Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-07-Problem Level
Uploaded by
Raju SinghCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-07-Problem Level
Uploaded by
Raju SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
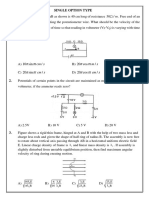
PROBLEMS
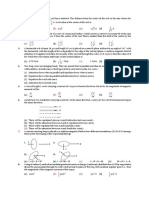
1. A rectangular loop PQRS made from a uniform wire has length a, z
width b and mass m, it is free to rotate about the arm PQ, which
remains hinged along a horizontal line taken as the y-axis (see fig-
ure). Take the vertically upward direction as the z-axis. A uniform P Q y
magnetic field B (3iˆ k)B
ˆ exists in the region. The loop is held
0 a
in the x-y plane and a current I is passed through it. The loop is now x S
R
released and is found to stay in the horizontal position in equilib- b
rium.
(a) what is the direction of the current I in PQ?
(b) find the magnetic force on the arm RS.
(c) find the expression for I in terms of B0 , a, b and m.
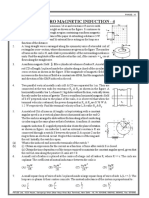
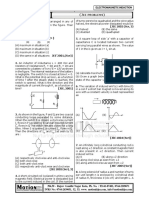
2. A metal bar AB can slide on two parallel thick metallic rails A
separated by a distance l. A resistance R and an inductance L
are connected to the rails as shown in the figure. A long straight R
I0 l
wire carrying a constant current I 0 is placed in the plane of the L
rails and perpendicular to them as shown. The bar AB is held
B
at rest at a distance x 0 from the long wire. At t = 0, it is made x0
to slide on the rails away from the wire. Answer the following
questions :
di d
(a) Find a relation among i, and , where I is the current in the circuit and is the flux of
dt dt
the magnetic field due to the long wire through the circuit.
(b) It is observed that at time t = T, the metal bar AB is at a distance of 2x 0 from the long wire and
the resistance R carries a current i1 . Obtain an expression for net charge that has flown
through resistance R from t = 0 to t = T.
(c) The bar is suddenly stopped at time T. The current through resistance R is found to be i1 / 4 at
time 2T. Find the value of L/R in terms of the other given quantities.
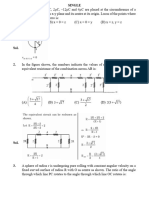
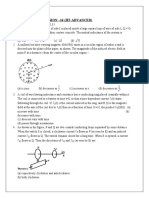
y
I0
3. A uniform constant magnetic field B is directed at an angle of 45º S R
to the x-axis in xy plane. PQRS is a rigid square wire frame carry-
ing a steady current I 0 , with its center at the origin O. At time t =
x
0, the frame is at rest in the position shown in the figure with its
sides parallel to x and y axes. Each side of the frame is of mass M
and length L :
P Q
(a) What is the torque about O acting on the frame due to the
magnetic field ?
(b) Find the angle by which the frame rotates under the action of this torque in a short interval of
time t , at the axis about which this rotation occurs ( t is so short that any variation in the
torque during this interval may be neglected). Given : the moment of inertia of the frame about
4
an axis through its center perpendicular to its plane is ML2 .
3
4. A thermocole vessel contains 0.5 kg of distilled water at 30ºC. A metal coil of area 5 103 m 2 ,
number of turns 100, mass 0.06 kg and resistance 1.6 is lying horizontally at the bottom of the
vessel. A uniform, time varying magnetic field is set up to pass vertically through the coil at time
t 0 . The field is first increased from zero to 0.8 at a constant rate between 0 and 0.2 s and then
decreased to zero at the same rate between 0.2 and 0.4 s. This cycle is repeated 12000 times. Make
sketches of the current through the coil and the power dissipated in the coil as functions of time for
the first two cycles. Clearly indicate the magnitude of the quantities on the axes. Assume that no
heat is lost to the vessel, or the surroundings. Determine the final temperature of the water under
thermal equilibrium. Specific heat of the metal 500 Jkg 1 K 1 and the specific heat of water
4200Jkg 1 K 1 . Neglect the inductance of the coil.
