Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Scheme of The Discourse Analysis
Uploaded by
Gallina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
The Scheme of the Discourse Analysis (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe Scheme of The Discourse Analysis
Uploaded by
GallinaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
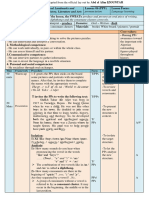
The scheme of the discourse analysis
1. It is an example of written /oral discourse |ˈdɪskɔːs|.
The piece of information under analysis is written /oral discourse.
The title is….
2. As I see it / I guess / I suppose it is…
- an extract from a …
- аn article
- an interview …
- a part of a TV programme.
3. It can be found / We can read it / It can be heard/watched …
- on an Internet site.
- in TV news.
- in an encyclopedia.
- in an newspaper
- in social networks
4. The main idea / intention of the author / purpose of the narrator …
- as I understand it
- to my mind
- in my opinion
- as I see it
… - is to describe…
- to give an outline
- to tell us about
- to make us closer to
- to entertain … etc.
5. The target audience is / the participants are teenagers / elderly people / general public / animals
friendly people …
- because there are a lot of modern terms describing gadgets.
- as the article deals with specific problems of retired people.
- because the information is given in simple words and a clear way.
6. As for the structure / What about the structure, the article / presentation / interview / text
- can be divided into several parts
- is a monologue
- is a chain of questions and answers
- has an introduction where … , the main part …, and a conclusion etc.
7. The text / article / extract / interview is full of specific vocabulary / words / set expressions that
make us …
- understand the problem
- feel the situation
- get details / a clear picture of ….. etc.
For example nouns: pollution, contamination, extinction, etc.
verbs and verb phrases: become extinct, cut down, destroy, etc.
adjectives: drastic, catastrophic, renewable, etc.
8. Grammar and Linguistic peculiarities of the text:
Tenses, the sentence structure (simple/ compound/ complex sentences), Modals, Count and non-
Count Nouns, Definite and Indefinite Articles, Quantifiers, Modification of Nouns, Adjective
Clauses, The Passive, Gerund, Infinitive, Adverb clauses, Connectors, Direct and Indirect Speech,
Conditionals, The Subjunctive.
The Past Simple and The Present Simple Tenses are used to show the contrast between the past and the
present situation in / with / about ….
The Present Continuous is used to emphasize the idea that it / … is happening right now / at the present
time.
The Present Perfect is necessary to show the result of …
The Future Simple and future be going to are actively used …
- to picture the perspectives of … \ to show a possible solution … etc.
9. In general / In conclusion I would say / To sum up I must admit that …
- the article make an interesting reading
- the text gives much food for thinking and discussions
- I feel I’ve got the message / the main idea of what can be done about …
10. I would recommend such articles / TV shows / stories to the people who … .
You might also like
- Lý thuyết dịchDocument96 pagesLý thuyết dịchnguyenmaithanh100% (5)
- FIDP for Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementDocument3 pagesFIDP for Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementByerus Tv100% (4)
- Elm-490 Step UnitDocument20 pagesElm-490 Step Unitapi-477884458No ratings yet
- The Scheme of The Discourse AnalysisDocument4 pagesThe Scheme of The Discourse AnalysisaminaNo ratings yet
- CollocationDocument105 pagesCollocationAlexandra Pascu100% (2)
- Aspect in Reading ComprehensionDocument9 pagesAspect in Reading ComprehensionEristiana Sri Agustin50% (2)
- Critical Thinking MemorandumDocument5 pagesCritical Thinking MemorandumGarretNo ratings yet
- Beowulf Circles - Senior - Entire Literature Circle Information and FormsDocument8 pagesBeowulf Circles - Senior - Entire Literature Circle Information and Formsapi-148362218No ratings yet
- A Research Paper On "Study of Employee's Performance Appraisal System"Document6 pagesA Research Paper On "Study of Employee's Performance Appraisal System"Anonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- The Scheme of The Discourse AnalysisDocument2 pagesThe Scheme of The Discourse AnalysisМария ПавловаNo ratings yet
