Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vaccines: Immunity
Uploaded by
John0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageVaccines: Immunity
Uploaded by
JohnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
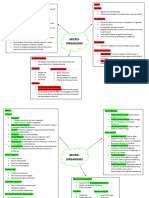
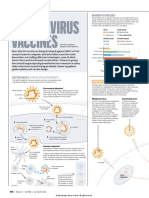
Body defends against disease causing
organisms.
Innate immunity non specific, present at
birth
Acquired immunity : pathogen specific
memory based immunity
Immunity
B cells produce antibodies, T cells help B
cells as well as participate in Cell Mediated
Immunity
Active Immunity : antibodies of the host.
passive immunity : ready made antibodies.
Autolmmunity : against self
Based on the principles Of memory Of the
immune system.
Antigens vS pathogens : the difference
Active Vaccination : training the immune
Vaccination system with weakened pathogens
passive Immunisation : directly injecting
antibodies,
dverse Effects following immunisation No
accine is perfect
Intramuscular
Intravenous
Based on administration Subcutaneous
Vaccines
Nasal
Oral
Live attenuated weak form of germs
Types Of Vaccines
Inactivated : Killed Germs
Subunit vaccines : Purified Antigens only
Conjugate vaccine Weak and Strong
Antigen Together
Based on pathogen
Polysaccharide Vaccine Poly carbohydrate
vaccines
Recombinant Vaccines Genetic
Modification
Of Virus and bacteria
mRNA vaccines : messenger RNA delivered
to the body
Covishield viral vector vaccine
Covaxin : Inactivated Viral Vaccine
Covid-19 Vaccines
Sputnik Viral vector Vaccine
Pfizer / Moderna mRNA vaccines,
You might also like
- Supplementary Lecture - Vaccine 101Document11 pagesSupplementary Lecture - Vaccine 101KarizzaNo ratings yet
- Vakcinų RūšysDocument1 pageVakcinų RūšysPaulius SungailaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Does Guarantee Protection From InfectionDocument17 pagesVaccination Does Guarantee Protection From Infectionhjchoi68No ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument29 pagesVaccinesCassandra EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Covid PresentationDocument1 pageCovid PresentationDexiel Kay RomiscalNo ratings yet
- Report COVID 19Document30 pagesReport COVID 19Luke Jovanni TAOCNo ratings yet
- Antigen Body.: Classification VaccinesDocument9 pagesAntigen Body.: Classification VaccinesMohamed AlsaabNo ratings yet
- Recombinant VaccinesDocument11 pagesRecombinant VaccinesAshna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Micro OrganismsDocument5 pagesMicro Organismsnikitaria1603No ratings yet
- MON2 Friedland For FellowsDocument21 pagesMON2 Friedland For FellowsNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- Imun VaksinDocument62 pagesImun VaksinLaksmi DwiNo ratings yet
- Immune Function ReviewDocument3 pagesImmune Function Reviewjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- EXPANDED PROGRAM IMMUNIZATION - Self ReviewerDocument6 pagesEXPANDED PROGRAM IMMUNIZATION - Self ReviewerIana CastigadorNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Production (L1F17PHMD0174)Document22 pagesVaccine Production (L1F17PHMD0174)Faizah Khalid100% (1)
- Fogsi Statement On Covid Vaccination in Pregnancy and BFDocument16 pagesFogsi Statement On Covid Vaccination in Pregnancy and BFM AbhiNo ratings yet
- Vaccination PDF.'''''Document14 pagesVaccination PDF.'''''Ompriya SNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Pitfalls in The Pursuit of A COVID-19 VaccineDocument4 pagesAvoiding Pitfalls in The Pursuit of A COVID-19 VaccinePonco PrakosoNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Awareness 01Document54 pagesVaccination Awareness 01Avie LeeveNo ratings yet
- Viral VaccinesDocument7 pagesViral VaccinesMoon nieNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - 15Document8 pagesMicrobiology - 15karmylle andradeNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccines & Immune Response: Update OnDocument19 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccines & Immune Response: Update OnHarshitBediNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Communicable DiseasesDocument1 page3.1 Communicable Diseaseswill hayNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Natural Immunization ProgramDocument10 pagesWeek 7 Natural Immunization ProgramKAREN CARI�ONo ratings yet