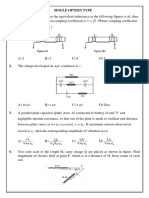
R3 C
5. A circuit containing a two position switch S is shown in figure.
(a) The switch S is in position ‘1’. Find the potential difference R1 2 E1 2F R5
VA VB and the rate of production of joule heat in R1 . 2 12V
1 A E2 R2 B
(b) If now the switch S is put in position 2 at t 0 find S 2
2 3V R4
L
(i) Steady current in R4 and
10mH
(ii) The time when current in is half the steady value.
Also calculate the energy stored in the inductor L at
that time.
You might also like
- Doosan DX225LCA Electric Circuit 110705Document1 pageDoosan DX225LCA Electric Circuit 110705Eduardo Ariel Bernal97% (30)
- Rebuilding The 6.6L Duramax Diesel PDFDocument13 pagesRebuilding The 6.6L Duramax Diesel PDFJuan Contreras100% (3)
- LBO Case Study - Volta Electronics Co. - v3Document14 pagesLBO Case Study - Volta Electronics Co. - v3madamaNo ratings yet
- AS5780-Core Requirement Specification For Aircraft Gas Turbine Engine LubricantsDocument9 pagesAS5780-Core Requirement Specification For Aircraft Gas Turbine Engine LubricantsJicheng PiaoNo ratings yet
- Gemeinsam Etwas Planen b1 MT 1 5 - CompressDocument5 pagesGemeinsam Etwas Planen b1 MT 1 5 - CompressDịu Trần ThịNo ratings yet
- DPP 6th May 2020Document12 pagesDPP 6th May 2020KaushikNo ratings yet
- DPP 6TH May 2020Document12 pagesDPP 6TH May 2020Nishit PNo ratings yet
- Assessment Test Test (Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics) PhysicsDocument13 pagesAssessment Test Test (Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics) PhysicsPratham MaanNo ratings yet
- Emi AitsDocument31 pagesEmi AitsAnmolNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Induction - 4: SANKALP 2014 - EMI - 4 Phase - ViDocument2 pagesElectro Magnetic Induction - 4: SANKALP 2014 - EMI - 4 Phase - ViAnmolNo ratings yet
- Inc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 3 (A)Document7 pagesInc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 3 (A)VijayKakarlaNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Assignment-2Document19 pagesMagnetics Assignment-2THE EXPLAINERNo ratings yet
- PT 12 Physics Solution (30 Aug 2023)Document10 pagesPT 12 Physics Solution (30 Aug 2023)AnujNo ratings yet
- DPP 7TH May 2020Document12 pagesDPP 7TH May 2020Nishit PNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields Assignment 9: Q1 40 Marks, Q2 25marks, Q3 35 MarksDocument2 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields Assignment 9: Q1 40 Marks, Q2 25marks, Q3 35 MarksShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- 01.EMI - Motional EMFDocument7 pages01.EMI - Motional EMFNibha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Inc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 4 (A)Document7 pagesInc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 4 (A)VijayKakarlaNo ratings yet
- Selection 2 2013Document3 pagesSelection 2 2013Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Magnetics - 02-Objective SolvedDocument7 pagesMagnetics - 02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 10-02-24 XPL 2.0 Module Exam 6 QuestionsDocument22 pages10-02-24 XPL 2.0 Module Exam 6 Questionsrathika1882007No ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document4 pagesExercise 1Anurag KumarNo ratings yet
- 12th MPCDocument4 pages12th MPCThriloknathNo ratings yet
- Fig 1Document1 pageFig 1Hamza SohailNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Magnetic FieldDocument9 pagesMCQ On Magnetic Fieldanupam9932642No ratings yet
- Magnetics-03-Subjective SolvedDocument12 pagesMagnetics-03-Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- bbcdc400b7bf09431818100d1a8b9fd4Document25 pagesbbcdc400b7bf09431818100d1a8b9fd4PrashantNo ratings yet
- Emi AcDocument53 pagesEmi AcSUKH RAM VAISHNAVNo ratings yet