- Useful Phrases For Discussion and AnalysisDocument7 pagesUseful Phrases For Discussion and AnalysisAnna SobolevaNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech EssentialsDocument3 pagesInformative Speech EssentialstamazzookeyNo ratings yet
- essay writingDocument3 pagesessay writingCristiana PetrideanNo ratings yet
- PhrasesDocument6 pagesPhrasesЮлия МатрёнинаNo ratings yet
- Eapp - Module 1Document44 pagesEapp - Module 1Ardy Garcia AgaciteNo ratings yet
- TechnicalDocument32 pagesTechnicalMark Jayson BacligNo ratings yet
- Writing Tips: SentenceDocument16 pagesWriting Tips: SentenceAleNo ratings yet
- CPGE - TAZA - COLLE - METHODOLOGY - BY - MR. - BOUSSETTA - TARIK - PDF - Filename - UTF-8''CPGE - 20TAZA - 20 - 20COLLE - 20METHODOLOGY - 20BY - 20MR. - 20BOUSSETTA - 20TARIK PDFDocument8 pagesCPGE - TAZA - COLLE - METHODOLOGY - BY - MR. - BOUSSETTA - TARIK - PDF - Filename - UTF-8''CPGE - 20TAZA - 20 - 20COLLE - 20METHODOLOGY - 20BY - 20MR. - 20BOUSSETTA - 20TARIK PDFhichamNo ratings yet
- METHODOLOGY OF THE TEXT ANALYSIS in Terminale 2020 Docx-1Document3 pagesMETHODOLOGY OF THE TEXT ANALYSIS in Terminale 2020 Docx-1Lome t1-monstreNo ratings yet
- Writing Tips - CaeDocument16 pagesWriting Tips - CaeRachael FranklinNo ratings yet
- CAE WritingDocument13 pagesCAE Writinglaursavu100% (2)
- Vocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionDocument2 pagesVocabulary For Text Analysis and Text ProductionchloNo ratings yet
- Word List On Presentations: Stating Your OpinionDocument5 pagesWord List On Presentations: Stating Your OpinionSevdaNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation SkillsDocument8 pagesOral Presentation SkillsSweetMaina100% (1)
- Paragraph Sentence CompletionDocument55 pagesParagraph Sentence CompletionHuyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Presentation Language and Expressions - Speaking in Academic ContextsDocument6 pagesPresentation Language and Expressions - Speaking in Academic ContextsSiyeon YeungNo ratings yet
- Reading Activities InventoryDocument5 pagesReading Activities Inventoryines ailanNo ratings yet
- First Exam: Writing BookletDocument31 pagesFirst Exam: Writing BookletAgusbdl2No ratings yet
- جابتر1Document8 pagesجابتر1احمد خاشع ناجي عبد اللطيفNo ratings yet
- How To Render An ArticleDocument1 pageHow To Render An ArticleAnastassia SazonovaNo ratings yet
- Eo Expressions UtilesDocument7 pagesEo Expressions Utilessamuelkacou55No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO MUET-MEETING 3 Part 2Document9 pagesINTRODUCTION TO MUET-MEETING 3 Part 2Rahmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Writing English Texts GuideDocument11 pagesWriting English Texts GuidealexNo ratings yet
- The Proper Ways Increasing English Speaking Skill On TeenagersDocument9 pagesThe Proper Ways Increasing English Speaking Skill On Teenagersstudio satuNo ratings yet
- SPEAKING Task - S1Document3 pagesSPEAKING Task - S1HelenaNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument6 pagesEssayinfoNo ratings yet
- Handout EappDocument8 pagesHandout EappRalyn Cando AquindeNo ratings yet
- PPGDfinalDocument10 pagesPPGDfinalNhân Đức BùiNo ratings yet
- ESSAY WritingDocument3 pagesESSAY Writinghtpthao0406No ratings yet
- speaking buổi 1 học thuộcDocument3 pagesspeaking buổi 1 học thuộcHà Trang TrầnNo ratings yet
- EnglischDocument1 pageEnglischnina.joana.leinweberNo ratings yet
- How To Render The ArticleDocument4 pagesHow To Render The ArticleОльгаNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Beginning ReadingDocument76 pagesIntroduction To Beginning ReadingPRECIOUS ANN NATIVIDADNo ratings yet
- Doc2 DikonversiDocument8 pagesDoc2 DikonversiMeta SariNo ratings yet
- TMR - English For Pyssics - Group 4Document18 pagesTMR - English For Pyssics - Group 4Meta SariNo ratings yet
- Teaching Reading: Why Do We Read?Document7 pagesTeaching Reading: Why Do We Read?phụng KimNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument35 pagesListening SkillsChuaNo ratings yet
- OPINION ESSAY UpdatedDocument10 pagesOPINION ESSAY UpdatedNgô An KhánhNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: Writers' Effect Helpful Tips!: You Will Need Three Different Colour Highlighters For This QuestionDocument4 pagesPaper 1: Writers' Effect Helpful Tips!: You Will Need Three Different Colour Highlighters For This QuestionVighneshwar NarayanNo ratings yet
- Reading For Uae OverviewDocument8 pagesReading For Uae Overviewapi-236417442No ratings yet
