Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Health Education Reviewer (Midterm)
Uploaded by
Carrie Anne Aquila GarciaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Health Education Reviewer (Midterm)
Uploaded by
Carrie Anne Aquila GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
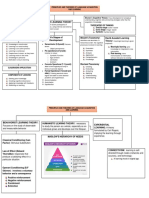
HEALTH EDUCATION REVIEWER Reinforcement or unpleasant stimulus
(Midterms) Escape Conditioning Aversive stimulus is
applied, organism
PART I makes a response that
Learning Theories causes unpleasant
Learning stimulus to cease
-defined as a relatively permanent change in Avoidance Anticipated by the
mental processing, emotional functioning, skill Conditioning organism
and/or behavior as a result of exposure to different Non-reinforcement No action
experiences. Punishment Aversive stimulus that
-lifelong dynamic process by which individuals is applied that an
acquire new knowledge or skills that alter their organism cannot avoid
feelings, attitudes, and actions or escape
Learning Theory Cognitive Learning Theory
-coherent framework of integrated constructs and o Jean Piaget
principles that describe, explain, or predict how o One concern in the CLT is that it
people learn.
neglects emotions
o Involves perceiving the information,
PSYCHOLOGICAL LEARNING THEORIES
interpreting it based on what is
Behaviorist Learning Theory
already known, and reorganizing the
o Directly Observable and a product of
information into new insights or
(S) Stimulus and (R) Response understanding
conditioning o METACOGNITION- understanding
o Respondent Conditioning
the way of learning
(association learning, classical o Gestalt Perspective- emphasizes
conditioning, Pavlovian
the importance of perception in
Conditioning)
learning and lays the groundwork for
Emphasizes the importance
various other cognitive perspectives
of stimulus conditions and
o Information Processing-
the associations formed in
emphasizes the thinking process,
the learning process
thought, reasoning, and memory
Systematic Desensitization
function
o Technique used by psychologists o
o Cognitive Development-
reduce fear and anxiety
perspective on learning that focuses
o Has been use to treat drug
on qualitative changes in perceiving,
addiction, phobias, and tension thinking, and reasoning
headaches
Stimulus Generalization Social Learning Theory
o Tendency of initial learning o Largely based on the work of Albert
experiences to be easily applies to Bandura
other similar stimuli o Individuals must have a direct
Discrimination Learning experience to learn by watching
o Can differentiate the methods and other people
the environment o Significant others have a huge
Spontaneous Recovery impact on the learning
o Useful respondent concept that o Role Modeling- central concept of
needs to be given careful social learning theory
consideration in relapse prevention o Vicarious reinforcement-
programs. determinant whether role models are
rewarded of punished
Operant Conditioning o MODEL OF SLT
o Developed by B.F. Skinner Attentional Phase-Retention
o Focuses on the behavior of the Phase-Reproduction Phase-
organisms and the reinforcement Motivational Phase
that occurs after the response Psychodynamic Learning Theory
Reinforcer- stimulus or event o Stresses on theory of motivation that
applied after a response stresses on emotions rather than
strengthens the probability cognitions or responses
that the response will be o Based on Sigmund Freud
performed again
o Behavior may be conscious or
Positive Reinforcement Application of a
unconscious
pleasant stimulus
o Primitive source of motivation is
Reward Conditioning Pleasant stimulus is
libidinal energy (instincts) id: eros
applied following an
(pleasure and sex; life force) &
organism’s response
Negative Removal of an aversive
Thanatos (aggressive and 1. Learning Needs- what the learner needs
destructive impulses; death wish) and wants to learn
o Defense Mechanisms- activated 2. Readiness to learn- when the learner is
when ego is threatened receptive to learning
Intellectualization Avoiding any emotion 3. Learning Style- how the learner best learns
