Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd QE AK
Uploaded by
Juniel BarriosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd QE AK
Uploaded by
Juniel BarriosCopyright:
Available Formats
Rotational Motion (8)
1. Two children sit on a merry-go-round. One sits 1 m from the center, and the other sits 3 m
from the center. If the children are in a straight line from the center, which child has a
greater angular speed? C
A. The child 1 m from the center
B. The child 3 m from the center
C. The children share equal angular speed.
D. We must know their angular acceleration to draw a conclusion.
rad
2. A fan spins with a constant angular speed of 250 . How long will it take to cover a
s
revolution? B
A. 0.013 s
B. 0.025 s
C. 19.89 s
D. 39.79 s
For items 3-5, refer to the scenario below:
rad
The bugs ride a turntable that rotates at a constant rate of 5 . Bug A is at a radius of 3 cm ,
s
while bug B is at a radius of 7 cm .
3. Which of the following is TRUE about the angular speed of the bugs? C
A. Bug A has a greater angular speed.
B. Bug B has a greater angular speed.
C. The bugs share equal angular speed.
D. We must know their angular acceleration to draw a conclusion.
4. Which of the following is TRUE? D
A. Bug A has a greater angular speed.
B. Bug B has a greater angular speed.
C. Bug A has a greater speed.
D. Bug B has a greater speed.
5. What is the speed of bug A ? C
cm
A. 1
s
cm
B. 2
s
cm
C. 15
s
cm
D. 35
s
For items 6-8, refer to the scenario below:
rad rad
A 1.5-m-radius grinding wheel takes 3 s to speed up from 2.5 to 7.5 .
s s
6. What is the average angular acceleration of the wheel? A
rad
A. 2 2
s
rad
B. 3 2
s
rad
C. 5 2
s
rad
D. 15 2
s
7. What is the approximate final centripetal acceleration of the wheel? D
rad
A. 9.38 2
s
rad
B. 11.3 2
s
rad
C. 37.5 2
s
rad
D. 84.4 2
s
8. What is the approximate final acceleration of the wheel? D
rad
A. 9.85 2
s
rad
B. 11.7 2
s
rad
C. 37.6 2
s
rad
D. 84.5 2
s
Periodic Motion (8)
9. Which of the following is NOT an example of periodic motion? D
A. Ocean waves
B. A playground swing
C. The rotation of a wheel
D. A car driving down a straight road
For items 10-12, refer to the scenario below:
m
A 1.5-kg ball rolls around the edge of a 1-m-radius circle at a speed of 3 .
s
10. What is the period of the ball? B
2π s
A.
3m
2π
B. s
3
s
C. 6 π
m
D. 6 π s
11. What is the frequency of the ball? B
3m
A.
2π s
3
B.
2π s
6m
C.
πs
6
D.
πs
12. If the ball has the same period and frequency but in a different scenario, such that it is
now attached to a spring, what is the spring constant k of the spring? B
2
kg ∙ m
A. 9
s2
kg
B. 9 2
s
kg
C. 216 2
s
2
kg ∙ m
D. 216
s2
13. Simple harmonic motion is a type of periodic motion wherein the restoring force is
_______ to the displacement of the body relative to its equilibrium position. A
A. directly proportional
B. inversely proportional
C. equal
D. Any of the choices, depending on the situation
14. A stiff material has a _______. A
A. high spring constant
B. low spring constant
C. spring constant of vague value
D. spring constant that cannot be predicted
15. Which of the following springs is the stiffest? C
A. A spring that requires a force of 2000 N to compress it by 6.8 m.
B. A spring that requires a force of 8000 N to compress it by 45 m .
C. A spring that requires a force of 4000 N to stretch it by 9.0 m .
D. A spring that requires a force of 4800 N to stretch it by 14 m .
16. A spring has a length of 0.10 m. When the spring is stretched by a force of 15 N , its
length is increased to 0.17 m . What is the spring constant k of the spring? A
N
A. 214
m
N
B. 170
m
N
C. 88
m
N
D. 56
m
Fluid Mechanics (4)
17. What is the speed of a fluid coming out from an orifice of a closed container? D
√
A. v= 2 gy +
2∆ p
ρ
√
B. v= 2 gy +
2∆ ρ
p
√
C. v= 2 gy +
D. v=√ 2 gy
∆p
ρ
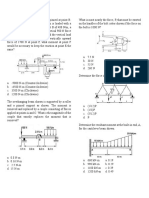
18. Which of the following comparisons is TRUE? Refer to the figure below. D
A. F A=F B
B. PA> PB
C. F A> FB
D. P A =PB
For items 19-20, refer to the scenario below:
An object weighing 50.0 N displaces a volume of water with a weight of 10.0 N .
