Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Major Landforms of The Earth Notes
Uploaded by
SIMMA SAI PRASANNAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Major Landforms of The Earth Notes
Uploaded by
SIMMA SAI PRASANNACopyright:
Available Formats
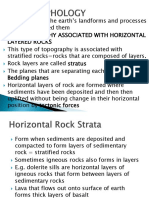
Various Landforms
Mainly there are three types of landforms - Mountains, Plateaus, Plains.
Mountains:
The height of mountains is over 600 m and have conical peaks. On the basis of origin there are four types
of mountains: Block Mountains, Residual Mountains, Accumulated Mountains and Fold Mountains.
Block Mountains
The middle part of such mountains is lower and the parts on both the sides are higher. The middle
lower portion is called as Rift valley. The longest rift valley is the valley of the Jordan river.
Black Forest (Germany) Vindhyachal and Satpura (India), Salt Range (Pakistan) are some
examples of block mountains.
Residual Mountains
Such mountains are formed as a result of weathering. Examples - Aravalli, Nilgiri, Parasnath, Hills
of Rajmahal (India), Siera (Spain).
Accumulated Mountains
These are formed due to accumulation of sand, soil, rocks, lava etc. on the Earth's Crust., e.g. Sand
Dunes.
Fold Mountains
These are formed because of the folds in the rocks due to internal motions of the earth. These are
wavelike mountains which have numerous peaks and lows, e.g.
Himalayas, Ural, Alps, Rockies, Andes etc.
Plateaus:
Plateaus are extensive upland areas characterised by flat and
rough top surface and steep walls which rise above the
neighbouring ground surface at least for 300 m.
Generally, the height of plateau ranges from 300 to 500 feet.
Intermountainous Plateaus: Plateaus formed between
mountain, Example - Tibetan Plateau.
Mountainstep Plateaus: The flat region between a plain and
the base of a mountain.
Continental Plateaus: These are formed when the Lacolith
inside the Earth comes to the surface due to weathering, e.g.
1 www.teachersadda.com | www.sscadda.com| www.bankersadda.com | www.adda247.com
the Southern Plateau.
Bank Plateaus: These are the plateaus on the banks of the oceans.
Domelike Plateaus: These are formed due to the movement of man and animals on the surface.
e.g. Ramgarh Plateau.
Some plateaus having more than average height
Tibetan Plateau 16,000 ft
Bolivian Plateau 11,800 ft
Columbian Plateau 7,800 ft
Plains:
Plains can be defined as flat areas with low height (below 500 ft.)
Weathered Plains: The plains formed due to weathering by rivers, glaciers, winds etc.
Loess Plains: These are formed by the soil and sands brought by winds.
Karst Plains: Plains formed due to the weathering of limestone.
Erosional Plains: Plains near the river banks formed by river erosion
Glacial Plains: Marshy plains formed due to the deposition of ice.
Desert Plains: These are formed as a result of the flow of rivers.
Deposition Plains: Large plains are formed due to the silt brought by the rivers. Such plains are
plains of Ganga Sutlej, Mississippi, Hwang - Ho.
Pastures (or Grasslands):
They can be divided into two types:
(i) Tropical Pastures and
(ii) Temperate Pastures
Tropical Pastures: They have different names in different countries. Savanna in Africa, Campos in Brazil,
Lanos in Venezuela and Columbia.
Temperate Pastures: They are known by the following names - Prairies in USA and Canada, Pampas in
Argentina Veld in South Africa, Rangelands or Downs in Australia and New Zealand, Steppes in Eurasia
(Ukraine, Russia).
Land forms created by the river system V - shaped valley:
A river flows with a greater velocity in the mountainous region
and big pointed fragments of rock also flow with a great speed
along with the water.
The river bed is scoured and down cutting starts, ultimately
giving rise to a deep valley with steep sides.
This valley is called a v - shaped valley.
These valleys are found in mountainous regions.
A deep and narrow valley with steep sides is called a gorge.
The gorge of the river Ulhas in Thane district in Maharashtra
and the gorge of the river Narmada at Bhedaghat near Jabalpur
2 www.teachersadda.com | www.sscadda.com| www.bankersadda.com | www.adda247.com
in Madhya Pradesh are well known.
There are many gorges in the Himalayas.
Waterfall
If there are both hard (resistant) and soft (less resistant) rocks in the course of the river, the less
resistant rock is eroded faster
The resistant rock does not erode so easily. That is why, the river falls with a great speed from a
cliff - like part of hard rock. This is called a waterfall.