Displacement Aggression towards
another ASSESSING LEARNING NEEDS
Regression Returning to early (a) Learning Needs
maturity -gaps in knowledge that exist between a
Denial Ignoring desired level of performance and actual
Projection Reflecting one’s level of performance
mistake to others o Important steps in the assessment of
Reaction Formation Opposite of what they the learning needs:
really felt 1. Identify the learner
Sublimation Converting to socially 2. Choose the right setting
accepted action 3. Collect data about the learner
Compensation Making up 4. Collect data from the learner
weaknesses by 5. Involve members of the
excelling in other healthcare team
areas 6. Prioritize needs
Rationalization Excusing
Repression Keeping Criteria for prioritizing
unacceptable learning needs:
thoughts from Mandatory- for
conscious awareness survival or situations
for life and safety
o Erikson’s Stages of Life Desirable- not life
o Resistance- indicator of underlying dependent but related
to overall well being
emotional difficulties, which must be
dealt with for them to move ahead Possible- nice to
know but not required
o Humanistic Learning Theory
7. Determine availability of
o Every individual is unique and has a
educational resources
need to grow in a positive way
8. Assess the demands of the
o Highly motivational for the reason
organization
that they are influenced by society 9. Take time management issues
o Subjective desire to grow into account
o Abraham Maslow- major contributor
in the HLT with the hierarchy or METHODS TO ASSESS LEARNING NEEDS
needs 1. Informal Conversations
o Carl Rogers- argues that people 2. Structured Interviews
want unconditional positive self- 3. Focus Groups
regard (love without strings 4. Questionnaires
attached) 5. Tests
o Rather that being an AUTHORITY, 6. Observations
be a FACILITATOR 7. Documentation
PART II READINESS TO LEARN
Determinants of Learning Readiness to learn
(1) Needs of the Learner -time when the learner demonstrates an interest in
(2) State of readiness to learn learning the information necessary to maintain
(3) Preferred learning styles optimal health or to become skillful in a job
-occurs when the learner is receptive, willing, and
CHARACTERISTICS OF A LEARNER able to participate in the learning process.
o Age
o Education Level PEEK Scheme
o Culture and language P= Physical Readiness
o Learning Style o Measures of Ability
o Health Literacy o Complexity of Task
o Motivation o Gender
o Health Status o Environmental Effects
o Health Status
ASSESSMENT OF THE LEARNER E= Emotional Readiness
Assessment of the learner includes o Anxiety Level
attending to three determinants of learning Fear is a major contributor in
(Haggard, 1989): anxiety
o Support System
Social support is important in
buffering the effects of
stressful events
Reachable moments- time
when a nurse truly connects
with the client by directly
meeting the individual TEACHING METHODS AND SETTINGS
o Motivation Teaching Method
o Risk Taking Behavior -way information is taught that brings the learner
o Frame of Mind into contact to what is being learned
o Developmental Stage
Teachable moment (a) Lecture
E=Experiential Readiness -Highly structured method by which the
o Level of Aspiration educator verbally transmits information
directly to a group of learners
o Past Coping Mechanism
-came from the latin word legere “to read”
o Cultural Background
-Five approaches to an effective lecture:
o Locus of Control
Use opening and summary
o Internal Locus of Control statements
o External Locus of Control Present Key terms
K=Knowledge Readiness Offer examples
o Present Knowledge Base Use analogies
o Level of Cognitive Ability Use visual backups
o Existence of any Learning Disabilities -three main parts of a lecture:
o Preferred Style of Learning a. Introduction
b. Body
LEARNING STYLES c. Conclusion
-refers to the ways in which and conditions under -variables of speech:
which the learners most efficiently and most a. volume
effectively perceive, process, store, and recall b rate
-Cognitive, Affective, Physiological Factors c. pitch/tone
d. pronunciation
