Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2
Uploaded by
Princess ManaloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2
Uploaded by
Princess ManaloCopyright:
Available Formats
M2 Lesson 1: Converging & Diverging
Lenses-2
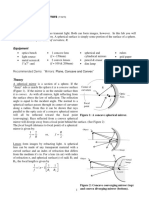
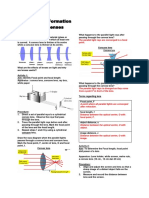
1. A light ray coming from a rarer medium
to a denser medium will be bents towards
the normal.
2. A light ray coming from a denser
medium to a rarer medium will be bent
away from the normal.
A light ray that is incident on the front M2 Lesson 2: Physical & Optical Properties
surface, will be bent towards the normal. of Lens-2
The light ray will then be incident on the
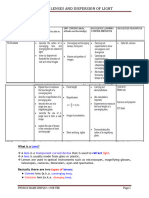
The following is a table showing the
back surface. Since it is coming from a
Physical and Optical Properties of a Lens.
denser medium, it will be refracted away
from the normal.
PLUS MINUS
If we trace another light ray below it will Converging Lens Diverging Lens
follow the same behavior. We can then
appreciate the convergence of Positive Lens Negative Lens
light. Hence, we call this lens Thicker at the
a CONVERGING LENS. A converging lens is Thinner at the Center,
Center, Thinner at
also known as a Plus Lens. Thicker at the Sides
the Sides
Magnifies Image Minifies Image
Real, Inverted
Virtual, Erect Image
Image
Correction of
Correction of Myopia
Hyperopia(Farsight
(Nearsightedness)
edness)
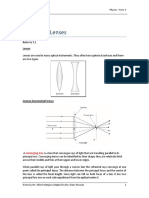
M2 Lesson 3 : Primary Points of Lens-2
Apply the same behavior of light on the
lens given, using the behavior of light
during refraction.
This time, the light rays will be
divergent. Hence, this lens is a DIVERGING
LENS. A converging lens is also known as a
Minus Lens.
These are the basic points or references on Note: It takes at least 2 light rays to trace
a lens: the formation of the image.
PRINCIPAL / OPTICAL AXIS: Imaginary line
passing through the center of the front &
back surfaces.
PRINCIPAL FOCUS: Point where rays of light
coming from infinity after passing through a
lens meet or seem to come from.
M2 Lesson 4b : Definite Behaviors of Light
OPTICAL CENTER: It is a point on a lens on a Minus Lens-2
where a ray of light will be undeviated
The following are the definite behaviors of
after passing through. light on a Minus Lens.
FOCAL LENGTH: Linear distance from the 1. A ray of light parallel with the principal
optical center to the lens. axis will be bent as if coming from the
principal focus.
M2 Lesson 4 A : Definite Behaviors of Light
on a Plus Lens-2 2. A ray of light passing through the optical
center is undeviated.
There are infinite bundles of light that are 3. A ray of light directed to the principal
emanating from an object. And there are focus will be bent parallel with the
only 3 light rays that will have a definite principal axis.
behavior when it passes through a lens.
The following are the definite behaviors of
light on a Plus Lens.
1. A ray of light parallel with the principal
axis will be bent passing through the
principal focus.
2. A ray of light passing through the optical
center is undeviated.
3. A ray of light passing through the
principal focus will be bent parallel with the
principal axis.
M2 Lesson 5 : Object & Image Location-2 M2 Lesson 6 : The Diopter-2
The following table shows the object and The focal length as stated before is the
image location on a Plus Lens. distance between the principal focus and
the lens.
The focal length is inversely proportional to
Object Nature of Size of Image
the power of a lens.
Location Image
The higher the power of the lens, the
At Real Point Image (at shorter the focal length.
Infinity f)
A 1 Diopter lens will have a 1 Meter focal
length. The power of the lens refers to its
Between Real, Minimize converging and diverging capacity.
Infinity & Inverted
2f The relationship between the Diopter and
the Focal Length is shown in this formula:
At 2f Real, Equal with D=1/f
Inverted Object (at 2f)
Between Real, Magnified
2f & f Inverted
At f Real, Magnified (at
Inverted Infinity)
Between Virtual, Magnified
f & lens Erect
Below are the Object and Image Location
on a Minus Lens.
Object Nature of Size of
Location Image Image
At Infinity Virtual Point
Image (at
f)
Between Virtual, Minimize
Infinity & Erect
lens
You might also like
- 15 AQA Physics Final PDFDocument67 pages15 AQA Physics Final PDFKafka LukNo ratings yet
- 05 Thin Lenses 2Document7 pages05 Thin Lenses 2HelenNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument25 pagesOpticsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument7 pagesLensesKatlo KgosiyangNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Week 6Document5 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Week 6Jess Anthony Efondo100% (1)
- Group 4Document9 pagesGroup 4madiha raoNo ratings yet
- 05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 pages05 LIGHT Physics Form 4Nikki NinjaNo ratings yet
- Light PDFDocument1 pageLight PDFsatish dongardiyeNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3Document13 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Lens Ray DiagramsDocument24 pagesLens Ray DiagramsCarla Dane ManalangNo ratings yet
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 pagesRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Plane MirrorJazelle PaciaNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - NotesDocument17 pagesDelhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - Notesbaby doodlesNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Forensic PhotographyDocument2 pagesActivity 2. Forensic PhotographyElla Mei OralloNo ratings yet
- LENSESDocument8 pagesLENSESspammy fammyNo ratings yet
- Refraction LensesDocument42 pagesRefraction LenseswhybangadNo ratings yet
- Physics of The EyeDocument11 pagesPhysics of The EyeLilsamz PyrettNo ratings yet
- Thin Converging LensDocument34 pagesThin Converging Lenstouch grassNo ratings yet
- Evennett Oct2008 01 Principles-Of-MicrosDocument96 pagesEvennett Oct2008 01 Principles-Of-MicrosAjish joNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Phyiscs LensesDocument10 pagesIGCSE Phyiscs LensesneelNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q2 Mod3 QualitativeCharacteristicsOfImagesDocument12 pagesScience10 Q2 Mod3 QualitativeCharacteristicsOfImagesKOBE BRYANT TIDOYNo ratings yet
- ZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecDocument8 pagesZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecJaymarie ZabateNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W5Document13 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - W5rawisadaniNo ratings yet
- Physics - Convex LensDocument15 pagesPhysics - Convex LensdivyapriyaNo ratings yet
- Physic - LensesDocument33 pagesPhysic - Lensesfelitrochristopher924No ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument2 pagesHandoutsArque John Bertumen AbieraNo ratings yet
- Unit 15Document5 pagesUnit 15SherazNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Refraction Through LensDocument9 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Refraction Through LensNamdeo JadhavNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 pagesLIGHT Physics Form 4Amrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Basics of Physics (Optics Notes)Document30 pagesBasics of Physics (Optics Notes)omkardashetwar100% (1)
- OPTICSDocument40 pagesOPTICSJanelle Ann BacoNo ratings yet
- 31 Medical PhysicsDocument91 pages31 Medical PhysicshinaNo ratings yet
- In-Class Activities: I. SimulationDocument6 pagesIn-Class Activities: I. SimulationKeisha Therese AllenbyNo ratings yet
- U9 - Astrophysics: 1.1 - LensesDocument17 pagesU9 - Astrophysics: 1.1 - LensesArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- 02 Measurement of Lens PowerDocument13 pages02 Measurement of Lens PowerEye KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 5Document8 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 5Jess Anthony Efondo100% (1)
- Ray OpticsDocument77 pagesRay OpticsDiksha PublicationNo ratings yet
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- LightDocument22 pagesLightPeerchand Chaudhary100% (1)
- 10-3-4 Optics Lenses and Dispersion My NC NotesDocument24 pages10-3-4 Optics Lenses and Dispersion My NC NoteskupakwashenyakurerwaNo ratings yet
- Q4 GenPhysic2 USLeM3 Week-3 Jayar Version-3Document10 pagesQ4 GenPhysic2 USLeM3 Week-3 Jayar Version-3Arjen Lei VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lenses Ppt. Observation 2222Document33 pagesLenses Ppt. Observation 2222bagasmarylord88No ratings yet
- Activity #11: Lens Lab Part 1. Image FormationDocument4 pagesActivity #11: Lens Lab Part 1. Image FormationJuan Carlos Mejia MaciasNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument64 pagesLight Wavesceline.the988No ratings yet
- 6.3 Images Formation by Lens Answer PDFDocument7 pages6.3 Images Formation by Lens Answer PDFAin NadiaNo ratings yet
- Light RefractionDocument9 pagesLight RefractionTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - Lesson 2 and 3Document12 pagesGRADE 10 - Lesson 2 and 3Christian ConsignaNo ratings yet
- Lenses Phyisics Trim 3Document4 pagesLenses Phyisics Trim 3delphinevynckeNo ratings yet
- Eve Ross - 10.2 - Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesEve Ross - 10.2 - Reflection of LightEve RossNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument72 pagesLight WavesJeffrey MaNo ratings yet
- Concave and Convex LensDocument7 pagesConcave and Convex LensannmarieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 22: Thin LensesDocument7 pagesExperiment 22: Thin LenseserzaNo ratings yet
- Additional NotesDocument29 pagesAdditional Notesanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 3: Lenses Chapter 3: LensesDocument10 pagesPhysics Chapter 3: Lenses Chapter 3: LensesMatthewtongNo ratings yet
- Refraction Through A Lens PDFDocument3 pagesRefraction Through A Lens PDFPrudhvi JoshiNo ratings yet
- P08 LightDocument6 pagesP08 LightBoedisantosoNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Document22 pagesCH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Mohammad MujtabaNo ratings yet
- TAX-502 (Excise Tax Rates - Part 2)Document3 pagesTAX-502 (Excise Tax Rates - Part 2)Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- TAX-101 (Estate Tax)Document11 pagesTAX-101 (Estate Tax)Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- TAX-401 (Other Percentage Taxes - Part 1)Document5 pagesTAX-401 (Other Percentage Taxes - Part 1)Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- TAX-301 (VAT-Subject Transactions)Document9 pagesTAX-301 (VAT-Subject Transactions)Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- TAX-303 (Input Taxes)Document7 pagesTAX-303 (Input Taxes)Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- TAX-302 (VAT-Exempt Transactions) PDFDocument5 pagesTAX-302 (VAT-Exempt Transactions) PDFclara san miguelNo ratings yet
- Lit 2 - Midterm Lesson Part 2Document5 pagesLit 2 - Midterm Lesson Part 2Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- Acctg 15 - Midterm Lesson Part1Document10 pagesAcctg 15 - Midterm Lesson Part1Angelo LabiosNo ratings yet
- Lit 2 - Midterm Lesson Part 1Document4 pagesLit 2 - Midterm Lesson Part 1Princess ManaloNo ratings yet
- Acctg 15 - Midterm Lesson Part2Document10 pagesAcctg 15 - Midterm Lesson Part2Angelo LabiosNo ratings yet
- Acctg 15 - Midterm Lesson Part3 3Document10 pagesAcctg 15 - Midterm Lesson Part3 3Angelo LabiosNo ratings yet
- Zeiss Opmi 6 Series: The Refurbished Zeiss Opmi 6 Microscope Can Be Fully Customized To Suit Your NeedsDocument2 pagesZeiss Opmi 6 Series: The Refurbished Zeiss Opmi 6 Microscope Can Be Fully Customized To Suit Your NeedsJuan ChatoNo ratings yet
- D 6557 - 00 Rdy1ntctmda - PDFDocument17 pagesD 6557 - 00 Rdy1ntctmda - PDFqueno1No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesMacroeconomics Theories and Policies 10th Edition Froyen Solutions Manualpearlgregoryspx100% (29)
- Nidek AR600 PDFDocument70 pagesNidek AR600 PDFMilton CâmeraNo ratings yet
- Argus C3 Service ManualDocument6 pagesArgus C3 Service ManualRicardo Luis AbboudNo ratings yet
- Electron MicrosDocument28 pagesElectron MicrosVEENA DEVINo ratings yet
- VT 10 InstructionManualDocument29 pagesVT 10 InstructionManualJorge Alfonso FernandezNo ratings yet
- Good NotesDocument43 pagesGood NotesShubhamNo ratings yet
- THE AVANT-GARDE CINEMA OF THE 1920s CONNECTIONS TO FUTURISM, PRECISIONISM, AND SUPREMATISM-Martin F. NordenDocument6 pagesTHE AVANT-GARDE CINEMA OF THE 1920s CONNECTIONS TO FUTURISM, PRECISIONISM, AND SUPREMATISM-Martin F. NordenNatalia100% (2)
- DH Hac Hdw1200tl (A)Document3 pagesDH Hac Hdw1200tl (A)ascoNo ratings yet
- Vray For 3ds MaxDocument1 pageVray For 3ds MaxharikumarindiaNo ratings yet
- Homework B2Document8 pagesHomework B2mariaNo ratings yet
- Making Your Own Telescope PDFDocument221 pagesMaking Your Own Telescope PDFSean Sebastian FelimNo ratings yet
- Pre-Production BookletDocument17 pagesPre-Production Bookletapi-526359833No ratings yet
- Elecrical Rate 075-076 (Siraha)Document113 pagesElecrical Rate 075-076 (Siraha)Sirhali BuildersNo ratings yet
- Siemens SafeZone Speed CamerasDocument4 pagesSiemens SafeZone Speed CamerasmicroHackerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To White Light Interferometry: IndexDocument12 pagesIntroduction To White Light Interferometry: Indexlil10zinNo ratings yet
- Handout 4Document5 pagesHandout 4Екатерина СероклинNo ratings yet
- Options Plus VSPDocument1 pageOptions Plus VSPGowell SupportNo ratings yet
- ANASTESI - LAPORAN Stock Opname Unit RS Januari '22Document122 pagesANASTESI - LAPORAN Stock Opname Unit RS Januari '22ANTONIUS BAYUNo ratings yet
- The Microscope: Summary of ExerciseDocument18 pagesThe Microscope: Summary of Exerciserashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Project Product Catalogue 2020Document100 pagesProject Product Catalogue 2020yahiaNo ratings yet
- 3600 DetikDocument2 pages3600 DetikValeria ZhangNo ratings yet
- Pan A Vision SetDocument1 pagePan A Vision SetsaumyavishNo ratings yet
- Alternate ScriptDocument4 pagesAlternate Scriptapi-505601570No ratings yet
- Self Images: Name: - ClassDocument3 pagesSelf Images: Name: - ClassantoshkaffNo ratings yet
- Portwest Pw13 Clear View Safety Glasses Clear Data SheetDocument2 pagesPortwest Pw13 Clear View Safety Glasses Clear Data SheetohiozuaNo ratings yet
- Authenticating Vintage NASA PhotographyDocument11 pagesAuthenticating Vintage NASA PhotographyJoseph Wolenski100% (1)
- Marketing Final Plan - Diff EyewearDocument12 pagesMarketing Final Plan - Diff Eyewearapi-335100289100% (1)
- Bulb DVR Camera PriceDocument22 pagesBulb DVR Camera PriceIKSAN HADINo ratings yet