Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Difference Between Internal Energy and Enthalpy
Uploaded by
King KOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Difference Between Internal Energy and Enthalpy
Uploaded by
King KCopyright:
Available Formats
Difference between internal energy and enthalpy
Internal energy and enthalpy are two thermodynamic properties that describe the state of a
system, but they are not the same thing.
Internal energy, denoted by U, is the total energy of the molecules that make up a system. It
is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all the particles in the system, including
electrons, nuclei, and molecules. Internal energy is a state function, which means it depends
only on the initial and final states of the system and not on how the system got there.
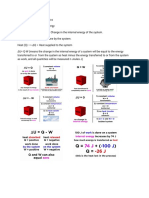
Enthalpy, denoted by H, is defined as the sum of the internal energy and the product of
pressure and volume. H = U + PV. Enthalpy is also a state function and is related to the heat
absorbed or released during a process at constant pressure. When a system undergoes a
process at constant pressure, the enthalpy change, ΔH, is equal to the heat absorbed or
released by the system, q.
In other words, enthalpy takes into account not only the internal energy of a system, but also
the work that can be done by the system as it expands or contracts. This makes it a more
useful thermodynamic property for describing processes that occur at constant pressure,
which is often the case in chemical reactions and industrial processes.
In summary, internal energy is the total energy of the molecules in a system, while enthalpy
is the sum of the internal energy and the product of pressure and volume. Enthalpy is a more
useful thermodynamic property for processes that occur at constant pressure, such as
chemical reactions.
You might also like
- EnthalpyDocument2 pagesEnthalpyIvy Pearl TabagNo ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesLaws of ThermodynamicsvaniNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy and ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesInternal Energy and ThermodynamicsVISWANATHAN GNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is Defined As The Branch of Science That Deals With The RelationshipDocument8 pagesThermodynamics Is Defined As The Branch of Science That Deals With The Relationshipibro4khadNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ShubhaDocument17 pagesThermodynamics ShubhaShubhajyoti KarmakarNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument13 pagesEnthalpy224883061No ratings yet
- Internal Energy: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToDocument8 pagesInternal Energy: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump Toramphy298950No ratings yet
- Energy Thermodynamic System Internal Energy Environment Thermodynamic Potential State Function ExtensiveDocument11 pagesEnergy Thermodynamic System Internal Energy Environment Thermodynamic Potential State Function ExtensiveKapten Eko Sang PemimpiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Thermochemistry Key Notes: Fundamentals Aspects Thermochemistry Is AnDocument11 pagesChapter 15: Thermochemistry Key Notes: Fundamentals Aspects Thermochemistry Is AnSarthakNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy and The Ideal GasDocument9 pagesInternal Energy and The Ideal GasfagroupandahmadsonsNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument63 pagesThermodynamicssavita patilNo ratings yet
- What Is Heat?: Transferred To An Object in Order To Perform Work On, or To Heat, The Object) Following Are TypicalDocument7 pagesWhat Is Heat?: Transferred To An Object in Order To Perform Work On, or To Heat, The Object) Following Are Typicalabdulk_basitNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument5 pagesEnthalpyzzaanNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument5 pagesEnthalpyzzaanNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy: The Total of All The Possible Kinds of Energy of A System, Is Called Its Internal Energy. TheDocument3 pagesInternal Energy: The Total of All The Possible Kinds of Energy of A System, Is Called Its Internal Energy. TheAnila zafarNo ratings yet
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesFirst Law of ThermodynamicsFlorecel CaudillaNo ratings yet
- XI CH 5 NotesDocument4 pagesXI CH 5 Notesiroonmaan123No ratings yet
- Internal Energy and The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesInternal Energy and The First Law of Thermodynamicskoko blueNo ratings yet
- Energetics of Chemical ReactionDocument68 pagesEnergetics of Chemical ReactionSolar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ThermodynamicsParivesh LuniaNo ratings yet
- Cursul 1 Termodinamica 1 Merged CompressedDocument182 pagesCursul 1 Termodinamica 1 Merged CompressedTeodor OlaruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesChapter 6. Thermodynamicshoney1002No ratings yet
- Summary Group 2 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSummary Group 2 Laws of ThermodynamicsNorhida PantaranNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Cheem CH 6 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesHsslive XI Cheem CH 6 ThermodynamicsAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument16 pagesEnthalpyMazen AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesChapter - 6 ThermodynamicsJASRA THAJUDEENNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument6 pagesThermochemistrytechtycoons01No ratings yet
- The Energy LandscapeDocument7 pagesThe Energy LandscapeTHE MAGNUMNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Basics of Thermodynamics: Historical MilestonesDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Basics of Thermodynamics: Historical MilestonesJhonrick MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Thermo EngineeringDocument68 pagesThermo EngineeringAsmaa WajeahNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (I) References: Dr. Farhan Altaee Thermodynamics/Chapter OneDocument25 pagesThermodynamics (I) References: Dr. Farhan Altaee Thermodynamics/Chapter OneYuliman AididNo ratings yet
- Work IE Enthalpy-1Document32 pagesWork IE Enthalpy-1Aiman MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 13 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2Document1 page13 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2PranayNo ratings yet
- Solid States Assignment 1, Shristi SahuDocument6 pagesSolid States Assignment 1, Shristi Sahushristi sahuNo ratings yet
- Book Summary: A. The Nature of Energy and Types of EnergyDocument9 pagesBook Summary: A. The Nature of Energy and Types of EnergyFildzahNo ratings yet
- Report - Fundamental Property Relation and Its UsageDocument11 pagesReport - Fundamental Property Relation and Its UsageShreyash patilNo ratings yet
- Relation Entropy, Energy: Between Corrosion, Enthalpy and FreeDocument9 pagesRelation Entropy, Energy: Between Corrosion, Enthalpy and FreeTanmay BohraNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument5 pagesEnthalpy - Chemistry LibreTextsshiel175No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument21 pagesThermodynamicsXenon ClassesNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Cheem CH 6 - ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesHsslive XI Cheem CH 6 - ThermodynamicsasinriazNo ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesThe First Law of ThermodynamicsIan Dimayuga100% (1)
- Boiler and Power Plant 20011 FinalDocument187 pagesBoiler and Power Plant 20011 FinalGebeyehu GetachewNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument65 pagesBasicsBas RamuNo ratings yet
- 3thermodynamics 2020Document55 pages3thermodynamics 2020Montassar Dridi100% (1)
- Physical Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesPhysical Biochemistry Lecture Noteschc300No ratings yet
- DP ThermodynamicsDocument24 pagesDP ThermodynamicsYash AkhauriNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument7 pagesThermochemistryLover BoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6Farhan Mahmood FahimNo ratings yet
- 470 - Mce 204 Lecture Note 2Document61 pages470 - Mce 204 Lecture Note 2Wahyu WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- 7.01 Endothermic and ExothermicDocument4 pages7.01 Endothermic and ExothermicYangelis Martinez50% (2)
- Thermodynamics Tut. 1Document4 pagesThermodynamics Tut. 1Atif MohamedNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument8 pagesQuestionsAntonioNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy: Internal EnergyDocument2 pagesEnthalpy: Internal EnergysnehatripathNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: EnergyDocument20 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: EnergyMohamed nasserNo ratings yet
- 1 BmeDocument44 pages1 BmepmagrawalNo ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesEngineering Thermodynamicsnagu nagaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes ch06 Thermodynamics PDFDocument4 pages11 Chemistry Notes ch06 Thermodynamics PDFRangbaaz DA FIRENZENo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Thermodynamics: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Thermodynamics: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4JwalantNo ratings yet
- Steam Condenser - Lecture SlideDocument43 pagesSteam Condenser - Lecture SlideKing KNo ratings yet
- Steam Condenser ChapterDocument29 pagesSteam Condenser ChapterKing KNo ratings yet
- PsychrometryDocument65 pagesPsychrometryKing KNo ratings yet
- Steam Condenser Solved Problems PDFDocument8 pagesSteam Condenser Solved Problems PDFKing KNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (553)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (147)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Step By Step Mixing: How to Create Great Mixes Using Only 5 Plug-insFrom EverandStep By Step Mixing: How to Create Great Mixes Using Only 5 Plug-insRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)