Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trojan Virus
Uploaded by
SeutepiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trojan Virus
Uploaded by
SeutepiCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1: Midpoint Formula Example # 2:
Distance The midpoint of CS has coordinates (2, –1). If the
The Distance Formula is derived from the Pythagorean coordinates of C are (11, 2), what are the
Theorem coordinates of S?
Distance Between two points (𝑥1 , 𝑥2 ) and (𝑦1 , 𝑦2 ) Solving for x:
√(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )2 + (𝑦2 − 𝑦1 )2 11 + 𝑥
𝑥= =2
Example: 2
11 + 𝑥
=2∗ =2∗2
2
= 11 + 𝑥 = 4
𝑥 = −7
Solving for y:
2+𝑦
𝑦= = −1
2
2+𝑦
=2∗ = −1 ∗ 2
2
= 2 + 𝑦 = −2
𝑦 = −4
𝑺 = (−𝟕, −𝟒)
Lesson 2: Equation of a Circle
Perfect Square Trinomial
Perfect square trinomial is an algebraic expression that
What is the Distance between P (1, 3) and Q (7, 11) is of the form 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 = 𝑐, which has three terms. It is
𝑃𝑄 = √(7 − 1)2 + (11 − 3)2 obtained by the multiplication of a binomial with itself
= √(6)2 + (8)2
= √36 + 64 Example: 𝑥 2 + 6𝑥 + 9 is a perfect square polynomial
= √100 obtained by multiplying the binomial (𝑥 + 3)by itself.
𝑃𝑄 = 10 1. 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 4 = (𝑥 + 2)2
Midpoint 2. 𝑡 2 + 10𝑡 + 25 = (𝑡 + 5)2
If 𝐿(𝑥1 , 𝑦1 ) and 𝑁(𝑥2 , 𝑦2 ) are the endpoint of the 3. 𝑟 2 − 14𝑟 + 49 = (𝑥 − 7)2
segment and 𝑀 is the midpoint, then the coordinates of 4. 𝑤 2 + 9𝑥 + 20.25 = (𝑤 + 4.5)2
(𝑥1 ,𝑦1 ) (𝑥2 ,𝑦2 ) 5. 3𝑥 2 + 18𝑥 + 9 = (3𝑥 + 3)2
𝑀 is[ + ]. This is also referred as the
2 2
Midpoint Formula.
Definition
Circle: The set of all points that are the same distance
from a center points
Radius: a segment whose endpoints are the center and
a point on the circle
Example #1:
The coordinates of the endpoints of LG are (-3, -2) and
(8, 9) respectively. What are the coordinates of its
midpoint M?
−3 + 8 −2 + 9 5 7
𝑀=[ + ] 𝑀= ,
2 2 2 2
Transcript: ENTERESO, Steffi Tricia B 1
Diameter: A segment that goes through the center and If you actually perform the multiplication you’ll find that
end points are points on the circle 5! = 120
A rather special case is 0! This is defined as equal to 1
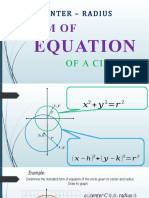
Equation of a Circle
(𝒙 − 𝒉)𝟐 + (𝒚 − 𝒌)𝟐 = 𝒓𝟐
Center: (h, k)
Radius: r
Standard Form of the Equation of a Circle
The standard equation of a circle with a center at (h, k)
and a radius of r units is (x − h)2 + (y − k)2 = r 2 . The
values of h and k indicate that the circle is translated h
units horizontally and k units vertically from the origin
If the center of the circle is at the origin, the equation of
the circle is 𝑥 2 + y 2 = r 2
Permutation
Permutation is an arrangement of ‘n’ different objects
with consideration given to the order of the objects,
Notice, ORDER MATTERS
The number of permutation of n objects take n at a time
is:
𝑛! 𝑛! 𝑛!
𝑛𝑃𝑛 = = = = 𝑛!
(𝑛 − 𝑛)! 0! 1
General form of the Equation of Circle 𝑛! = 𝑛 × (n − 1) × (n − 2) … 1
The general form of the equation of a circle is Example:
𝐴𝑥 2 + 𝐵𝑦 2 + 𝐶𝑦 + 𝐷𝑦 + 𝐸 = 0 1. 5P5
Example #1 2. 7P7
𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 + 4𝑥 − 6𝑦 − 23 = 0
𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 − 4𝑥 − 4𝑦 − 1 = 0 The number of permutation n objects taken r at a time
is defines as,
Example #2: 𝑛!