- FT-19 - Jee Adv - 03032021Document19 pagesFT-19 - Jee Adv - 03032021Hari SinghNo ratings yet
- Inc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 2 (M)Document7 pagesInc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 2 (M)VijayKakarlaNo ratings yet
- Phy SheetsDocument11 pagesPhy SheetsKuljeet YadavNo ratings yet
- Magnetism For JEEDocument15 pagesMagnetism For JEEJatin SonwalNo ratings yet
- DPP 5TH May 2020Document14 pagesDPP 5TH May 2020Nishit PNo ratings yet
- Exercise - IV: (Tough Subjective Problems)Document2 pagesExercise - IV: (Tough Subjective Problems)Tejas SalviNo ratings yet
- Revision - 16 (Iit-Advanced)Document7 pagesRevision - 16 (Iit-Advanced)Devansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Exercise.4Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity Exercise.4Chaitanya JoshiNo ratings yet
- 05 Tutorial ElectrodynamicsDocument4 pages05 Tutorial ElectrodynamicsmukeshNo ratings yet
- DeThi Final PHY212 - Jan - 2016Document3 pagesDeThi Final PHY212 - Jan - 2016Kanekii HaiseNo ratings yet
- PHYS 102 - General Physics II Final Exam Solutions: Friday, 04 January 2019, 15:30Document4 pagesPHYS 102 - General Physics II Final Exam Solutions: Friday, 04 January 2019, 15:30Nano SuyatnoNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE SHEET - 04 (Physics) : B R R A O B C R R ADocument5 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 04 (Physics) : B R R A O B C R R AABD 17No ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Induction - 1: SANKALP 2015 - EMI - 1 Phase - ViDocument2 pagesElectro Magnetic Induction - 1: SANKALP 2015 - EMI - 1 Phase - ViAnmolNo ratings yet
- Paper - 1 (Question Paper) - 5 PDFDocument22 pagesPaper - 1 (Question Paper) - 5 PDFSaumya MundraNo ratings yet
- SHM Exercise 4B4Document3 pagesSHM Exercise 4B4Rushwin VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pagesSubjective Questions: Electromagnetic InductionrgNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 May 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 13 May 2023naivadhya gargNo ratings yet
- Selection132 SolDocument8 pagesSelection132 SolMarcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Physics-Part Test-4Document8 pagesPhysics-Part Test-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Vacation 1styear emDocument5 pagesVacation 1styear emgeorgiNo ratings yet
- Assgn 3Document2 pagesAssgn 3Zhiguang LiNo ratings yet
- HW7 Ind 31oct11Document4 pagesHW7 Ind 31oct11nghiachi.comNo ratings yet
- AUTO400 Homework Assignment 3 SOLUTION PDFDocument11 pagesAUTO400 Homework Assignment 3 SOLUTION PDFLove StrikeNo ratings yet
- Reshuffl Test 1Document12 pagesReshuffl Test 1PiyushNo ratings yet
- Paper - 1 (Question Paper) - 6Document17 pagesPaper - 1 (Question Paper) - 6Saumya MundraNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-02-Objective SolvedDocument7 pagesELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Neet Paper Mock TestDocument15 pagesNeet Paper Mock TestVector AcademyNo ratings yet
- 64e48eeaf4cb5500180a97d7 ## Electromagnetic Induction Practice SheetDocument14 pages64e48eeaf4cb5500180a97d7 ## Electromagnetic Induction Practice SheetdevanshbcollabNo ratings yet
- Chinese Physics Olympiad 2017 Finals Theoretical Exam: Translated By: Wai Ching Choi Edited By: Kushal ThamanDocument7 pagesChinese Physics Olympiad 2017 Finals Theoretical Exam: Translated By: Wai Ching Choi Edited By: Kushal Thamansmritidipa m100% (1)
- Taiwan Physics National Team Selection Test Round 3 2021 Part 1Document6 pagesTaiwan Physics National Team Selection Test Round 3 2021 Part 1Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnatic Induction WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectromagnatic Induction WorksheetDEEPNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja MoonNo ratings yet