The Niagara Falls on the Niagara river is in North America.
Potholes
In areas where the river bed consists of hard rock, the stones carried along with the river water
due to the whirling impact of water.
That is why holes of various shapes are formed in the rocky river bed. Such holes are called
potholes.
Many potholes are observed in the river bed of the Kukadi, Krishna, Godavari etc. in Maharashtra.
Fan - shaped plains
In the region near the source of a river the tributaries joining the main river deposit materials
carried by them on the banks of the main river.
This deposition creates fan - like plains. They are called fan - shaped plains or alluvial fans.
Flood plains
When, during the floods, the river - water overflows its banks and spreads in the surrounding
areas, the silt carried by the water gets deposited in those areas. This creates flat plains on both
the banks of the river. Plains created by this depositional work done during floods are called flood
plains.
The Gangetic Plain is a flood plain.
3 www.teachersadda.com | www.sscadda.com| www.bankersadda.com | www.adda247.com
You might also like
- Pakistan: Insights Into Its Geography and Economy by Mohammmad Anwar For O Levels/IGCSEDocument219 pagesPakistan: Insights Into Its Geography and Economy by Mohammmad Anwar For O Levels/IGCSEMohammad Anwar94% (97)
- Exit GradientDocument5 pagesExit GradientAmandeep Singh100% (1)
- Mineral Oil Centrifuge Ose-5-91-0374Document210 pagesMineral Oil Centrifuge Ose-5-91-0374Andriy Siemens62% (13)
- Earth Surface and ClimateDocument7 pagesEarth Surface and ClimateSofia MeloNo ratings yet
- Types and Characteristics of Major Landforms:: MountainsDocument14 pagesTypes and Characteristics of Major Landforms:: MountainsPappu DiaNo ratings yet
- India's Diverse LandformsDocument24 pagesIndia's Diverse LandformsChitti BabuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 and 2 (Topography and Climate)Document95 pagesTopic 1 and 2 (Topography and Climate)usmanrandhawa67889No ratings yet
- How Are Mountains Worn Down? Erosion by Weather and Running Water, AND How Do Mountains Affect Human Life?)Document22 pagesHow Are Mountains Worn Down? Erosion by Weather and Running Water, AND How Do Mountains Affect Human Life?)Raghina YudiansyahNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes 2Document52 pagesGeography Notes 2ayan mitraNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument52 pagesGeographyyash91400rajNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology GR 11Document85 pagesGeomorphology GR 11YONDELA MbandezeloNo ratings yet
- Aeolian LandformsDocument2 pagesAeolian Landformsromelio salumbidesNo ratings yet
- 2 PlateauDocument18 pages2 PlateauAnuj SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Physical Features of IndiaDocument6 pagesClass 9 Physical Features of IndiaYashNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms-1Document11 pagesGlacial Landforms-1Satarupa BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Major Landforms: Plateaus, Plains, Deserts & MoreDocument4 pagesMajor Landforms: Plateaus, Plains, Deserts & MoreSiyana SheikNo ratings yet
- India's Diverse Landforms and Relief FeaturesDocument40 pagesIndia's Diverse Landforms and Relief FeaturesUjjwal SinghNo ratings yet
- India's Major Physiographic Divisions and Their FormationDocument10 pagesIndia's Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Formationvivek pareek100% (1)
- Physical Features of India Chapter 2class 9Document27 pagesPhysical Features of India Chapter 2class 9poonam goswamiNo ratings yet
- Major Landforms WaterbodiesDocument7 pagesMajor Landforms WaterbodiesAnita FernandesNo ratings yet
- OLEVEL GEOGRAPHY NOTES ON PAKISTAN'S TOPOGRAPHY AND LANDFORMSDocument23 pagesOLEVEL GEOGRAPHY NOTES ON PAKISTAN'S TOPOGRAPHY AND LANDFORMSSyed Muhammad Saleem FeroziNo ratings yet
- Physical Features of IndiaDocument5 pagesPhysical Features of IndiaTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Gs Study Notes SSC 16-01-19 EnglishDocument12 pagesGs Study Notes SSC 16-01-19 EnglishKESHAB BHOINo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13Document16 pagesChap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13abhaykumarkans054No ratings yet
