Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geoscience For The Future Poster
Uploaded by
hkuruogluOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geoscience For The Future Poster
Uploaded by
hkuruogluCopyright:
Available Formats
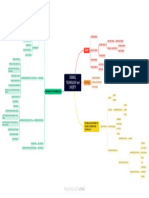
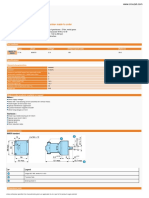
GEOSCIENCE FOR THE FUTURE
Geoscientists will be crucial in meeting society’s future challenges, be PLANETARY SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
that through the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, the
Paris Agreement to avoid dangerous climate change, or through other GEOLOGY
important policies to protect the environment and ensure the
availability of vital resources for all.
Geoscientists will be critical in:
Ensuring access to clean and sustainable water supplies GLACIOLOGY GIS & REMOTE
Sourcing and extracting critical minerals needed from green PALAEOCLIMATOLOGY SENSING
technologies like solar and wind power
Understanding the subsurface to harness geothermal energy, enable
safe infrastructure development, and carbon capture and storage
technologies
Mitigating climate change and influencing governmental policy through
understanding past climates, modelling potential future outcomes and HYDROPOWER
understanding climate impacts on the environment, livelihoods and
natural hazards
GEOMORPHOLOGY THE GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF LONDON SUPPORTS THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
RENEWABLE ENERGY NUCLEAR ENERGY
VOLCANOLOGY
GEOPHYSICS GEOSCIENCE
RESEARCH ENVIRONMENTAL/
EARTH SCIENCE LABORATORY
UNIVERSITY LANDSCAPE PROTECTION
GEOHAZARD MITIGATION SSSI
CONTAMINATED
LAND
SCIENCE OUTREACH SCIENCE ENVIRONMENTAL
SEISMOLOGY & COMMUNICATION POLICY GEOCHEMISTRY
MUSEUM EROSION
BATTERY TECHNOLOGY MUSEUM NON-GOVERNMENTAL
Li o
C MANAGMENT
Cu CURATION ORGANISATIONS
Nd
OCEANOGRAPHY
CARBON CAPTURE
PALAEONTOLOGY
SCHOOL TEACHING & STORAGE
MINING & MINERAL
CENTRAL STATION
RESOURCES
HYDROCARBONS
H 2O
H 2O
H 2O H 2O HYDROGEOLOGY ENGINEERING GEOLOGY
CO2 ENERGY STORAGE (GAS,
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY HYDROGEN, COMPRESSED AIR)
*MINIMUM DEPTH 200m
GEOLOGICAL DISPOSAL CONTAMINATED GROUNDWATER
OF RADIOACTIVE WASTE* H2 ,CH4 OR AIR
CRITICAL MINERALS
You might also like
- SM00092A - NX Fault CodesDocument43 pagesSM00092A - NX Fault Codesdario_es60% (5)
- Geometallurgy PDFDocument5 pagesGeometallurgy PDFEdythMarcaNo ratings yet
- LIFTCALC 30aDocument101 pagesLIFTCALC 30aareks30% (1)
- 880-Div2Document182 pages880-Div2Manuel Victor ChandomiNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Permian (Karoo) Coal Deposits of Southern AfricaDocument35 pagesAn Overview of The Permian (Karoo) Coal Deposits of Southern AfricaLibardo Correa ChaparroNo ratings yet
- Daikin Chiller SelectionDocument3 pagesDaikin Chiller Selectionosama alabsiNo ratings yet
- Lista Stand Iec 60034Document4 pagesLista Stand Iec 60034nikola CHECNo ratings yet
- Thermal Rehabilitation (Azuma House)Document47 pagesThermal Rehabilitation (Azuma House)Haseeb Uz Zaman67% (6)
- Pdac Peru 2019Document99 pagesPdac Peru 2019qwerty123No ratings yet
- Sogi Poster 31may23 - OnlineDocument2 pagesSogi Poster 31may23 - OnlineRicky SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Nanocomposite Membranes and Their Applications in Oily Wastewater TreatmentDocument115 pagesFabrication of Nanocomposite Membranes and Their Applications in Oily Wastewater TreatmentAhmet EmreNo ratings yet
- ZGE4301 BSMA2E ACTIVITY1A GROUP2 DoringoJ PDFDocument7 pagesZGE4301 BSMA2E ACTIVITY1A GROUP2 DoringoJ PDFha-ahawNo ratings yet
- Cover Laporan PetrologiDocument1 pageCover Laporan PetrologiCanggahNo ratings yet
