Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3
Uploaded by
Aaron De DiosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3
Uploaded by
Aaron De DiosCopyright:
Available Formats
School: CABALAWAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL Grade Level: V
GRADE 5 Teacher: ZYRUSE AARON D. ARMIAN Learning Area: MATHEMATICS
DAILY LESSON LOG Teaching Dates and Time: MAY 15 – 19, 2023 (WEEK 3) Quarter: 4TH QUARTER
MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards demonstrates understanding of area, volume and temperature.
B. Performance Standards is able to apply knowledge of area, volume and temperature in mathematical problems and real-life situations.
C. Learning a.Visualize the Volume of a Cube and .Name the unit of measure for measuring the volume of cube and a.Derive a formula for finding the volume of a cube and a
Competencies/Objectives Rectangular Prism rectangular prism. rectangular prism using cubic centimeter and meter.
Write the LC code for each - M5ME-IVc-77 /Page 64 of 109 b.Write the value of measuring accurately b.Appreciation of application of volume in daily life situations.
- M5ME-IVc-78/ Page 64 of 109 M5ME-IVc-79
II. CONTENT Visualizes the Volume of a Cube and Names the Appropriate Unit of Measure Used for Measuring the Volume Derives the Formula in Finding the Volume of a Cube and A
Rectangular Prism of a Cube and a Rectangular Prism. Rectangular Prism Using Cubic Centimeter and Cubic Meter
III. LEARNING
RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide pages K to 12 Grade 5 Curriculum K to 12 Grade 5 Curriculum K to 12 Grade 5 Curriculum
2. Learner’s Material pages TM Math Grade 4 pages 298 - 307 LM Math Grade 5 pages 1 to 3
3. Textbook pages
4. Additional Materials https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
from Learning Resource Volume
(LR) portal
B. Other Learning Resources cubes (big and small), rectangular flash cards (mm, cm, dm, m, etc.), real objects, pictures flash cards containing questions on finding area of parallelogram
prism, ruler, flash cards, marbles, (square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram)
worksheet, 1 transparent rectangular
container
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous 1.Drill 1.Drill 1.Drill
lesson or presenting Have a drill on the multiplication facts Drill on Choosing the Appropriate Unit of Measure
the new lesson using the activity sheets. Game: “Korek Ka Ba Dyan?” Mental computation/drill on finding the area or missing side of a
1) 5x5 Materials: flash cards (mm, cm, dm, m, etc.), real objects, pictures parallelogram
6) 7 x 7 Mechanics:
2) 9 x 11 a. Pupils will be grouped into 4. Each group will have flashcards
Materials: flash cards containing questions on finding area of
7) 11 x 11 (mm, cm, m, etc.)
parallelogram (square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelogram)
3) 10 x 12 b. Teacher will ask, “What unit of measure will you use?”
8) 9 x 12 Ex.: Teacher will show a pencil.
4) 4x4 c. Pupils in the group will flash their answer. (Ex. cm) Finding the missing side on the given area
9) 8 x 5 d. Teacher announces the correct answer. Repeat the process. Teacher Mechanics:
5) 6x8 will show another object or picture. a. Divide the class into 3 groups. Have members of the group
10) 4 x 12 e. Group with the most number of correct answers is the winner. count off. Pupils remember their #s in the team.
2.Review b. Teacher shows card to pupils for 10 seconds or depending on
Have a review on the meaning of 2.Review the level of difficulty of questions.
volume. What is difference between cube and rectangular prism?
Volume is the amount of space What are the dimensions of cube and rectangular prism?
occupied by any quantity.
1) A=?
4 cm
5cm
3) A=?
8cm 6 cm
2) L?
4) Rectangle:
Width 2 cm,
Area 10 cm2
L=?
5) Square A = 1 unit2, S = ?
c. Teacher calls out a number randomly. The three pupils having
that number stand up and call out the answer with
correct units. The pupil who gives the correct answer first gets
the point for the team.
d. Teacher may do drawings first before shifting to
pure numerical problems. Teacher may also include finding
area of trapezoids making sure that the dimensions can be
solved mentally.