Right-Brain/ Left-Brain/ Whole Brain Thinking e. enunciation
o Left Brain is for the verbalization and f. proper grammar
analytical side. Reality based and logical g. avoiding annoying habits such the
thinking. use of “ums”
Convergent -Body language:
o Right Brain is for the emotional, visual- a. Enthusiasm
spatial, and non-verbal side b. Frequent Eye contact
Divergent c. Posture movement
o Corpus Callosum- connector between the d. Gestures
two brains Distance Learning- an ideal way to
maximize resources an to transmit current
FIELD INDEPENDENT information to people separated by space
Have internalized frames of reference such and time
as they experience themselves as separate
or differentiated from others and the (b) Group Discussion
environment -defined as the method of teaching whereby
Less sensitive to social cues learners get together to actively exchange
Not affected by criticisms information, feelings, and opinions with one
Eager to test their ideas another and educator
-Group Size: major consideration and
FIELD DEPENDENT should be determined by the purpose or
Externally focused and are socially oriented task to be accomplished
More dependent on others for reinforcement
(c) Team based learning
DUNN AND DUNN LEARNING STYLES -enriches the students’ learning experience
1. Environmental elements through active learning strategies
2. Emotional elements -formation of heterogenous groups of 5-10
3. Sociological Patterns students
4. Physical elements
5. Psychological elements (d) Cooperative Learning
-methodology of choice for transmitting
foundational knowledge
(e) Case Studies
-Lead to the development of analytical and c. Physiological Variables
problem-solving skills, exploration of d. Environmental Variables
complex issues, and application of new e. Educator-Learner Relationship System
knowledge and skills in clinical practice f. Experiential Variables
arena
(f) Seminars
-consists of several sessions in which group Asynchronous
of staff nurses or students facilitated, -allows users to work in concert with one another
discuss questions and issues that arise from but not necessarily simultaneously
readings
Traditional Learning
(g) One to One Instruction I. Lecturing
-may be given formally or informally, -conveying of facts, information, and ideas that
involves face to face delivery of information would not be readily obtained elsewhere.
specifically designed to meet the needs of Parker’s loss of novel stimulation (1993)
the individual learner -people are engaged in the first times, but
they become immune to it.
(h) Simulation
-a trial and error method of teaching LECTURE FRAMEWORKS
whereby an artificial experience is created (1) Hierarchal or classical format
that engages the learner in an activity that -info. is grouped; simplest form of lecture
reflects real life conditions but without risk-
taking consequences of an actual situation (2) Problem-centered format
-Simulation is a technique and not -problem is introduced and varied
technology hypothesis are created
o Types of simulations: (3) Comparative framework
Written Simulations -objective is to differentiate to identities
Clinical Simulations
Model Simulations (4) Thesis format
Computer Simulations -taking a side and then justifying with logic
DELIVERY OF THE LECTURE
COMPLIANCE, MOTIVATION, AND HEALTH (1) Controlling anxiety
BEHAVIORS OF THE LEARNER (2) Spontaneity
Compliance (3) Voice Quality
-defined as the “extent to which the patient’s (4) Body Language
behavior coincides with the clinical advice (5) Speed of Delivery
-act or process of complying to a desire, demand, (6) Getting off on the right foot
proposal, or regimen (7) Clarifying during the lecture
-It has an authoritative undertone (8) Facilitating retrieval from memory:
-Healthcare provider is seen as the authority a. Repetition
b. Elaboration
Adherence c. Imagery
-extent to which a person’s behavior corresponds
with the agreed recommendations from a health II. Discussion
care provider -talk between two or more people about a subject,
-steady or faithful attachment usually the exchange of ideas to reach a
conclusion.
