Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Bipolar 1 Disorder
Uploaded by
Kristine Nicole0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
385 views1 pageOriginal Title
Pathophysiology-of-Bipolar-1-Disorder
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
385 views1 pagePathophysiology of Bipolar 1 Disorder
Uploaded by
Kristine NicoleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
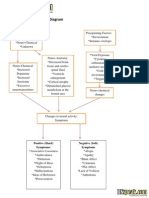
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF BIPOLAR DISORDER
Environmental Factors
Life stressors
Legend:
Pathophysiology Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Excess of serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine
Mechanism
Abnormal Neurocircuitry
Sign/Symptom Dysregulation of neuronal activity
Disorder BIPOLAR DISORDER
Decreased inhibitory control of emotional circuitry
Disruption of emotional homeostasis Depressed mood
Elevated, expansive,
irritable mood
Oscillation between mood states
Individual variability in disease course Increased withdrawal,
Increased goal directed guilt, anxiety,
behaviors and agitation hopelessness
MANIC EPISODE DEPRESSIVE
EPISODE
Increased euphoria, Increased suicidal
EUTHYMIC MOOD
grandiosity thoughts and behavior
BIPOLAR 1 DISORDER:
Increased euphoria, 1+ manic episodes +/- Decreased pleasure,
grandiosity 1+ major depressive episodes concentration
Estimated 10 episodes of mania and
depression per lifetime if untreated
You might also like
- Psychopathophysiology: Psychosocial Stressor and Interpersonal EventsDocument2 pagesPsychopathophysiology: Psychosocial Stressor and Interpersonal EventsMiyuki Bartolaba MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis and Interventions Pyschopathology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument1 pageCase Analysis and Interventions Pyschopathology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorSydelle GravadorNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for chlorpromazine administrationDocument3 pagesNursing responsibilities for chlorpromazine administrationkaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaAgeededin Hart100% (1)
- Citicoline Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiticoline Drug StudyJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- NCP & Discharge PlanningDocument12 pagesNCP & Discharge PlanningStephanie Mae Amoylen OdchigueNo ratings yet
- Paroxetine Wsiness, Diz ZinessDocument3 pagesParoxetine Wsiness, Diz Zinessunkown userNo ratings yet
- Nahco3 Vancomycin AmlodipineDocument3 pagesNahco3 Vancomycin AmlodipineShan Dave TupasNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug Analysiskristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Zoloft Sertraline Drug CardDocument1 pageZoloft Sertraline Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Epirubicin 10Document1 pageEpirubicin 10PdianghunNo ratings yet
- Paxil: Generic Name: Paroxetine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesPaxil: Generic Name: Paroxetine Hydrochloridenasir khanNo ratings yet
- RisperidoneDocument3 pagesRisperidoneapi-3797941No ratings yet
- NCM 117 Psychiatric Nursing MODULE 7Document27 pagesNCM 117 Psychiatric Nursing MODULE 7Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- SildenafilDocument2 pagesSildenafilSheryl Ann PedinesNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument2 pagesSeroqueldanaNo ratings yet
- Drug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismDocument2 pagesDrug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation FormatDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Formatdeliciouslyme0688% (8)
- BupivacaineDocument6 pagesBupivacaineAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- ISONIAZIDDocument2 pagesISONIAZIDXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument48 pagesBipolar DisorderRey Jayvee Arcuino Hinunangan50% (2)
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Escivex 10 2Document1 pageEscivex 10 2Havier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Treatment For My Patient: Drug Dose Route Action Indication Side Effect Nurse's ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesTreatment For My Patient: Drug Dose Route Action Indication Side Effect Nurse's ResponsibilityValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug StudyCath Bril100% (1)
- Azithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint of Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocument14 pagesPowerpoint of Undifferentiated SchizophreniaGian Carlo Soriente0% (1)
- Silver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSilver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyKenn Siasar100% (1)
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- Linagliptin - DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageLinagliptin - DRUG STUDYAcads useNo ratings yet
- CebUN Drug Study for HypothyroidismDocument4 pagesCebUN Drug Study for HypothyroidismGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DesyrelDocument1 pageDesyrelKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Schematic Diagram: Positive (Hard) Symptoms: Negative (Soft) SymptomsDocument1 pageSchizophrenia Schematic Diagram: Positive (Hard) Symptoms: Negative (Soft) SymptomsLovely Acabado Tampoco100% (1)
- Drug Monograph: Cyclophosphamide PharmacokineticsDocument2 pagesDrug Monograph: Cyclophosphamide PharmacokineticsShane PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Rle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingDocument5 pagesRle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Case StudyDocument13 pagesSchizophrenia Case StudyAnonymous Hfrl594No ratings yet
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument1 pageDrug Study IsoniazidEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Neurological Assessment Monitoring Sheet: C O M ADocument2 pagesNeurological Assessment Monitoring Sheet: C O M AAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyzenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument3 pagesDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Dug Study PsycheDocument33 pagesDug Study PsycheAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia Case StudyDocument64 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia Case StudyKeepItSecretNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderPae EdejerNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJezen SucalitNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 Lec - MidtermDocument40 pagesNCM 117 Lec - MidtermJayson SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneDocument5 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneCLARENCE REMUDARONo ratings yet
- ABPSYCH Case StudyDocument8 pagesABPSYCH Case StudyCharmaine MaghirangNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument29 pagesMood DisordersDon Marcus100% (1)
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- BETAXOLOLDocument2 pagesBETAXOLOLjulieNo ratings yet
- Biperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsDocument1 pageBiperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsMFQ.RN100% (2)
- PrimidoneDocument6 pagesPrimidoneKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder: Presented By: Group 2Document19 pagesBipolar Disorder: Presented By: Group 2Pao DelossantosNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders: Mental Health Nursing-NUR 417Document44 pagesMood Disorders: Mental Health Nursing-NUR 417preeti vermaNo ratings yet
- Reporting in Ethical Principles Group 1 BSN 3ADocument89 pagesReporting in Ethical Principles Group 1 BSN 3AKristine NicoleNo ratings yet
- Bioethics and Its Application in Various Health Care SituationsDocument44 pagesBioethics and Its Application in Various Health Care SituationsAngelica Olivar0% (1)
- 1 The MicroscopeDocument42 pages1 The MicroscopeKristine NicoleNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument40 pagesUntitledCrescia Jane TerazaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument38 pagesCognitive DisordersKristine NicoleNo ratings yet