Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in 1D Short Note and Exercies Questions
Uploaded by
Yabisira ayeleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in 1D Short Note and Exercies Questions
Uploaded by
Yabisira ayeleCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethio-Physics
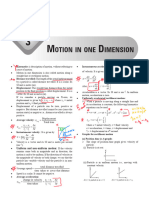
UNIT - 2
Motion in a straight line
✓ Motion: Is the continuous change in position of a moving body, with respect to some
frame of reference.
Uniform motion
✓ Uniform motion: is the motion of a body with steady speed in a straight line.
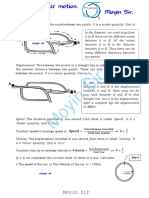
✓ Distance (S): Is the actual path length travelled by a moving body.
• Distance is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is meter (m).
✓ Displacement (S): Is the shortest path length covered by a body between two points.
• Displacement is a vector quantity and its SI unit is meter (m).
✓ Speed (V): Is distance travelled by a moving body divided by the time taken.
That is, speed = distance travelled V= S
time taken t
✓ Speed is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is m/s.
✓ Average speed: Is the total distance travelled by a moving body divided by the total
time taken.
Average speed = Total distance travelled
Total time taken
Vav = ST
tT
✓ Velocity (V): Is displacement of the moving body divided by the time taken.
✓ That is, velocity = displacement V= S
time taken t
✓ Velocity is a vector quantity and its SI unit is m/s. 1m/s = 3.6 km/hr0tc0
✓ Instantaneous speed is the speed of a body at a given instant of time or particular
position.
✓ Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of a body at a given instant of time or particular
position.
Exercise 1
1. A car moves 8 km due East and then 6 km due North, if it takes 2 hours to cover the
trip. Find, a) The speed
b) The velocity of the car
2. A boy runs at 10 m/s for 4 sec, then walks at 8 m/s for 6 sec and rides a bicycle at 20
m/s for 12 sec. What is the average speed of the boy for the-entire trip?
3. A moving object increases its velocity uniformly from 20 m/s to 40 m/s in 2 min.
What is; a) Average velocity
b) Displacement of the object during the 2 min.
4. A car travels up a hill at a constant speed of 40km/h and returns down the hill at a
constant speed of 60 km/h. Calculate the average speed for the round trip.
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 1
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
Uniformly accelerated motion
✓ Acceleration (a) is the time rate of change of velocity.
✓ Uniformly accelerated motion is motion of an object along a straight line with a constant
increase in its velocity.
✓ Motion of a freely falling body is the natural example of a uniformly accelerated rectilinear
motion.
✓ Acceleration is vector and its unit is m/s2.
Acceleration= Change in velocity
Time taken
a = ∆V = Vf-Vi
t t
Exercise 2
1. A car started from rest and moves at 90 km/h in 20 seconds, find the acceleration of the car.
2. A car travelling at 4 m/s towards west accelerates uniformly at a rate of 3 m/s2 for 3 seconds.
What is the velocity of the car after 3 seconds?
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 2
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
✓ Representation of Uniform Motion and Uniformly Accelerated Motion Using Graphs
Table Representation of Uniform Motion and Uniformly Accelerated Motion Using Graphs
Uniform Motion Uniformly Accelerated Motion
V vs t V vs t
V V
V is constant V is change uniformly
t t
✓The slope of V vs. t graph is acceleration (a). ✓The slope of V vs. t graph is acceleration
m = ∆y = ∆V = a = 0 (a).
∆x ∆t m = ∆y = ∆V = a
✓The area under V vs. t graph is distance ∆x ∆t
(displacement). ✓The area under V vs. t graph is distance
A= l x w = v x t= s (displacement).
A= ½bh = ½v x t= s = ½a x t2
S vs t S vs t
S S
V is constant
t t
✓The slope of S vs. t graph is speed (velocity). ✓The slope of S vs. t graph is speed
m = ∆y = ∆S = V (velocity).
∆x ∆t m = ∆y = ∆S = V
∆x ∆t
a vs t a vs t
a a
a= 0m/s2 since V is constant (∆V=0) a is constant
t t
Equations Of Uniformly Accelerated Motion
➢ The five basic equations of U.A.M
➢ V = u + at where S= displacement
➢ S= ½ (u+v)t V= final Velocity
➢ S= ut + ½at 2 U = initial Velocity
➢ V2 = u2 + 2as a= acceleration
➢ S = Vt – ½ at 2 t = time
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 3
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
E.g.1. A cheetah accelerates at 3m/s2 for 5s. if its final velocity is 24m/s, determine its
initial velocity?
