Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO3 Finals
Uploaded by
LERMA, Cheenee B.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO3 Finals
Uploaded by
LERMA, Cheenee B.Copyright:
Available Formats
BIO3 – Statistical Biology FINALS
Z(Mjay)= 26.2-27.2 / 0.8 = -.1.25
Normal Distribution
Z(Ardee)= 27.3-30.1 / 1.4 = -2
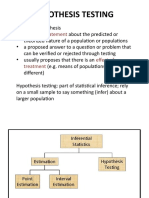
Hypothesis Testing
Z-Test TRY THIS: 3 Students were applying to the same medical
T-Test school. They came from undergraduate schools w/
different grading systems. Which student had the best
One-proportion Test
GWA when compared to other students at their school?
ANOVA
Student GWA School Ave. S.D
Micha 2.7 3.2 0.8
Jollebe 87 75 20
I. Normal Distribution Chinee 8.6 8 0.4
- symmetrical and it is a bell-shaped curve.
- considered to be the basis distribution of statistical Z(Micha)=
interference, representing the distribution of possible Z(Jollebe)=
estimates of a population parameter. Z(Chinee)=
- gives a useful approximation for other distributions
including discrete distributions (binomial) A:
- mean for a normal distribution is 0.
Probability
Ex: Crate of mangoes (m= 150g, SD=10g)
1. What is the probability that 1 mango is greater than
150g? P(x > 150g)
S: 47.5% = 50%=97.5%
A; 97.5%
𝑥−𝜇
2. Between 160g and 170g
Formula for Z-Score: 𝑧 = S: 95%-68%= 27% / 2 = 13.5%
𝜎
1. 2 Students, John and Ali, from different high schools,
wanted to find out who had the highest GWA when II. HYPOTHESIS TESTING
compared to his school:
Hypothesis- is a proposition, statement or assumption
Student GWA School Mean S.D based on previous observations about the value of a
JOHN 2.85 3.0 0.7 population parameter for testing purposes.
ALI 77 80 10
𝜇 − 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑛 𝜎 − 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑆. 𝐷
**Note: the higher the S.D, the more compressed 𝜎 2 − 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑣𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝜌 − 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
Z(John) = 2.85-3.00 / 0.7 = -0.21 5 steps for hypothesis testing
Z(Ali) = 77-80 / 10 = -0.3 1. Set up Ho and Ha
2. Test
Conclusion: John is smarter/brighter than Ali. 3. Compute the probability
4. Decision
2. 2 swimmers, Mjay and Ardee, from different teams, 5. Conclusion
wanted to find out who had the fastest time for the 50m
freestyle when compared to his team. Decision Ruling
Reject Ho if p < α
Student Time (s) Team Mean S.D Fail to reject if p ≥ α
MJAY 26.2 27.2 0.8
ARDEE 27.3 30.1 1.4
Q: Which swimmer had the fastest time when compared Rules in setting up Ho and Ha
to his team? 1. Ho must include the equal sign
2. one of the hypotheses must represent the claim
A: Ardee 3. the hypotheses must be contradicting statements.
III. Z TEST
Null (=, ≥, ≤)
Alternative (≠, >,<)
SETTING UP HO AND HA EXAMPLES
1. A certain chemical corp. makes a fabric cleaner, the
company claims that its product successfully removes 90
percent of all stains. A consumer organization questions
this claim and decides to test the product. They select 100
stained garments and apply the product to each. They find
that the product cleaned only 78 of them. Does the sample
data provide evidence that the success rate is less than
90 percent?
Ho: P = 0.9
Ha. P < 0.9
2. We wish to claim that more than 30% of registered
voters in a certain country voted in the elections. Z test for a single population mean:
N ≥ 30
Ho: P ≤ 0.3 When σ is knowns
Ha: P > 0.3 Normally distributed
3. We want to test whether the mean height of Ex.
sophomore students is 5’4’’. 1. a baker claims that his bread height is more than 15cm,
on average. Several of his customers do not believe him.
