Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Complex Loaded System Sheet L.O3
Uploaded by
Tarek Els0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThis document discusses calculating stresses, strains, and dimensional changes in materials subjected to various loading conditions. It includes examples of:
1. Calculating stress and strain in a metal bar under tensile loading.
2. Finding percentage decrease in thickness of a titanium alloy bar under axial loading.
3. Determining strains in two directions given stresses and material properties.
4. Determining strains in two directions where one stress is negative.
5. Calculating dimensional changes in a part under multiaxial loading, including adding a third load and resulting volumetric strain.
6. Finding changes in length and cross-sectional dimensions of a bar under axial loading.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses calculating stresses, strains, and dimensional changes in materials subjected to various loading conditions. It includes examples of:
1. Calculating stress and strain in a metal bar under tensile loading.
2. Finding percentage decrease in thickness of a titanium alloy bar under axial loading.
3. Determining strains in two directions given stresses and material properties.
4. Determining strains in two directions where one stress is negative.
5. Calculating dimensional changes in a part under multiaxial loading, including adding a third load and resulting volumetric strain.
6. Finding changes in length and cross-sectional dimensions of a bar under axial loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesComplex Loaded System Sheet L.O3
Uploaded by
Tarek ElsThis document discusses calculating stresses, strains, and dimensional changes in materials subjected to various loading conditions. It includes examples of:
1. Calculating stress and strain in a metal bar under tensile loading.
2. Finding percentage decrease in thickness of a titanium alloy bar under axial loading.
3. Determining strains in two directions given stresses and material properties.
4. Determining strains in two directions where one stress is negative.
5. Calculating dimensional changes in a part under multiaxial loading, including adding a third load and resulting volumetric strain.
6. Finding changes in length and cross-sectional dimensions of a bar under axial loading.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Behavioral Characteristics of Materials subjected to Complex
Loading Systems
1. A metal bar which is part of a frame is 50 mm diameter and 300
mm long. It has a tensile force acting on it of 40 kN which tends to
stretch it. The modulus of elasticity is 205 GPa. Calculate the
stress and strain in the bar and the amount it stretches.
2. A bar of titanium alloy of length 120 mm and square cross-section,
7.5 mm × 7.5 mm, is pulled axially by a force of 15 kN. Find the
percentage decrease in thickness if E= 106 GN/m2 and = 0.33.
3. A material has stresses of 2 MPa in the x direction and 3 MPa in
the y direction. Given the elastic constants E = 205 GPa and ν=
0.27, calculate the strains in both direction.
4. A material has stresses of -2 MPa in the x direction and 3 MPa in
the y direction. Given the elastic constants E = 205 GPa and ν=
0.27, calculate the strains in both direction.
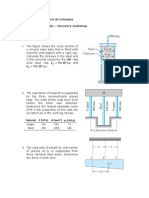
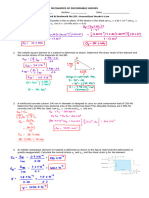
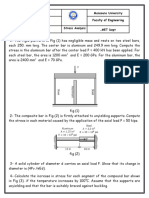
5-A part of a testing mechanical machine is loaded as shown in the figure is
made from a stainless steel (E=200 Gpa, γ= 0.3). In your lab you will
measure change in dimensions of this part due to this loading, but you
wanted to ensure these measurements by using formulas and calculations.
Determine:
(a) The change in dimensions due to this 2-D loading (X, Z).
(b) If we loaded this component with third load of (10) kN which acts in (Y)
direction (the
third dimension); determine the new dimensions under this 3-D loading.
(c) Determine the volumetric strain and change in volume due to 3-D
loading.
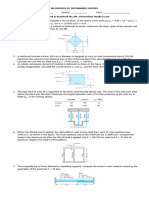
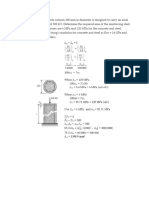
6-A bar made of stainless steel has the dimensions shown the Figure. If an axial
force of 80 kN is applied to the bar. Determine the change in its length and the
change in the dimensions of its cross section after applying the load. The material
behaves elastically.
(E=200 Gpa, γ= 0.32).