E.g.2 A runner in area decides to accelerate right up to the moment he crosses the line. He
is initially travelling at 5m/s and accelerates at 0.4m/s2 for 5s. Find
A) The distance from the line when he decides to accelerates.
B) His final velocity at he crosses the line.
E.g.3. An athlete running at a constant rate of 4m/s2 each second covered a distance of
100m, starting from rest. How fast the athlete running at the end of the 100m?
Free fall
✓ Free fall is a kind of motion where the 𝑎⃗ of the object is just due to the acceleration due to
gravity. When an object accelerates under gravity is call free fall.
✓ Free fall is the motion of a body under the influence of gravity alone.
✓ Gravity the force of attraction between an object in the earth’s gravitational field & the
earth itself.
✓ In the absence of air resistance, all bodies fall with the same acceleration regardless of
their mass. i.e. 𝑔⃗ = 9.81 m/s2
✓ Free fall is an example of U.A.M. and we use the same formula.
➢ For a body dropped from some height => U = 0, S = h, a = g
➢ For a body thrown upward => V = 0, a = -g, s =h
E.g. 1 A ball dropped from a height of 4m.
a) How long would it take to hit the ground?
b) what is its final velocity?
E.g. 2 A ball is kicked upwards with an initial 𝑉 ⃗⃗ of 20m/s from the ground How long will it
take the ball to return to its initial position? (Use g = 10m/s
Relative Velocity
✓ Reference from a point from with measurements are taken.
✓ A form of reference refers to a certain point of view observer is stationary or moving at
a Constance velocity.
✓ The laws of motion only apply if the reference from of the observer is stationary or
moving at a constant velocity.
✓ The velocity of an object depends on the frame of reference of the observer.
✓ Relative velocity is the difference between the velocities of two moving objects.
✓ Relative velocity is the velocity of a body with respect to other body.
VRab = Va – Vb ………… if they have the same direction
VRab = Va + Vb …………...if they are moving in opposite direction.
Where VRab – Relative velocity of body A with respect to B
Va – Velocity of body A
Vb - Velocity of body B
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 4
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
Exercise 1
Choose the correct answer from the given alternatives.
1. Which one of the following is correct?
A. Average speed and average velocity are the same.
B. There is no difference between uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion.
C. Acceleration is the rate of change of speed.
D. Uniformly accelerated motion is a motion with constant acceleration.
2. If a moving body covers equal distances with equal time interval its motion is termed as
A. accelerated motion C. uniformly accelerated motion
B. uniform motion D. vibration motion
3. In a uniformly accelerated motion,
A. velocity changes equally in equal time intervals C. acceleration is zero
B. acceleration changes equally in equal time intervals D. velocity is constant
4. If a body moves a distance of 100m in 10 sec, what is the average speed of the body?
A. 10m/sec B. 15m/sec C. 20m/sec D. 25m/sec
5. Which one of the following defines the average acceleration?
A. it is the displacement per unit time
B. distance moved double the time taken
C. it is the change in velocity by the time taken
D. is the product of displacement and speed
6. A car is travelling from Addis Ababa to Adama. It travelled 51 km in the first one hour
and 49 km in the second one hour. What is the average speed of the car?
A. 22.5 km/h B. 25 km/h C. 25.5 km/h D. 50 km/h
7. Which of the following is an example of uniform motion?
A. Motion of an insect around a light bulb
B. A falling body in a straight line
C. Motion of a car in a flat ground with curved path
D. A car moving with constant velocity
8. Which of the following is correct about velocity? It is
A. speed with direction C. scalar quantity
B. acceleration with direction D. speed with no direction
9. The quantity that describes how fast you are going between two positions without
regard for direction is known as _______
A. velocity B. speed C. displacement D. acceleration
10. Which of the following is TRUE about uniform motions? It is
A. a motion with the same nonzero acceleration C. a motion with zero speed
B. a motion with the same nonzero speed D. a motion with increasing acceleration
11. Which one of the following graphs best describes a uniformly accelerated motion?
A. C.
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 5
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
B. D.
12. From the v-t graph above which part of the path of the graph shows uniform motion?
A. A to B B. B to C C. C to D D. D to E
13. A player run and moves with constant speed through the points A, B, x, y, P, Q, R and
S as shown in the diagram. Which of these pairs of points has the player run with
constant velocity?
