Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 20
Uploaded by
ABISHAI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesLecture 20
Uploaded by
ABISHAICopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
EE-118-Basic Electricity and Electronics
Lecture No:20
Dr.Saqib Jamshed Rind
NED University of Engineering and Technology
Department of Automotive and Marine Engineering
Lecture Contents
After completing this lecture student should know about:
• Impedance and Phasor Diagram
• Series R-L-C Circuits
• Some Examples
Impedance And The Phasor Diagram
Resistive Elements:
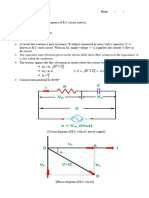
Example:
Using complex algebra, find the current i for the circuit. Sketch
the waveforms of v and i.
Impedance And The Phasor Diagram
Inductive Reactance:
Impedance And The Phasor Diagram
Capacitive Reactance:
Example:
Using complex algebra, find the voltage v for the circuit. Sketch
the v and i curves.
Example:
Impedance Diagram
The networks combining
different types of elements will
have total impedances that
extend from +90° to -90°. If
the total impedance has an
angle of 0°, it is said to be
resistive in nature. If it is closer
to +90°, it is inductive in
nature; and if it is closer to -
90°, it is capacitive in nature.
Example:
Determine the input impedance
to the series network. Draw the
impedance diagram.
Example: R-L-C Series Circuit
Determine the unknown quantities for the given circuit.
Example: R-L-C Series Circuit
Example: R-L-C Series Circuit
Example: R-L-C Series Circuit
Phasor diagram: The phasor diagram indicates that the current I
is in phase with the voltage across the resistor, leads the voltage
across the inductor by 90°, and lags the voltage across the
capacitor by 90°.
Example: R-L-C Series Circuit
Example: R-L-C Series Circuit
Lecture Summary
In this lecture we have discussed:
• Impedance and Phasor Diagram
• Series R-L-C Circuits
• Some Examples
Text Books & References
1) Electric Circuits by TF Bogart latest edition
2) Introductory Circuit Analysis by Robert L. Boylestad, 9th Ed.
3) Engineering Circuit Analysis by WH Hayt
You might also like
- First Set PDF 2018-19 PDFDocument22 pagesFirst Set PDF 2018-19 PDFLavankumar MudirajNo ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument119 pagesDiode ApplicationsFlorenzo Miguel AclanNo ratings yet
- FDC Lab ManualDocument25 pagesFDC Lab ManualtovilasNo ratings yet
- The Capacitors Store Electrical Power in The Electric Field, Their Effect Is Known As The Capacitance. It Is Also Called The CondenserDocument3 pagesThe Capacitors Store Electrical Power in The Electric Field, Their Effect Is Known As The Capacitance. It Is Also Called The Condenserbirabaraswain4No ratings yet
- EEET2249 Lecture Notes 1 2013Document78 pagesEEET2249 Lecture Notes 1 2013Garry YinNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument47 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Experiment ManualDocument17 pagesExperiment ManualKavita BishtNo ratings yet
- Circuit Lab AssignmentDocument20 pagesCircuit Lab AssignmentYeab SraNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument45 pagesEDC Lab ManualChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- Group5 - Laboratory No. 3Document13 pagesGroup5 - Laboratory No. 3Angel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesData Structures and AlgorithmsAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument87 pagesBasic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDr-Ahmed ElkoranyNo ratings yet
- RL Series Circuit Analysis (Phasor Diagram, Examples & Derivation)Document12 pagesRL Series Circuit Analysis (Phasor Diagram, Examples & Derivation)Naksh bhatiNo ratings yet
- EE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument7 pagesEE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryMohammed KhouliNo ratings yet
- Series A.C. Ccts (Complex Numbers App)Document36 pagesSeries A.C. Ccts (Complex Numbers App)Kalikene MwambeloNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-I: Instructions For Experiment No. 1Document4 pagesPower Systems-I: Instructions For Experiment No. 1Priya GuptaNo ratings yet
- CircuitDocument9 pagesCircuitMy BusinessNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Rectifier OperationDocument21 pagesAnalysis of Rectifier Operationmcrahan100% (2)
- A192-AE-W6-R, XC & Z - RC circuit-SV-PKPDocument47 pagesA192-AE-W6-R, XC & Z - RC circuit-SV-PKPMuhammad Nurazin Bin RizalNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument55 pagesPe Lab ManualNorbert John IberaNo ratings yet
- Monday Thermodynamic (Assignment)Document5 pagesMonday Thermodynamic (Assignment)abdulmajeedabdussalam09No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document28 pagesLecture 5abdullahzahid197No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics-L2Document33 pagesBasic Electronics-L2Sushmitha AcharyaNo ratings yet
- ENGR 120 - RLC CircuitsDocument6 pagesENGR 120 - RLC CircuitsKaung Myat HtetNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument23 pagesBee Labdurgesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PPT - Second PartDocument48 pagesUnit 2 PPT - Second PartABHI GOUDNo ratings yet
- Ec8261 CD Lab ManualDocument92 pagesEc8261 CD Lab ManualthasleemaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - RC Cirucit: Name: - Sri Kanishk Senagana Branch: - ECE Roll Number: - 2001091 AIMDocument3 pagesExperiment 8 - RC Cirucit: Name: - Sri Kanishk Senagana Branch: - ECE Roll Number: - 2001091 AIMDr sggNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuits: Learning ObjectiveDocument18 pagesSeries RLC Circuits: Learning Objectiveandrew smithNo ratings yet
- RLC Series-Parallel Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pagesRLC Series-Parallel Circuit AnalysisShah Zeb YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Parallel-Series CircuitDocument42 pagesParallel-Series CircuitLenis Thambi100% (2)
- RC Circuit and Its ApplicationTerm PaperDocument13 pagesRC Circuit and Its ApplicationTerm PapersummitzNo ratings yet
- Design of Class E Resonant Rectifiers and Diode Evaluation For VHF Power ConversionDocument14 pagesDesign of Class E Resonant Rectifiers and Diode Evaluation For VHF Power ConversionAdam RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document16 pagesLecture 15ABISHAINo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manualdinuarslan86% (7)
- Basic ElectronicsDocument1 pageBasic Electronics08mpe026100% (1)
- Basic Types of Circuit. The Study of Circuits Involves Three Basic Types of Units and Four PossibleDocument13 pagesBasic Types of Circuit. The Study of Circuits Involves Three Basic Types of Units and Four PossibleEduard LauronNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices & Circuit Lab ManualDocument53 pagesElectronics Devices & Circuit Lab Manualbiswajit7sarkar100% (1)
- Course Code: Bcs01T1003 COURSE Name: Linear Algebra and Differential EquationDocument19 pagesCourse Code: Bcs01T1003 COURSE Name: Linear Algebra and Differential EquationSatyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Introduction To Diodes, Rectifiers, and Construction of A DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesExperiment 5 Introduction To Diodes, Rectifiers, and Construction of A DC Power SupplyLaurentiu IacobNo ratings yet
- Series RC Circuit: Fundamentals of Electricity II LABDocument10 pagesSeries RC Circuit: Fundamentals of Electricity II LABMustafaNo ratings yet
- Experiment-No 2Document5 pagesExperiment-No 2carloNo ratings yet
- PoEC 8 Circuit Theorems and ConversionsDocument50 pagesPoEC 8 Circuit Theorems and Conversionsmohammad alajarmeh100% (1)
- II PUC ManualDocument31 pagesII PUC Manuals2263001No ratings yet
- Circuit and Network Theory Lab ReportDocument8 pagesCircuit and Network Theory Lab Reportpeaceissa695No ratings yet
- 101 ExercisesDocument94 pages101 ExercisesMichael A. Alonso RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PHY098 Topic1.6.4 Chapter21 Arda&SyikinDocument21 pagesPHY098 Topic1.6.4 Chapter21 Arda&SyikinDAYANG NURHAIZA AWANG NORAWINo ratings yet
- NT Lab MannualDocument31 pagesNT Lab MannualsagarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2010-2011Document68 pagesPower Electronics 2010-2011Adnan Younus100% (1)
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsDocument39 pagesLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-4Document6 pagesExperiment No-4devanshurajpoot1No ratings yet
- EEE 121 Circuit Theory 1: Circuit Theorems & Apllication To DC CircuitsDocument29 pagesEEE 121 Circuit Theory 1: Circuit Theorems & Apllication To DC CircuitsKamarul Syaril AzzahariNo ratings yet
- ENA ManualDocument60 pagesENA ManualAbdul Munim100% (1)
- Dept SLT (Assignment) Thermodynamis and Electromagnectic Blessing ThermoDocument6 pagesDept SLT (Assignment) Thermodynamis and Electromagnectic Blessing Thermoabdulmajeedabdussalam09No ratings yet
- Current & Circuits February 08Document43 pagesCurrent & Circuits February 08binu_10No ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument62 pagesBee Lab ManualSwetha VanamNo ratings yet
- Parallel and Series. Sec 1Document130 pagesParallel and Series. Sec 1Mahra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Thevenizing A Bridge CircuitDocument10 pagesThevenizing A Bridge CircuitSaddeg RaiesNo ratings yet