Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anant Achievement Classes Physics: SECTOR - 4, Gurgaon Topics: Current Electricity
Uploaded by
UTSAV JAINOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anant Achievement Classes Physics: SECTOR - 4, Gurgaon Topics: Current Electricity
Uploaded by
UTSAV JAINCopyright:
Available Formats
ANANT ACHIEVEMENT CLASSES PHYSICS
SECTOR – 4, Gurgaon TOPICS : CURRENT ELECTRICITY
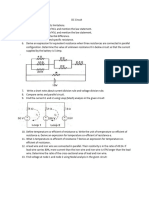
1. a. Derive an expression for drift velocity with R1, null point is obtained at
of electrons in a conductor. Hence AD=60cm.
deduce Ohm’s law. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
b. A wire whose cross-sectional area is
increasing linearly from its one end to
the other, is connected across a battery
of V volts. Which of the following
quantities remain constant in the wire ?
i. drift speed ii. current density
iii. electric current
iv. electric field 4. a. State, with the help of circuit diagram,
Justify your answer. the working principle of a meter bridge.
Obtain the expression used for
2. a. Define the term ‘drift velocity’ of determining the unknown resistance.
charge carriers in a conductor. Obtain b. What happens if the galvanometer and
the expression for the current density in cell are interchanged at the balance point
terms of relaxation time. of the bride ?
c. Why is it considered important to
obtain the balance point near the mid-
point of the wire ?
5. a. State the two Kirchhoff’s laws.
Explain briefly how these rules are
justified.
b. The current is drawn from a cell of
b. A 100V battery is connected to the emf E and internal resistance r connected
electric network as shown. If the power to the network of resistors each of
consumed in the 2 resistor is 200W, resistance r as shown in the figure.
determine the power dissipated in the 5 Obtain the expression for (i) the current
resistor. draw from the cell and (ii) the power
consumed in the network.
3. a. State Kirchhoff’s rules for a network.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, obtain the
balance condition in terms of the
resistances of four arms of Wheatstone
Bridge.
b. In the meter bridge experimental set 6. a. State the working principal of a
up, shown in the figure, the null point D potentiometer. With the help of the
is obtained at a distance of 40cm from circuit diagram, explain how a
end A of the meter bridge wire. If a potentiometer is used to compare the
resistance of 10 is connected in series emfs of two primary cells. Obtain the
required expression used for comparing
the emfs.
b. Write two possible causes for one
sided deflection in a potentiometer
experiment.
7. Two cells of emfs 1, 2 and internal When an unknown resistance X is
resistances r1 and r2 respectively are connected in parallel with the resistance
connected in parallel as shown in the S, the balance point shifts to a distance
figure. l2. Find the expression for X in terms of
Deduce the expression for l1, l2 and S.
a. The equivalent emf of the
combination. 11. State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in
b. The equivalent resistance of the electric networks. How are these rules
combination, and justified ?
c. The potential difference between the
points A and B 12. Define mobility of electron in a
conductor. How does electron mobility
change when (i) temperature of
conductor is decreased and (ii) applied
potential difference is doubled at
constant temperature ?
13. a. Define the term ‘conductivity’ of a
8. A potential difference V is applied metallic wire. Write its SI unit.
across a conductor of length L and b. Using the concept of free electrons in
diameter D. How are the electric field E a conductor, derive the expression for
and the resistance R of the conductor the conductivity of a wire in terms of
affected when (i) V is halved (ii) L is number density and relaxation time.
halved (iii) D is doubled. Justify your Hence obtain the relation between
answer. current density and the applied electric
field E.
9. State the underlying principle of a
potentiometer. Describe briefly, giving 14. Plot a graph showing the variation of
the necessary circuit diagram, how a current density (j) versus the electric
potentiometer is used to measure the field (E) for two conductors of different
internal resistance of a given cell. materials. What information from this
plot regarding the properties of the
10.a. State the principle of working of a conducting material, can be obtained
meter bridge. which can be used to select suitable
b. In a meter bridge balance point is (ii)connecting wires in electric circuit ?
found at a distance l1 with resistances R Electron drift speed is estimated to be of
and S as shown in the fig. the order of mms-1. Yet large current of
the order of few amperes can be set up in supply of voltage, V, consume powers P1
the wire. Explain briefly. and P2 respectively. Deduce the
expressions for the power of their
15. Define relaxation time of the free combination when they are, in turn,
electrons drifting in a conductor. How is connected in (i) series and (ii) parallel
it related to the drift velocity of free across the same voltage supply.
electrons ? Use this relation to deduce
the expression for the electrical
resistivity of the material.
16. Two students X and Y perform an
experiment on potentiometer separately
using the circuit given below.
Keeping other parameters unchanged,
how will the position of the null point be
affected if
i. X increases the value of resistance R
in the set-up by keeping the key K1
closed and the key K2 open ?
ii. Y decreases the value of resistance S
in the set-up, while the key K2 remains
open and the key K1 closed.
17. A cell of emf E and internal resistance r
is connected across a variable resistor R.
Plot a graph showing variation of
terminal voltage V of the cell versus the
current I. Using the plot, show how the
emf of the cell and its internal resistance
can be determined.
18. State the principle on which the working
of a meter bridge is based. Under what
condition is the error in determining the
unknown resistance minimized ?
19. Two heating elements of resistances R1
and R2 when operated at a constant
You might also like
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- 10 Years of Current ElectricityDocument6 pages10 Years of Current ElectricitydipeshjoonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Frequently Asked QuestionsNaveen rajNo ratings yet
- Electricity Question Bank ExplainedDocument7 pagesElectricity Question Bank ExplainedChithambaramNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Frequently Asked Questions in ExaminationsDocument30 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Frequently Asked Questions in ExaminationsArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument20 pagesFrequently Asked Questionsambujambuj65No ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board QuestionsDocument50 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board Questionsgurveer sainiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 2Document8 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 2Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Current Electricity: Question BankDocument9 pagesUnit 2: Current Electricity: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Qestion Bank Class 12 PhysicsDocument3 pagesQestion Bank Class 12 PhysicsLochana T SNo ratings yet
- Current Electricty 01 Board QuestionsDocument2 pagesCurrent Electricty 01 Board QuestionsDivyanshi KhareNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper IIDocument4 pagesPractice Paper IISingh PushparajNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity.Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity.fhd80000000No ratings yet
- 12th Physics EMI AC WorksheetDocument4 pages12th Physics EMI AC WorksheetlkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 PP Xii PhysicsDocument6 pagesChapter 03 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77No ratings yet
- XII Q Group 1Document3 pagesXII Q Group 1Sanskriti VermaNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework Class: XII Subject: PhysicsAlind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Xii Derivation List-2023-24 2Document3 pagesXii Derivation List-2023-24 2prachurjyapadhiNo ratings yet
- Electric Current Level A QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectric Current Level A QuestionsTushar RajNo ratings yet
- Unit I - IIDocument6 pagesUnit I - IINarendra SNo ratings yet
- 5 markersDocument9 pages5 markersshiviNo ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment For First TermDocument10 pages2nd Assignment For First TermRaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Physics XII 12-10-2017Document49 pagesPhysics XII 12-10-2017Neelkant DubeyNo ratings yet
- Physics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaDocument5 pagesPhysics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaGAME DEVNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- XII Worksheet (Electricity) PDFDocument2 pagesXII Worksheet (Electricity) PDFAyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Document15 pagesReduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Saher SaghirNo ratings yet
- Physics All IndiaDocument17 pagesPhysics All IndiahiNo ratings yet
- Sharjah Indian School, Sharjah. First Term Examination - June 2009Document3 pagesSharjah Indian School, Sharjah. First Term Examination - June 2009ram parthsaNo ratings yet
- Electricity2 PDFDocument17 pagesElectricity2 PDFPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument14 pagesCurrent ElectricityffffffgNo ratings yet
- PotentialDocument1 pagePotentialmili groupNo ratings yet
- Assignments - 12 ADocument8 pagesAssignments - 12 ARitika LalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Sheet HW PDFDocument5 pagesClass 12 Revision Sheet HW PDFAditya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Current Electricity 2023Document5 pagesWorksheet Current Electricity 2023Megha MondalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Current Electricity CBSEDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank Current Electricity CBSEjashankalsi811No ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Sboa Revision 1Document5 pagesCurrent Electricity - Sboa Revision 1President ObamaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Worksheet (Rvised ws1)Document2 pagesCurrent Electricity Worksheet (Rvised ws1)3D SAMINo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesCurrent Electricityatharvbaghel4444No ratings yet
- New Holiday Homework Class XiiDocument5 pagesNew Holiday Homework Class Xiiabhinavshrivastava04No ratings yet
- XII R PHY WORKSHEET 29-7-22Document13 pagesXII R PHY WORKSHEET 29-7-22Rahul GautamNo ratings yet
- SR AssignmentDocument24 pagesSR AssignmentdeveshNo ratings yet
- Current Ele Pre QDocument2 pagesCurrent Ele Pre QAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Current ElectricityDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 3 Current Electricitymanoj sharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Pattern Level - 0 ExamDocument52 pagesCBSE Pattern Level - 0 Exambrainx MagicNo ratings yet
- 4102607567674351Document28 pages4102607567674351guyanonymous017No ratings yet
- Cbse Electrostatics and Current ElectricityDocument6 pagesCbse Electrostatics and Current ElectricityHimanshu KatwalNo ratings yet
