Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current Electricty 01 Board Questions
Uploaded by
Divyanshi KhareOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current Electricty 01 Board Questions
Uploaded by
Divyanshi KhareCopyright:
Available Formats
CURRENT & ELECTRICITY
1. (i) Define drift velocity? Write a relationship between the drift velocity and electric current.
(ii) Define specific resistance or resistivity. Write its SI unit and dimensional formula.
(iii) How does increase temperature affect the conductivity of a semi-conductor?
(iv) When a potential difference is applied across the ends of a conductor, how is the drift
velocity of the electrons related to the relaxation time?
(v) How is the drift velocity in a conductor affected with the rise in temperature?
2. A copper wire of non-uniform area of cross-section is connected to a cell. Which physical
quantity remains constant along the wire?
3. A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a variable external resistance R.
Draw the graph of terminal potential difference V as a function of R.
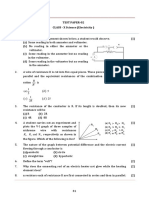
4. A uniform of resistance 4R is bent in the form of a circle. What will be effective resistance
between the ends of any diameter of the circle?
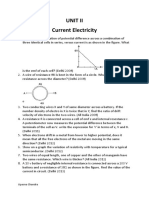
5. A 10 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a
resistance of 38 W as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current in the circuit.
6. Nichrome and copper wires of same length and same radius are connected in series. Current I
is passed through them. Which wire gets heated up more? Justify your answer
7. Define the conductivity of a conductor. Write its SI unit.
8. Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material Ga, As is shown in the
figure, identify the region of :
(i) Negative resistance
(ii) Where Ohm’s law is obeyed
9. What is the unit of conductance ?
Ans. The unit of conductance is mho or Siemens.
10. How does the drift velocity in a conductor change with increase of flowing current ?
Ans. Drift velocity in a conductor increases with the increase of current flowing
11. Show variation of resistivity of copper as a function of temperature in a graph
12. A wire of resistance R is divided in 10 equal parts. These parts are connected in parallel, the
equivalent resistance of such connection will be
13. Two electric bulbs P and Q have their resistances in the ratio of 1 : 2. They are connected in
series across a battery. Find the ratio of the power dissipation in these bulbs.
14. Two cells of emfs 1.5 V and 2.0 V having internal resistances 0.2 Ω and 0.3 Ω respectively are
connected in parallel. Calculate the emf and internal resistance of the equivalent cell
15. Derive an expression for drift velocity of electrons in a conductor. Hence deduce Ohm’s law
16. (i) Define the term drift velocity.
(ii) On the basis of electron drift, derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms of
number
density of free electrons and relaxation time. On what factors does resistivity of a conductor
depend?
(iii) Why alloys like constantan and manganin are used for making standard resistors?
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- GR Xii Holiday Homework Worksheet-3Document2 pagesGR Xii Holiday Homework Worksheet-3PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Electricity Question Bank ExplainedDocument7 pagesElectricity Question Bank ExplainedChithambaramNo ratings yet
- Electric Current Level A QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectric Current Level A QuestionsTushar RajNo ratings yet
- XII R PHY WORKSHEET 29-7-22Document13 pagesXII R PHY WORKSHEET 29-7-22Rahul GautamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Current Electricity: Question BankDocument9 pagesUnit 2: Current Electricity: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Board Exam Questions on Electricity and Circuits (2007-2016Document38 pagesBoard Exam Questions on Electricity and Circuits (2007-2016Rishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- New Holiday Homework Class XiiDocument5 pagesNew Holiday Homework Class Xiiabhinavshrivastava04No ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Sboa Revision 1Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity - Sboa Revision 1President ObamaNo ratings yet
- 10 Years of Current ElectricityDocument6 pages10 Years of Current ElectricitydipeshjoonNo ratings yet
- Curr Elec Imp QuestionsDocument2 pagesCurr Elec Imp QuestionsShyamNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 2Document8 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 2Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Current ElectricityDocument11 pagesAssignment - Current ElectricityPresident ObamaNo ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- Question Bank Current Electricity CBSEDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank Current Electricity CBSEjashankalsi811No ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity ConceptsDocument10 pagesElectrostatics and Current Electricity ConceptsAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument20 pagesFrequently Asked Questionsambujambuj65No ratings yet
- Current Electricity Imp QuestionsDocument2 pagesCurrent Electricity Imp QuestionsAkshith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (Unit: Ii) : One Mark QuestionsDocument13 pagesCurrent Electricity (Unit: Ii) : One Mark Questionsmechanical_lecturer100% (1)
- Current Electricity.Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity.fhd80000000No ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Ncert Practice QuestionsDocument15 pagesChapter-3 Ncert Practice QuestionsRAHIM MDNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Frequently Asked Questions in ExaminationsDocument30 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Frequently Asked Questions in ExaminationsArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Questions 1.: Question BankDocument4 pages1 Mark Questions 1.: Question Bankharipriya3011No ratings yet
- XII PHYSICS Summer Vacation Homework PDFDocument3 pagesXII PHYSICS Summer Vacation Homework PDFSoniyaNo ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document6 pagesPhysics 3Aadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- CH-3 SAMPLE -1Document3 pagesCH-3 SAMPLE -1jayNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics WorksheetDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics WorksheetRakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Qestion Bank Class 12 PhysicsDocument3 pagesQestion Bank Class 12 PhysicsLochana T SNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics EMI AC WorksheetDocument4 pages12th Physics EMI AC WorksheetlkNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class X NotesDocument15 pagesElectricity Class X NotesGrgg Hkhkk100% (5)
- Worksheet X PhysicsDocument31 pagesWorksheet X PhysicsGuru PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 PP Xii PhysicsDocument6 pagesChapter 03 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77No ratings yet
- Work Sheet of Current ElectricityDocument18 pagesWork Sheet of Current ElectricityRam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Question Bankof Physicsfor Class 10 THDocument16 pagesQuestion Bankof Physicsfor Class 10 THmeerneelofarh455No ratings yet
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics: SECTOR - 4, Gurgaon Topics: Current ElectricityDocument3 pagesAnant Achievement Classes Physics: SECTOR - 4, Gurgaon Topics: Current ElectricityUTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Resistivity and Conductivity of MaterialsDocument3 pagesResistivity and Conductivity of MaterialsAsher MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Current, Resistance and EMF - DONEDocument7 pagesCurrent, Resistance and EMF - DONEcindy boysilloNo ratings yet
- XII Worksheet (Electricity) PDFDocument2 pagesXII Worksheet (Electricity) PDFAyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Current Electricity 2023Document5 pagesWorksheet Current Electricity 2023Megha MondalNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityMohit GargNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity WorksheetDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity WorksheetRohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current ElectricityShuchi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Worksheet (Rvised ws1)Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity Worksheet (Rvised ws1)3D SAMINo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsAlind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument14 pagesCurrent ElectricityffffffgNo ratings yet
- COMPETANCY BASED QUESTIONSDocument7 pagesCOMPETANCY BASED QUESTIONSLochana T SNo ratings yet
- Current Ele Pre QDocument2 pagesCurrent Ele Pre QAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- HHW Class12 New PDFDocument58 pagesHHW Class12 New PDFSannidhi ShettyNo ratings yet
- Variation of Potential Difference Across Cells in SeriesDocument77 pagesVariation of Potential Difference Across Cells in SeriesAashish kpNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)Document3 pages12th Physics Worksheet (ch3 To ch7)lovecatsaninalsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Current ElectricityDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 3 Current Electricitymanoj sharmaNo ratings yet
- SHORT ANSWER QUESTION Current Electricity SubjectiveDocument2 pagesSHORT ANSWER QUESTION Current Electricity Subjectivephysicist sharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th science electric circuit assignment questionsDocument2 pagesClass 10th science electric circuit assignment questionsPriyanka Kasturia100% (1)
- Current Electricity HDHW Vsa & Sa 2023Document6 pagesCurrent Electricity HDHW Vsa & Sa 2023mishra.sanskar12345No ratings yet
- X ScienceDocument7 pagesX ScienceSanghamitra ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Revision WorksheetDocument7 pagesElectricity - Revision Worksheetmk.afeefuddinNo ratings yet
- Unit I - IIDocument6 pagesUnit I - IINarendra SNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit WorksheetDocument1 pageElectric Circuit WorksheetSydney AureliaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - NCERT at Your Fingertips OCR PDFDocument47 pagesCurrent Electricity - NCERT at Your Fingertips OCR PDFPushkar NawaleNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effects of Electrical CurrentDocument4 pagesChemical Effects of Electrical CurrentAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Applications in Electric and Magnetic TheoryDocument6 pagesVector Calculus Applications in Electric and Magnetic TheorySadeep MadhushanNo ratings yet
- (P) 197162 November 2013 Question Paper 21Document16 pages(P) 197162 November 2013 Question Paper 21Edita Rosanna TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics Practice Book AnswersDocument22 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics Practice Book AnswersRonnie Quek50% (2)
- 12SDMS01Document14 pages12SDMS01hafezasadNo ratings yet
- Thermionic EmissionDocument22 pagesThermionic EmissionMuhammadShabbirNo ratings yet
- Electric Current & Resistance ExplainedDocument13 pagesElectric Current & Resistance ExplainedRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- Artigo Fator de PotênciaDocument4 pagesArtigo Fator de PotênciaDiego FaenelloNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign16Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign16Tapas Banerjee100% (1)
- 10 Test ElectricityDocument2 pages10 Test ElectricityDeepakNo ratings yet
- Exploring alternating current and its applicationsDocument14 pagesExploring alternating current and its applicationsMaxNo ratings yet
- APGenco Test Question Paper Answer JbigDeaLDocument10 pagesAPGenco Test Question Paper Answer JbigDeaLPrem ChandarNo ratings yet
- Voltage Variation - Pol - DepolDocument6 pagesVoltage Variation - Pol - DepolDeepu MishraNo ratings yet
- 1923 - Wave Antenna - BeverageDocument52 pages1923 - Wave Antenna - Beveragenestor.escala7666No ratings yet
- Power Enhance Technics-Cpe13Document204 pagesPower Enhance Technics-Cpe13Sarath Chandra VNo ratings yet
- Module 8 ElectromagnetismDocument35 pagesModule 8 ElectromagnetismMelvin Cabonegro80% (10)
- Nordac Vector MC PDFDocument64 pagesNordac Vector MC PDFTonino08No ratings yet
- CP Physics Final Exam Review 2Document25 pagesCP Physics Final Exam Review 2eltytanNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Chapter-14-Chemical Effects of CurrentDocument4 pages8 Science Chapter-14-Chemical Effects of CurrentSagarJadhavNo ratings yet
- Tut Relay FinalDocument10 pagesTut Relay FinalAravind KaraNo ratings yet
- Neutral Earthing Resistors or Reactors Application GuideDocument98 pagesNeutral Earthing Resistors or Reactors Application Guideecordero78100% (1)
- Automotive Electrical-Electronic Systems: Fundamentals of Electrics & ElectronicsDocument39 pagesAutomotive Electrical-Electronic Systems: Fundamentals of Electrics & ElectronicsMinh TríNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Part - A (2 Marks)Document6 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Part - A (2 Marks)1050 SAKTHIVEL SNo ratings yet
- Plasma DisplaysDocument13 pagesPlasma Displaysaji2000No ratings yet
- Adwa SSUDocument91 pagesAdwa SSUAdrian MariusNo ratings yet
- 111 - New 48v Battery ChargerDocument14 pages111 - New 48v Battery Chargersaurabhjerps231221No ratings yet
- HKCEE PHYSICS REVISION NOTES ON HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSESDocument40 pagesHKCEE PHYSICS REVISION NOTES ON HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSESLibertyTong100% (1)
- Power Electronics: An IntroductionDocument201 pagesPower Electronics: An IntroductionNeeraj SinghalNo ratings yet