2.Review
Memory Game
Materials: pocket chart, flash cards
Mechanics:
a. Teacher prepares flash cards with figure and dimensions on a
set of cards and the corresponding area of the figure on another
set of cards. Teacher then place the shuffled cards into pocket
chart slots. At the back of each card, label them with letters.
Ex. front back
b. Divide class into 3 groups.
c. Have a member of group 1 choose 2 letters corresponding to 2
cards. Teacher turns over the cards. If the cards match (figure
and its area), then the team gets the point and the cards taken
out of the pocket chart. If the cards do not match, then the
cards are turned over again in the same place/position in the
pocket chart.
d. Have a member of group 2 call out another pair of cards.
Continue the game until all the cards have been used up. Team
with the most number of points wins.
e. Teacher may divide set of cards into a) finding area of
parallelograms and trapezoid making sure that the dimensions
given are manageable by the pupils, or b) finding the missing
side/dimension given the area.
B. Establishing a purpose for 3.Motivation 3.Motivation 3.Motivation
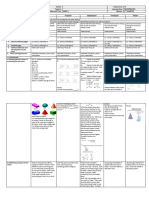
the lesson Show a transparent cube and Richard has a rectangular box with sand inside. He wants to know the Show a transparent plastic container filled with balls. Ask pupils
rectangular prism filled with marbles. amount of space the sand occupied. He wants to know also what unit of to guess the number of balls inside the container. Let a
Ask pupils to guess the number of measure he will use. Elicit the value of accuracy. volunteer count the balls to find out the answer. Elicit from
marbles inside the cube and Original File Submitted and Formatted by DepEd Club Member - them how they can make a good guess of the total number of
rectangular prism. Let a volunteer visit depedclub.com for more balls. Relate this to the concept of volume.
count the marbles to find out the
answer. Elicit from them how they
can make a good guess of the total
number of marbles. Instill the value
of patience and orderliness. Relate
this to the concept of volume.
C. Presenting Tell the class that the number of 1.Presentation Let a pupil fill a rectangular box with cubes. For purposes of
examples/instances of the small cubes that make up the Rubik’s A.Present a rectangular box with sand inside. having exact measurements and no half-cubes, it is ideal that
new lesson cube is its volume. teacher prepares boxes/ rectangular prisms that have
corresponding measurements as the cubes that are going to be
used in the activity.
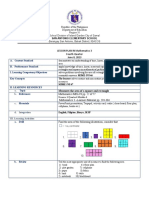
D. Discussing new concepts . Activity – Group Work Ask the following questions: Ask the pupils the following questions:
and practicing new skills #1 Materials: worksheet, 1 transparent a. How can we be able to measure the capacity of the box? a. How many cubes did it take to fill the prism? How many cubic
rectangular container, small cubes b. What will you use? What do you think are we looking for? units is the length? The width? The height?
Procedure: Fill the container with c. What unit of measure will you use? b. What similar situations require you to fill up a solid such as
small cubes until its upper portion. The volume of a solid is the amount of space the solid occupies. Volume is the rectangular prism?
Example measured in cubic units. One way to find the volume of a rectangular c. Define these situations as finding the volume of solids. Define
prism is to multiply the 3 dimensions: volume as the number of cubic units (unit cubes) used
Volume = length x width x height to fill up a space. Use correct unit of measure.
d. Using this definition, ask the pupils the volume of the
Ask the pupils to measure the 3 dimensions of some objects inside the rectangular prism.
Guide Questions: room using cm3 and m3. e. Ask: Without actually counting the number of unit cubes in
1) What kind of solid figure is the 1 liter = 1 dm3 the solid how can you find its volume? What formula can
container? we use to find the number of cubic units in it or the
2) How many cubes did you put inside volume of the rectangular prism?
B.Teacher shows a cube (box) filled with blocks 2 cm on each side. Ask a
the rectangular container? f. Elicit from the pupils that
pupil to get one block and describe it.