- Selection 4 2013Document3 pagesSelection 4 2013Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- 03 - Ohms Law and Its Applications - MQDocument7 pages03 - Ohms Law and Its Applications - MQohyeah142008No ratings yet
- AIPMT Mains 2004 SolvedDocument17 pagesAIPMT Mains 2004 SolvedS A ABDUL SUKKURNo ratings yet
- (Only Starred Problems Are To Be Solved in Class) : PH108: Electricity & Magnetism: Tutorial 11Document2 pages(Only Starred Problems Are To Be Solved in Class) : PH108: Electricity & Magnetism: Tutorial 11ruhi kulweNo ratings yet
- Curent Electricity PDF Documents Topic - 2 PDFDocument48 pagesCurent Electricity PDF Documents Topic - 2 PDFSurya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Modern Physics-09 - AnswersDocument4 pagesModern Physics-09 - AnswersRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-02-Objective Solved Problems1Document5 pagesModern Physics-02-Objective Solved Problems1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-07-Subjective Unsolved Problems Level-1Document2 pagesModern Physics-07-Subjective Unsolved Problems Level-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-06-Subjective Unsolved LevelDocument3 pagesModern Physics-06-Subjective Unsolved LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-03-Subjective Solved Problems1Document9 pagesModern Physics-03-Subjective Solved Problems1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 18 - Modern Physics-01-TheoryDocument19 pages18 - Modern Physics-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-05-Subjective Unsolved C.B.S.EDocument1 pageModern Physics-05-Subjective Unsolved C.B.S.ERaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-04 - Objective Unsolved LevelDocument4 pagesModern Physics-04 - Objective Unsolved LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- COLM-06 - Subjective UnSolved Level-IIDocument4 pagesCOLM-06 - Subjective UnSolved Level-IIRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Colm-07-Problems LevelDocument2 pagesColm-07-Problems LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 17-Simple Harmonic Motion-01-Theory-Package Page 3-25Document23 pages17-Simple Harmonic Motion-01-Theory-Package Page 3-25Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion-02-OBJECTIVE UNSOLVED Package Page (26 - 38)Document15 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion-02-OBJECTIVE UNSOLVED Package Page (26 - 38)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- COLM-04 - Objective UnSolvedDocument5 pagesCOLM-04 - Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Colm-05 - Cbse LevelDocument2 pagesColm-05 - Cbse LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetics-05 - Cbse Subjective Level-IDocument3 pagesMagnetics-05 - Cbse Subjective Level-IRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetics-04-Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesMagnetics-04-Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 16-CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM - 01-TheoryDocument15 pages16-CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM - 01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- COLM-03 - Subjective SolvedDocument15 pagesCOLM-03 - Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- COLM-02 - Objective SolvedDocument5 pagesCOLM-02 - Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetics 08 AnswersDocument5 pagesMagnetics 08 AnswersRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM-08 - AnsWERSHEETDocument4 pagesLOM-08 - AnsWERSHEETRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetics-03-Subjective SolvedDocument12 pagesMagnetics-03-Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetics - 02-Objective SolvedDocument7 pagesMagnetics - 02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM-07-PROBLEMS