- Elana's Notes TA Lesson 3Document6 pagesElana's Notes TA Lesson 3mark16514919No ratings yet
- Oral Commentary L1 2023 - Students' HandoutsDocument10 pagesOral Commentary L1 2023 - Students' HandoutsrodrigueNo ratings yet
- Makalah BHS InggrisDocument9 pagesMakalah BHS InggrisLudmila KiyaraNo ratings yet
- Project: The Communicative Competence Suggests The Ability To Put Forward StrongDocument4 pagesProject: The Communicative Competence Suggests The Ability To Put Forward StrongAbobus223No ratings yet
- FCE Practice TestsDocument5 pagesFCE Practice TestsLien HoangNo ratings yet
- Language Templates For Debates: Stages Sample ExpressionsDocument2 pagesLanguage Templates For Debates: Stages Sample ExpressionsHoctienganh HhNo ratings yet
- Dzexams Docs 4am 906144Document6 pagesDzexams Docs 4am 906144hasna.nafirNo ratings yet
- CAE Writing (Useful Language)Document15 pagesCAE Writing (Useful Language)Marceta BrankicaNo ratings yet
- How to Make PresentationsDocument11 pagesHow to Make PresentationsJoaquin FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Umm Al Qura University Methodology 2 Teaching Receptive SkillsDocument29 pagesUmm Al Qura University Methodology 2 Teaching Receptive SkillsVidya1986No ratings yet
- AR12ING0499Document5 pagesAR12ING0499fatwadiniNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Wording of Dissertation TitlesDocument19 pagesFormulation and Wording of Dissertation Titleshaya bisNo ratings yet
- M 1 - Unit 5 - ReadingDocument6 pagesM 1 - Unit 5 - ReadingRania singerNo ratings yet
- Khôlle, A Methodology 2021Document3 pagesKhôlle, A Methodology 2021Youssef MzabiNo ratings yet
- Writing The Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument11 pagesWriting The Advantages and DisadvantagesDuy Minh PhamNo ratings yet
- Kenny-230717-Google Data Scientist GuideDocument8 pagesKenny-230717-Google Data Scientist GuidevanjchaoNo ratings yet
- Taking NotesDocument3 pagesTaking Notesapi-247620221No ratings yet
- Neuro Immuno PsychologyDocument8 pagesNeuro Immuno PsychologyNSDNo ratings yet
- 5b Face-To-Face TeachingLearning - Term Paper (Final Draft) - 25nov2016Document7 pages5b Face-To-Face TeachingLearning - Term Paper (Final Draft) - 25nov2016She's Amalina100% (2)
- How To Read A Film-J MonacoDocument38 pagesHow To Read A Film-J MonacobendjaniNo ratings yet
- 30DayWM Call17 With Dr. Joe RubinoDocument35 pages30DayWM Call17 With Dr. Joe Rubinolisa252100% (1)
- Dynamic Face Recognition: From Human To Machine Vision: Massimo Tistarelli, Manuele Bicego, Enrico GrossoDocument11 pagesDynamic Face Recognition: From Human To Machine Vision: Massimo Tistarelli, Manuele Bicego, Enrico GrossopavanNo ratings yet
- MORAL DEVELOPMENT EXAM REVIEWDocument1 pageMORAL DEVELOPMENT EXAM REVIEWAbigail N. DitanNo ratings yet
- The Power of FarDocument12 pagesThe Power of Fargenn katherine gadunNo ratings yet
- Mapeh AssessmentDocument116 pagesMapeh AssessmentFrizel del RosarioNo ratings yet
- English Worksheet 5Document6 pagesEnglish Worksheet 5Chandra TappyNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument7 pagesCommunicationJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Autoethnography Essay AssignmentDocument2 pagesAutoethnography Essay AssignmentevansNo ratings yet
- Articles Present PastDocument2 pagesArticles Present PastMcCherry CNo ratings yet
- In Brief (Summer 11) AphasiaDocument1 pageIn Brief (Summer 11) AphasiaSpeech & Language Therapy in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Outline Community HelpersDocument2 pagesLesson Outline Community Helpersapi-215875823No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 10 e 6 Mar 2019Document7 pagesLesson Plan 10 e 6 Mar 2019Sabina Lucia GrapiniNo ratings yet
- English KSSR Year 5Document2 pagesEnglish KSSR Year 5Anita LeeNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Large Language ModelsDocument97 pagesA Survey of Large Language Modelsdeepak2083No ratings yet
- Teaching English in MoroccoDocument11 pagesTeaching English in MoroccoYounes AbajtitNo ratings yet
- Presentational Rubric - SpeakingDocument1 pagePresentational Rubric - Speakingapi-263239965No ratings yet
- Steve Jobs' Management Style and Its Impact on AppleDocument15 pagesSteve Jobs' Management Style and Its Impact on AppleVennNo ratings yet
- Prelim Adtech Week4 BDocument5 pagesPrelim Adtech Week4 BLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Research DefinitionsDocument51 pagesResearch DefinitionsHari PrasadNo ratings yet