3) How can you find the number of → To find the volume of an object means to find the
What can you say about the block?
cubes in the container without number of cubic units it contains or holds
What are the dimensions?
counting them all? g. Lead them to state the formula for the volume of a
A cube is a special type of rectangular prism having equal edges. Empty
a) Count the cubes in one layer. rectangular prism as
the box then let the pupils fill the box with the number of cubes. The total V = l x w x h.
number of cubes that will fill the box represents the volume of the box. h. Define volume as the number of unit cubes in the solid figure.
When finding volume, the units of volume are cubic units. Mention the correct label (cubic units).
Example What are the units of volume? (cubic millimeters – mm3, cubic i. Using this definition, ask the pupils the volume of the cube.
4 x 2 = 8 cubes centimeters – cm3, cubic decimeter – dm3, cubic meters – m3, etc.) j. Ask: Without actually counting the number of unit cubes, how
b) Count the layers. Ex.: 3 layers can you find the volume of the cube? What formula can
c) How many cubes in all? 8 x 3 = 24 we use to find the number of cubic units in it?
cubes k. Try to elicit from the pupils that to find the volume of a cube,
the length of its side is multiplied by itself three times.
4) When we get the total number of l. Lead them to state the formula for the volume of a cube as
cubes that the container has, what V = S x S x S or V = S³
have we looked for? (Answer: m. Let pupils apply the rule by actually measuring and finding
Volume) the volume of some rectangular prisms and cube inside the
5) What kind of polygon is the base of room.
the container? What are its n. Present situations like how much water does it take to fill the
dimensions? aquarium, how far does it take to run around the park, etc. and
6) How many cubes fit the length? distinguish perimeter/ circumference from area and volume.
the width? Elicit similar applications of volume in daily life situations.
7) What other dimension does the
rectangular container have? How
many cubes fit the height?
8) Can you give the volume of the
rectangular prism by just using the
dimensions (length, width, height)?
How?
(Note: Teacher must tell the pupils
that by multiplying the length x width
x height will give the volume thus,
Volume = L x W x H))
E. Discussing new concepts Group the pupils into 4 working 2. Performing the Activities 2. Performing the Activities
and practicing new skills #2 teams and have them perform the Group the class into four. Let them perform the give activity. Group the pupils into 4 working teams and have them perform
task. Give the appropriate unit of measure to be used in the task.
Activity 1. They need small cubes, big finding the volume of Find the Volume write the Given, Formula and Answer
cubes and rectangular prism. (Select from the given choices: mm3, cm3, dm3, m3) : Refer to LM
Refer to LM a) room _______
b) shoe box _______
If each is a cubic unit, how c) globe _______
many cubic units are in the figures? d) refrigerator _______
How many cubic units are there in e) ice cream cone _______
one row? f) baseball _______
How many cubic units are there in
one layer?
How many layers are there?
What have you notice in the number
of layers and rows of cube and prism?
What can you say about the number
of layers and rows of a cube?
What have you notice in the length,
width and height of a cube?
What can you say about the number
of layers and rows of a prism?
What have you notice in the length,
width and height of a prism?
a.Have pupils count the number of
cubes in the figures.
b. Define volume as the
number of unit cubes in the solid
figure. Mention the correct label
(cubic units)
c.Have them imagine filling up the
classroom with such cubes. Then we
find the volume of the classroom.
Elicit similar application of volume in
daily situations.
=
F. Developing mastery 3.Processing the Activities 3.Processing the Activities 3.Processing the Activities
(Leads to Formative Ask the groups to present and discuss Ask the groups to present and discuss their answers on the board. Ask the groups to present and discuss their answers on the
Assessment 3) their answers on the board. Expected answer: board.
