Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UNIT CIRCLE and Graph of Trigonometric Functions
Uploaded by
hacker johnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT CIRCLE and Graph of Trigonometric Functions
Uploaded by
hacker johnCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT CIRCLE
A unit circle is a circle whose center is at the origin and the radius is equal to 1. The equation of the
unit circle:
𝑥2 + 𝑦2 = 1
Unit circle in a coordinate system:
Quadrant Angles Point of Intersection
0° (1, 0)
90° (0, 1)
180° (-1, 0)
270° (0, -1)
360° (1, 0)
CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS
Let (x, y) be the point of intersection of the terminal side of angle θ with the unit circle of an angle θ.
Then we have the following definitions:
cosine function: cos θ = x
sine function: sin θ = y
tangent function: tan θ = y/x , x ≠ 0
secant function: sec θ = 1/x , x ≠ 0
cosecant function: csc θ = 1/y , y ≠ 0
cotangent function: cot θ = x/y, y ≠ 0
QUADRANT ANGLES:
Angles whose terminal sides lie on the axes:
Quadrantal Angle
Function 0° 90° 180° 270°
cos θ 1 0 -1 0
sin θ 0 1 0 -1
tan θ 0 Undefined 0 Undefined
sec θ 1 Undefined -1 Undefined
csc θ undefined 1 Undefined -1
cot θ undefined 0 undefined 0
GRAPH OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
A sine wave or sinusoid, named after the sine function, is a mathematical curve that describes a
smooth repetitive oscillation.
A function f is said to be periodic if there is a positive integer p such that f(x+p) = f(x) for all x in the
domain of f. The smallest number p is called the period of the function f.
The amplitude of a periodic function is defined as the absolute value of one-half the difference
between the maximum and minimum y-values.
Graph of sine function:
Graph of cosine function:
Graph of tangent function:
Graph of secant function:
Graph of cosecant function:
Graph of cotangent function:
You might also like
- Chapter 8 Special AnglesDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Special AnglesShina GalvezNo ratings yet
- Success Mathematics SPM Free ChapterDocument22 pagesSuccess Mathematics SPM Free ChapterDaryl Lls100% (1)
- Trigonometric Functions: by Daria EiteneerDocument15 pagesTrigonometric Functions: by Daria EiteneerAnderson AlfredNo ratings yet
- SPLM Trigonometry Part 1Document59 pagesSPLM Trigonometry Part 1Joey TelinNo ratings yet
- MATH30-1 Unit 3 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsDocument44 pagesMATH30-1 Unit 3 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsBecca BobsterNo ratings yet
- 1 Trigonometry 2 MH CET Class 11th Syllabus PDF Notes by DineshDocument21 pages1 Trigonometry 2 MH CET Class 11th Syllabus PDF Notes by DineshPRANAVNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument22 pagesGraphs of Trigonometric FunctionsRishu RajNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Angle MeasuresDocument36 pagesTrigonometry: Angle MeasuresKiran Kumar100% (1)
- Pre-Calculus Chapter 3 TrigonometryDocument13 pagesPre-Calculus Chapter 3 TrigonometryaiNo ratings yet
- Maths+Term+2+ +All+Formulas+in+one+shot +Formula+Cheat+Sheet +class+11Document59 pagesMaths+Term+2+ +All+Formulas+in+one+shot +Formula+Cheat+Sheet +class+11Rupashri ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Review in Plane TrigonometryDocument51 pagesReview in Plane TrigonometryDoone Heart Santander CabuguasNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Trigonometric Functions: Graphing The Trigonometric FunctionDocument55 pagesUnit 7: Trigonometric Functions: Graphing The Trigonometric FunctionNoli NogaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 NotesDocument3 pages5.2 NotesAM - 11DA 747745 Turner Fenton SSNo ratings yet
- Math Fundamentals: 1. Conventions and Definitions 2. Matrices 3. Fundamentals of Rigid TransformsDocument29 pagesMath Fundamentals: 1. Conventions and Definitions 2. Matrices 3. Fundamentals of Rigid TransformsZaidKhanNo ratings yet
- PRE-CALCULUS REVIEWER: TRIG FUNCTIONSDocument15 pagesPRE-CALCULUS REVIEWER: TRIG FUNCTIONSndjwndnnd sjwjhsbdbdbdNo ratings yet
- UMANG Class 11th - Trigonometric Functions - 1 - VMathDocument74 pagesUMANG Class 11th - Trigonometric Functions - 1 - VMathnabhijain9No ratings yet