Perspectives on Compliance
1. Biomedical Theory- depends on the TYPES OF DISCUSSIONS
client’s medication, demographics, severity (1) Formal Discussion
of disease -topic is announced in advance and ask the
2. Behavioral/Social Learning Theory- on class to prepare
the motivation
3. Communication Models- communication (2) Informal Discussion
between patient and health care provider -takes place at the end of the class
4. Rational Belief Theory- cost benefit
analysis III. Questioning
5. Self-regulatory systems- patient is seen -strategy of which the origin if traced way back from
as a problem solver Socrates in which every question of a student is
6. answered with a question
LEON POINTS TO PONDER
LEVELS OF QUESTIONS:
ASSESSMENT OF MOTIVATION (1) Convergent or Divergent
a. Cognitive Variable Convergent Questions
b. Affective Variables
o Require learners to recall or
integrate information they have Virtual Reality
learned; short expected answers -computer based simulate three dimensional
environment in which interaction happens in the
Divergent Questions virtual world
o Asks the learner to generate new
ideas and to form a new perspective Distance Learning
-is a type of learning that studies from a distance
(2) Lower order or Higher order of questioning but still has communication likened to a classroom
Lower Order setting
o Require learners to recall info.
a. Synchronous Class- interact in real time
Higher Order electronically via the internet
o Have to think critically b. Asynchronous Class- materials and
prescribed activities are located on a web
(3) Bloom’s Taxonomy page that can be accessed anytime at the
-qs that elicit levels of knowledge, learner’s convenience
comprehension, application, analysis,
synthesis, and evaluation Teaching Psychomotor Skills
-are action-oriented that requires neuromuscular
TYPES OF QUESTIONING coordination and that promote patient healing and
1. Factual Questions comfort
2. Probing Questions
a. Extension Probes Stage 1: Getting the ideas of the movement
b. Clarification -initial step is to have a goal.
c. Justification
d. Prompting Regulatory Stimuli- conditions that influence
e. Redirection the performance
3. Multiple Choice Questions Non regulatory Stimuli- does not influence
4. Open Ended questions the performance
5. Discussion-Stimulating Questions Open Skill- performance in changing
conditions
IV. Using Audiovisuals Closed Skill- performance in non-changing
-address all three modes of learning: conditions
cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.
Motor Plan
TYPES OF TRADITIONAL -learner studies to choose the right action to takes
AUDIOVISUALS: or movement that is necessary
a. Handouts-communicates facts,
figures, and concepts; ensures Stage 2: Fixation/Diversification
that everyone has the same -if the performance is successful, this is the next
information stage
b. Chalkboards and Whiteboards-
writing on only 2/3 of the board Fixation- practicing the skill in the same way
and allowable for math, spelling, to fix a reproducible
and new material Diversification- practicing the skill in a
c. Overhead Transparencies - variety of ways so it can be reproduced in a
sheets and acetates placed on modified way to meet changing
overhead projector that enlarges environments
ad projects the image onto a
screen Feedback
d. Videotapes- used to film -may be extrinsic or intrinsic
students while they role play,
interview, communicate and Intrinsic Feedback- originates with the
counsel; motion enhances the learner
realism of the situation Extrinsic Feedback- supplied by the teacher
e. Digital Video/Versatile Discs and other sources
(DVDs)- smaller and portable
than videotapes Practice
-motor pattern that is practiced and refined as the
Activity Based Learning learner attempts to reach an adequate skill level
-essential in order to fix the sequential order of
Case Study movements in the learner’s memory
-analysis of an incident or situation in which
characters and relationships are described, factual, Massed Practice
or hypothetical events transpire, and problems -practice that has no rest or little intervals
need to be resolved.
-Started in Harvard School
Distributed Practice
-planned rest periods that are longer or equal to the
trial
Mental Practice
-known as mental imagery, mental rehearsal,
guided imagery and visualization
Haggard, 1989 stated the determinants of learning
1. Learning needs—what the learner
needs and wants to learn.
2. Readiness to learn—when the learner
is receptive to learning.
3. Learning style—how the learner
best learns
Lewin, 1935
-an early field theorist, conceptualized motivation
in terms of positive or negative movement toward
goals. Once an individual’s equilibrium is
disturbed, such as in the case of illness, forces of
approach and avoidance may come into play.
Lewin noted that if avoidance endured in an
approach–avoidance conflict, there would be
negative movement away from a goal. His theory
implies the existence of a critical time factor
relative to motivation. This time factor, however, is
generally not a serious consideration in
motivational models of health behavior or
motivational research.