LevelDocument1 pageLOM-07-PROBLEMS LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM - 04-Objective UnSolvedDocument5 pagesLOM - 04-Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 15 - Magnetics-01 - ThoeryDocument15 pages15 - Magnetics-01 - ThoeryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM-05 - (Cbse) LevelDocument3 pagesLOM-05 - (Cbse) LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM-06 - Subjective UnSolvedDocument4 pagesLOM-06 - Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM-03 - Subjective SolvedDocument13 pagesLOM-03 - Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM-02 - Objective SolvedDocument5 pagesLOM-02 - Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Heavy-Duty Circuit Tester: Item 30779Document4 pagesHeavy-Duty Circuit Tester: Item 30779isshmangNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 V2 TM 18ME54Document1 pageAssignment 2 V2 TM 18ME54rudresh JmNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrient CycleDocument13 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2 Nutrient CycleMohd Amiruddin Malek100% (1)
- AP Chemistry 1994 Free ResponseDocument5 pagesAP Chemistry 1994 Free ResponseWes BristleconeNo ratings yet
- Physics Cropped PDFDocument150 pagesPhysics Cropped PDFMeenu vNo ratings yet
- Bab 3 StoikiometriDocument28 pagesBab 3 StoikiometriM Nur M. Mahmud0% (1)
- CCUS in Steel IndustryDocument52 pagesCCUS in Steel IndustryJonson CaoNo ratings yet
- Stulz Cyberair 3pro DX Brochure 2303 enDocument20 pagesStulz Cyberair 3pro DX Brochure 2303 enmelese gideyNo ratings yet
- CSR-Policy of Tata Steel Company 2014-15 PDFDocument98 pagesCSR-Policy of Tata Steel Company 2014-15 PDFGreatAkbar1No ratings yet
- Boiler Normal Shut DownDocument13 pagesBoiler Normal Shut Downgaurav tiwari100% (1)
- Seismic Response of Structure With Lead Extrusion DamperDocument7 pagesSeismic Response of Structure With Lead Extrusion DamperIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems of The Theoretical CompetitionDocument16 pagesSolutions To The Problems of The Theoretical CompetitionDejan DjokićNo ratings yet
- Sector Bending Blurring Lines Between Non-Profit and For-ProfitDocument13 pagesSector Bending Blurring Lines Between Non-Profit and For-ProfitKevNo ratings yet
- Rad Lec 1 Machine OverviewDocument4 pagesRad Lec 1 Machine OverviewTiti DarabanNo ratings yet
- 0411 001Document8 pages0411 001None None NoneNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Transposition On ATPDrawDocument4 pagesTransmission Line Transposition On ATPDrawRogerio Lucena100% (1)
- Nondissipative Clamping Benefits DC-DC ConvertersDocument5 pagesNondissipative Clamping Benefits DC-DC ConvertersMateusz LiszczykNo ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide To Radio. F.JDocument82 pagesBeginner's Guide To Radio. F.Japi-3695871No ratings yet
- Singel OutdoorDocument4 pagesSingel OutdoorMuhammad WazirNo ratings yet
- SR30 Series - Overcurrent Protection Components - Polymer PTC - Resettable Fuse - Yantai Xinrui Electronics Co., LTDDocument4 pagesSR30 Series - Overcurrent Protection Components - Polymer PTC - Resettable Fuse - Yantai Xinrui Electronics Co., LTDAmitNo ratings yet
- EMI and AC TYPE 1Document19 pagesEMI and AC TYPE 1sanits591No ratings yet
- ZTE Rectifier SettingsDocument4 pagesZTE Rectifier SettingsRicardo Chavarria50% (2)
- 3RH29111FA22 Datasheet enDocument6 pages3RH29111FA22 Datasheet enFlavioNo ratings yet
- WWTFSP - App.F14 - Sludge and Biogas CharacterizationDocument48 pagesWWTFSP - App.F14 - Sludge and Biogas CharacterizationHuy Nguyen100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Forces Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Forces Exam QuestionsNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet