Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mcq's Thermal and Statistical Physics-1
Uploaded by
Ehtasham Ahmad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
538 views6 pagesN/ A
Original Title
Mcq's thermal and statistical physics-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentN/ A
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
538 views6 pagesMcq's Thermal and Statistical Physics-1
Uploaded by
Ehtasham AhmadN/ A
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
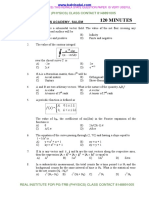
Thermal & Statistical Physics
1. If energy E is quadratic in momentum P then
a. E = b/P2
b. E = bP2
c. E = -bP2
d. E = b2P
2. Which one is an example of qualitative properties?
a. entropy
b. volume
c. pressure
d. enthalpy
3. The Boltzmann transport equation is given as.
a. (∂f/∂t) + p.(∂f/∂r) + F/m.(∂f/∂v) = Ω(f)
b. (∂f/∂t) + v.(∂f/∂r) + F.(∂f/∂p) = f(Ω)
c. (∂f/∂t) + v.(∂f/∂r) + F.(∂f/∂p) = Ω(f)
d. (∂f/∂t) + r.(∂f/∂v) + F.(∂f/∂p) = Ω(f)
4. The zero point energy of the elastic mode of vibration is.
a. ℏω
b. (n+1/2)ℏω
c. ℏω/2
d. 0
5. The phonon interactions may result in.
a. scattering collision
b. b & c
c. inelastic collision
d. elastic collision
6. The average kinetic energy associated with each degree of freedom is equal to.
a. 2β
b. 2/β
c. β/2
d. 1/2β
7. The entropy of a system approaches a constant as its temperature.
a. becomes infinite
b. decreases
c. increases
d. becomes zero
8. Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics is applicable to.
a. perfect gas
b. ideal gas
c. ordinary gas
d. real gas
9. For a system satisfying Hamilton’s canonical equation, the phase space fluid is.
a. Compressible
b. Incompressible
c. Not conserved
d. Ideal
10. A system and the surrounding taken together is called as the.
a. ensemble
b. environment
c. Universe
d. assembly
11. Which one is an example of a reversible process?
a. clouds
b. convection
c. rustling of iron
d. radiation
12. The sum of all the microscopic form of energy is called _____.
a. Phase energy
b. System energy
c. Total energy
d. Internal energy
13. Which law of thermodynamics is directional one?
a. 2nd law
b. 4th law
c. 1st law
d. 3rd law
14. Following Maxwell relations, (∂V/∂T)p = ?
a. (∂S/∂V)T
b. − (∂S/∂P)T
c. −(∂V/∂S)T
d. (∂S/∂P)T
15. The mean no. of particles in a given state while following quantum statistics, are given
by.
a. (eα+βE ± 1)
b. 1/ (eα+βE ± 1)
c. 1/ (e-α+βE ± 1)
d. 1/ (eα+βE + 1)
16. The possible values of nr, ¬in case of Fermi-Dirac statistics, are.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 0
d. ∞
17. Phonon is the quantum of.
a. Elastic wave
b. Transverse wave
c. Electromagnetic wave
d. Longitudinal wave
18. In Boltzman transport equation ‘(∂f/∂t) + v.(∂f/∂r) + F.(∂f/∂p) = Ω(f)’, which term on L.H.S
gives spatial variation in the distribution function?
a. 3rd term
b. 1st term
c. Term on R.H.S
d. 2nd term
19. At absolute temperature, the thermodynamic beta becomes.
a. 1/2
b. 1
c. 0
d. ∞
20. Boltzman equation is an equation of ___________ in one particle phase space.
a. Helmholtz function
b. Gibb’s function
c. Partition function
d. Distribution function
21. The number of meaningful ways in which 5 Fermions can be arranged into 4 cells is.
a. 0
b. 4
c. 6
d. 9
22. Which function gives the number of particles per volume in phase space?
a. Helmholtz function
b. Gibb’s function
c. Distribution function
d. Partition function
23. 1st and 2nd laws of thermodynamics are related by the relation?
a. dU = TdS – VdP
b. dU = TdS + PdV
c. dU = PdV – TdS
d. dU = TdS – PdV
24. Even at very low temperature, electrons donot condense into the _________ energy
state.
a. highest
b. lowest
c. normal
d. ionized
25. The law of equipartition breaks down when the thermal energy kBT is significantly
_______the spacing between energy levels.
a. equal to
b. independent of
c. greater than
d. smaller than
26. If the concentration of a gas is made sufficiently low at a given temperature T, then the
factor.
a. (eα+βE ) = 1
b. (eα-βE ) >>1
c. (eα+βE ) <<1
d. (eα+βE ) >>1
27. Second law of thermodynamics gives the definition of.
a. Temperature
b. Heat
c. Energy
d. Entropy
28. In MB statistics, the mean no. of particles is represented by.
a. Ae-E/kT
b. AeE/kT
c. 1- e-E/kT
d. 1/ (eα+βE ± 1)
29. Helmholtz function is the amount of useful work done by a thermodynamic system at
constant.
a. pressure
b. temperature & volume
c. temperature & pressure
d. pressure & volume
30. Gibbs free energy is the amount of useful work done by a thermodynamic system at
constant.
a. temperature & volume
b. pressure
c. temperature & pressure
d. pressure & volume
31. The relation TdS = ?
a. CvdT−T(∂P/∂S)vdV
b. CvdT+T(∂P/∂S)vdV
c. CvdT+T(∂P/∂T)vdV
d. CvdT+T(∂V/∂S)vdV
32. “At absolute zero the entropy of a pure crystal is zero” is the statement of.
a. 1st law of thermodynamics
b. 2nd law of thermodynamics
c. 3rd law of thermodynamics
d. 4th law of thermodynamics
33. In a grand canonical ensemble, a system A of fixed volume is in contact with a large
reservoir B. Then.
a. A can exchange neither energy nor particles with B
b. A can exchange only energy with B
c. A can exchange both energy & particles with B
d. A can exchange only particles with B
34. Which law of thermodynamics imposes constraints on the process?
a. 2nd law
b. 1st law
c. 4th law
d. 3rd law
35. What is a process during which the pressure remains constant?
a. Isothermal process
b. Isobaric process
c. Isometric process
d. Isochoric process
36. Fermions include quarks and.
a. photons
b. protons
c. neutrons
d. laptons
37. The drop in the temperature of a crystal is responsible for the destruction of.
a. phonons
b. neutrons
c. electrons
d. photons
38. He4 is an example of?
a. FD statistics
b. none of these
c. BE statistics
d. MB statistics
39. If the energy of a quantum harmonic oscillator is En = nhυ, n = 0,1,2,3,…….∞, the
partition function of the system of oscillators is.
a. e-hυ/kT
b. 1/(1- ehυ/kT)
c. 1/(1- e-hυ/kT)
d. ehυ/kT
40. In which of the following thermodynamic processes the density remains constant?
a. isochoric
b. isothermal
c. adiabatic
d. isobaric
41. Following Maxwell relations, (∂T/∂V)s = ?
a. −(∂V/∂S)T
b. − (∂P/∂S)v
c. (∂S/∂P)T
d. (∂S/∂V)T
42. Following Maxwell relations, (∂T/∂P)s = ?
a. − (∂S/∂P)T
b. (∂V/∂S)p
c. (∂S/∂P)T
d. (∂S/∂V)T
43. The concept of ensemble was introduced by.
a. Boltzmann
b. Gibbs
c. Maxwell
d. Carnot
44. The frequency of phonon waves may vary from _______________ count per seconds.
a. 10 to 102
b. 10-4 to 10-6
c. 104 to 1012
d. 10-4 to 10-12
45. When the heat flows from hot to cold body, the entropy of the system.
a. becomes infinite
b. decreases
c. increases
d. remains constant
46. The average K.E of a harmonic oscillator in 3-dimention is.
a. 3kT
b. ½ kT
c. 3/2 kT
d. kT
47. The entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero becomes zero, was stated by.
a. Maxwell
b. Carnot
c. Boltzmann
d. Planck
48. Equipartition theorem is valid only in.
a. Solid state physics
b. Classical statistical mechanics
c. Quantum statistical mechanics
d. Quantum electrodynamics
49. What is a process with identical end states called?
a. Cycle
b. Path
c. phase
d. Either path or phase
50. The cyclic relation (∂P/∂T)V (∂T/∂V)P (∂V/∂P)T = ?
a. O
b. ∞
c. -1
d. 1
You might also like
- Axial Fan Experiment SheetDocument8 pagesAxial Fan Experiment Sheetpranesh0% (1)
- Voltage Drop Calculation-TransformerDocument2 pagesVoltage Drop Calculation-TransformerLPKumar290% (1)
- Thermo2 MidDocument4 pagesThermo2 MidnoelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Materials Question BankDocument50 pagesAdvanced Engineering Materials Question Banksufiyan sheikhNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics-Module 1Document14 pagesStatistical Mechanics-Module 1Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Full Book MCQ 2ND Year With Answer KeyDocument5 pagesFull Book MCQ 2ND Year With Answer KeyAdnanNo ratings yet
- CLEVER MIND Final exam questionsDocument4 pagesCLEVER MIND Final exam questionskrishna prasad ghanta0% (1)
- Physical Chemistry MCQS Question BankDocument5 pagesPhysical Chemistry MCQS Question BankMUHAMMAD JUNAID0% (2)
- Sop Maintenance Final - Part1Document57 pagesSop Maintenance Final - Part1Ashfaque Hussain0% (2)
- Sky Rider - Measure Speed and Acceleration on a Ferris WheelDocument4 pagesSky Rider - Measure Speed and Acceleration on a Ferris WheelWills BicuaNo ratings yet
- Electrical T Est EquipmentDocument13 pagesElectrical T Est EquipmenthophancongnhanNo ratings yet
- PSPH301 QP Website Statastical MechanicsDocument9 pagesPSPH301 QP Website Statastical MechanicsLol Blah100% (1)
- Thermodynamics & Statistical Physics QuizDocument4 pagesThermodynamics & Statistical Physics QuizM. BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Classical AssignmentDocument4 pagesClassical AssignmentbenNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQ I To Iv Units PDFDocument43 pagesPhysics MCQ I To Iv Units PDFsample use100% (1)
- The Educators, Sir Syed Campus, Pattoki: Round #Document7 pagesThe Educators, Sir Syed Campus, Pattoki: Round #Hamza TECHNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Formulation QuestionsDocument15 pagesLagrangian and Hamiltonian Formulation QuestionsRahul SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics McqsDocument19 pagesModern Physics McqsCh asimNo ratings yet
- MCQ Thermal PhyDocument14 pagesMCQ Thermal PhyGajendraNo ratings yet
- Angular Momentum ModuleDocument5 pagesAngular Momentum ModuleIjaz Talib0% (1)
- ES/MS 401 Nuclear Physics: Multiple Choice Questions (01: Mark Each, Total Marks: 100)Document13 pagesES/MS 401 Nuclear Physics: Multiple Choice Questions (01: Mark Each, Total Marks: 100)Chudaman Mahajan100% (1)
- Mcqs With Answers Waves and OscillationDocument18 pagesMcqs With Answers Waves and OscillationGovt.GraduateCollege TobaTekSinghNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics and Spectroscopy Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesQuantum Physics and Spectroscopy Multiple Choice QuestionsPrasanthNo ratings yet
- 11 FIRST Revision Question and Answer 2022 EMDocument12 pages11 FIRST Revision Question and Answer 2022 EMMuthu SelvamNo ratings yet
- DPP-4 (Electric Flux and Gauss' Law)Document8 pagesDPP-4 (Electric Flux and Gauss' Law)Youtuber RSNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics MCQ Level - 1: EdurevDocument13 pagesStatistical Physics MCQ Level - 1: EdurevVinayak SavarkarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2nd 5-CHAPTER-ATOMIC-STRUCTURE-MCQs PDFDocument11 pagesChemistry 2nd 5-CHAPTER-ATOMIC-STRUCTURE-MCQs PDFNaeem Malik0% (2)
- Questions & Answers On Electric Fields in Material SpaceDocument20 pagesQuestions & Answers On Electric Fields in Material Spacekibrom atsbha100% (2)
- 07A1EC03 - Classical MechanicsDocument12 pages07A1EC03 - Classical Mechanicsnakkantis80% (5)
- JSPM's Bhivrabai Sawant Polytechnic MCQ Question Bank on Magnetic Circuits and AC FundamentalsDocument25 pagesJSPM's Bhivrabai Sawant Polytechnic MCQ Question Bank on Magnetic Circuits and AC Fundamentalssourav temgireNo ratings yet
- MTE Practice MCQs on Vector Calculus and ElectromagnetismDocument15 pagesMTE Practice MCQs on Vector Calculus and ElectromagnetismPriyansu Singh100% (2)
- PG TRB Physics Fulltest - 5 - K.s.academy SalemDocument18 pagesPG TRB Physics Fulltest - 5 - K.s.academy SalemBaskar CyrilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Electronics Solved Mcqs Instructor: Prof. Hassan S. AshourDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Electronics Solved Mcqs Instructor: Prof. Hassan S. Ashourموسى محمدNo ratings yet
- Sybsc Sem IV Paper IIDocument13 pagesSybsc Sem IV Paper IISayantan DeyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions on Crystal Structures and DefectsDocument10 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on Crystal Structures and Defectsshivansh upadhyay100% (1)
- AMP QuizDocument8 pagesAMP Quizfiza choudhary100% (2)
- Chapter # 05 Torque, Angular Momentum, and EquilibriumDocument10 pagesChapter # 05 Torque, Angular Momentum, and EquilibriumSIR USMAN KHAN100% (4)
- Kavin's Physics Study Materials TRB (SCERT-DIET) - 2016: Prepared by C.Hebshifa M.SC., M.Phil., (NET)Document9 pagesKavin's Physics Study Materials TRB (SCERT-DIET) - 2016: Prepared by C.Hebshifa M.SC., M.Phil., (NET)Jagan EashwarNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties and Particle DualityDocument37 pagesWave Properties and Particle DualityManoj Reddy33% (3)
- Quiz 2, Chapter 3-5Document7 pagesQuiz 2, Chapter 3-5Mansoor AslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 17 Advent of Modern PhysicsDocument5 pagesChapter # 17 Advent of Modern PhysicsSIR USMAN KHAN100% (4)
- Quantum Theory QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuantum Theory Questionsdevender singh50% (2)
- MCQ Adsorpt - Catalysis. UNIT 4Document16 pagesMCQ Adsorpt - Catalysis. UNIT 4ismaeel247100% (6)
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsDocument16 pagesSemiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuitspawan paudelNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Practice Problems & Reactions (40chDocument10 pagesNuclear Physics Practice Problems & Reactions (40chChudaman MahajanNo ratings yet
- (Physics) R Gupta's Popular Master Guide 2022Document150 pages(Physics) R Gupta's Popular Master Guide 2022beniiiNo ratings yet
- +2 PHYSICS 200 MCQ EM Test WITH Answer Key and Problems Key PDFDocument25 pages+2 PHYSICS 200 MCQ EM Test WITH Answer Key and Problems Key PDFRAJA100% (1)
- Textbook of Physical Chemistry, Second Edition by Moudgil, H. KDocument3 pagesTextbook of Physical Chemistry, Second Edition by Moudgil, H. KAanchal PathakNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Crystal StructureDocument6 pagesMCQ On Crystal StructureJamilur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Physics ch-1 McqsDocument20 pagesPhysics ch-1 McqstdcgxgchhcNo ratings yet
- Solid and Semiconductor - MCQDocument3 pagesSolid and Semiconductor - MCQmasterbro915No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions in Measurements: C) Less Than Full-Scale ErrorDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions in Measurements: C) Less Than Full-Scale Errorlovelyosmile253No ratings yet
- Chapter # 9 Nature of LightDocument7 pagesChapter # 9 Nature of LightSIR USMAN KHAN100% (6)
- Multiple Choice Questions on Quantum PhysicsDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on Quantum PhysicsJamilur Rahman60% (5)
- Velammal EC8701 MCQ Questions on Antenna and Microwave EngineeringDocument29 pagesVelammal EC8701 MCQ Questions on Antenna and Microwave EngineeringAhamedNo ratings yet
- MCQ PolaDocument10 pagesMCQ PolaKrishnamohan VaddadiNo ratings yet
