Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics of Rigid Bodies
Uploaded by
Ann NavarroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamics of Rigid Bodies
Uploaded by
Ann NavarroCopyright:
Available Formats
DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES
Dynamics – part of mechanics that deals with the analysis of bodies in motion.
Kinematics – is the study of the geometry of motion. It is used to relate speed, displacement, velocity,
acceleration, and time, without reference to the cause of the motion.
Kinetics - is the study of the relation exiting between the forces acting on a body, the mass of the body,
and the motion of the body. It is used to predict the motion cause by given forces or to determine the forces
required to produce a given motion.
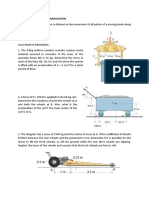
ILLUSTRATIVE PROBLEMS.
1. A particle starts from rest and moves in a straight line with an acceleration of a = (2t – 6) m/s2, where t is
in seconds. What is the particle’s velocity when t = 6 second, and what is its position when t = 11 seconds?
2. If a particle has an initial velocity of 12 ft/s to the right, at zero initial position, determine its position when
t = 10 seconds if a = 2 ft/s2 to the left.
3. A particle moves along a straight line such that its position is defined by s = (t 2 – 6t + 5) m. Determine the
average velocity, the average speed, and the acceleration of the particle when t = 6 seconds.
4. Traveling with an initial speed of 70 kph, a car accelerates at 6000 km/hr2 along a straight road. How
long will it take to reach a speed of 120 kph? Also, through what distance does the car travel during this
time?
You might also like
- Resonance KinematicsDocument60 pagesResonance Kinematicsrahuljain168% (22)
- Chapter 3: KinematicsDocument70 pagesChapter 3: KinematicsCk100% (1)
- 01 Kinematics Motion in 1D 2DDocument20 pages01 Kinematics Motion in 1D 2DSivakumar SarmaNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee StudyDocument955 pagesIit Jee StudyGarlapati Srinivasa Rao88% (17)
- Fundamentals of Engineering MechanicsDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Engineering MechanicsayingbaNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument21 pagesPhysics ReviewerainnahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDave Lumas100% (1)
- Kinematics of A Particle:: Particle Motion Along A Straight Line (Rectilinear Motion)Document48 pagesKinematics of A Particle:: Particle Motion Along A Straight Line (Rectilinear Motion)tomodachiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - KinematicsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - KinematicsGerman MartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Kinematics of ParticlesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Kinematics of ParticlesAnas NazmiNo ratings yet
- MCE312 (Module 1)Document32 pagesMCE312 (Module 1)Muiruri JacobNo ratings yet
- Applied Mech. IIDocument38 pagesApplied Mech. IIJanaki RamanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Module 1Document8 pagesDynamics Module 1Jed IsidtoNo ratings yet
- ME100-Kinematics of A ParticleDocument18 pagesME100-Kinematics of A ParticleMuhammad NabeelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines-NotesDocument58 pagesMechanics of Machines-Notessatisfying videosNo ratings yet
- Project For Midterms - DORB001Document31 pagesProject For Midterms - DORB001Trina ArmeaNo ratings yet
- Session 5: Mechanics Post-Session HomeworkDocument9 pagesSession 5: Mechanics Post-Session Homeworkalexandra owNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line Wkst3 202324Document1 pageMotion in A Straight Line Wkst3 202324Vinayak AnilNo ratings yet
- Engr. Rodolfo A. Chua, JRDocument19 pagesEngr. Rodolfo A. Chua, JRojan_cheNo ratings yet
- 06-Kinematics and Dynamics (Motion)Document36 pages06-Kinematics and Dynamics (Motion)GISELLE DOCKERYNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument30 pagesKinema Ticsthinkiit100% (1)
- B222 CHAPTER1-IntroductionDocument14 pagesB222 CHAPTER1-IntroductionJohn Carlo CortezNo ratings yet
- Seeds Instittute: Motion in One DimensionDocument1 pageSeeds Instittute: Motion in One DimensionAshwin JambhulkarNo ratings yet
- Week 01Document34 pagesWeek 01UĞURCAN KÖMÜRNo ratings yet
- Es 1-BDocument6 pagesEs 1-BRaffy Manzano BeoncioNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics: KinematicsDocument5 pagesBiomechanics: Kinematicsالقداري القداريNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Kinematics 1Document15 pagesModule 2: Kinematics 1Green BrainNo ratings yet
- Lectur-1 12.2Document21 pagesLectur-1 12.2FaIz FauziNo ratings yet
- Dynamics For ReworkDocument1 pageDynamics For ReworkHaile SimachewNo ratings yet
- Qs (Calculus) ClassXIDocument2 pagesQs (Calculus) ClassXISanyam BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Mechanic Static DynamicDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Mechanic Static DynamicAlia RizalNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 4a - Laws of Motion. ForceDocument11 pagesChapter: 4a - Laws of Motion. ForcepatelnihitNo ratings yet
- Com121-Eng131.linear MomentumDocument31 pagesCom121-Eng131.linear Momentummatarabdullah61No ratings yet
- ENSC 22 Lecture 1 2Document10 pagesENSC 22 Lecture 1 2Cristine Joy CaporadoNo ratings yet
- Applying Equations of Linear Motion and Understanding Newton's Second Law and Dynamic Equilibrium and Its ApplicationsDocument34 pagesApplying Equations of Linear Motion and Understanding Newton's Second Law and Dynamic Equilibrium and Its ApplicationsFELIX KEUYANo ratings yet