Ho: μ = 5’4’’ To persuade his customers that he is right, the baker
Ha: μ ≠ 5’4’’ decides to do a hypothesis test. The bakers known from
his baking hundreds of loaves of bread that the S.D for
D.R the height is 1.5cm and the distribution of heights is
Reject Ho: - Since we reject Ho, we have sufficient data normal. He makes 30 loaves of bread and finds that the
to say that the mean height of sophomore students is no mean height for the sample is 15cm. using alpha = 0.005,
equal 5’4’’ does this data provide evidence that the mean height is
more than 5cm?
Fail to reject Ho: Since we fail to reject Ho, we do not have
sufficient data to say that the mean height of sophomore Ho: μ ≤ 15 μx=15 n=30 alpha= 0.05
students is not 5’4’’ Ha: μ > 15 x=17 o=1.5
TYPES OF HYPOTHESIS TEST P Value:
1. One tailed (left, right tailed test) – increase or decrease 𝑥−𝜇 17−15
of a parameter. Z= 𝜎 = 1.5 = 7.303
- Left tailed (Ha: parameter < value) √𝑛 √30
- Right tailed (Ha: parameter > value)
2. Two tailed – looks for any change in the parameter.
Ex: Ho: p > 5 yrs
Ha: p < 5 yrs (LEFT TAILED TEST)
Assumptions
N < 30
Other samples
O is unknown
Sample comes from a normally distributed
population
IV. T TEST (STUDENT’S T TEST)
William S. Gosset
Characteristics:
Graph of t distribution is similar to the standard
normal curve; however, it has more probability in
its tails.
The graph of t distribution is thicker at the tails
and shorter at the center of the standard normal
distribution
Mean is 0 and is symmetric about 0.
Exact shape of the t distribution depends on the
degrees of freedom
As DF increases, graph of t distribution becomes
like the graph of a normal distribution.
𝑥−𝜇
Formula : , s – simple standard deviation
𝑠√𝑛
Df= n-1
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 1Document11 pagesHypothesis Testing 1Paris Azarcon TajanlangitNo ratings yet
- Section#7Document8 pagesSection#7Ahmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Hypothesis TestingDocument26 pagesWeek 6 - Hypothesis TestingFatma AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob - Q4 Week 4 - Module 12 Hilario GarciaDocument18 pagesStat and Prob - Q4 Week 4 - Module 12 Hilario Garciagabezarate071100% (1)
- Module 7 Hypothesis TestingDocument16 pagesModule 7 Hypothesis TestingShiela TenidoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 2 Hypothesis Testing CANVASDocument63 pagesMODULE 7 2 Hypothesis Testing CANVASMary Charlin BendañaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing - 1533369452Document49 pagesHypothesis Testing - 1533369452Nelly ChooNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument30 pagesHypothesis TestingNishikata ManipolNo ratings yet
- Statistics For College Students-Part 2Document43 pagesStatistics For College Students-Part 2Yeyen Patino100% (1)
- Section V Notes With Answers - PDF BDocument8 pagesSection V Notes With Answers - PDF BDeivid William TorresNo ratings yet
- Module 3b - One Sample Tests - Docx 1 PDFDocument12 pagesModule 3b - One Sample Tests - Docx 1 PDFSam Rae LimNo ratings yet
- Z TestDocument38 pagesZ Testlen100% (2)
- Lecture (Chapter 8) : Hypothesis Testing I: The One-Sample CaseDocument43 pagesLecture (Chapter 8) : Hypothesis Testing I: The One-Sample CaseMarvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 19Document6 pagesTutorial 19Dewi RahmasariNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Z-Test and T-TestDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing Z-Test and T-TestmochiNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Z-Test and T-TestDocument13 pagesHypothesis Testing Z-Test and T-TestmochiNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing (Lecture) PDFDocument50 pagesHypothesis Testing (Lecture) PDFSour Wolf50% (2)
- Hypothesis Testing 1,2 PPT 1Document30 pagesHypothesis Testing 1,2 PPT 1Said VarshikNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics Hypothesis TestingDocument42 pagesAdvanced Statistics Hypothesis TestingShermaine CachoNo ratings yet