𝑛𝑃𝑟 =
Center: (2, 7) (𝑛 − 𝑟)!
Radius: 6 Where 𝑛 ≥ 𝑟
(𝑥 − 2)2 + (𝑦 − 7)2 = 62 Example:
𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 + 4 + 𝑦 2 − 14𝑦 + 49 = 36 1. 5P3
𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 − 4𝑥 − 14𝑦 + 17 = 0
2. 10P3
Lesson 3: Permutation
Factorial 3. 11P5
The factorial function says to multiply all whole
numbers from our chosen number down to 1 with the
symbol ‘!’ Distinguishable Permutation
The equation 5×4×3×2×1 The number of distinguishable permutations, P, of n
is written as 5!, objects where p objects are alike, q objects are like r
Which is read as five factorial objects are alike and so on. It is defined as,
𝑛!
𝑝! 𝑞! 𝑟! …
Transcript: ENTERESO, Steffi Tricia B 2
Example #1:
In how many ways can the letter of the word STATISTICS Example #1
be arranged? In how many ways can a committee consisting of 4
n= 10 members be formed from 8 people?
S=3
T=3 8P4
I=2
Example #2
Example #2: Suppose now, that you are asked to form different
In how many ways can the letter of the of the words be triangles out of 4 points plotted, say, A, B, C, and D, of
arranged? which no three are collinear.
a) MATHEMATICS 4P3
n= 11
M= 2 Lesson 4: Probability
A= 2
Vocabulary
T= 2
b) CANON
Experiment - Activities such as rolling a die,
n= 5 tossing a coin, or randomly choosing a ball
N= 5 from a box which could be repeated over
and over again and which have well-defined
Circular Permutation results.
The number of permutation of n objects around a circle Outcome - The results of an experiment.
is defined as (𝑛 − 1) Sample Space – The set of all outcomes in
an experiment.
Example:
Event – A subset of the sample space.
In how many ways can 4 people be arranged to sit
Trial – Repetition of an event. (Trial yung
around a circular table?
number of times na gagawin ung experiment.
(𝑛 − 1)! = (4 − 1)! = 3! = 6 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠
Each trial has one outcome. Example you will
toss a coin twice, 2 trial un)
Lesson 4: Combination
It is taking r things from a set of n things without
replacement and where order is not important. It’s Probability
defined as, It is the measure of how likely something
𝑛! will occur
𝑛𝐶𝑟 =
(𝑛 − 𝑟)! 𝑟! Probability is a number between 0 and 1
Where n is the number of things from the set and r is
the number of things taken.
What’s the Difference? Types of Event
When the order does matter it is a Permutation. Sample point – each outcome in a sample
space. Also called element/member of the
The different arrangement of books in a shelf is sample space
permutation. Reordering/rearranging the books
Simple Event – If an event E has only one
is different from each other.
sample point in sample space
When the order doesn't matter, it is a Combination. Compound Event – If an event has more
than one sample point. Consist of more
Fruit salad is a combination of sliced apples, than 2 outcomes
grapes and pineapples. We don't care what
order the fruits are in, they could also be Probability of Simple Event
“pineapples, grapes and apples" or "grapes, If each of the outcome in a sample space is equally
apples and pineapples", it’s the same fruit likely to occur, then the probability of an event E, is
salad. denoted as P(E) is given by
Transcript: ENTERESO, Steffi Tricia B 3
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑐𝑎𝑛 𝑜𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟 3. M(3, 5) and B(-3, 2)
𝑃(𝐸) =
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠
or
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑃(𝐸) =
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑠 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑎𝑐𝑒 4. C(4, 3) and K(-4, -3)
Example #1
Two fair of coins are flipped
𝑆 = {𝐻𝐻, 𝐻𝑇, 𝑇𝑇, 𝑇𝐻} 5. J(-5, -1) and E(8, 6)
B. Give the standard and general form
1. Center (2, 4) Radius 6
a) Probability of getting at least one head 2. Center (-4, 9) Radius 12
𝐴 = {𝐻𝐻, 𝐻𝑇, 𝑇𝐻}
3
𝑃(𝐸) = = 0.75 = 75%
4
3. Center (6, 1) Radius 9
Example #2
Three coins are flipped
𝑆 = {𝐻𝐻𝐻, 𝐻𝐻𝑇, 𝐻𝑇𝐻, 𝐻𝑇𝑇, 𝑇𝐻𝐻, 𝑇𝐻𝑇, 𝑇𝑇𝐻, 𝑇𝑇𝑇}
4. Center (8, -7) Radius 15
5. Center (5, 5) Radius 5
a) Getting two tails
𝐴 = {𝐻𝑇𝑇, 𝑇𝐻𝑇, 𝑇𝑇𝐻, 𝑇𝑇𝑇}
4
𝑃(𝐸) = = 0.5 = 50% C. Transform general form to standard Form
8
b) Getting exactly one tail 1. 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 − 8𝑥 + 6𝑦 = 11
𝐵 = {𝐻𝐻𝑇, 𝐻𝑇𝐻, 𝑇𝐻𝐻}
3
𝑃(𝐸 ) = ≈ 0.375 ≈ 37.5%
8 2. 4𝑥 2 + 4𝑦 2 − 20𝑥 + 12𝑦 − 2 = 0
Exercises
A. Find the distance and the midpoint of the 3. 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 + 8𝑦 − 84 = 0
given
1. I(0, 0) and L(6, 8)
4. 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 + 4𝑥 − 4𝑦 − 28 = 0
2. U(5, 11) and S(9, 5) 5. 9𝑥 2 + 9𝑦 2 − 12𝑥 − 6𝑦 − 31 = 0
Transcript: ENTERESO, Steffi Tricia B 4
D. Solve the problem 2. Checking out 4 library books from a list of 8
1. 5P 5 books for a research.
2. 9P 3
3. 6P 4
4. 7P 7
5. 11P8
3. How many hockey teams of 6 players can be
formed from 14 players without regard to
E. How many distinguishable permutations are
position played?
there for the word
A) BUSINESS
B) SLEEPLESS 4. Choosing the 1st, 2nd, 3rd place finishers in a race
with 10 competitors
C) CHOICE
F. Solve the Problem. 5. Electing 4 people to a municipal planning board
1. How many ways can 8 people be seated at a from a field of 7 candidates
circular table?
H. Solve the problem
2. How many different arrangements of 8 balls are 1. A six-sided die it tossed
possible in a circle? a) Probability of getting a 2
b) Probability of getting a 3 or 5
3. In how many ways can four couples be seated
at a round table if the men and women want to
sit alternately? c) Probability of getting a number that is at
most 4
G. Determine whether the problem is a
permutation and combination. Then find the d) Probability of getting a number that is
probabilities. greater than 3
1. Seating 8 students in 8 seats in the front row of
the auditorium
e) Probability of getting a number that is less
than or equal to 5
Transcript: ENTERESO, Steffi Tricia B 5
You might also like
- Understanding Running Effectiveness and Its UsesDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Running Effectiveness and Its UsesmaorpeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PreCal ReviewerDocument13 pagesPreCal ReviewerJan Clyde Cortez100% (1)
- MATH 10-3 Lesson 3 Rational ExpressionsDocument38 pagesMATH 10-3 Lesson 3 Rational ExpressionsRalph100% (1)
- FAT Procedure of LV SwitchboardsDocument17 pagesFAT Procedure of LV SwitchboardsWilliam Wong100% (2)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Defects in GalvanizingDocument10 pagesDefects in GalvanizingBalaji GuruNo ratings yet
- Ansi Wdma - Is 1a 2013 FlushDocument53 pagesAnsi Wdma - Is 1a 2013 FlushJoseph Allan TolentinoNo ratings yet
- COME AWAY WITH ME - Ukulele Chord Chart PDFDocument1 pageCOME AWAY WITH ME - Ukulele Chord Chart PDFDiego EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Document19 pagesCaie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Nat Gari100% (2)
- Mathematics: Quarter 1 Week 7Document10 pagesMathematics: Quarter 1 Week 7ALTHEA KIM100% (2)
- Iso 527-1 V 2019Document16 pagesIso 527-1 V 2019Ben Nsir SoniaNo ratings yet
- Distance FormulaDocument13 pagesDistance FormulaNoemi Rosario SanchezNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming SIMPLEX METHODDocument18 pagesLinear Programming SIMPLEX METHODNicole Vinarao100% (1)
- 15 Finding Center and Radius of A CircleDocument5 pages15 Finding Center and Radius of A CircleElaine BarrosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Circles ParabolasDocument7 pagesReviewer - Circles Parabolasrhyss.bunyi27No ratings yet
- Pre Calculus - Circle (Conic Section)Document10 pagesPre Calculus - Circle (Conic Section)CHRISTINE JOYCE JUANATANo ratings yet
- Lessons 11 and 12 Engineering Mathematics I Production OptionDocument33 pagesLessons 11 and 12 Engineering Mathematics I Production OptionRobert K OtienoNo ratings yet
- Pure 1 PDFDocument8 pagesPure 1 PDFSteveNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Quicksilver 1975No ratings yet
- AS A LEVEL Pure Maths 1 NotesDocument5 pagesAS A LEVEL Pure Maths 1 Noteshillkwok99No ratings yet
- Review of Analytic Geometry-1Document15 pagesReview of Analytic Geometry-1Kaze Yoshira Otomaki100% (1)
- Mathematics 9 Quarter 1 Week 8: NAME: - GR & SEC: - CompetencyDocument11 pagesMathematics 9 Quarter 1 Week 8: NAME: - GR & SEC: - CompetencyPARMAN, REGINE MAYE C.No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Analytic GeometryDocument10 pagesLecture Notes Analytic Geometryalagonmiles06No ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument3 pagesCircles PDFChong Xue ErNo ratings yet
- Precal Notes MidtermsDocument21 pagesPrecal Notes MidtermsJudge Angelo De La Cruz100% (1)
- 12th Maths Chapter 5 EM Question Paper JPRABU MATHSDocument2 pages12th Maths Chapter 5 EM Question Paper JPRABU MATHSSaravanan JNo ratings yet
- Math10 Module 7Document16 pagesMath10 Module 7Kyle Atienza dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - RotationDocument7 pagesModule 2 - Rotationmae.sanmiguel.17No ratings yet
- Ellipse Objective/sDocument5 pagesEllipse Objective/sNot MeNo ratings yet
- Lines and CirclesDocument3 pagesLines and CirclesIlliad De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Revision Set 4A - Paper 1: 1. Given ThatDocument19 pagesRevision Set 4A - Paper 1: 1. Given ThatRonald HirschNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument12 pagesConic SectionJohn Aldwin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Answers - Online Daily Test 2 - Trockers-1Document5 pagesAnswers - Online Daily Test 2 - Trockers-1Michael MyamboNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry - Wrob212Document5 pagesAnalytic Geometry - Wrob212bryan04avilesNo ratings yet
- DONOR - M - Differential CalculusDocument5 pagesDONOR - M - Differential Calculusmatt DonorNo ratings yet
- A4 - G10 - Q2 - Module 6 - Week-8Document11 pagesA4 - G10 - Q2 - Module 6 - Week-8Jayzi VicenteNo ratings yet
- Precal 1PDocument18 pagesPrecal 1Pmissumissy2No ratings yet
- DE LEC 1b FAMILIES OF CURVESDocument17 pagesDE LEC 1b FAMILIES OF CURVESChristian FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument12 pagesPre CalculusMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus HandoutsDocument14 pagesPre Calculus HandoutsVince Leo Panoncillon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Analytical Geometry AssignmentDocument11 pagesAnalytical Geometry AssignmentMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Chemistry - Solution Set 1Document8 pagesQuantum Chemistry - Solution Set 1mozNo ratings yet
- SQ2Document2 pagesSQ2film.group222No ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 2 Circles 1Document13 pagesModule 2 Lesson 2 Circles 1Hilan Gel GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Ma 210 Lecture 8Document10 pagesMa 210 Lecture 8James MukopaNo ratings yet
- CIRCLESDocument4 pagesCIRCLESNot MeNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry CAPE Integrated Mathematics-1 PDFDocument18 pagesCoordinate Geometry CAPE Integrated Mathematics-1 PDFDequanNo ratings yet
- Application of Integrals - Area Under A CurveDocument5 pagesApplication of Integrals - Area Under A CurveHayabusa Future EnforcerNo ratings yet
- MTPPT The Conic SectionsDocument132 pagesMTPPT The Conic Sectionskathyrin anocheNo ratings yet
- DX Dy: Topical Test Chapter 9 DifferentiationDocument1 pageDX Dy: Topical Test Chapter 9 DifferentiationsiunghuaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Transformation and Graphs of QFDocument5 pagesLesson 13 Transformation and Graphs of QFMarion Nico EspiloyNo ratings yet
- Geometry - 1 Translation and RotationDocument13 pagesGeometry - 1 Translation and RotationJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- Center - Radius: Form ofDocument14 pagesCenter - Radius: Form ofClaire parrasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParabolaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ParabolaMelvin EstoleroNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument21 pagesPre CalculusSUSANA, NIÑA FELIZ C.No ratings yet