- Motion: Immobile, Stationary, or To Have A Constant or TimeDocument9 pagesMotion: Immobile, Stationary, or To Have A Constant or TimeJohn HenryNo ratings yet
- Ce 123 Dynamics of Solids: Prof. Beda M. Mutagahywa Faculty of Engineering. SAUTDocument16 pagesCe 123 Dynamics of Solids: Prof. Beda M. Mutagahywa Faculty of Engineering. SAUTAwadhiNo ratings yet
- What Is Physics?: Physics Is The Branch of Science Which Deals With Matter and Its Relation To EnergyDocument42 pagesWhat Is Physics?: Physics Is The Branch of Science Which Deals With Matter and Its Relation To EnergycoolNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesModule 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesBilly Joel DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 ModuleDocument62 pagesGrade 10 ModuletabilinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: MAT113: Elementary MechanicsDocument41 pagesUnit 1: MAT113: Elementary MechanicsỌláOlúwakìítán AgboọláNo ratings yet
- Principles of DynamicsDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Dynamicsmaria.olivaaa.rossNo ratings yet
- Centre of Mass of System of The Discrete ParticlesDocument7 pagesCentre of Mass of System of The Discrete Particleseka123No ratings yet
- Physics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 7 System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument12 pagesPhysics Notes Class 11 CHAPTER 7 System of Particles and Rotational MotionAnkit Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- AMM 207-Classical MechanicsDocument71 pagesAMM 207-Classical MechanicsËvans MogeniNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Rectilinear - Continuous and ErraticDocument67 pagesDynamics Rectilinear - Continuous and ErraticJJ EnzonNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 General Principles of StaticsDocument52 pagesChap 1 General Principles of StaticsHassan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Mechanics: Statics Statics Dynamics DynamicsDocument7 pagesMechanics Mechanics: Statics Statics Dynamics DynamicsMovie MagazineNo ratings yet
- 1.lecture Notes 1 - Kinematics of ParticleDocument15 pages1.lecture Notes 1 - Kinematics of ParticleBlack SkyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicDocument66 pagesEngineering Mechanics 2mohanad Engineering Mechanics DynamicNefer PitouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Force Systems - Part ADocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Force Systems - Part ACheong JkNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Fisika Kelas 2 SmaDocument10 pagesSoal Latihan Fisika Kelas 2 SmaNisrina Azizah LubisNo ratings yet
- Lect1 DynamicsDocument28 pagesLect1 Dynamicsأميرول فاروقاNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument19 pages1 Introductionmsi appleNo ratings yet
- Dynamics LectureDocument220 pagesDynamics LectureShiro Emiya0% (2)
- 11 Phy ln3 Notes 1629708273Document4 pages11 Phy ln3 Notes 1629708273Raje SwariNo ratings yet
- Full Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?From EverandFull Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Gec 2a Readings in The Philippine HistoryDocument36 pagesChapter 5 - Gec 2a Readings in The Philippine HistoryAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument54 pagesElements and Principles of ArtAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- GEC 6 Activity 1 - February 12, 2024Document2 pagesGEC 6 Activity 1 - February 12, 2024Ann NavarroNo ratings yet
- I Love You Sagad Hanggang For LifersDocument1 pageI Love You Sagad Hanggang For LifersAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- ME 312 Allowed Formulas and Chart UpdateDocument6 pagesME 312 Allowed Formulas and Chart UpdateAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Bes 04Document6 pagesBes 04Ann NavarroNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument37 pagesResistanceAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument33 pagesOhm's LawAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- What Is DisinfectionDocument22 pagesWhat Is DisinfectionAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Edrada Judy Ann N. - Bsme 3aDocument3 pagesActivity 1 - Edrada Judy Ann N. - Bsme 3aAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Progress Report Group SansDocument5 pagesProgress Report Group SansAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitDocument33 pagesElectric CircuitAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Handout 4Document1 pageHandout 4Ann NavarroNo ratings yet
- Project Progress ReportDocument2 pagesProject Progress ReportAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- ME 221 03 Ideal GasesDocument17 pagesME 221 03 Ideal GasesAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management HandoutDocument2 pagesEngineering Management HandoutAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- TuronDocument6 pagesTuronAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop TheoryDocument15 pagesMachine Shop TheoryAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Project Progress ReportDocument2 pagesProject Progress ReportAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Rizal AssignmentDocument2 pagesLife and Works of Rizal AssignmentAnn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Milling Operation Group 6Document55 pagesMilling Operation Group 6Ann NavarroNo ratings yet