- 4th Lesson 1Document58 pages4th Lesson 1Micha BenedictoNo ratings yet
- Z TestDocument29 pagesZ TestJhianne Estacoja0% (1)
- Test of Significance: Made By: 404 Tanushree D. 405 Swati Dhoke 406 Husain SaifyDocument16 pagesTest of Significance: Made By: 404 Tanushree D. 405 Swati Dhoke 406 Husain SaifyHusain SaifyNo ratings yet
- Inferential StatisticsDocument35 pagesInferential StatisticsxandercageNo ratings yet
- JAMOVI AND Basic StatisticsDocument28 pagesJAMOVI AND Basic StatisticsKyle RonquilloNo ratings yet
- 7b Z-TestDocument69 pages7b Z-Teststevegitoi39No ratings yet
- 8mmw Simple Test of Hypothesis Z TDocument11 pages8mmw Simple Test of Hypothesis Z TMarean BosquillosNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument4 pagesHypothesis TestingJan Darren D. CabreraNo ratings yet
- Testing HypothesisDocument41 pagesTesting HypothesisJean PampagNo ratings yet
- Tests of Hypothesis Single MeanDocument5 pagesTests of Hypothesis Single MeanMhar G-i SalalilaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing MBADocument39 pagesHypothesis Testing MBAaksabhishek88No ratings yet
- Eda Group5 Hypothesis TestingDocument32 pagesEda Group5 Hypothesis TestingKyohyunNo ratings yet
- 6-7. Chi Square Test, Goodness of FitDocument20 pages6-7. Chi Square Test, Goodness of Fittri ambar sariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Hypothesis TestDocument22 pagesChapter 6 Hypothesis TestManraz ManrazNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Autosaved)Document75 pagesStatistics (Autosaved)sabel sardillaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7Document26 pagesTopic 7Zienab AhmedNo ratings yet
- BIOSTAT Module 4 - Part 1Document44 pagesBIOSTAT Module 4 - Part 1Joddie LoplopNo ratings yet
- T-Distribution and T-Test AABR - Updated Fall 2019Document11 pagesT-Distribution and T-Test AABR - Updated Fall 2019Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: One Sample CasesDocument35 pagesHypothesis Testing: One Sample Casesdivya aryaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing-1,2Document22 pagesHypothesis Testing-1,2Said VarshikNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Hypothesis TestingDocument5 pagesBasic Concepts of Hypothesis Testingjudith matienzo100% (3)
- Lecture 7-Statistics DecisionsDocument43 pagesLecture 7-Statistics DecisionsAshraf SeragNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics On Hypothesis TestingDocument38 pagesInferential Statistics On Hypothesis TestingMark Kevin AguilarNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistic IDocument83 pagesInferential Statistic IThiviyashiniNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing22sept21Document68 pagesHypothesis Testing22sept21Charmalou Pampilo OgarteNo ratings yet
- Sparkling OneDocument7 pagesSparkling OneNorth StarNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Advance Statistics 2ND QuarterDocument11 pagesGrade 9 - Advance Statistics 2ND QuarterLeico Raieg B. SchuwardNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Test - 1Document27 pagesHypothesis Test - 1Shahadat HossainNo ratings yet
- Quantitative MethodsDocument3 pagesQuantitative MethodsOKbroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Hypothesis TestingDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Hypothesis Testingkidi mollaNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Powerpoint PresentationDocument6 pagesChi Square Powerpoint PresentationShaneNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing 15pagesDocument15 pagesHypothesis Testing 15pagesAravindan RNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module For 04-08-24Document14 pagesStatistics and Probability Module For 04-08-24Arcky Adrian BasilasNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing With T Tests Edited 1Document31 pagesHypothesis Testing With T Tests Edited 1Katharine MalaitNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Complete SlidesDocument54 pagesHypothesis Testing Complete Slidesghabel11No ratings yet
- Stastic Chap 6Document19 pagesStastic Chap 6nityaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Goodness of Fit and Contingency TableDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Goodness of Fit and Contingency TableberapiNo ratings yet
- Compare Means One Sample Cases: T-Test (Z-Test)Document42 pagesCompare Means One Sample Cases: T-Test (Z-Test)Frischa NataliaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Discrete Distribution - BinomialDocument20 pagesWeek 5 Discrete Distribution - BinomialkinsNo ratings yet
- Latin Square DesignDocument5 pagesLatin Square DesignDewi yermajuniTVNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document20 pagesWeek 5UMAIR JAVEDNo ratings yet
- hw5 PDFDocument3 pageshw5 PDFbenjy321No ratings yet
- Paul C. Shields The Ergodic Theory of Discrete Sample Paths Graduate Studies in Mathematics 13 1996Document259 pagesPaul C. Shields The Ergodic Theory of Discrete Sample Paths Graduate Studies in Mathematics 13 1996Yuval Dor100% (1)
- MEAN - Stats and ProbabilityDocument19 pagesMEAN - Stats and ProbabilityCharisse Buenaventura50% (2)
- MAS-01 Cost Behavior AnalysisDocument6 pagesMAS-01 Cost Behavior AnalysisPaupauNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis: Case Study 1: Dr. Kempthorne September 23, 2013Document22 pagesRegression Analysis: Case Study 1: Dr. Kempthorne September 23, 2013Esaú CMNo ratings yet
- Bayesian LearningDocument49 pagesBayesian Learning18R 368No ratings yet
- RMD-Assignment-2 - Group-4 PDFDocument7 pagesRMD-Assignment-2 - Group-4 PDFSanyam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Uji KebebasanDocument57 pagesUji KebebasanIrwan NilhamNo ratings yet
- 2018 Central Limit Theorem For TodayDocument2 pages2018 Central Limit Theorem For TodayBrendon SubhaneeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 QuestionsDocument4 pagesAssignment 4 QuestionsAmy ParkerNo ratings yet
- Cointegration R WorkshopDocument121 pagesCointegration R Workshopshal1nNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Multiple Choice Review Questions: 1.96 B) 1.645 C) 1.699 D) 0.90 E) 1.311Document5 pagesCh. 9 Multiple Choice Review Questions: 1.96 B) 1.645 C) 1.699 D) 0.90 E) 1.311payal khatriNo ratings yet
- Measurement TerminologyDocument3 pagesMeasurement TerminologyAbishaNo ratings yet
- J Model TestDocument3 pagesJ Model TestErika MacasNo ratings yet
- Stationary Stochastic Processes: Maria SandstenDocument24 pagesStationary Stochastic Processes: Maria SandstenganjeyNo ratings yet
- Six SigmaDocument92 pagesSix SigmaKamran MusaNo ratings yet
- StatProb Lesson 9Document28 pagesStatProb Lesson 9Lee HeeseungNo ratings yet
- 06control Chart 1Document37 pages06control Chart 1abishank09100% (1)
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledAnnie NguyenNo ratings yet
- MM Assignment Stochastic Programming and Applications2023Document22 pagesMM Assignment Stochastic Programming and Applications2023PHAN SONNo ratings yet
- (Oct. 13, Part 1) Individual Risk ModelDocument16 pages(Oct. 13, Part 1) Individual Risk Modelsetyo luthfiNo ratings yet
- Eda Presentation ContinuousDocument27 pagesEda Presentation Continuousjosel catubing (jcat)No ratings yet
- PS - Gtu PaperDocument3 pagesPS - Gtu Papersujal patelNo ratings yet
- Generalized Poisson Regression Models For Drop Out of Senior High School in East JavaDocument8 pagesGeneralized Poisson Regression Models For Drop Out of Senior High School in East Javalina izzahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Quiz ArchiveDocument4 pagesTutorial Quiz Archivesiti nadhirahNo ratings yet
- Robust Portfolio Optimization With CopulasDocument31 pagesRobust Portfolio Optimization With CopulasHiển HồNo ratings yet
- Kennedy A Guide To EconometricsDocument942 pagesKennedy A Guide To EconometricsJesús Treviño100% (2)