- Mineral Resources and OreDocument99 pagesMineral Resources and OreAnonymous jxjbLUNo ratings yet
- 2018AsthrdpNscGradCourse PDFDocument2 pages2018AsthrdpNscGradCourse PDFrujean romy p guisandoNo ratings yet
- Direct Estimation of Hydrocarbon in Place of JAKS Offshore Field, Niger Delta Using Empirical Formulae TechniqueDocument10 pagesDirect Estimation of Hydrocarbon in Place of JAKS Offshore Field, Niger Delta Using Empirical Formulae TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY and SOCIETYDocument1 pageSCIENCE TECHNOLOGY and SOCIETYKen ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sustainable Development Report PDFDocument2 pages2019 Sustainable Development Report PDFanrffNo ratings yet
- Photoacoustic Microscopy of Sandstone Reservoirs RocksDocument4 pagesPhotoacoustic Microscopy of Sandstone Reservoirs RockswangcosimoNo ratings yet
- Research 3Document2 pagesResearch 3jobel colleraNo ratings yet
- Program Studi Teknik Geologi Fakultas Teknologi Kebumian Dan Energi Universitas TrisaktiDocument29 pagesProgram Studi Teknik Geologi Fakultas Teknologi Kebumian Dan Energi Universitas TrisaktiSindy Febri NNo ratings yet
- 2020 KU1164 Pengantar SDME - Materi 06bDocument35 pages2020 KU1164 Pengantar SDME - Materi 06bfaizahNo ratings yet
- Bari Delage OZ Course 2 Behaviour Soft ClaysDocument36 pagesBari Delage OZ Course 2 Behaviour Soft ClaysmasterhamzamNo ratings yet
- Lokasi 2Document129 pagesLokasi 2yuliuskisworoNo ratings yet
- Detection of A Fracture Zone Using Microtremor Array Measurement. GeophysicsDocument30 pagesDetection of A Fracture Zone Using Microtremor Array Measurement. GeophysicsangeysaccisNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: Universitas Bandar LampungDocument1 pageCivil Engineering: Universitas Bandar Lampunganjusurbakti09No ratings yet
- Astronomy For Development Strategic Plan 2010-2020: International Astronomical UnionDocument62 pagesAstronomy For Development Strategic Plan 2010-2020: International Astronomical UnionMuda SarmeNo ratings yet
- Geochemical Techniques For The Analysis of Geochemical Data and Its Application in The Nigerian Oil and Gas Industries 2150 3494 1000137Document8 pagesGeochemical Techniques For The Analysis of Geochemical Data and Its Application in The Nigerian Oil and Gas Industries 2150 3494 1000137Yuda GestriNo ratings yet
- Souvik Sen, Mohamed Abioui, Shib Sankar Ganguli, Ahmed Elsheikh, Akash Debnath, Mohammed Benssaou, Ahmed Awad AbdelhadyDocument16 pagesSouvik Sen, Mohamed Abioui, Shib Sankar Ganguli, Ahmed Elsheikh, Akash Debnath, Mohammed Benssaou, Ahmed Awad Abdelhadyshib ganguliNo ratings yet
- GeoStrata Magazine IndexDocument1 pageGeoStrata Magazine IndexMartin GriffinNo ratings yet
- Index: Mining EngineeringDocument5 pagesIndex: Mining EngineeringÁngel YeysonNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Kelas 45 Menit PDFDocument18 pagesJadwal Kelas 45 Menit PDFZaki FuadiNo ratings yet
- PDF Materiales MagnetDocument8 pagesPDF Materiales MagnetGiancarlo CcosccoNo ratings yet
- Jamaluddin 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 118 012070Document6 pagesJamaluddin 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 118 012070JamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal GeomagnetDocument6 pagesJurnal GeomagnetTati ZeraNo ratings yet
- Fournier and Borgomano 2007Document25 pagesFournier and Borgomano 2007Kevin RamiroNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan - 6Document115 pagesSkripsi Tanpa Bab Pembahasan - 6rdwiki96No ratings yet
- Day 1: November 07, 2017: 16:30 - 17:30 Poster Session (Salle - RDC) Topic 1Document6 pagesDay 1: November 07, 2017: 16:30 - 17:30 Poster Session (Salle - RDC) Topic 1foufouNo ratings yet
- 02a. Level of Petroleum InvestigationDocument28 pages02a. Level of Petroleum Investigationdina mutia sariNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical Characterization of Limestones and Sandstones in A Complex Geological Context, Example North-East Constantine: Preliminary ResultsDocument5 pagesPhysico-Chemical Characterization of Limestones and Sandstones in A Complex Geological Context, Example North-East Constantine: Preliminary ResultsAbdisa GemechuNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: Universitas Bandar LampungDocument1 pageCivil Engineering: Universitas Bandar Lampunganjusurbakti09No ratings yet
- ExploracionDocument12 pagesExploracionClaudia Arce CruzNo ratings yet
- Thesis Shale Gas NSB PDFDocument15 pagesThesis Shale Gas NSB PDFLulut Fitra FalaNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Characterization Using Electrofacies Analysis in The Sandstone Reservoir of The Norne Field (Offshore Norway)Document12 pagesReservoir Characterization Using Electrofacies Analysis in The Sandstone Reservoir of The Norne Field (Offshore Norway)Nehemiah DominickNo ratings yet
- 2017 - State-Of-The-Art Remote Characterization of Shallow MarineDocument17 pages2017 - State-Of-The-Art Remote Characterization of Shallow Marinefaris nauvalNo ratings yet
- Introducing Students To Surface Modi Cation and Phase Transfer of Nanoparticles With A Laboratory ExperimentDocument6 pagesIntroducing Students To Surface Modi Cation and Phase Transfer of Nanoparticles With A Laboratory ExperimentMarbella CotaNo ratings yet
- Benyoussef Qualitative 52 2022Document6 pagesBenyoussef Qualitative 52 2022Ali LahlaliNo ratings yet
- Fathiyah Jamaludin 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 88 012011 PDFDocument8 pagesFathiyah Jamaludin 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 88 012011 PDFHcene HcenNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science - An Interdisciplinary DisciplineDocument1 pageEnvironmental Science - An Interdisciplinary DisciplineLorraine CaliwanNo ratings yet
- Chang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 549 012025Document10 pagesChang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 549 012025oktrijayaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: Universitas Bandar LampungDocument1 pageCivil Engineering: Universitas Bandar Lampunganjusurbakti09No ratings yet
- New Template Capsule Group 5Document5 pagesNew Template Capsule Group 5Red SkiNo ratings yet
- SPE 92779 Oil-Based Mud Micro-Imager (OBMI) Application in Sangatta: A Field Case StudyDocument12 pagesSPE 92779 Oil-Based Mud Micro-Imager (OBMI) Application in Sangatta: A Field Case StudySyukur BancoaNo ratings yet
- Swelling PotentialDocument8 pagesSwelling PotentialDiyaning RatriNo ratings yet
- Results in Geophysical Sciences: A.A. Akinlalu, G.M. Olayanju, K.A.N. Adiat, G.O. OmosuyiDocument17 pagesResults in Geophysical Sciences: A.A. Akinlalu, G.M. Olayanju, K.A.N. Adiat, G.O. OmosuyiADELEKEADEDOYINNo ratings yet
- Journal of Applied Geophysics: Franjo Šumanovac, Jasna Ore ŠkovićDocument17 pagesJournal of Applied Geophysics: Franjo Šumanovac, Jasna Ore ŠkovićDea DharaNo ratings yet
- Feart 09 638862Document18 pagesFeart 09 638862VmanuloNo ratings yet
- Ensayo de GeoquímicaDocument4 pagesEnsayo de GeoquímicaNatalia ParraNo ratings yet
- Geochemical Mapping in SS - CarajásDocument18 pagesGeochemical Mapping in SS - CarajásalexaareisNo ratings yet
- Abdullah 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 917 012008Document11 pagesAbdullah 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 917 012008Jovana StojkovićNo ratings yet
- Day 2: November 08, 2017: 11:30 - 12:30 Poster Session (Salle - RDC) Topic 1Document4 pagesDay 2: November 08, 2017: 11:30 - 12:30 Poster Session (Salle - RDC) Topic 1foufouNo ratings yet
- Contour Map-Exercise No.1Document2 pagesContour Map-Exercise No.1Gabriel MalasiqueNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stability, Crystallization, Structure and Morphology of Syndiotactic 1,2-Polybutadiene/organoclay NanocompositeDocument16 pagesThermal Stability, Crystallization, Structure and Morphology of Syndiotactic 1,2-Polybutadiene/organoclay NanocompositeAmit Kumar SenNo ratings yet
- Laboratorium Geologi Optik: BO RA NG Praktikum Mineral Optik Acara: Mineral UniaxialDocument3 pagesLaboratorium Geologi Optik: BO RA NG Praktikum Mineral Optik Acara: Mineral UniaxialRahmat Alam AkbarNo ratings yet
- Bases Del Concur SoDocument1 pageBases Del Concur Sojose ramirezNo ratings yet
- Minerals 11 00453 v2 3Document3 pagesMinerals 11 00453 v2 3bello belloNo ratings yet
- Synchrotron-Based Techniques in Soils and SedimentsFrom EverandSynchrotron-Based Techniques in Soils and SedimentsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry, PPT 3Document33 pagesElectrochemistry, PPT 3Ernest Nana Yaw AggreyNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical Kineticsvivek daveNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling PlantDocument6 pagesAsh Handling Plantapumoni123No ratings yet
- 35-3000RKA-LEL Sample Draw Combustible Gas Detector: SpecificationsDocument18 pages35-3000RKA-LEL Sample Draw Combustible Gas Detector: SpecificationspcatruongNo ratings yet
- Bye Bye Blue Sky - Documentary by Patrick PasinDocument52 pagesBye Bye Blue Sky - Documentary by Patrick PasinThought HackerNo ratings yet
- Stonier Towards A New Theory of Information 1991Document7 pagesStonier Towards A New Theory of Information 1991BabsbNo ratings yet
- Overview of Led LightingDocument63 pagesOverview of Led Lightingpcharwood100% (3)
- Enron Company PDFDocument18 pagesEnron Company PDFJebin JamesNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 43-10Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 43-10lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 02 Name: Mussadiq Shah Reg #: Uw-14-Me-Bsc-054 Course Title: Cad/Cam Semester: 6 - BDocument2 pagesAssignment # 02 Name: Mussadiq Shah Reg #: Uw-14-Me-Bsc-054 Course Title: Cad/Cam Semester: 6 - BMian Mussadiq ShahNo ratings yet
- 5 NM RC65 10 and 17 Watts 17 W Part Number Made To OrderDocument3 pages5 NM RC65 10 and 17 Watts 17 W Part Number Made To OrderasdasdghtNo ratings yet
- Model C-30Hdz: Operations & Parts ManualDocument106 pagesModel C-30Hdz: Operations & Parts ManualGerardo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ad00267v Ledeen BrochureDocument28 pagesAd00267v Ledeen Brochureetd_1988No ratings yet
- Seal of BushingDocument6 pagesSeal of BushingB.k. BirtiaNo ratings yet
- Spray Pump: Technical ManualDocument15 pagesSpray Pump: Technical ManualNal AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Unit V - Metrology and Instrumentation NotesDocument34 pagesUnit V - Metrology and Instrumentation NotesmanisekNo ratings yet
- Teilekatalog (VX800 VS51A 1990-1996)Document76 pagesTeilekatalog (VX800 VS51A 1990-1996)Andreas PauliNo ratings yet
- Vc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJDocument6 pagesVc-90200.01.03-En Ecoline DJGary IrawanNo ratings yet
- Ernest Rutherford 1Document8 pagesErnest Rutherford 1api-400268497No ratings yet
- California Air Tools 20040SPCAD Owner's Manual 11-18Document16 pagesCalifornia Air Tools 20040SPCAD Owner's Manual 11-18mmeneses07No ratings yet
- World Standard Sheet LinesDocument4 pagesWorld Standard Sheet LinesAlejandro RubianoNo ratings yet
- Eng Sicor Catalogue GearlessDocument52 pagesEng Sicor Catalogue GearlessEmeka Pius OramunwaNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Units & SymbolDocument3 pagesA Level Physics Units & SymbolXian Cong KoayNo ratings yet