You might also like
- Learning Theories Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesLearning Theories Lecture NotesHerme BorladoNo ratings yet
- Psychological Learning TheoriesDocument10 pagesPsychological Learning TheoriesJeru Margareth TingsonNo ratings yet
- 1h.ed Principles Theories Learning TeachingDocument24 pages1h.ed Principles Theories Learning TeachingZen Gesner Kenneth G. EganaNo ratings yet
- Ob presentationDocument28 pagesOb presentationAbhinayaa SharmaNo ratings yet
- He Principles Theories in Teaching Learning NOTESDocument5 pagesHe Principles Theories in Teaching Learning NOTESAriane NobleNo ratings yet
- Report in Psycho SocialDocument5 pagesReport in Psycho SocialJay-r Perez LabradorNo ratings yet
- Renz Morales Module 4Document20 pagesRenz Morales Module 4Renz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Matrix - San Juan, Aprel P.Document5 pagesLearning Theories Matrix - San Juan, Aprel P.Aprel SJNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressDocument31 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressGlory Mae ProllesNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development Principles of TeachingDocument20 pagesCurriculum Development Principles of TeachingMichelle GravitoNo ratings yet
- Uts FinalsDocument3 pagesUts FinalsMORALES, V.No ratings yet
- Summarize The Five (5) Learning Theories and Their Impacts To EPP Teaching Using The Table BelowDocument4 pagesSummarize The Five (5) Learning Theories and Their Impacts To EPP Teaching Using The Table BelowRosalinda Samong100% (5)
- Health Education Chapter 4Document8 pagesHealth Education Chapter 4Jazti GracielNo ratings yet
- Qualities of Effective EducatorDocument18 pagesQualities of Effective Educatorapi-665220631No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 0617022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 0617022api-618483692No ratings yet
- UTS Lesson 1 BETTER STUDENTDocument45 pagesUTS Lesson 1 BETTER STUDENTAguirre, John CastorNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Psychological Foundatios of EducationDocument8 pagesMatrix of Psychological Foundatios of EducationSignorina MargaritaNo ratings yet
- Tabañag April Joy V.-Ped 7 - Task #3Document5 pagesTabañag April Joy V.-Ped 7 - Task #3April Joy TabañagNo ratings yet
- 5 Theory HE NotesDocument6 pages5 Theory HE Notesslonreginmae85No ratings yet
- Constructivist Learning Theory Cognitive Learning Theory: Principles and Theories of Language Acquisition and LearningDocument2 pagesConstructivist Learning Theory Cognitive Learning Theory: Principles and Theories of Language Acquisition and LearningPatricia Mae PajesNo ratings yet
- Ailawilliams - Ib Psychology Revision SheetDocument3 pagesAilawilliams - Ib Psychology Revision SheetHanie OriginalNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Riley Skains FinalDocument17 pagesGo To Page Riley Skains Finalapi-734710904No ratings yet
- Five Educational Learning TheoriesDocument7 pagesFive Educational Learning TheoriesNicole DuranNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGYDocument46 pagesPSYCHOLOGYEstefiNo ratings yet
- Health Education-Sas3Document3 pagesHealth Education-Sas3Shine Samm EstoseNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-677047016No ratings yet
- Principles and Theories of Learning and MotivationDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Theories of Learning and Motivationnhicabonit7No ratings yet
- Psychology ReviewerDocument4 pagesPsychology ReviewerRegine EmperadoNo ratings yet
- Cebu Roosevelt Memorial Colleges College of Teacher EducationDocument2 pagesCebu Roosevelt Memorial Colleges College of Teacher EducationIoannes Rovēros Rhoa NovelNo ratings yet
- Health Education (Midterm) : PPT Based NotesDocument7 pagesHealth Education (Midterm) : PPT Based NotesKysha HuangNo ratings yet