- Class: XII Subject: Physics Assignment 1 Chapter: ElectrostaticsDocument2 pagesClass: XII Subject: Physics Assignment 1 Chapter: ElectrostaticsAryan KhannaNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Exam XII PhysicsDocument3 pagesHalf Yearly Exam XII PhysicstdcgxgchhcNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document4 pagesWa0006.Qusay saifyNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityMohit GargNo ratings yet
- Bee DC Circuit Question Bank-1Document2 pagesBee DC Circuit Question Bank-1Mona PadhyNo ratings yet
- STD.12 Abc-PhysicsDocument4 pagesSTD.12 Abc-PhysicsSwappyNo ratings yet
- C5&-11 Electromagnetics Revision TestDocument14 pagesC5&-11 Electromagnetics Revision Test2193693752No ratings yet
- Physics XII Assignment 1 M.M 30 Part A (1 Marks Question)Document9 pagesPhysics XII Assignment 1 M.M 30 Part A (1 Marks Question)Nisha RajnwalNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Grade 12 PhysicsDocument5 pagesSample Paper Grade 12 PhysicsRohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Case Source BaseDocument15 pagesCurrent Electricity Case Source BaseArnav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Current Electricity ConceptsDocument10 pagesElectrostatics and Current Electricity ConceptsAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics TestDocument2 pagesAnant Achievement Classes Physics TestUTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics TestDocument2 pagesAnant Achievement Classes Physics TestUTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics TestDocument2 pagesAnant Achievement Classes Physics TestUTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATING CURRENT 2020 Together With Physics 21012020Document3 pagesALTERNATING CURRENT 2020 Together With Physics 21012020UTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Sui Gas Connection FormsDocument1 pageSui Gas Connection Formsare50% (2)
- Ic F3022SDocument36 pagesIc F3022SEfren.galNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerFrank Jomari MurilloNo ratings yet
- Brass Valves Spec SheetDocument1 pageBrass Valves Spec SheetSharjeel AbidNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing Mineral Exploration LithiumDocument16 pagesRemote Sensing Mineral Exploration LithiumGerald Darshan MogiNo ratings yet
- 3204-9-Resource Use and SustainabilityDocument25 pages3204-9-Resource Use and SustainabilityKezia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Agard Ar 138 PDFDocument612 pagesAgard Ar 138 PDFAshwani AssamNo ratings yet
- Operating - System - Concepts - Essentials8thed - CH 6 SolutionDocument2 pagesOperating - System - Concepts - Essentials8thed - CH 6 SolutionAmirreza Saheb FosoulNo ratings yet
- IR Spectroscopy Identification GuideDocument28 pagesIR Spectroscopy Identification GuideAby JatNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety Procedure Rev.08Document41 pagesRadiation Safety Procedure Rev.08manz29No ratings yet
- 1,16Document138 pages1,16niztgirlNo ratings yet
- IndictmentDocument2 pagesIndictmentCBS Austin WebteamNo ratings yet
- SP18368 Automotive Radar Comparison 2018 Sample 2Document33 pagesSP18368 Automotive Radar Comparison 2018 Sample 2Chipisgood YuNo ratings yet
- The Mini Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (Mini-PCNL) and Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in Pediatric PatientsDocument4 pagesThe Mini Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (Mini-PCNL) and Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) in Pediatric PatientsMarius DanilaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon ReactionsDocument2 pagesHydrocarbon ReactionsJessa Libo-onNo ratings yet
- DL Throughput Improvement with Aperiodic CQI ReportingDocument10 pagesDL Throughput Improvement with Aperiodic CQI ReportingAqeel HasanNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Water, Ecosystems and Society A Confluence of Disciplines. by Jayanta BandyopadhyayDocument2 pagesBook Review - Water, Ecosystems and Society A Confluence of Disciplines. by Jayanta BandyopadhyayPDNo ratings yet
- User Manual For Digital Logic Trainer KitDocument6 pagesUser Manual For Digital Logic Trainer KitHonnura HarijanaNo ratings yet
- Persian Polymath Physician Al-Rāzī's Life and WorksDocument10 pagesPersian Polymath Physician Al-Rāzī's Life and WorksAnonymous 29PN6AZTNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Analysis Short Ciruit Load Flow and HarmonicsDocument1 pagePower Systems Analysis Short Ciruit Load Flow and HarmonicsJurij BlaslovNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 - Pengantar Remote SensingDocument60 pagesModul 1 - Pengantar Remote SensingNgurah Ade KalyanaNo ratings yet
- Vammika Sutta - Mahasi SayadawDocument108 pagesVammika Sutta - Mahasi SayadawtravelbootsNo ratings yet
- Rodriguez ViereaDocument51 pagesRodriguez ViereaAwawawawa UwuwuwuwuNo ratings yet
- Strength of CSG and TBGDocument10 pagesStrength of CSG and TBGTiffany DacinoNo ratings yet
- Week 05 - Mechanical Properties Part 1Document48 pagesWeek 05 - Mechanical Properties Part 1Dharshica MohanNo ratings yet
- SP 5300DN SP 5310DN SÑljguideDocument32 pagesSP 5300DN SP 5310DN SÑljguidepaypkerry_179706015No ratings yet
- SOLAR DRYER v1Document43 pagesSOLAR DRYER v1Maria Angelica Borillo100% (1)
- 2K6 Ec 307 (P) : Basic Electronics Lab: Sessional Work AssessmentDocument1 page2K6 Ec 307 (P) : Basic Electronics Lab: Sessional Work AssessmentJoseph JohnNo ratings yet
- Ajuste IAC and TPSDocument17 pagesAjuste IAC and TPSLuis Ignacio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Case StudiesDocument26 pagesHospitality Case StudiesKarthik PalaniswamyNo ratings yet