- The Circle LCHL Reference SheetDocument5 pagesThe Circle LCHL Reference Sheetmarco.chiappero.ieNo ratings yet
- Internal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaDocument4 pagesInternal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaSneha SankhlaNo ratings yet
- Introducation To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesIntroducation To Conic Sections and CirclesMARYBETH DIABORDONo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document4 pagesUnit 3SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations HW1Document2 pagesDifferential Equations HW1Peter Simon SantosNo ratings yet
- G9 Q1 M17 Ttransforming QFsDocument7 pagesG9 Q1 M17 Ttransforming QFsMarichu BejunaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry - by TrockersDocument48 pagesCoordinate Geometry - by TrockersGracious ChiweraNo ratings yet
- Admath Examples Polar FormDocument17 pagesAdmath Examples Polar FormNiño Vince VallespinNo ratings yet
- Module 10: Geometry Essentials and Conic Sections PostestDocument12 pagesModule 10: Geometry Essentials and Conic Sections PostestIvy PerezNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Electronic Components Database Samples 2022Document3 pagesBangalore Electronic Components Database Samples 2022Pradeep KNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding MachineDocument34 pagesArc Welding Machinersgk75100% (1)
- Thermo Scientific Ramsey Series 17: Belt Scale System For Conveyor Weighing of Bulk MaterialsDocument4 pagesThermo Scientific Ramsey Series 17: Belt Scale System For Conveyor Weighing of Bulk MaterialsFloyd Mejia GamarraNo ratings yet
- .archivetempMOD01 1-1.1 Intro Python - IpynbDocument9 pages.archivetempMOD01 1-1.1 Intro Python - IpynbSekkak MarouaneNo ratings yet
- CorrectionDocument3 pagesCorrectionbougmazisoufyaneNo ratings yet
- Excel Chart Trendline FormulasDocument3 pagesExcel Chart Trendline FormulasSZaungg NauuNo ratings yet
- Pavement Thesis 5 2Document120 pagesPavement Thesis 5 2Marko PopovicNo ratings yet
- Front Page MarqueeDocument5 pagesFront Page Marqueeedward_sheed28No ratings yet
- GymnaUniphy Phyaction 740,790 - Service ManualDocument68 pagesGymnaUniphy Phyaction 740,790 - Service ManualRaul Alejandro QLNo ratings yet
- Auditory Verbal Hallucinations in Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder Are Similar To Those in SchizophreniaDocument7 pagesAuditory Verbal Hallucinations in Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder Are Similar To Those in SchizophrenializardocdNo ratings yet
- Portable Savonius Wind Turbine With Deflectors: by AdriancubasDocument15 pagesPortable Savonius Wind Turbine With Deflectors: by AdriancubasLê VinhNo ratings yet
- Math Quiz BeeDocument32 pagesMath Quiz BeeChristine BacordoNo ratings yet
- TLF UqpDocument25 pagesTLF Uqpshanu priNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Finfets From 22Nm To 7Nm: September 2019Document44 pagesEvolution of Finfets From 22Nm To 7Nm: September 2019Krisumraj PurkaitNo ratings yet
- Chap. 4 Force System ResultantDocument127 pagesChap. 4 Force System ResultantNOMAD TVNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Control ValveDocument13 pagesExperiment 1 - Control ValveRobert Gilmore100% (3)
- Ch. 09 - Rotational DynamicsDocument23 pagesCh. 09 - Rotational Dynamicssthembisosthera992No ratings yet
- Alz Ha PDFDocument16 pagesAlz Ha PDFΓεώργιος ΠαπαδόπουλοςNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Effects of Airborne Acoustic Ultrasound and Plasma Activated Water From Cold and Thermal Plasma Systems On BiofilmsDocument10 pagesAntimicrobial Effects of Airborne Acoustic Ultrasound and Plasma Activated Water From Cold and Thermal Plasma Systems On BiofilmsJulio MoralesNo ratings yet
- Functional Data StructuresDocument14 pagesFunctional Data StructuresTushar ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- PK45I en 01 Drive-In PiezometersDocument5 pagesPK45I en 01 Drive-In PiezometersSDLCNo ratings yet
- Curve Table R4Document13 pagesCurve Table R4Vijay ChauhanNo ratings yet