You might also like
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Sothea ChimNo ratings yet
- SOM Question BankDocument5 pagesSOM Question BankbmdbmdbmdNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Som TutorialsDocument22 pagesSom TutorialsbaizubirajiNo ratings yet
- Mem-402-Mos Final QB-2015Document9 pagesMem-402-Mos Final QB-2015Rohit DiwakarNo ratings yet
- 02Document16 pages02Vergel Pabunan NogadasNo ratings yet
- Strength WorksheetDocument9 pagesStrength WorksheetHabtamu GetaNo ratings yet
- SOM Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesSOM Assignment QuestionsPrajwal RpNo ratings yet
- ME 303 Study Set PDFDocument44 pagesME 303 Study Set PDFFajar RumantoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - StrengthDocument1 pageFinal Exam - StrengthJonathan PacaldoNo ratings yet
- SOM3601 Assignment 2Document3 pagesSOM3601 Assignment 2Elendu Emmanuel ChigozieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions 4523Document29 pagesTutorial Questions 4523Toby Joseph ThomasNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document11 pagesExercise 1John RoyNo ratings yet
- Problems in I UnitDocument6 pagesProblems in I UnitjeroldscdNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Stress Strain and DeformationDocument94 pagesUnit I - Stress Strain and DeformationMonesh kumarNo ratings yet
- SOM Question Bank For RevisionDocument11 pagesSOM Question Bank For RevisiongoldencometNo ratings yet
- Strength Materials WorkshopDocument3 pagesStrength Materials WorkshopIsabella Gutierrez BurbanoNo ratings yet
- Seatwork No.2M Generalized Hookes LawDocument2 pagesSeatwork No.2M Generalized Hookes LawReyn Ma G.No ratings yet
- Shear Stress Tut 1Document3 pagesShear Stress Tut 1Erastus KandumeNo ratings yet
- S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseDocument3 pagesS. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseTejas AdakNo ratings yet
- Mom AssignmentDocument8 pagesMom AssignmentfrogNo ratings yet
- Ib Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2Document5 pagesIb Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2omarnasriNo ratings yet
- Ce 6306 Som QBDocument11 pagesCe 6306 Som QBHODMECHANICAL AKTMCETNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirNo ratings yet
- Seatwork No.2M Generalized Hookes LawDocument3 pagesSeatwork No.2M Generalized Hookes LawReyn Ma G.No ratings yet
- Shearing DeformationDocument21 pagesShearing DeformationRyan Joseph Rabino100% (1)
- Worked Solution To Various QuestionsDocument29 pagesWorked Solution To Various QuestionsJohn MutumaNo ratings yet
- Som Part B CDocument16 pagesSom Part B CSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 Subject: Solid Mechanics Code: CE-126Document2 pagesAssignment-1 Subject: Solid Mechanics Code: CE-126Aviral UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 MKM - Sifat Mekanis MaterialDocument2 pagesTugas 3 MKM - Sifat Mekanis MaterialMuh AsharNo ratings yet
- MosDocument3 pagesMosrajapratyNo ratings yet
- MOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23Document6 pagesMOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23PankajNo ratings yet
- Geas FormulaDocument29 pagesGeas Formularoy016No ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics (ME 14.101) Tutorial Sheet-6: (Tension, Compression & Shear)Document1 pageApplied Mechanics (ME 14.101) Tutorial Sheet-6: (Tension, Compression & Shear)atulkumargaur26No ratings yet
- Stress and Strain 4th Class Power Engineering QuestionsDocument2 pagesStress and Strain 4th Class Power Engineering QuestionsCalvin Jude GoveiaNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 AnswerDocument8 pagesTutorial 2 AnswerservetNo ratings yet
- 1545913554Document1 page1545913554ajay kumarNo ratings yet
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 pagesEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNo ratings yet
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1Document2 pagesSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemNo ratings yet
- 108F13 Homework 2Document1 page108F13 Homework 2Nhan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 PGDocument1 pageTutorial 3 PGHarryNo ratings yet
- Mf8761-End Sem QPDocument9 pagesMf8761-End Sem QPPriyadharshan RNo ratings yet
- Som TutorialsDocument13 pagesSom Tutorialsdearsaswat100% (1)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materialsgirish_deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document17 pagesLecture 3aqsa zahidNo ratings yet
- Sec Module 03Document22 pagesSec Module 03kenji belanizo100% (1)
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithNo ratings yet
- Amd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017Document5 pagesAmd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017rip111176No ratings yet
- 7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsDocument5 pages7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsSrikant Potluri100% (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)