- Trig Functions & Reference AnglesDocument12 pagesTrig Functions & Reference AnglesLisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1-Basic Mathematics-01-TheoryDocument37 pages1-Basic Mathematics-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Arbitary Rotation ProofDocument3 pagesArbitary Rotation Proofmohamed2010526No ratings yet
- Conic Sections Conic sections: θ2 = 90° (Only one nappe ofDocument10 pagesConic Sections Conic sections: θ2 = 90° (Only one nappe ofSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios: Opposite & Adjacent Sides in A Right Angled TriangleDocument5 pagesTrigonometric Ratios: Opposite & Adjacent Sides in A Right Angled Trianglesimran kaurNo ratings yet
- Ch 12Document37 pagesCh 12luismasantos991No ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument12 pagesHYPERBOLAYsham KamidNo ratings yet
- SINE and COSINEDocument25 pagesSINE and COSINEGehg malaqueNo ratings yet
- Graphing Trig Functions 1Document32 pagesGraphing Trig Functions 1api-276566085No ratings yet
- Ms6 Trig2 BookDocument21 pagesMs6 Trig2 BookErnest OpokuNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 21 35Document7 pagesTrigonometry 21 35vishnusubs8989No ratings yet
- Trignometric Functions ExemplerDocument27 pagesTrignometric Functions ExempleramiNo ratings yet
- Robotics Assignment TwoDocument19 pagesRobotics Assignment Twomisgana etichaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Quadrants 2 - 4Document11 pagesLesson Quadrants 2 - 4api-444439435No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Function: Group MembersDocument87 pagesTrigonometric Function: Group MembersKevinNo ratings yet
- CNC Milling Sample ProgramDocument16 pagesCNC Milling Sample ProgramjayyadavvpcNo ratings yet
- Week 009 Trigonometric FunctionsDocument6 pagesWeek 009 Trigonometric Functionsvit.chinnajiginisaNo ratings yet
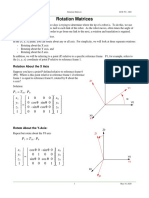
- Rotation Matrix TransformationsDocument13 pagesRotation Matrix TransformationssolteanNo ratings yet
- Sadler Methods Unit 1 Text Chapter 1Document28 pagesSadler Methods Unit 1 Text Chapter 1lilpekkarapNo ratings yet
- 1 Trigonometry Function NewDocument57 pages1 Trigonometry Function Newnebokambi123No ratings yet
- QuizDocument4 pagesQuizNitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Objective: Use The Unit Circle To Determine Circular FunctionsDocument18 pagesObjective: Use The Unit Circle To Determine Circular FunctionsLamette Austria AyongNo ratings yet
- Torsion (Circular & Composite Shafts)Document19 pagesTorsion (Circular & Composite Shafts)Subham meenaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Functions ExplainedDocument30 pagesTrigonometry Functions ExplainedRishu RajNo ratings yet
- Project TrignometicDocument8 pagesProject TrignometicAffy LoveNo ratings yet
- Notes_5Document10 pagesNotes_5kv8nrv5kdzNo ratings yet
- Precal SLM Q2W7-8Document9 pagesPrecal SLM Q2W7-8Anjanette RiparipNo ratings yet
- Robotics Assignment TwoDocument19 pagesRobotics Assignment Twomisgana etichaNo ratings yet
- Graphing Trig FunctionsDocument55 pagesGraphing Trig FunctionsNcube ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- CG 3D TransformationDocument34 pagesCG 3D Transformationpiu2853No ratings yet
- 006 Kinematics and Dynamics of Rotation PDFDocument34 pages006 Kinematics and Dynamics of Rotation PDFNIEVA LOU ORBOCNo ratings yet
- 9) Trigonometric GraphsDocument10 pages9) Trigonometric GraphsboobooNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument24 pagesGraphs of Trigonometric FunctionsAbrham TamiruNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions For The Engineering Module: Subtest "Formalising Technical Interrelationships"Document18 pagesSample Questions For The Engineering Module: Subtest "Formalising Technical Interrelationships"Phương LanNo ratings yet
- Reference Angle (Trigo)Document2 pagesReference Angle (Trigo)Nadine Clare FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document42 pagesChapter 9jordanhub05No ratings yet
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument11 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringPaulyne TuganoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TrigonometryDocument47 pagesChapter 4 TrigonometrySHAHRUL100% (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Exogenic and Endogenic Process 1Document34 pagesExogenic and Endogenic Process 1hacker johnNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Lesson1Document24 pagesFabm1 Lesson1hacker johnNo ratings yet
- PLAGIARISM HandoutDocument31 pagesPLAGIARISM Handouthacker johnNo ratings yet