Expected answer: a) room m3 Expected answer:
•Cube is a solid whose length, width b) shoe box cm3 1. Given:L = 6 cm W = 10 cm
and height are equal. c) globe cm3 H = 12 cm Answer : V = 23 100 cm3
• Rectangular prism whose d) refrigerator dm3 2. Given:L = 25 cm W = 3 cm H = 7 cm
length, width and height are not e) ice cream cone cm3 Answer : V = 525 cm3
equal f) dice mm3 3. Given:S = 9 cm Answer : V = 729 m3
Discuss the presentation on Explore and Discover of page 1 of LM Math 4. Given:S = 6 m Answer : V = 324 m3
Grade 5. Ask pupils to work on exercises A under Get Moving on pages 1
LM Math Grade 5. Check the pupils’ answers. For mastery, have them
answer the exercises A under Keep Moving on page 2 of LM Math Grade
5. Check on the pupils’ answers.
G. Finding practical 6.Applying to New and Other 5.Applying to New and Other Situations 6.Applying to New and Other Situations
applications of concepts Situations Give the cubic unit of measure used in the following problems. Find the volume of the following figures
and skills in daily living Have the pupils do the exercises 1) A piece of soap is 9 cm by 4 cm by 3cm. Refer to LM
under Apply Your Skills on page 3 LM 2) An aquarium is 0.8 m long, 0.4 m wide, and 0.45 dm deep.
Math 3) An iron bar 2 m long and 0.05 m in diameter.
4) An ice cream cone 2 cm in radius and 6 cm in height.
H. Making generalizations and Summarize the lesson by asking: 4.Summarizing the Lesson Summarize the lesson by asking:
abstractions about the How can we visualize the volume of Summarize the lesson by asking: How can you find the volume of a cube and a rectangular prism?
lesson cube and rectangular prism? What do you call the capacity of things or the total space within •The formula in finding the Volume of a cube is;
Lead the pupils to give the a 3-dimensional figure? Volume = side x side x side or V = S x S x S or V = S3
generalization What unit of measure will you use in measuring volume? •In rectangular prism we need L = Length, W = Width and H =
•Volume is the amount space a solid Height, the formula in finding the Volume of a rectangular prism
figure occupies. • Volume is the amount of space occupied by a space figure. is;
• We can visualize volume of cube • Volume measured in cubic units, such as Volume = Length x Width x Height V=LxWxH
and rectangular prism cubic centimeter (cm3) •Volume is measured in cubic units, such as cubic centimeters
a.using more units to fill the cubic meter (m3) ( cm3), cubic meters (m3), and millimeters (mm3)
container (like the used of marbles, cubic millimeter (mm3)
pebbles, rice grains, seed, etc) this is cubic decimeter (dm3)
what we called non-standard units.
Non standard units do not give
consistent and accurate measure of
the volume of a container.
b.Using standard units, to find the
volume o a space figure, count the
number of cubic units needed to fill
the space. Standard units are
consistent and accurate.
I. Evaluating learning C.Assessment C.Assessment B.Assessment
Find the volume of these solid figures
Ask the pupils to find the volume of A. Write the cubic unit of measure used.
each figure by counting the cubes.
Refer to Lm 1) 20 mm
20 mm 20mm 2) 2 dm
10 cm 8 dm
3cm 2cm 1 dm
3)
B.Use cm3, m3, dm3 to tell which cubic unit of measure is appropriate to
be used.
a) box of chocolate
b) tent
c) glass
d) gymnasium
e) math book
J. Additional activities for Find the volume. Give the cubic unit of measure for finding the volume of the following: Draw the figure with their measurements and find their volume.
application or remediation Refer to Lm a) a box 44 cm by 9 cm by 6 cm 1. L=9m W=4m H=3m
b) a room 4m by 5m by 6 m 2. L = 10 m W=7m H = 15 m
c) a cabinet 1.2 m by 0.9 m by 0.5 m 3. L = 14 m W = 10 m H=9m
d) a ball with radius 10 cm 4. S = 12 cm
e) a cylindrical tank 25 dm long and radius 8 dm 5. S = 7 cm
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation
B. No. of learners who require
additional activities for
remediation who scored
below 80%
C. Did the remedial lessons
work? No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did these work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials did I
use/discover which I wish
to share with other
teachers?