- McqsDocument142 pagesMcqsZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For PracticeDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For PracticeF085-Rohit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Practice Test AtomStrctrPeriodicTrend GOOD-KEY1Document5 pagesChapter 7 Practice Test AtomStrctrPeriodicTrend GOOD-KEY1Senthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics Work Sheet 12Document8 pagesStatistical Mechanics Work Sheet 12davididosa40No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Week 1 Assignment 1 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer Week 1 Assignment 1 Multiple Choice QuestionschandrakiranNo ratings yet
- Gate 1996 PDFDocument11 pagesGate 1996 PDFVammsy Manikanta SaiNo ratings yet
- TSM 2014Document4 pagesTSM 2014rujintoNo ratings yet
- Che 401Document7 pagesChe 401MD SHAHJADNo ratings yet
- Needs Based Scholarships Application Form-2016-17 PDFDocument7 pagesNeeds Based Scholarships Application Form-2016-17 PDFSadiqKannerNo ratings yet
- Special Semester 2023Document2 pagesSpecial Semester 2023Ehtasham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Conduction Electrons in MetalsDocument2 pagesConduction Electrons in MetalsEhtasham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportsDocument28 pagesLab ReportsEhtasham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics 2020Document3 pagesApplied Mathematics 2020Naeem RehmanNo ratings yet
- FGH 40 N 60 SFDocument8 pagesFGH 40 N 60 SFWinston diaz valeraNo ratings yet
- Lewin's Circuit Paradox: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544Document10 pagesLewin's Circuit Paradox: Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544aiace00No ratings yet
- LHC Project Report Analyzes Large Hadron Collider as a Mega-Science ProjectDocument9 pagesLHC Project Report Analyzes Large Hadron Collider as a Mega-Science ProjectBinay Prasanna JenaNo ratings yet
- GIC Bourdon SensingDocument2 pagesGIC Bourdon SensingNCNo ratings yet
- Danfoss FC51 DesignGuideDocument94 pagesDanfoss FC51 DesignGuideahirraodhavalNo ratings yet
- UP33TOP140KGAAZ01B - Datasheet - Garun 40KL - DatasheetDocument2 pagesUP33TOP140KGAAZ01B - Datasheet - Garun 40KL - DatasheetAnton TonchevNo ratings yet
- Power Design With Ferrite Cores 2021Document9 pagesPower Design With Ferrite Cores 2021juanNo ratings yet
- Abb - 1sda054321r1 PDFDocument3 pagesAbb - 1sda054321r1 PDFInnov8 OilNo ratings yet
- CIV321 Volumetric-Gravimetric Soil ExperimentDocument6 pagesCIV321 Volumetric-Gravimetric Soil ExperimentGuhan DayudayNo ratings yet
- Brava One He Erp Inst (En-Ru)Document68 pagesBrava One He Erp Inst (En-Ru)AdrianNo ratings yet
- Compact NS - 630A - 34022 PDFDocument2 pagesCompact NS - 630A - 34022 PDFTrai Nhà NôngNo ratings yet
- Internal House Wiring Regulations GuideDocument13 pagesInternal House Wiring Regulations GuideKarun100% (1)
- Data Sheet - Kodaki - 2.5kW6.0kWDocument2 pagesData Sheet - Kodaki - 2.5kW6.0kWmustang460No ratings yet
- Test Result MotorDocument1 pageTest Result MotoragungNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Ideal Op-AmpDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of Ideal Op-AmpShubham MannaNo ratings yet
- Energy Powering Ontarios Growth Report en 2023-07-07Document86 pagesEnergy Powering Ontarios Growth Report en 2023-07-07Randolph SeccafienNo ratings yet
- MANUAL DIGITAL - OrkliDocument2 pagesMANUAL DIGITAL - OrkliJavier HsNo ratings yet
- Chih WuDocument2 pagesChih WuCristian AndradeNo ratings yet
- Pipe 2023 Diagnostics 1Document8 pagesPipe 2023 Diagnostics 1Tyron RebellonNo ratings yet
- LWCO Basic WiringDocument12 pagesLWCO Basic WiringJhoNo ratings yet
- Micom P40 Agile: P544/P546 (With Distance)Document870 pagesMicom P40 Agile: P544/P546 (With Distance)RonaldNo ratings yet
- Victron Pylontech Up2500 Us2000 Us3000 Us2000c Us3000c Us5000 Us5000b Us5000c Pelio-L Up5000 Phantom-S Force-L1 l2Document15 pagesVictron Pylontech Up2500 Us2000 Us3000 Us2000c Us3000c Us5000 Us5000b Us5000c Pelio-L Up5000 Phantom-S Force-L1 l2Warren MorseNo ratings yet
- Villanueva, Brian Harvey A. BE-4/2015108217 CHE143-1/E01Document4 pagesVillanueva, Brian Harvey A. BE-4/2015108217 CHE143-1/E01Renren PNo ratings yet
- BSC Physics Iind SemDocument4 pagesBSC Physics Iind SemDavid JonesNo ratings yet
- Holiday Detector Operating InstructionsDocument7 pagesHoliday Detector Operating InstructionsBhavani PrasadNo ratings yet