18 pagesPhilips & Kitch 2011Gonzalo Quispe AlcocerNo ratings yet
- Dam Design HAFIZ OMAR SUNIYDocument29 pagesDam Design HAFIZ OMAR SUNIYMohamad HafizNo ratings yet
- InfiltrationDocument22 pagesInfiltrationTsumaNo ratings yet
- The National Academies Press: Manual On Subsurface Investigations (2019)Document6 pagesThe National Academies Press: Manual On Subsurface Investigations (2019)Andres PuertaNo ratings yet
- BT ResearchDocument7 pagesBT ResearchTamika AguilarNo ratings yet
- Review Paper ReportDocument15 pagesReview Paper ReportKushal ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Collapsible SoilDocument39 pagesCollapsible SoilMuhammad Iqbal HamidiNo ratings yet
- Btech Project WorkDocument66 pagesBtech Project Workbenjamin kwasi boatengNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: (Topic)Document10 pagesGujarat Technological University: (Topic)nvnagarajuNo ratings yet
- A-2 SoilsDocument6 pagesA-2 SoilsJohny Lou LuzaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Management: Unit - 3Document6 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment and Management: Unit - 3vinodh159No ratings yet
- Water 14 03320 v2Document20 pagesWater 14 03320 v2Thoa HồNo ratings yet
- Omar Y. Mohammed and Ammar A. Shiekha: Dewatering System Control by MATLAB SoftwareDocument9 pagesOmar Y. Mohammed and Ammar A. Shiekha: Dewatering System Control by MATLAB SoftwareLucas sckuvieNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Surigao State College of Technology Module No. 3 Infiltration I. TopicDocument9 pagesLearning Module: Surigao State College of Technology Module No. 3 Infiltration I. TopicCyralie MaglipacNo ratings yet
- Present Status of Soil Moisture EstimationDocument22 pagesPresent Status of Soil Moisture EstimationcbuuwfbuwebfwiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Aspects of Geotechnical Tunnel Design - Franklin Lecture - 2013 - VERY GOODDocument12 pagesEngineering Aspects of Geotechnical Tunnel Design - Franklin Lecture - 2013 - VERY GOODkrainajackaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2467967419300923 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S2467967419300923 MainSlavoljub IlicNo ratings yet
- Reviewofcausesoffoundationfailuresandtheirpossiblepreventiveandremedialmeasures KKU PDFDocument7 pagesReviewofcausesoffoundationfailuresandtheirpossiblepreventiveandremedialmeasures KKU PDFAjay AshokNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Physical Processes of Pollutant Build-Up and WashoffDocument16 pagesUnderstanding The Physical Processes of Pollutant Build-Up and WashoffJussanã MilogranaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of Different Types of Seepage Control Measures For Earth Dam Using FEMDocument15 pagesA Comprehensive Study of Different Types of Seepage Control Measures For Earth Dam Using FEMMeku TNo ratings yet
- USLE ModelDocument41 pagesUSLE ModelRendhy Dimas RNo ratings yet
- Pwede Na MatulogDocument5 pagesPwede Na MatulogDENIEL MIKE DUKANo ratings yet
- F2004-06 09d Risk Management For Microtunneled SewersDocument15 pagesF2004-06 09d Risk Management For Microtunneled SewersswhuntNo ratings yet
- INFILTRATION Lecture PDFDocument5 pagesINFILTRATION Lecture PDFsammy lopez0% (2)
- Erosion in Geomechanics Applied to Dams and LeveesFrom EverandErosion in Geomechanics Applied to Dams and LeveesStephane BonelliNo ratings yet
- Gec008 Ce42s5 TionkoDocument2 pagesGec008 Ce42s5 Tionko羅伊約翰No ratings yet
- Sample Request Letter Format - SIMULTANEOUS - OVERLOAD CoursesDocument1 pageSample Request Letter Format - SIMULTANEOUS - OVERLOAD Courses羅伊約翰No ratings yet
- Examples of Lean CanvasDocument3 pagesExamples of Lean Canvas羅伊約翰No ratings yet
- Biographical SpeechDocument1 pageBiographical Speech羅伊約翰No ratings yet
- Iii-V. Flood Mitigation ReservoirDocument6 pagesIii-V. Flood Mitigation ReservoirPajarillaga Franz Erick QuintoNo ratings yet
- Science of The Environment: Earth FactsDocument3 pagesScience of The Environment: Earth FactsGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- Seq - Strat. PosamentierDocument19 pagesSeq - Strat. Posamentierc_b_umashankarNo ratings yet
- Agricultural and Forest Meteorology: Miguel Saavedra, Ken TakahashiDocument13 pagesAgricultural and Forest Meteorology: Miguel Saavedra, Ken TakahashiAlejandro MattosNo ratings yet
- Soil ResourcesDocument17 pagesSoil ResourcesEji AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Control of Water: Reporter: Debbie A. Nacilla, Ce5-1Document14 pagesControl of Water: Reporter: Debbie A. Nacilla, Ce5-1Jef de LeonNo ratings yet
- Module 8 and 9 - Permeability - Constant Head and Falling Head TestDocument17 pagesModule 8 and 9 - Permeability - Constant Head and Falling Head Test24ks72xn8jNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument7 pagesClimate ChangedominiqueNo ratings yet
- Book 1: Climate Change Impact in Sikka, Lembata, and Timor Tengah Utara (TTU)Document40 pagesBook 1: Climate Change Impact in Sikka, Lembata, and Timor Tengah Utara (TTU)Paramita KelakanNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law and Hydraulic ConductivityDocument49 pagesDarcy's Law and Hydraulic ConductivityDotan NutodNo ratings yet
- Yazoo 4 Pupils BookDocument122 pagesYazoo 4 Pupils BookArtem Skinov0% (1)
- Physical Setting Earth ScienceDocument17 pagesPhysical Setting Earth SciencesaileikNo ratings yet
- Lab Report No. 2 LBYCV2BDocument12 pagesLab Report No. 2 LBYCV2BEugene Embalzado Jr.0% (1)
- Global Warming: Products.)Document3 pagesGlobal Warming: Products.)nara3333No ratings yet
- Butzer Geomorphology Landforms MainDocument17 pagesButzer Geomorphology Landforms MainParmita DasarwarNo ratings yet
- Ring of FireDocument4 pagesRing of Firemira01No ratings yet
- Biomes 1.1Document23 pagesBiomes 1.1cristinejoygenova43No ratings yet
- Hydrology: The Flow of Water Across and Through Near Surface EnvironmentsDocument9 pagesHydrology: The Flow of Water Across and Through Near Surface EnvironmentsSN2-0620 Theeban Rau A/L ChanthiranNo ratings yet
- A Strange Place To Call HomeDocument7 pagesA Strange Place To Call HomeChronicleBooks33% (3)
- Lesson 1 Volcano IntroductionDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Volcano IntroductionLena OrsolinoNo ratings yet
- Irrig 2 PDFDocument3 pagesIrrig 2 PDFMichael Angelo AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Harn Map KeysDocument4 pagesHarn Map KeysDaniel Green100% (1)
- презентація про погодуDocument5 pagesпрезентація про погодуКарина ГуцуNo ratings yet
- Dreno Horizontal Profundo Manual - 787.1Document390 pagesDreno Horizontal Profundo Manual - 787.1patricioalonsoNo ratings yet
- G7 Effect of Changes in The Abiotic Factor On EcosystemDocument22 pagesG7 Effect of Changes in The Abiotic Factor On EcosystemJaycee Nicasio OliverNo ratings yet
- DRRR 11 Reviewer Q2Document7 pagesDRRR 11 Reviewer Q2Ralph Louis RosarioNo ratings yet
- Exploring Biomes ReadingDocument3 pagesExploring Biomes Readingapi-254428474No ratings yet
- Environment Class 7 MCQS Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesEnvironment Class 7 MCQS Questions With AnswersKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- 7 MoigradeanDocument12 pages7 MoigradeanRoxana RoxNo ratings yet
- CE-461 Doc MRKDocument143 pagesCE-461 Doc MRKMahmoud I. Mahmoud100% (2)