PREPARED BY:
ZYRUSE AARON D. ARMIAN CHECKED BY:
TEACHER ELGEAN T. ZAMORA NOTED BY:
MASTER TEACHER LEAH D. ARMIAN
PRINCIPAL
You might also like
- DLL MATHEMATICS 6-w7 Q3Document7 pagesDLL MATHEMATICS 6-w7 Q3Arvin LeynesNo ratings yet
- Math6 q3 DLP Surface Area Cot Latest FormatDocument7 pagesMath6 q3 DLP Surface Area Cot Latest FormatCherry Ocampo Sales100% (2)
- Olympiad Sample Paper 4: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsFrom EverandOlympiad Sample Paper 4: Useful for Olympiad conducted at School, National & International levelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Josie CarpzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 5 q4 w3 DLLDocument7 pagesMathematics 5 q4 w3 DLLLovely ParaisoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Beverly Amora Serada100% (1)
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Beverly Amora SeradaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Luis SalengaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Jeward TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3shiela pandacNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W3Anthonette Llyn Joice BermoyNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document6 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Nerissa Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- DLL in Math V Q4 Week 2Document16 pagesDLL in Math V Q4 Week 2Uola HDNo ratings yet
- QRT4 WEEK 3 TG Lesson 86Document5 pagesQRT4 WEEK 3 TG Lesson 86Madonna Arit MatulacNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 9Document15 pagesQ3 Week 9Grace AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q4 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q4 - W4Lisette Senoc-GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLL Math-5 Q4 W4Document8 pagesDLL Math-5 Q4 W4SALIHA OMARNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W10Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W10Ariel PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar: Learning Area Mathematics Learning Delivery Modality Modular Distance Modality (Learners-Led Modality)Document10 pagesLesson Exemplar: Learning Area Mathematics Learning Delivery Modality Modular Distance Modality (Learners-Led Modality)JEFFREY SORIANONo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3rochelle littauaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Co1Document9 pagesLesson Plan Co1ronald malicdemNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 DLL MATH 6 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 6 DLL MATH 6 Q4 Week 3ivan abando100% (1)
- DLL Mathematics-6 Q4 W3Document8 pagesDLL Mathematics-6 Q4 W3EDERLYN ABEQUIBELNo ratings yet
- Math Week 2Document7 pagesMath Week 2Camille TorresNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q4 w3Document8 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q4 w3marinette vasoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W9Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W9JAS SAJ100% (1)
- DLL Mathematics 6 q4 w1Document9 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q4 w1rochelle littauaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3JannahNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument5 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayKeith CatbaganNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 DLL MATH 4 Q4 Week 4Document5 pagesGrade 4 DLL MATH 4 Q4 Week 4Lelanie FloresNo ratings yet
- April 17, 2024Document3 pagesApril 17, 2024cindy dizonNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 6 - Q4 - W3Document10 pagesDLL - Math 6 - Q4 - W3mary rose cornitoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Document9 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Dagoc Wil Jr.No ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Rosebuds NvjsNo ratings yet
- Math Week 10Document6 pagesMath Week 10KirstenFayeMiraplesNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q4 - W4Document5 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q4 - W4valerieNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q4 w3Document8 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q4 w3Pamela BulawitNo ratings yet
- Intro Geo 4 - Surface Area NetsDocument8 pagesIntro Geo 4 - Surface Area NetsTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- Math6 Week9Document10 pagesMath6 Week9Donna Lornne CabutajeNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument9 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayBernadine Jacob TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Math6 Week8Document10 pagesMath6 Week8Donna Lornne CabutajeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Document9 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Melanie DucalangNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Document9 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1magtoliscanilloanaleeNo ratings yet