- Physiographic Divisions of India: Mountains, Plains and PlateausDocument32 pagesPhysiographic Divisions of India: Mountains, Plains and PlateausBipul Biplav75% (4)
- Fluvial and Glacial Landforms and Erosion CyclesDocument27 pagesFluvial and Glacial Landforms and Erosion CyclesPappu DiaNo ratings yet
- Physical Features of INDIADocument16 pagesPhysical Features of INDIAdmanish211No ratings yet
- Major Landforms - Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains - Learn Faster - ClearIASDocument11 pagesMajor Landforms - Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains - Learn Faster - ClearIASAmar SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 (Notes) Major Relief Feature of The EarthDocument4 pagesLesson 6 (Notes) Major Relief Feature of The Earthmohamedaahil12318No ratings yet
- SST Notes: GeographyDocument6 pagesSST Notes: GeographyGeetNo ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument94 pagesOceanographyKokila AmbigaeNo ratings yet
- Mountains: Made by - Naman Gupta Class-VICDocument9 pagesMountains: Made by - Naman Gupta Class-VICnamanNo ratings yet
- Major Landforms of The EarthDocument29 pagesMajor Landforms of The EarthRajiv Mahajan100% (1)
- Geomorphology of River (Group-D)Document32 pagesGeomorphology of River (Group-D)Rajesh ranaNo ratings yet
- My Physical Divisions of IndiaDocument20 pagesMy Physical Divisions of IndiaSushmaNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Landforms (Discription & PictureDocument4 pagesDifferent Kinds of Landforms (Discription & Picturestephencolangoy100% (2)
- Notes Chapter 2 CBSE GeographyDocument8 pagesNotes Chapter 2 CBSE Geographynio7851No ratings yet
- Physical Features of India: Made by N.SrinivasaraoDocument26 pagesPhysical Features of India: Made by N.SrinivasaraoMitesh SarawgiNo ratings yet
- 3000m Is Said To Be A Hill How Can It Shows Hills and Mountains and Also The Rise and Falls of The LandDocument12 pages3000m Is Said To Be A Hill How Can It Shows Hills and Mountains and Also The Rise and Falls of The Landhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Physiographic Divisions of India FinalDocument32 pagesPhysiographic Divisions of India FinalAshish Juneja100% (2)
- 9th Geo 2Document5 pages9th Geo 2Priyanka BaisNo ratings yet
- 9th Geography Chapter 2 NotesDocument11 pages9th Geography Chapter 2 NotesSandhya SinghNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentAmna QayoumNo ratings yet
- GeoDocument6 pagesGeomohammadshadankhan5No ratings yet
- Kid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureFrom EverandKid’s Guide to Types of Landforms - Children's Science & NatureNo ratings yet
- Landforms NoorDocument21 pagesLandforms Nooramrinder singhNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision List Geography 205902Document62 pagesQuick Revision List Geography 205902Zayd JawadNo ratings yet
- Landforms of The EarthDocument4 pagesLandforms of The EarthSrinjon SahaNo ratings yet
- The Physiographic Features of IndiaDocument64 pagesThe Physiographic Features of IndiaJnanam100% (1)
- Physical Features Notes Geo Class9 Term1Document7 pagesPhysical Features Notes Geo Class9 Term1vinod1577100% (1)
- Taal Lake: Batangas' Historic Volcanic LakeDocument28 pagesTaal Lake: Batangas' Historic Volcanic LakeJiji Laspiñas OlarteNo ratings yet
- GEO L3 Plateus Planes 0.2Document99 pagesGEO L3 Plateus Planes 0.2Amit VermaNo ratings yet
- History ProjectDocument7 pagesHistory ProjectEshanNo ratings yet
- LandformsDocument7 pagesLandformsAtulJhaKumarNo ratings yet
- LandformsDocument3 pagesLandformsJacki Pauline VinoyaNo ratings yet
- Desert Landforms and ProcessesDocument9 pagesDesert Landforms and ProcessesHarsh DevNo ratings yet
- 6 Landforms - SCIENCEDocument9 pages6 Landforms - SCIENCEArwen MargalloNo ratings yet
- Physical Features of IndiaDocument26 pagesPhysical Features of IndiaGurjant Bhangu100% (1)
- PDF - CRUXMountainsOfIndiaDocument18 pagesPDF - CRUXMountainsOfIndiajimaleidNo ratings yet