- Vaccine Evaluation and Selection Townhall April 12, 2021 Dr. Nina GlorianiDocument14 pagesVaccine Evaluation and Selection Townhall April 12, 2021 Dr. Nina GlorianiebrandeNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunityDocument35 pagesTypes of ImmunityKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Vaccine, Vaccination Schedule, & Disease (I) : Dr. Shristi Ram 15-11-2021Document22 pagesVaccine, Vaccination Schedule, & Disease (I) : Dr. Shristi Ram 15-11-2021Soummyadip RoyNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Concept of Vaccination PDFDocument48 pages1 Basic Concept of Vaccination PDFdonNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument4 pagesImmunityMiran HussienNo ratings yet
- Vaccine and Cold Chain ManagementDocument30 pagesVaccine and Cold Chain ManagementrsadNo ratings yet
- Principles of VaccinationDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Vaccinationp1awh1786No ratings yet
- Coronavirus VaccinesDocument2 pagesCoronavirus VaccinesFabio PintoNo ratings yet
- Defense System (IMMUNITY)Document33 pagesDefense System (IMMUNITY)Restu DwikelanaNo ratings yet
- Adverse Event Following ImmunizationDocument28 pagesAdverse Event Following ImmunizationLalitKarkiNo ratings yet
- Vaccines and Immunization Summer 2020Document48 pagesVaccines and Immunization Summer 2020Gia LeNo ratings yet
- MED2 2.01b - Adult ImmunizationDocument11 pagesMED2 2.01b - Adult ImmunizationJorem Paulo LabaoNo ratings yet
- Communicable-Diseases 48897647 2Document1 pageCommunicable-Diseases 48897647 2JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Pengantar ImunologiDocument20 pagesPengantar ImunologiAni SafitriNo ratings yet
- Updated Immunzation TopicDocument58 pagesUpdated Immunzation TopicAbbey FritschNo ratings yet
- VNS Faculty of Pharmacy: Mentors - Presented byDocument1 pageVNS Faculty of Pharmacy: Mentors - Presented bypoplu100% (1)
- VaccinationDocument28 pagesVaccinationM AQIB ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Types of VaccinesDocument2 pagesTypes of VaccinesErika Bea PaculanangNo ratings yet
- EPI Vaccines: - Inactivated (Killed) Microorganisms - Attentuated Microorganisms Fragments From Microorganisms ToxoidsDocument3 pagesEPI Vaccines: - Inactivated (Killed) Microorganisms - Attentuated Microorganisms Fragments From Microorganisms ToxoidsIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Immunological ProductsDocument35 pagesImmunological ProductsUMME SADEA RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Mindmap4 1Disease&ImmunityDocument1 pageMindmap4 1Disease&ImmunityAndrew ColvilleNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study Hepa BDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Hepa BPauline Doronila100% (1)
- Prevention of DiseasesDocument6 pagesPrevention of DiseasesbahacdNo ratings yet
- Brochure Vaccine 2022Document2 pagesBrochure Vaccine 2022HilmißinÄbüBäkärNo ratings yet
- VaccinationsDocument31 pagesVaccinationsحامد يوسفNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyArvi MandaweNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument6 pagesPharma - Chemotherapeutic AgentsSae YanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Hepa BDocument3 pagesDrug Study Hepa BKwebblekop JordiNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Handbook Process Br5237en MKDocument26 pagesVaccine Handbook Process Br5237en MKhadeer100% (2)
- MODULE 2: Types of Vaccine and Adverse ReactionsDocument29 pagesMODULE 2: Types of Vaccine and Adverse ReactionsnandaNo ratings yet
- Vaccines & Its Types: Ms Saajida Sultaana MahusookDocument16 pagesVaccines & Its Types: Ms Saajida Sultaana MahusookGayathri deviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Lesson 2 Defenses of Body Againts PathogensDocument18 pagesChapter 10 Lesson 2 Defenses of Body Againts Pathogensmotarekthebest320No ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument35 pagesImmunityMavi 1.13.7No ratings yet
- Group 5 - Immunotherapy and VaccineDocument78 pagesGroup 5 - Immunotherapy and VaccineThe KingNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Indications: CnsDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Indications: CnsSeno HyeonNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine - RBDocument15 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine - RBRajNo ratings yet
- CRISIL Mutual Fund Ranking: For The Quarter Ended September 30, 2020Document48 pagesCRISIL Mutual Fund Ranking: For The Quarter Ended September 30, 2020MohitNo ratings yet
- Jean-Pierre Wybauw - Fine Chocolates 2 - Great Ganache Experience-Lannoo (2008)Document209 pagesJean-Pierre Wybauw - Fine Chocolates 2 - Great Ganache Experience-Lannoo (2008)Mi na100% (1)
- Consumer ReportsDocument64 pagesConsumer ReportsMadalina Pilipoutanu100% (1)
- Exercise 3 ASC0304 - 2019-1Document2 pagesExercise 3 ASC0304 - 2019-1Nuraina NabihahNo ratings yet
- Marine Turtle Survey Along The Sindh CoastDocument106 pagesMarine Turtle Survey Along The Sindh CoastSyed Najam Khurshid100% (1)
- Crew Resource Management Phil O'DonnellDocument39 pagesCrew Resource Management Phil O'DonnellMostafaNo ratings yet
- Commented (JPF1) : - The Latter Accused That Rizal HasDocument3 pagesCommented (JPF1) : - The Latter Accused That Rizal HasLor100% (1)
- Physical Fitness TestDocument1 pagePhysical Fitness TestGiessen Fran RamosNo ratings yet
- Recipe Booklet PRINT VERSIONDocument40 pagesRecipe Booklet PRINT VERSIONjtsunami815100% (1)
- 8291 w13 Ms 22Document8 pages8291 w13 Ms 22Caterina De LucaNo ratings yet
- TinyEYE Online Speech Therapy Media GuideDocument4 pagesTinyEYE Online Speech Therapy Media GuideTinyEYE Therapy ServicesNo ratings yet
- Eaton BECOPAD P Range TechnicalDataSheet enDocument4 pagesEaton BECOPAD P Range TechnicalDataSheet enEsteban Fernando Meza IbacetaNo ratings yet
- Fishing Broken Wire: WCP Slickline Europe Learning Centre SchlumbergerDocument23 pagesFishing Broken Wire: WCP Slickline Europe Learning Centre SchlumbergerAli AliNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Financial Statements of Company, Oil and Gas.Document105 pagesComparative Study of Financial Statements of Company, Oil and Gas.Ray Brijesh AjayNo ratings yet
- NG Uk RTR 0220 r15 PDFDocument9 pagesNG Uk RTR 0220 r15 PDFDuong Thai BinhNo ratings yet
- Philosophy For Management and DisciplineDocument8 pagesPhilosophy For Management and Disciplineapi-300120362No ratings yet
- OSCE Pediatric Dentistry Lecture-AnswersDocument40 pagesOSCE Pediatric Dentistry Lecture-AnswersR MNo ratings yet
- NSF 型錄2Document2 pagesNSF 型錄2Nermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- 6L45, 6L50, 6L80, 6L90: Time Tested - Industry TrustedDocument1 page6L45, 6L50, 6L80, 6L90: Time Tested - Industry TrustedCelso BidinotiNo ratings yet
- Tom Kenyon - ImmunityDocument9 pagesTom Kenyon - ImmunityDren Hoti100% (2)
- Bagmati River Rejuvenation.1.0Document27 pagesBagmati River Rejuvenation.1.0navonil.senNo ratings yet
- Steel Scrap Recycling Policy 06.11.2019 PDFDocument31 pagesSteel Scrap Recycling Policy 06.11.2019 PDFAnshul SableNo ratings yet
- Clobazam For The Treatment ofDocument3 pagesClobazam For The Treatment ofpronto4meNo ratings yet
- Phillips LoFloDocument29 pagesPhillips LoFlokawaiiriceNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae Staphylococci Faculty: Dr. Alvin FoxDocument32 pagesStreptococcus Pneumoniae Staphylococci Faculty: Dr. Alvin Foxdanish sultan100% (1)
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQJagdishVankar100% (1)
- Park Ch. 1 - A1000 - Spring13Document21 pagesPark Ch. 1 - A1000 - Spring13lingyeeNo ratings yet
- Cwts ThesisDocument7 pagesCwts Thesisbufukegojaf2100% (2)
- MS Fresher HR DocumentDocument4 pagesMS Fresher HR DocumentJahanvi KambojNo ratings yet
- (Clinical Sociology - Research and Practice) Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Auth.), Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Eds.) - Handbook of Clinical Sociology-Springer US (2001) PDFDocument441 pages(Clinical Sociology - Research and Practice) Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Auth.), Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Eds.) - Handbook of Clinical Sociology-Springer US (2001) PDFMuhammad AliNo ratings yet