- DLL MeasurementsDocument4 pagesDLL MeasurementsLetCatalystNo ratings yet
- WLP GR3 WK3 Q4Document5 pagesWLP GR3 WK3 Q4Shiela Marie de Belen - AmbionNo ratings yet
- QRT4 WEEK 3 TG Lesson 87Document4 pagesQRT4 WEEK 3 TG Lesson 87Madonna Arit MatulacNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Gian Carlo RebutocNo ratings yet
- Q4 Wk3 Le Math5 Quines KenetteDocument4 pagesQ4 Wk3 Le Math5 Quines KenetteKenette QuinesNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W3Nerissa Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Math DLP G6 Q4 W1Document9 pagesMath DLP G6 Q4 W1Raquel FamorcaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson Planmangalam manjuNo ratings yet
- GR4 DLL Mathematics Feb5-9 2018Document44 pagesGR4 DLL Mathematics Feb5-9 2018Sheryl Ilagan Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Document9 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Gina HerraduraNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 6 Q3 W10Document9 pagesDLL Math 6 Q3 W10cherry salesNo ratings yet
- Measure Square and Rectangle For Grade 3Document4 pagesMeasure Square and Rectangle For Grade 3Maricar Omega DabalosNo ratings yet
- DLL Math Q4 W6Document8 pagesDLL Math Q4 W6MARIA ANNA LOU PERENANo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Document10 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W1Virgie Bercida LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Gomez Demo FinalDocument5 pagesGomez Demo FinalMELVIN OTOMNo ratings yet
- DLL Lesson Log Formulas For Area For Traingles, Parallelograms Ad TrapezoidsDocument6 pagesDLL Lesson Log Formulas For Area For Traingles, Parallelograms Ad TrapezoidsAira Rica ApuraNo ratings yet
- CO Lesson Plan Math (Volume)Document3 pagesCO Lesson Plan Math (Volume)Khyme HermosoNo ratings yet
- Acr-Pta MeetingDocument4 pagesAcr-Pta MeetingAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Divisibility Rules BDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Divisibility Rules BAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Program Design PESPA Re EchoDocument8 pagesProgram Design PESPA Re EchoAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ledesma R. Layon FRV Graduate School Material 2 Found. Ed 202 Philosophical and Psychological Foundation in EducationDocument4 pagesDr. Ledesma R. Layon FRV Graduate School Material 2 Found. Ed 202 Philosophical and Psychological Foundation in EducationAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ledesma R. Layon FRV Graduate School Material 2 Found. Ed 202 Philosophical and Psychological Foundation in EducationDocument4 pagesDr. Ledesma R. Layon FRV Graduate School Material 2 Found. Ed 202 Philosophical and Psychological Foundation in EducationAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 5 - Q4 - W2Document8 pagesDLL - Mapeh 5 - Q4 - W2Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q4 - W2Document5 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q4 - W2Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- SMEA Form NewDocument3 pagesSMEA Form NewAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W2Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q4 - W2Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 5 - Q4 - W3Document8 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q4 - W3Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q4 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q4 - W3Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 5 - Q4 - W3Document7 pagesDLL - Mapeh 5 - Q4 - W3Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- CABALAWAN ES Program Design INSET Midyear Feb 2023Document8 pagesCABALAWAN ES Program Design INSET Midyear Feb 2023Aaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- DM s2023 008Document145 pagesDM s2023 008Joy CristineNo ratings yet
- Sample BallotDocument1 pageSample BallotAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG School: Cabalawan Elementary Grade Level: 5 - NARRADocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG School: Cabalawan Elementary Grade Level: 5 - NARRAAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG School: Cabalawan Elementary Grade Level: 5 - NARRADocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG School: Cabalawan Elementary Grade Level: 5 - NARRAAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Cabalawan Elementary SchoolDocument6 pagesCabalawan Elementary SchoolAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Cabalawan Elementary SchoolDocument6 pagesCabalawan Elementary SchoolAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Cabalawan Elementary School-Contingency Plan - COVID-19: BackgroundDocument8 pagesCabalawan Elementary School-Contingency Plan - COVID-19: BackgroundAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VII Cebu Province Sogod DistrictDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VII Cebu Province Sogod DistrictAaron De DiosNo ratings yet