- Cognitivism and Gestalt ReviewerDocument4 pagesCognitivism and Gestalt ReviewerRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lesson 2Document54 pagesUnit II Lesson 2Xandra Loren OrencioNo ratings yet
- W1.teori PembelajaranDocument47 pagesW1.teori Pembelajaranamil9709No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-673370235No ratings yet
- Group 7Document7 pagesGroup 7Nur Faizal DamaNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022Document18 pagesGo To Page Word 2022api-623469645No ratings yet
- Inbound 1176654853125739966Document17 pagesInbound 1176654853125739966kristine11012005No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ego Defense MechanismsDocument50 pagesChapter 3 Ego Defense MechanismsmalindaNo ratings yet
- UTS Reviewer For FinalsDocument9 pagesUTS Reviewer For FinalstokyoescotoNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories in Teaching Health SciencesDocument7 pagesLearning Theories in Teaching Health SciencesAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- he mod 4 (1)Document5 pageshe mod 4 (1)andreagonzalooo27No ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 Dev Psych PapaliaDocument8 pagesCHAPTER-2 Dev Psych PapaliaDump Acc 2No ratings yet
- General Psychology ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Psychology ReviewerSherry Lyn Fernandez Lamsen-OrjaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.learning, Perception, and AttributionDocument27 pagesChapter 3.learning, Perception, and AttributionKimberly Shane TuraNo ratings yet
- 5-3.2. Cognitive-Behavior Therapies, Therapeutic Milieu and Other Psychological Interventions - CICdocxDocument2 pages5-3.2. Cognitive-Behavior Therapies, Therapeutic Milieu and Other Psychological Interventions - CICdocxDane Mikhael CalicaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Behavioral Management TheoriesDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Behavioral Management TheoriesRei Diaz ApallaNo ratings yet
- COGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES SummaryDocument7 pagesCOGNITIVE LEARNING THEORIES SummaryLoreto Dela Torre Marzan IIINo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document3 pagesChapter 14Herman AucampNo ratings yet
- Theories of Motivation What Is Motivation? Cherry (2020), Motivation Is TheDocument12 pagesTheories of Motivation What Is Motivation? Cherry (2020), Motivation Is TheFhayee Sulaik HaronNo ratings yet
- How People Learn: Theories of Learning Didactics 1Document56 pagesHow People Learn: Theories of Learning Didactics 1Annie WallaceNo ratings yet
- Winnykammen 1982Document7 pagesWinnykammen 1982perfilstshibalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To I-O PsychologyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To I-O PsychologyAl-Aziz EduardoNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundations of Curriculum: Key Learning TheoriesDocument25 pagesPsychological Foundations of Curriculum: Key Learning TheoriesEJ LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Psychological Foundations of Education: Theories and ImplicationsDocument77 pagesPsychological Foundations of Education: Theories and ImplicationsAriel De La CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro. TheoriesDocument67 pages1 Intro. TheoriesKatherine LaurencianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PsychDocument5 pagesChapter 6 PsychGerry Jimenez Sao-anNo ratings yet
- PYC2015 - Social Cognitive Learning Approach - Summary No. 1Document8 pagesPYC2015 - Social Cognitive Learning Approach - Summary No. 1Sbongiseni NgubaneNo ratings yet
- Human Motivation 6th Edition Franken Test BankDocument20 pagesHuman Motivation 6th Edition Franken Test BankKyleFitzgeraldyckas100% (11)
- Chapter Three: Learning and Theories of LearningDocument68 pagesChapter Three: Learning and Theories of LearningNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Drug Alcohol AwarenessDocument59 pagesDrug Alcohol AwarenessCharlotte VertudazoNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument3 pagesUntitled NotebookMuhammad Abelsea OktanzaNo ratings yet
- Keratoconus An Updated Review PDFDocument26 pagesKeratoconus An Updated Review PDFMaria Jose SanjinesNo ratings yet
- 033 - SOP On Batch Release SystemDocument3 pages033 - SOP On Batch Release SystemDevender Malhotra86% (22)
- Miss Daydreame1Document1 pageMiss Daydreame1Mary Joy AlbandiaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Selection of Artificial TeethDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Selection of Artificial TeethSora Tensai100% (1)
- Soal 3 Diagnosis PK 1 LatenDocument12 pagesSoal 3 Diagnosis PK 1 LatenMade SuryaNo ratings yet
- Sbar Communication Model: Situation, Background, Assessment, and RecommendationDocument27 pagesSbar Communication Model: Situation, Background, Assessment, and RecommendationRaquel MonsalveNo ratings yet
- 2069-Article Text-8454-1-10-20210630Document19 pages2069-Article Text-8454-1-10-202106302012070520 TARMUDINo ratings yet
- Risk Takers Living on the EdgeDocument2 pagesRisk Takers Living on the Edgecalderonmaes3No ratings yet
- Summary and Response Essay ThreeDocument3 pagesSummary and Response Essay ThreeSeth RossNo ratings yet
- Front EndDocument23 pagesFront EndMadridista RaeeNo ratings yet
- Pruebas Específicas de Certificación de Nivel: Inglés Avanzado C1Document6 pagesPruebas Específicas de Certificación de Nivel: Inglés Avanzado C1BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Users GuideDocument68 pagesUsers GuideJordi BertranNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Understanding Global Networks: GlobalizationDocument4 pagesModule 5: Understanding Global Networks: GlobalizationKasnhaNo ratings yet
- SAFETY DATA SHEET FOR PHTHALIC ANHYDRIDEDocument7 pagesSAFETY DATA SHEET FOR PHTHALIC ANHYDRIDESergio Mendoza ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- August 2022 Current Affairs 1Document43 pagesAugust 2022 Current Affairs 1Vishal MauryaNo ratings yet
- Free Medical Form Templates - SmartsheetDocument16 pagesFree Medical Form Templates - SmartsheetDanielNo ratings yet
- Camp Inspection ChecklistDocument5 pagesCamp Inspection Checklistsubhanmusadiq63% (8)
- OET Nursing - Official OET Practice Book 1Document229 pagesOET Nursing - Official OET Practice Book 1vidyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Pre-Launch Problem StatementDocument1 pageDrug Pre-Launch Problem StatementkutasunilNo ratings yet
- Vonoprazan Diference From PPIDocument11 pagesVonoprazan Diference From PPIHaseeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Ryan Lyn: For The Attention of The Recruiting PanelDocument1 pageRyan Lyn: For The Attention of The Recruiting PanelMaesie IgubanNo ratings yet
- SSPC SP6Document7 pagesSSPC SP6Jorge BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Optimal Fitting of Oticon More: WhitepaperDocument11 pagesOptimal Fitting of Oticon More: WhitepaperAlNo ratings yet
- Cal Q - ADVIA Centaur Systems - Rev 04 DXDCM 09017fe980777d93-1669396270867Document3 pagesCal Q - ADVIA Centaur Systems - Rev 04 DXDCM 09017fe980777d93-1669396270867cassNo ratings yet
- HSSE-R-011 - Project HSSE Reviews (PHSSER)Document17 pagesHSSE-R-011 - Project HSSE Reviews (PHSSER)AHMED AMIRANo ratings yet
- Global Distribution of Alveolar and Cystic Echinococcosis PDFDocument181 pagesGlobal Distribution of Alveolar and Cystic Echinococcosis PDFTataNo ratings yet
- TheNewCommunicationRevolutiona The Rise of Influencers LoraSimeonovaDocument28 pagesTheNewCommunicationRevolutiona The Rise of Influencers LoraSimeonovalinhgtran010305No ratings yet
- Analysis and Presentation Cummulative AntibiogramDocument7 pagesAnalysis and Presentation Cummulative AntibiogramApril LarasatiNo ratings yet