A. A→B, x→y B. A→B, P→Q C. x→y, R→S D. P→Q, R→S
14. The acceleration of a moving body can be calculated from _____.
A. the area of v vs t graph C. the area of s vs t graph
B. the slope of s vs t graph D. the slope of v vs t graph
15. The graph below shows uniformly accelerated motion of a body in a straight line. What
is the acceleration of the body?
A. 10 m/s2 B. 5 m/s C. 5 m/s2 D. 15 m/s
16. The motion of a car is indicated by the following s vs t graph. What is the speed of the car?
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 6
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
A. 5 m/s B. 10 m/s C. 20 m/s D. 40 m/s
17. Which one of the following is correct about displacement-time (s-t) and velocity-time
(v-t) graphs of motion?
A. The slope of s-t graph is equal to acceleration.
B. The slope of s-t graph is equal to distance.
C. The slope of s-t graph is equal to velocity.
D. The slope of s-t graph is equal to deceleration.
18. The area under velocity-time (v-t) graphs equals to the
A. acceleration of a body C. time of a body
B. displacement of a body D. velocity of a body
19. Consider the v against t graph shown below, what is the total distance covered in 4 seconds?
A. 10 m B. 30 m C. 35 m D. 40 m
20. The area under the acceleration versus time graph gives the change in _____.
A. Acceleration B. Displacement C. Distance D. Velocity
21. Almaz has drawn v-t graph of a moving car as shown below. What is the distance
travelled by the car?
A. 350 m B. 500 m C. 550 m D. 850 m
22. Referring to the V − t graph shown below what is the acceleration and the distance
covered in 5 seconds?
⃗⃗ (m/s)
𝑉 A. 4m/s2 and 25m/s
B. 4m/s2 and 37.5m/s
20 C. 3m/s2 and 62.5m/s
15 D. 5m/s2 and 100m/s
10
5
1 5 6 t(sec)
2 3 4
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 7
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
23. Two cars moving in the same direction have velocities of 20m/s and 25m/s. What is
the relative velocity of the faster car?
A. 45m/s B. 5m/s C. 40m/s D. 15m/s
24. A body initially at rest accelerates at a rate of 4 𝑚/𝑠 . How long will it take the body
2
to travel 200m?
A. 100 sec B. 10sec C. 50sec D. 25sec
25. A ball dropped from a bridge strikes the ground in 5 sec. What is the height of the
bridge? (Use g = 10 𝑚/𝑠 2 )
A. 250 sec B. 125 sec C. 500 sec D. 50 m/s
Join
Telegram: https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
YouTube: Https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpCfqdYZxW3bzzq7xcDrrLA
“Life is like riding a bicycle. To
keep your balance, you must
keep moving!!!”