- Hills vs. Mountains : Knowing the Difference - Geology Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandHills vs. Mountains : Knowing the Difference - Geology Books for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Evolution of the Landscape of the San Francisco Bay RegionFrom EverandEvolution of the Landscape of the San Francisco Bay RegionNo ratings yet
- A Countermeasure for Prevention of Reservoir Floating DebrisDocument54 pagesA Countermeasure for Prevention of Reservoir Floating Debriszulkifli1220No ratings yet
- Twin Pines Minerals - Saunders Demonstration Mine - Surface Mining Application - 6-19-2020Document14 pagesTwin Pines Minerals - Saunders Demonstration Mine - Surface Mining Application - 6-19-2020Mary LandersNo ratings yet
- A Genetic Classification of Floodplains: GeomorphologyDocument28 pagesA Genetic Classification of Floodplains: Geomorphologyresacoxis9No ratings yet
- A Review of The Revised Universal Soil Loss EquatiDocument34 pagesA Review of The Revised Universal Soil Loss EquatiMaulana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Elvis Presley BiographyDocument6 pagesElvis Presley BiographyAlixon Carolay Montaño SanchezNo ratings yet
- Specification Accredited A Level Gce Geography h481 2Document92 pagesSpecification Accredited A Level Gce Geography h481 2Alice MoodieNo ratings yet
- Field Testing of Bio-Engineering Techniques UsingDocument10 pagesField Testing of Bio-Engineering Techniques UsingEutiquio Rotaquio100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentFatima Grace TambaoanNo ratings yet
- Car 2016 9geo T4 ExamDocument12 pagesCar 2016 9geo T4 ExamPoTTie10No ratings yet
- GHT-102 MMR Lecture-4Document25 pagesGHT-102 MMR Lecture-4Md. Mostafizur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Brabant Pierre, 2010. A Land Degradation Assessment and Mapping Method. A Standard Guideline ProposalDocument56 pagesBrabant Pierre, 2010. A Land Degradation Assessment and Mapping Method. A Standard Guideline ProposalCSFDNo ratings yet
- FDOT Item Average Unit Cost Report for 2015-2016Document37 pagesFDOT Item Average Unit Cost Report for 2015-2016Roberteau HarrisNo ratings yet
- Sand Laden FluidsDocument13 pagesSand Laden FluidsSherine WongNo ratings yet
- Richmond-Steveston Dike Master Plan PDFDocument25 pagesRichmond-Steveston Dike Master Plan PDFMartinvdHNo ratings yet
- Manual On Procedures IN Operational Hydrology: Ministry of Water Energy and Minerals TanzaniaDocument111 pagesManual On Procedures IN Operational Hydrology: Ministry of Water Energy and Minerals TanzaniaingaboNo ratings yet
- g5 K-12 DLL q4 Week 1 ScienceDocument7 pagesg5 K-12 DLL q4 Week 1 ScienceelfelicitycortezNo ratings yet
- ScourDocument42 pagesScourRamkumarNo ratings yet
- Asian Ice Shields and Climate ChangeDocument25 pagesAsian Ice Shields and Climate ChangecrestednewtNo ratings yet
- Development Geography of Uganda's Location, Physiography and LandscapeDocument6 pagesDevelopment Geography of Uganda's Location, Physiography and LandscapeChemutai EzekielNo ratings yet
- Filter Sediment and Protect Cropland with Riparian BuffersDocument5 pagesFilter Sediment and Protect Cropland with Riparian BuffersimeldaelisabethNo ratings yet
- Earth DamsDocument22 pagesEarth DamsAbubakr Mustafa100% (1)
- INDE 1001 Engineering Foundations: Design and ProcessesDocument17 pagesINDE 1001 Engineering Foundations: Design and ProcessesCalvinhaoweiNo ratings yet
- RUSLEDocument16 pagesRUSLEVivek KasarNo ratings yet
- ASTM G76-95 (Reapproved 200) Standard Test Method For Conducting Erosion Tests by Solid Particle Impingement Using Gas JetsDocument5 pagesASTM G76-95 (Reapproved 200) Standard Test Method For Conducting Erosion Tests by Solid Particle Impingement Using Gas JetsPoovelan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Settlement and Community in Tringkap NewDocument20 pagesSettlement and Community in Tringkap NewMuhammad AsyrafNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Đục Lỗ 1- Cô Trang AnhDocument4 pagesBài Tập Đục Lỗ 1- Cô Trang AnhHiền TrangNo ratings yet
- Erosion GuidelineDocument223 pagesErosion Guidelinefarahazura100% (3)
- River Basin ProcessesDocument16 pagesRiver Basin Processes3alliumcourtNo ratings yet