19. What is the magnitude of buoyant force on the object? B
A. 5 N
B. 10 N
C. 40 N
D. 60 N
20. What happens to the object? A
A. The object sinks.
B. The object floats.
C. The object stays where it was.
D. The object sticks to the side of the container.
PROBLEM-SOLVING
21-50.
You might also like
- Student's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Document2 pagesStudent's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Nam Anh Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Test 2 NDocument1 pageGrade 12 Physics Test 2 NAmanNo ratings yet
- 2nd QE QDocument3 pages2nd QE QJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- 2018 NMAT REVIEW Reinforcement - Physics Module ADocument2 pages2018 NMAT REVIEW Reinforcement - Physics Module AEllah Gutierrez100% (1)
- Physics Inter Part 1 (Sample/Guess Paper) For Exams in 2020Document3 pagesPhysics Inter Part 1 (Sample/Guess Paper) For Exams in 2020Aftab AhmadNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS HSSC 1 Pre BoardDocument5 pagesPHYSICS HSSC 1 Pre BoardEman AliNo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerNeil VelascoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDocument38 pagesMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书No ratings yet
- Test BankDocument14 pagesTest BankAhmed aliNo ratings yet
- AP Phys 1 Quiz Rotational MotionDocument15 pagesAP Phys 1 Quiz Rotational MotionWenyang LiNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1.finalDocument12 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1.finalzamora pegafiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics ProblemsDocument64 pagesDynamics Problemsmostafa100% (1)
- 75 MCQ of PhysicsDocument47 pages75 MCQ of PhysicsFarah Anjum94% (35)
- Physics 1Document3 pagesPhysics 1Yohannes TessemaNo ratings yet
- Ss 1 PHDocument3 pagesSs 1 PHPrince BurnaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1 Summative ExamDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 1 Summative ExamLeizel MundoNo ratings yet
- Physic Eng Mech StremaDocument9 pagesPhysic Eng Mech StremaAllyssa ErcillaNo ratings yet
- Law of Cosines: C A + B - 2 - A - B - Cos Law of Sines: A/sina B/sinß C/sin Fluid, Air Drag: FD 1/2CD - Ar - R - VDocument8 pagesLaw of Cosines: C A + B - 2 - A - B - Cos Law of Sines: A/sina B/sinß C/sin Fluid, Air Drag: FD 1/2CD - Ar - R - VrileyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice 2Document37 pagesMultiple Choice 2Dave SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Grade 9 ScienceDocument3 pagesSummative Test in Grade 9 ScienceApolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- Tilak High School Annual Examination Physics Form 5: InstructionsDocument14 pagesTilak High School Annual Examination Physics Form 5: InstructionsSatbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and DynamicsDocument16 pagesKinematics and DynamicsmartinNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 10Document5 pagesPhysics Grade 10hannahNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesWork Energy and PowermartinNo ratings yet
- Physics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Document8 pagesPhysics: Samiksha's MBBS Entrance SOLVED QUESTIONS - 1Inesh0% (1)
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledClaire BalaisNo ratings yet
- Phys 1D03 Test 2 Online F20 Ave PDFDocument5 pagesPhys 1D03 Test 2 Online F20 Ave PDFMarc YorkNo ratings yet
- HW Circular Motion 1-3 - E - AnsDocument23 pagesHW Circular Motion 1-3 - E - AnsCHIU KEUNG OFFICIAL PRONo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Divyesh .RNo ratings yet
- ADocument2 pagesAsardarsndi96No ratings yet
- Pre Board Exam GEASDocument11 pagesPre Board Exam GEASart16marasiganNo ratings yet
- Science 7Document5 pagesScience 7Carlo Rico ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Document4 pagesReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.No ratings yet
- Physics Class 11Document8 pagesPhysics Class 11sindhu1975nairNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Complete PDFDocument215 pagesMachine Design Complete PDFJobert Arsenal CaroNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - Mock Exam - GE PDFDocument10 pagesProblem Set - Mock Exam - GE PDFKristine AnnNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Wizard Practice ExamDocument2 pagesDynamics Wizard Practice ExamMatthew MlacedaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination in General Physics 1Document10 pagesMidterm Examination in General Physics 1zamora pegafi100% (2)
- Grav, Rot, SHMDocument4 pagesGrav, Rot, SHMSandeep NeupaneNo ratings yet
- NAME: - Grade 9 NAME: - Grade 9Document1 pageNAME: - Grade 9 NAME: - Grade 9joy bazanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Sec 4 Pure Physics SA2 Chung Cheng High (Yishun) PDFDocument40 pages2018 Sec 4 Pure Physics SA2 Chung Cheng High (Yishun) PDFLing Li XuanNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics23 24sp04Document19 pages11 Physics23 24sp04Vettri PrintersNo ratings yet
- All Chemistry QuestionsDocument12 pagesAll Chemistry QuestionslawaljamiuadebayoNo ratings yet
- Q1: Circle The Correct OptionDocument2 pagesQ1: Circle The Correct OptionZahfran SajidNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Chapter5Document14 pagesMicrosoft Word Chapter5Luis AndersonNo ratings yet
- A B CD A B CD A B CD 1oooo 6 Oooo11Oooo 2oooo 7 Oooo12Oooo 3oooo 8 Oooo13Oooo 4oooo 9 Oooo14Oooo 5Oooo10Oooo15OoooDocument5 pagesA B CD A B CD A B CD 1oooo 6 Oooo11Oooo 2oooo 7 Oooo12Oooo 3oooo 8 Oooo13Oooo 4oooo 9 Oooo14Oooo 5Oooo10Oooo15Oooominh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Jgeebils Tifr Ncbs Gs Old Papers 2010 2019Document168 pagesJgeebils Tifr Ncbs Gs Old Papers 2010 2019Priyanka pNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion MCQDocument11 pagesCircular Motion MCQBhavita BhananiNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 M-1 AK PDFDocument3 pagesPhysics 1 M-1 AK PDFCherry Grace Articulo DabuconNo ratings yet
- Final Roud QBDocument3 pagesFinal Roud QBxerxes uclm100% (1)
- Review Exam2Document5 pagesReview Exam2EliezerNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion - P-SSDocument2 pagesCircular Motion - P-SSniharika dadiNo ratings yet
- Es Final Exam Set A AnswerDocument20 pagesEs Final Exam Set A AnswerjohnjabarajNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2 PDFDocument8 pagesPractice Exam 2 PDFDavid WeitzelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Q1 ST1 Answer KeyDocument4 pagesQ1 ST1 Answer KeyJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- G9 TosDocument3 pagesG9 TosJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 JDocument14 pagesWorksheet 2 JJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- G7 TosDocument4 pagesG7 TosJuniel Barrios100% (1)
- G12 TosDocument6 pagesG12 TosJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect DLP JDocument8 pagesPhotoelectric Effect DLP JJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy of 3D Printers DLP JDocument10 pagesBasic Anatomy of 3D Printers DLP JJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Creative Tech Q1 W7Document10 pagesCreative Tech Q1 W7Juniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Creative Tech Q1 W2Document10 pagesCreative Tech Q1 W2Juniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Reliability Web 5 Sources of Defects SecureDocument1 pageReliability Web 5 Sources of Defects SecureHaitham YoussefNo ratings yet
- Mechanism and Mechanical Vibration (Lab Work) Teaching PlanDocument8 pagesMechanism and Mechanical Vibration (Lab Work) Teaching PlanBelia NomeNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Water Harvesting Development and ChallengesDocument218 pagesAtmospheric Water Harvesting Development and ChallengesMohamed GaberNo ratings yet
- Contractor Daily Construction Report DEC13Document10 pagesContractor Daily Construction Report DEC13Kei-Ar MahiyaNo ratings yet
- The Idea of ProgressDocument1 pageThe Idea of Progressvictor carre poussinNo ratings yet
- Pathfinder PerbintanganDocument6 pagesPathfinder PerbintanganediesNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS and A Level Global Perspectives and ResearchDocument35 pagesCambridge International AS and A Level Global Perspectives and ResearchSwati RaiNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam Syllabus Class IVDocument3 pagesAnnual Exam Syllabus Class IVMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- PbO Al2O3 TeO2 GeO2 SiO2 CuODocument9 pagesPbO Al2O3 TeO2 GeO2 SiO2 CuOhanumatharao kNo ratings yet
- Homework #4 MEMS6460: (30 Points)Document7 pagesHomework #4 MEMS6460: (30 Points)vidhukiran100% (1)
- Table Differences Between Reggio Montessori SteinerDocument5 pagesTable Differences Between Reggio Montessori SteinerAswiniie100% (1)
- Qdoc - Tips - Cryptomancer Code Amp Dagger Vol 01Document48 pagesQdoc - Tips - Cryptomancer Code Amp Dagger Vol 01adyNo ratings yet
- 6640 MSDSDocument4 pages6640 MSDSShaikhRizwanNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2Document8 pagesNSTP 2Darren GreNo ratings yet
- Non Euclidean GeometryDocument14 pagesNon Euclidean GeometryMark Lacaste De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- How To Make SAG Template For Tower Spotting 1Document6 pagesHow To Make SAG Template For Tower Spotting 1Baris AybarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (5 Lectures)Document15 pagesChapter 1 (5 Lectures)PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Comparative Validation of Amperometric and Optical Analyzers of Dissolved Oxygen: A Case StudyDocument15 pagesComparative Validation of Amperometric and Optical Analyzers of Dissolved Oxygen: A Case StudyIsmael Morales PuenteNo ratings yet
- Insect Ecology Integrated Pest Management Dec. 3 2023Document16 pagesInsect Ecology Integrated Pest Management Dec. 3 2023bedalea07No ratings yet
- Electric PotentialDocument92 pagesElectric PotentialBanani BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Research: Newborn CareDocument119 pagesResearch: Newborn CareLouie Anne Cardines Angulo100% (2)
- "Valediction Sa Hillcrest" by Rolando S. Tinio Poem AnalysisDocument2 pages"Valediction Sa Hillcrest" by Rolando S. Tinio Poem AnalysisGlecy Adriano100% (1)
- Course 21F - Foreign Languages & Literatures - 2012Document2 pagesCourse 21F - Foreign Languages & Literatures - 2012MichaelNo ratings yet
- DIASS Week 1 Module (Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences)Document22 pagesDIASS Week 1 Module (Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences)Ricardo Acosta SubadNo ratings yet
- Measuring Performance of Microfinance Institutions A Framework For Reporting Analysis and Monitoring ToolkitDocument271 pagesMeasuring Performance of Microfinance Institutions A Framework For Reporting Analysis and Monitoring Toolkitigga d johnNo ratings yet
- 15 Professional Development Skills For Modern TeachersDocument3 pages15 Professional Development Skills For Modern TeachersAndevie Balili IguanaNo ratings yet
- The Roman Conquest of Wales AD 47-410Document64 pagesThe Roman Conquest of Wales AD 47-410Gamer4242No ratings yet
- Mathematical Argument, Language and Proof: AS/A LEVEL 2017Document4 pagesMathematical Argument, Language and Proof: AS/A LEVEL 2017Florita LagramaNo ratings yet
- BS5489-7 1992Document45 pagesBS5489-7 1992GEO MSc Group-2016No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of The Neurotoxin Domoic Acid in A Bloom-Forming DiatomDocument4 pagesBiosynthesis of The Neurotoxin Domoic Acid in A Bloom-Forming DiatomHamidun BunawanNo ratings yet