Albert Einstein
Grade 9 Unit 2 Motion in one-dimension short note and Exercises Page 8
@https://t.me/ethiophysicsgrade7upto12
You might also like
- Grade 7 Unit 2 Motion Short Note and Exercies QuestionsDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Unit 2 Motion Short Note and Exercies QuestionsYabisira ayeleNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chap 2 One D Motion FreefallDocument62 pagesLecture Chap 2 One D Motion FreefallMercy Adato GerailloNo ratings yet
- What About This???: Which One Is False?Document50 pagesWhat About This???: Which One Is False?Eng-Mahamed Dayib NourNo ratings yet
- ME100-Kinematics of A ParticleDocument18 pagesME100-Kinematics of A ParticleMuhammad NabeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Kinematics of ParticlesDocument34 pagesChapter 1 Kinematics of Particleshaidanial699No ratings yet
- 3-Kinematics - NotesDocument10 pages3-Kinematics - Notesnabiha137100% (1)
- Motion in A Straight Line NotesDocument15 pagesMotion in A Straight Line NotesbetsyNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument4 pagesKinematicshavertz291aNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: Chapter - 02Document15 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: Chapter - 02Raichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Week 3Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Week 3Levi AckermanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Document21 pagesLesson 2 - Kinematics Part 1Jonathan VillapanaNo ratings yet
- Physics 7Document12 pagesPhysics 7Raymond De AsisNo ratings yet
- Kinematics E 2018Document52 pagesKinematics E 2018sundararevathyhdNo ratings yet
- Kinematis 1 DDocument13 pagesKinematis 1 Dmeragaon456No ratings yet
- Inbound 2904806781622511170Document26 pagesInbound 2904806781622511170keepersilent2No ratings yet
- Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1 - 12.2)Document15 pagesIntroduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1 - 12.2)Mohamed DamraNo ratings yet
- 2 - Particle KinematicsDocument25 pages2 - Particle KinematicsAbdallah HassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: Continuous Motion: Today's ObjectivesDocument17 pagesIntroduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: Continuous Motion: Today's Objectivesجعفر السلطانNo ratings yet
- Dynamics PPT 1Document13 pagesDynamics PPT 1qurriyatus zahroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-KinematicsDocument57 pagesChapter 2-Kinematicsraie saadNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Mechanics Lecture Notes 2 For StudentsDocument27 pagesIntroduction of Mechanics Lecture Notes 2 For StudentsjianghuiNo ratings yet
- Kinema TikDocument29 pagesKinema TikZinger IqraNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line: Distance and DisplacementDocument10 pagesMotion in A Straight Line: Distance and DisplacementZeroNo ratings yet
- JEE Knockout - Kinematics - 13th MarchDocument94 pagesJEE Knockout - Kinematics - 13th MarchPrinanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics chp1 BlackboardDocument19 pagesDynamics chp1 BlackboarddmjkfloridaNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Kinematics - HibblerDocument547 pagesRectilinear Kinematics - HibblerJoeNo ratings yet
- Physics As NotesDocument28 pagesPhysics As NotesShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Kinematics I (With Answers)Document11 pagesCh1 Kinematics I (With Answers)ArborgerNo ratings yet
- The Branch of Mechanics That Studies The Motion of A Body Without Caring About What Caused The MotionDocument56 pagesThe Branch of Mechanics That Studies The Motion of A Body Without Caring About What Caused The MotionNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Particles: Contact: 9029006464Document42 pagesKinematics of Particles: Contact: 9029006464ravi maskeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1. Introduction To DynamicsDocument12 pagesMODULE 1. Introduction To DynamicsAron H Ocampo100% (1)
- LC 3 - KinematicsDocument7 pagesLC 3 - KinematicsSarah GanganNo ratings yet
- Share '1. Physics (1) .PPT'Document216 pagesShare '1. Physics (1) .PPT'Joanna BinanNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension 2Document3 pagesMotion in One Dimension 2Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document46 pagesChapter 02Gio PelobilloNo ratings yet
- Kinematics SummaryDocument4 pagesKinematics SummaryVoyce Xavier PehNo ratings yet
- Motion Along One Dimensions - Motion Under GravityDocument29 pagesMotion Along One Dimensions - Motion Under GravityVidanage CharithaNo ratings yet
- Ch02 Homework AnswersDocument114 pagesCh02 Homework Answersochori1No ratings yet
- Phy Sci Lesson 8Document9 pagesPhy Sci Lesson 8Raulene MoloNo ratings yet
- Kinematics For PDFDocument20 pagesKinematics For PDFjalanhello71No ratings yet