- Explicit and Implicit ClaimsDocument4 pagesExplicit and Implicit Claimshacker johnNo ratings yet
- Arc Length and VelocityDocument10 pagesArc Length and Velocityhacker johnNo ratings yet
- Puttaswamy 2012Document48 pagesPuttaswamy 2012arun rajaramNo ratings yet
- Santos - Jiunior Problem Seminar - 2008 - 26-26Document1 pageSantos - Jiunior Problem Seminar - 2008 - 26-26chengpeckNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 PDFOlla 8352No ratings yet
- Number and Consecutive Integer Problems: Supplementary Sheet 2 Elementary Algebra - Mat 0024 Professor Howard SorkinDocument2 pagesNumber and Consecutive Integer Problems: Supplementary Sheet 2 Elementary Algebra - Mat 0024 Professor Howard Sorkindony65No ratings yet
- CBSE CLass 10 Mathematics Standard Question Paper 2023 Set 1 30 2 1Document28 pagesCBSE CLass 10 Mathematics Standard Question Paper 2023 Set 1 30 2 1yashpawar4324No ratings yet
- GRADE 8 NotesDocument5 pagesGRADE 8 NotesIya Sicat PatanoNo ratings yet
- M-10 Content+Previous Years QuestionDocument65 pagesM-10 Content+Previous Years QuestionOnline Physics Care by Syed Al-NahiyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Fourier SeriesDocument195 pagesUnit 2 Fourier Seriespoojaabanindran100% (1)
- Handout 2.4 Inscribed AnglesDocument6 pagesHandout 2.4 Inscribed AnglesRyanNo ratings yet
- 1617 Level J Mathematics Grid Sample Questions PDFDocument60 pages1617 Level J Mathematics Grid Sample Questions PDFAndrew100% (1)
- Grade 5 Parent BrochureDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Parent Brochureapi-305026398No ratings yet
- 0901 Mathematics Paper-With-Ans-solution EveningDocument6 pages0901 Mathematics Paper-With-Ans-solution Eveningsudhanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- International Mathematics and Science Olympiad Primary Schools 2004 Taiwan ProblemsDocument50 pagesInternational Mathematics and Science Olympiad Primary Schools 2004 Taiwan ProblemsYessi Hasri67% (3)
- Precalculus: Functions and Their Graphs Homework AnswersDocument47 pagesPrecalculus: Functions and Their Graphs Homework Answersteach03No ratings yet
- 7.1 Inverse Trigonometric Derivatives PDFDocument5 pages7.1 Inverse Trigonometric Derivatives PDFHenry MagdayNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Antiderivatives, Differential Equations, and Slope Fields ReviewDocument15 pagesAP Calculus AB Antiderivatives, Differential Equations, and Slope Fields ReviewAyana SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry Problems and SolutionsDocument4 pages3D Geometry Problems and SolutionsisamalhassanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document15 pagesUnit 6Arthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- Implicit DifferentiationDocument26 pagesImplicit DifferentiationAhmad MarwadNo ratings yet
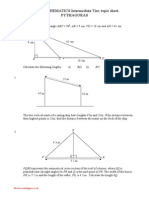
- Topic Sheet - PythagorasDocument4 pagesTopic Sheet - PythagorasEs LimNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument91 pagesDifferential EquationAseel JameelNo ratings yet
- Math10Q2M2 Activity SheetsDocument10 pagesMath10Q2M2 Activity SheetsLavinia RamosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Without Borders Age Group 4 SPRING 2021: PermissionDocument4 pagesMathematics Without Borders Age Group 4 SPRING 2021: PermissionSarah ChirigiuNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure: Unless Stated Otherwise, Approximate Results Are Given To 3 Significant Figures. Skills CheckDocument5 pagesCircular Measure: Unless Stated Otherwise, Approximate Results Are Given To 3 Significant Figures. Skills CheckTú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Inner Product and NormsDocument37 pagesInner Product and NormsSofwah AlaydrusNo ratings yet
- IIT Academy Matrix ProblemsDocument5 pagesIIT Academy Matrix ProblemsAnanya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Methods of Solving Quadratic Equations: FreebieDocument8 pagesMethods of Solving Quadratic Equations: FreebieSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Maths exam questions for class 2Document2 pagesMaths exam questions for class 2Mandeep ThakurNo ratings yet
- MR 1 2024 ProblemsDocument4 pagesMR 1 2024 Problemsaditya devNo ratings yet
- Translation:: English Phrases Into Algebraic ExpressionsDocument19 pagesTranslation:: English Phrases Into Algebraic ExpressionsRosen AnthonyNo ratings yet