- Dynamics - Kinematics 1 PDFDocument11 pagesDynamics - Kinematics 1 PDFChuck Dave DiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 KinematicsDocument49 pagesChapter-2 KinematicsAgustinus Aldi Irawan RahardjaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics - Kinematics 1 PDFDocument11 pagesDynamics - Kinematics 1 PDFChuck Dave DiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 6 Linear MotionDocument16 pagesChapter No. 6 Linear Motionravi maskeNo ratings yet
- Physics Lecture Notes: 1.1 Linear MotionDocument7 pagesPhysics Lecture Notes: 1.1 Linear Motionben10uzi100% (1)
- Ch02 ISMDocument116 pagesCh02 ISMphyseek01No ratings yet
- Chap 02 SMDocument116 pagesChap 02 SMCarla MedeirosNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument75 pagesKinematicsKunj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive - Plus One Chapter 2 - 2024Document9 pagesHsslive - Plus One Chapter 2 - 2024ritheshparas39No ratings yet
- 1-D MotionDocument71 pages1-D Motionsara fekriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Kinematics of Particle Rectilinear TranslationDocument33 pagesLecture 1 Kinematics of Particle Rectilinear TranslationKRISTINE MIRANDANo ratings yet
- MF006 Lecture 3 - Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Document34 pagesMF006 Lecture 3 - Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- 3rd WeekDocument7 pages3rd WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument13 pagesLinear Motiondevil's queenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PhysicDocument11 pagesChapter 2 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: in This ChapterDocument22 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: in This ChapterZiya Can OğuzNo ratings yet
- PDF - Chapter 1 - Particle Kinematic - BMCG - FullDocument92 pagesPDF - Chapter 1 - Particle Kinematic - BMCG - FullTakip MatNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- QB PSC Unit-IDocument4 pagesQB PSC Unit-IManigandan PriyaNo ratings yet
- Chap 23 64 Regular PhysicsDocument395 pagesChap 23 64 Regular Physicsmatthew_schreiber_2No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics PracticalDocument9 pagesBasic Electronics Practicalasfadare100% (2)
- Proton 200 220 WebDocument2 pagesProton 200 220 WebLUIS CORDOVA ZANCHESNo ratings yet
- Relative VelocityDocument7 pagesRelative VelocityJanaka Priyalal100% (3)
- Degenrate Fermi GasDocument15 pagesDegenrate Fermi GasArjun IyerNo ratings yet
- Thermal BucklingDocument11 pagesThermal BucklingAnonymous wWOWz9UnWNo ratings yet
- Piping Engineering Design GuideDocument255 pagesPiping Engineering Design GuideSandi Aslan80% (5)
- Waves and Sound Waves PDFDocument11 pagesWaves and Sound Waves PDFSanatan KumarNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Laser Experiment Lab ReportDocument11 pagesSemiconductor Laser Experiment Lab ReportSeema ChahalNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1Kuo Garol SarongNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions Manual 1Document67 pagesLinear Algebra With Applications 2nd Edition Holt Solutions Manual 1leon100% (50)
- Osram Light For Cine Projection Technology & Science Catalog 1979Document52 pagesOsram Light For Cine Projection Technology & Science Catalog 1979Alan Masters100% (1)
- 1212441515electricity WorksheetsDocument6 pages1212441515electricity Worksheetsaayush619_com3918No ratings yet
- Electric Current and Magnetic FieldDocument9 pagesElectric Current and Magnetic Fieldjob embalsadoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 22010 IbDocument16 pagesDynamics 22010 IbAshwin DanielNo ratings yet
- Space Physics NotesDocument30 pagesSpace Physics Notesfgthy100% (1)
- Effective ApertureDocument10 pagesEffective ApertureLeo HambirepiNo ratings yet
- Slinky Narrative ReportDocument2 pagesSlinky Narrative ReportJonathanNo ratings yet
- Calculations of The Exchange Current Density For Hydrogen Electrode Reactions PDFDocument6 pagesCalculations of The Exchange Current Density For Hydrogen Electrode Reactions PDFVandam65No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 1 PDFNama Desalew100% (1)
- Laminar and Turbulent in Pipe-2 PDFDocument20 pagesLaminar and Turbulent in Pipe-2 PDFBoos yousufNo ratings yet
- Dark Energy DissertationDocument7 pagesDark Energy DissertationBestPaperWritingServiceUK100% (1)
- Investigatory ProjectDocument10 pagesInvestigatory Projecttanmay100% (1)
- Final ProjectDocument4 pagesFinal ProjectChacho BacoaNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 4Document2 pagesPhysics Assignment 4happyworryNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell HandbookDocument18 pagesFuel Cell HandbookDiego AranibarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry XI Guess PapersDocument37 pagesChemistry XI Guess PapersAliLakhoNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Chapter 23 MagnetismDocument30 pagesGlencoe Chapter 23 MagnetismdioNo ratings yet
- Viscoelastic BehaviourDocument27 pagesViscoelastic BehaviourMD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet