Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2023 - Science 9 Exam Review
Uploaded by
Zunairah AdnanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2023 - Science 9 Exam Review
Uploaded by
Zunairah AdnanCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: _________________________Class: ______
Grade 9 Science Final Exam Study Guide
Unit 1: Biological Diversity
Investigate and interpret diversity AMONG species, WITHIN species and describe how diversity
contributes to species survival.
Steps to this include:
identify examples of variation between species and within species.
distinguish between a broad and a narrow niche.
describe characteristics of generalist and specialist organisms.
identify which types of organisms are likely to have higher populations.
describe how variation can increase survival during environmental changes.
explain how variation can increase survival of species living in the same ecosystem.
give examples of structural and behavioral adaptations and explain how these contribute to
species survival.
interpret symbiotic relationships and describe how they increase survival of organisms.
distinguish between discrete and continuous variation.
Investigate how organisms reproduce and describe how different characteristics are passed down
through a species.
Steps to this include:
describe different methods of asexual reproduction.
describe different methods of sexual reproduction.
Explain the processes involved in the stages of sexual reproduction.
Explain, in general terms, cell division by mitosis and meiosis
distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction methods.
describe advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproduction methods.
distinguish between characteristics that are heritable and those that are not.
identify characteristics that are influenced by both heredity and environment.
Describe how DNA is involved in variation of species and how it can be changed both naturally and
artificially.
Steps to this include:
describe the basic relationship between DNA, genes and chromosomes.
distinguish between mitosis and meiosis and describe each in general.
identify stages in cell division and development that involve doubling and halving of genetic
information.
Explain how traits can be passed down using simple dominant-recessive inheritance.
describe the ideas behind the Theory of Natural Selection.
Explain how DNA changes lead to variation.
distinguish between natural and artificial selection and can describe examples of each.
describe simple technologies for recombining genetic information.
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
Identify and analyze human impacts on species survival and diversity, both positive and negative.
Steps to this include:
describe environments that are likely to have higher biodiversity.
investigate factors that lead to extinction and extirpation of species.
evaluate different strategies for decreasing losses in biodiversity.
Guiding Questions:
1) describe environments that are likely to have higher biodiversity.
2) investigate factors that lead to extinction and extirpation of species.
3) evaluate different strategies for decreasing losses in biodiversity.
4) What is biological diversity?
5) What are the 5 kingdoms?
6) What are the different levels in Linnaean Classification? (KPCOFGS)
7) What value does variation have in an environment?
8) What are the two main components of a niche?
9) What is competition and why is it a healthy feature of environments? Who can it occur
between? What are some resources organisms might compete for?
10) What is a niche?
11) Where on Earth is the greatest biodiversity?
12) Briefly describe the three kinds of symbiotic relationships.
13) What does it mean if something is heritable?
14) What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproduction?
15) Explain how each of the following function in regards to asexual reproduction:
- Budding
- Binary fission
- Spore production
- Vegetative reproduction
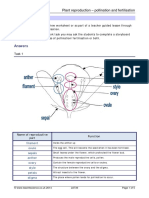
16) List the male and female parts of a plant and explain the process of pollination.
17) What is the difference between self-pollination and cross pollination?
18) What is fertilization?
19) What is the difference between an embryo and a zygote?
20) Gametes are sex cells. What are the male sex cells called? What are the female sex cells
called?
21) What is the difference between discrete and continuous traits? Identify three examples of
each.
22) Explain the difference between a dominant and recessive trait.
23) If an individual inherits both a dominant and recessive copy of a trait, which copy of the trait
will be expressed?
24) What is a Punnett square? What is it used for?
25) What is DNA? Describe the structure of DNA.
26) What are chromosomes and where are they located in cells?
27) What are genes and where are they located?
28) Somatic (body) cells divide by a process called mitosis. How many daughter cells are
produced in this process?
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
29) Sex cells are also known as ___________. They reproduce via a process called
____________. This produces ________ daughter cells. What is special about the number of
chromosomes in these cells?
30) What is biotechnology? What has biotechnology been used for?
31) Why is genetic engineering controversial?
32) What is artificial selection? Give an example of it being used.
33) What is natural selection
34) How do humans impact biodiversity?
35) What is the difference between in-situ conservation and ex-situ conservation. Provide
examples of each.
36) There are two main reasons why there is more biological diversity on Vancouver Island than
there is in the Boreal forest north of Edmonton. What are they?
37) Why is a tiger considered a different species than a lion?
38) Pick an organism that you might find in Alberta and describe its niche, habitat, and range.
39) Correctly use the words “gametes” and “zygote” in a sentence to show that you understand
their meaning.
40) In cats, the black colour gene is dominant to the white colour gene.
a) If purebred black and a purebred white cat have kittens, what colour will they be?
Give proof.
b) If two of those kittens are bred, what is the likelihood that they will have white
offspring? Use a Punnett square and show your work.
41) In humans, the gene for Huntington’s Disease is dominant to the normal gene. If a mother
who is heterozygous for Huntington’s has children with a man who does not have
Huntington’s, what is the probability their children will have the disease? Use a Punnett
square and show your work.
42) Roundup is a commonly used herbicide. It kills weeds that have not been genetically
engineered to resist it.
a) What is meant by the term “genetically engineered?”
b) Describe how the use of this herbicide might create “super weeds” as a result of
natural selection.
43) What is the difference between natural and artificial selection? Give an example of where
artificial selection may be useful.
44) Species can often be described as specialists or generalists.
a) Which would have a broader niche? A generalist or a specialist?
b) If the environment changes rapidly, would an organism with a broad niche or a
narrow niche have the best chance of surviving? Explain why.
45) A farmer is testing how well different varieties of corn grow in his field. He plants varieties
A, B, and C in alternating rows across a 50 m span in his field and at the end of the year
measures the mass of corn that he gets from each variety.
a) What’s the manipulated variable?
b) What is the responding variable?
c) List at least three good controls that the farmer should put in place for the experiment
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
Unit 2: Matter and Chemical Change
Can you?
identify and evaluate dangers of caustic materials and potentially explosive reactions
investigate and describe properties of materials
describe and apply different ways of classifying materials based on their composition and
properties
distinguish between observation and theory, and provide examples of how models and
theoretical ideas are used in explaining observations
demonstrate understanding of the origins of the periodic table, and relate patterns in the
physical and chemical properties of elements to their positions in the periodic table
Use the periodic table to:
identify the number of protons and electrons in each atom, as well as other information about
each atom
describe the relationship between the structure of atoms in each group and the properties of
elements in that group
distinguish between ionic and molecular compounds, and describe the properties of some
common examples
read and interpret chemical formulas for compounds of two elements, and give the IUPAC
name and common name of these compounds
identify/describe chemicals commonly found in the home, and write the chemical symbols
identify examples of combining ratios/number of atoms per molecule found in some common
materials, and use information on ion charges to predict combining ratios in ionic compounds
of two elements
assemble or draw simple models of molecular and ionic compounds
identify conditions under which properties of a material are changed, and critically evaluate if
a new substance has been produced
observe and describe evidence of chemical change in reactions between familiar materials
distinguish between materials that react readily and those that do not
observe and describe patterns of chemical change
describe familiar chemical reactions, and represent these reactions by using word equations
and chemical formulas and by constructing models of reactants and products
Guiding Questions:
1) What does WHMIS stand for? What is it used for?
2) What are the 5 main points of the particle model of matter?
3) What are homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures?
4) Pure substances can be either __________ or ___________.
5) What are the characteristics of a physical change?
6) What is a chemical change?
7) Before you can determine if a chemical change has occurred, you must be able to conclude
that a new substance has been formed. What observations could you make to determine that a
chemical change has occurred, and how many observations should you make to be sure?
8) Physical properties are broken down into two main categories. What are these two categories
and give two examples from each category?
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
9) What is the law of conservation of mass?
10) What is an element? What is a compound? How are they different?
11) What are protons, neutrons, and electrons? Where are they found? What are their charges?
What are their relative sizes?
12) Why are symbols used for elements? What do the letters represent?
13) What properties are used to tell the difference between metals, nonmetals and metalloids?
14) What are chemical families? On a periodic table, place the Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth
Metals, Halogens, Noble Gases, and Coinage Metals. Describe, in general terms, their
reactivity. Note the position of the elements in each family relative to each other. (Families in
a column)
15) How did Mendeleev arrange the periodic table of elements?
16) What does the atomic number tell you about the element?
17) How can you use the atomic mass to determine the number of neutrons in an atom?
18) What are the four main features of an ionic compound?
19) What are the four main features of a molecular compound?
20) What is a diatomic molecule?
21) What is an ion?
22) What are the rules for naming ionic and molecular compounds?
23) Practice the above rules for naming compounds on the following substances:
- Silicon dioxide
- Sodium iodide
- CCl4
- H20
- Aluminum oxide
- SO2
- NO2
24) What is the difference between reactants and the products in a chemical reaction?
25) What is a chemical reaction?
26) Write out the chemical equation for the following reaction: Magnesium oxide is produced
when magnesium reacts with oxygen.
27) Explain the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions. Do they feel hot or
cold? Do the reactants have more energy in their bonds or do the products have more energy
in their bonds?
28) Define reaction rate.
29) What are some things you can do to increase the rate of reaction or decrease the rate of
reaction?
30) What is a catalyst?
31) What is an enzyme?
32) Describe the process of combustion and corrosion? What element is always present in every
combustion and corrosion reaction?
33) Name two things that can be done to prevent corrosion or slow it down.
34) What’s the difference between hardness and malleability?
35) Do metals have high or low melting/boiling points?
36) Identify each of the following as either a physical or chemical change:
a) Dissolving sugar in water to make juice
b) A car rusting
c) Burning a piece of paper
d) Boiling copper until it all evaporates
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
e) Photosynthesis
f) A glass of pop fizzes a lot when ice is added
37) List four pieces of evidence you could use to identify whether a chemical change has
occurred.
38) Write the word equations for each of the following reactions. Below the word equations,
write the chemical equation. Put a circle around the reactants and a rectangle around the
products, and identify if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
a) Combustion
b) Photosynthesis
c) Cellular respiration
d) Corrosion of iron
39) Pretend you’re helping a younger child build a model volcano and you want to produce a
faster or more explosive eruption.
a) What four things could you do to the baking soda or vinegar to make that happen?
b) Let’s say you combine 80 g of baking soda with 50 g of vinegar and you are left with
110 g of liquid and precipitate following the reaction. What was the mass of the gas
given off?
40) Using a periodic table of the elements, complete the following table.
41) Complete the following table.
42) Complete the following table to identify the differences between ionic and molecular
compounds.
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
43) Complete the following table.
Unit 3: Environmental Chemistry
Can you:
understand the importance of cycles in nature, including the water and nitrogen cycles.
identify different types of pollutants in the environment including fertilizers, pesticides, solid
wastes, wastewater and hydrocarbon fossil fuels.
identify the pH of acids, bases and neutral substances.
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
I can describe how to use, and the advantages and disadvantages of different means of testing
pH including pH meters, litmus paper and universal indicator papers and liquids. _____
describe neutralization reactions including the reagents and the products.
define organic in a chemical sense, and identify examples of organic and inorganic chemicals.
give examples of micronutrients and macronutrients used by living things and the importance
of having optimum amounts of each.
describe the composition and function of the four macromolecules that make up living things:
lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins.
describe the difference between active and passive transport.
define and differentiate between diffusion and osmosis.
identify substrates and nutrient levels for living things.
describe the use various aquatic invertebrates such as fly and dragonfly larvae, leeches, and
snails for biological monitoring.
identify chemical factors that affect the health and distribution of living things such as
dissolved oxygen, pH and nutrients.
explain how plant nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, in excessive quantities can lead to
detrimental effects in aquatic ecosystems (ie. accelerated eutrophication).
identify the use of hazardous chemicals on the environment by using LD50.
calculate chemical concentration in pph, ppt, ppm & ppb.
explain the danger and importance of ozone to the planet it’s connection with VOCs and
CFCs.
identify four greenhouse gases and their role in the enhanced greenhouse effect.
explain the difference between dilution, dispersion, and deposition.
define the terms porosity and permeability as it relates to different soil types (clay, sand, etc).
describe and differentiate between biodegradation, photolysis and photodegradation.
describe what biomagnification/bioaccumulation is and why it’s important to humans.
identify WHMIS symbols and understand the importance of using MSDSs.
evaluate potential risks of everyday situations on the environment and can describe safe
storage of hazardous household chemicals.
identify manipulated, responding and controlled variables in an experiment or scientific
investigation.
Guiding Questions:
1) List the organic nutrients. Where do we get these nutrients from and what are their roles?
2) What elements are commercial fertilizers made of? What do each of these elements do?
3) What is a pesticide? How does this impact the environment?
4) Identify the relationship between burning fossil fuels and increased carbon emissions
5) Explain the nitrogen cycle.
6) How can water quality be measured?
7) Explain the relationship between the amount of dissolved oxygen in a water source and the
temperature of the water.
8) What is the difference between an acid and a base? How can you tell if something is acidic or
basic?
9) What is acid precipitation and what causes it?
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
10) What is a scrubber and how does it help the environment?
11) What is pollution? What is a pollutant?
12) What is toxicity? What is the difference between acute and chronic toxicity?
13) Explain LD50.
14) What types of organisms are used as biological indicators of water quality?
15) How does pollution reach populations in the far North?
16) How is water pollution controlled in groundwater?
17) What is the air quality index and how is it measured?
18) Caffeine has an LD50 of 127mg/kg. Explain what that means. How much caffeine would
need to be consumed to have a 50% chance of dying?
19) What’s the difference between phytoremediation and photolysis?
20) What two conditions speed up biodegredation?
21) Farmer Joe is building a new water dugout to collect rainwater. What soil type should he use
to line the dugout? Why?
22) Using pH as part of your answer, explain why the Alberta Government might want to add
calcium carbonate (limestone) to a lake that has been affected by acid precipitation.
23) One type of juice has a sugar concentration of 20000 ppm and one has a concentration of
20000 ppb. Which will be sweeter?
24) Allison adds 5 mL of concentrated fertilizer to 10 L of water. What’s the parts per million
concentration of her new solution? Remember to show your work.
25) Accelerated eutrophication is the result of excess nitrogen and phosphorous levels in aquatic
ecosystems. Why would excess plant nutrients be a problem?
26) Define each of the following terms and give an example of each. Dispersion, Dilution and
Deposition.
Unit 4: Electrical Principles
Describe technologies for transfer and control of electrical energy.
Steps to doing this include:
State the laws of charges
Describe factors influencing static electricity and electrical discharge.
Distinguish between static and current electricity
Identify materials that make good electrical conductors
Identify materials that are electrical insulators
Draw and interpret circuit diagrams
Distinguish between series and parallel circuits
Identify pros and cons to series and parallel circuits
Use models or analogies to describe current, voltage and resistance
Measure voltage & current in different circuits, describe how it changes through the
circuit
Describe how resistance in a circuit affects current and energy transformations
Calculate resistance using Ohm’s law
Construct, test and troubleshoot low voltage circuits
Evaluate the efficiency of energy conversions in various devices and systems.
Steps to doing this include:
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
Calculating power used by devices in one of two ways:
P = IV
P=E/t (where time is in seconds)
Describe where energy can be lost when being transferred or transformed.
Calculate the efficiency of a system when given the input and output of energy.
Identify and describe ways of making systems more efficient.
Investigate and interpret devices that transform energy in various forms.
Steps to doing this include:
identify , describe and interpret examples of mechanical, chemical, thermal, electrical
and light energy.
Define and describe components of electrochemical cells
Evaluate how changing electrodes, electrolyte (composition and concentration) will
affect the voltage of an electrochemical cell.
Construct, use and evaluate how motors and generators work to transform energy.
Evaluate and troubleshoot how changes to motors can change their function.
Describe and discuss societal and environmental implications of the use of electrical
energy
Steps to doing this include:
Identify sources of electrical energy including renewable and non-renewable sources.
State benefits and concerns with using these different sources.
Describe which sources can be used sustainably and which usually are not.
Describe by-products of electrical generation such as greenhouse gases.
Identify concerns regarding conservation of energy resources and evaluate means
for improving how we use energy sustainably.
Guiding Questions:
1) How do objects become charged?
2) What is static electricity?
3) What are the 3 Laws of Charges?
4) What are insulators, conductors, and superconductors?
5) What is an electrostatic discharge? How can you/why would you prevent this from occurring?
6) What are the four basic components that all circuits have?
7) ***Be able to read and interpret circuit diagrams*** Ex. “If switch B is closed, which
light will turn on?” For each of the following, current and voltage, give its symbol, the
instrument used to measure it and its units. Symbol Instrument Units Current Voltage
8) What is resistance? How is resistance measured and what are the units?
9) Give the formula used to calculate resistance(Ohm’s Law) as well as the other two variations
of the formula. A toaster with a resistance of 145 Ω is connected to a 120 V source. What
current will flow through the toaster?
10) Circuits can be connected in parallel or series. What are the differences between parallel and
series circuits? Parallel and Series (be able to identify these in diagrams)
11) Identify the different types of energy transformations in given circumstances.
12) What are the different types of energy transformations?
13) Use given formulas to calculate Ohm’s Law, Power and Efficiency.
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
14) A 900 W microwave oven requires 7.5 A of current to run. What is the voltage of the circuit
to which the microwave is connected?
15) A flashlight using two 1.5 V D-cells contains a bulb that can withstand up to 0.5 A of current.
What would be the maximum power of the bulb?
16) Bob has a stereo that operates at 120 V using 2.5 A of current. How much power does Bob's
stereo need to operate? If Bob plays his stereo for an average of 5 h each day, how much
electricity will he use in a 30- day period?
17) Fuses are designed to prevent short circuits from becoming dangerous. What is a short
circuit? How is a fuse different from a breaker?
18) If you dissolved a high concentration of salt in water, would it be a conductor or an insulator.
What does that mean and how do you know?
19) An oven with 15 amps of current has 14.7 ohms of resistance. What’s the voltage for the
oven? Show your work.
20) A toaster that is plugged into a 120 V outlet has a current of 5 A. What’s the resistance in the
toaster? Show your work.
21) If a resistor is added to a circuit with light bulb, what happens to the brightness of the light
bulb? Use the word “current” in your response.
22) Draw a circuit that has two cells, two lights arranged in series that are operated by one switch,
and a variable speed motor that is in parallel to the lights.
23) A 12 V electric drill has a current of 8 A.
a) How many watts of power does the drill produce? Show your work.
b) If you use the drill from the question above for 2 minutes, how much energy (in
Joules) will be generated? Show your work.
c) If 6,000 J of the energy produced above are lost as heat and the rest goes into
mechanical energy, how efficient is the drill? Show your work.
24) Two lights are on for 1 hour. A 54 W fluorescent light produces 2000 J of light energy and
1240 J of thermal energy. A 72 W LED light produces 4000 J of light energy and 320 J of
thermal energy.
a) What’s the efficiency of the fluorescent light bulb? Show your work.
b) What’s the efficiency of the LED light bulb? Show your work.
c) Which is more efficient? Why?
25) Complete the following table.
Type of Electricity Advantages Disadvantages Renewable or not?
Generation
Burning coal and
natural gas
Nuclear fission
Geothermal
Tides
Wind
Sunlight
Fuel cells
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
Unit 5: Space Exploration
I am able to:
Describe components of the universe and explain how understanding has changed over time
Classify planets in our Solar System as terrestrial/inner and gas giants/outer
Use given information to draw conclusions about planets and their characteristics
Describe major characteristics of planets, stars, galaxies, etc
Describe distribution of matter - I know which celestial bodies have greater or lesser mass in
general
Infer how observation & perspective led to different models of the universe
Explain both geocentric and heliocentric models of the universe
Use diagrams & models to explain how objects move in space - includes eclipses, orbits, etc.
Describe different kinds of telescopes and explain how each helps shape our understanding of
space.
Draw and define the parts of a basic optical telescope.
Calculate magnification of an optical telescope
Explain the differences between a refracting, reflecting and combination telescope
Describe advantages and disadvantages of each type of optical telescope
Define Adaptive Optics and explain why it is needed
Interpret how wavelength is related to frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum
Explain, in basic terms, how a radio telescope works
State the advantages and disadvantages of gathering information using radio telescopes
Explain how interferometry works to improve observation of space
Describe why space telescopes can give us more information about space than land-based
telescopes
Describe and measure location, distance, motion & composition of bodies in space.
Locate objects in the sky using altitude and azimuth coordinates
Use parallax and triangulation to estimate the distance of far away objects
Measure/estimate distance in space using appropriate units
Interpret spectra of stars to determine their composition
Use spectral analysis and the Doppler effect to determine the motion of stars relative to Earth
Explain scientific principles involved when solving the problems and developing technologies
for space travel.
Describe components of multi-stage rockets and how they work
Explain how Newton’s third law is used to launch rockets into space
Distinguish between Low Earth Orbit and Geosynchronous Orbit satellites.
Provide examples of different artificial satellites and explain how they are used. (eg.
Communication, GPS, Remote Sensing, weather, etc.)
Distinguish between satellites, space probes & rovers in terms of what they are used for and
how they function
Explain how Gravity Assist can be used to save fuel and help spacecraft travel farther into
space
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
Analyze risks versus rewards when developing and applying space technologies.
Consider challenges faced when planning large-scale exploration of space
Describe Canadian contributions to space research and development and to the astronaut
program
Describe technologies for life-support systems
Analyze space environments and identify challenges that must be met in developing life
support systems (e.g., analyze implications of variations in gravity, temperature, availability of
water, atmospheric pressure and atmospheric composition)
Explain, in general terms, how the International Space Station helps support life in space
Explain how materials and processes developed for space have helped meet our needs on
Earth.
Guiding Questions:
1) What is the difference between the heliocentric and the geocentric models of our solar
system?
2) What is retrograde motion?
3) What galaxy is our solar system a part of? What type of galaxy is it?
4) Identify 4 different types of galaxies.
5) What two coordinates are used to measure the location of celestial bodies? What devices are
used to measure these coordinates?
6) What is the geocentric model of the universe? What were some problems with this model, list
at least two? What model was developed in opposition to the geocentric model and by whom?
7) What did Kepler discover about the movement of planets?
8) What is the difference between a constellation and an asterism?
9) What is the process that all stars experience when they “die”?
10) What is a nebula?
11) What are the characteristics of Jovian planets? Which planets are considered to be Jovian?
12) What are the characteristics of the Terrestrial planets? Which planets are considered to be
Terrestrial?
13) What are the key features of our planet that allow organisms to survive?
14) What is a HR diagram and what does it measure?
15) Do stars stay in the same location on the HR diagram throughout its life cycle? Explain.
16) What kind of information does a spectroscope provide?
17) Identify four different gases that are commonly found in stars.
18) What is the Doppler effect? Using the Doppler effect what can be determined about the
movement of a star?
19) When is a star red-shifted? When is a star blue shifted?
20) What is an astronomical unit?
21) What is the difference between an optical telescope and a radio telescope?
22) What are the important life sustaining systems present on the International Space Station?
23) What are all the parts of the spacesuit for an astronaut, how do they work and what do they do
to keep the astronaut alive?
24) What are some Canadian contributions to space research?
25) What is the difference between a satellite, a space probe and rovers?
26) What are the important parts in a rocket and what do they do?
27) Explain the function of GPS.
28) When gasoline is spilled on the ground, a rainbow like sheen can bee seen. Are the colours
that you see being absorbed or emitted? Explain.
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
Name: _________________________Class: ______
29) List 4 differences between inner planets and outer planets in our solar system. In order (from
closest to the sun to furthest) identify each planet as either terrestrial or gas giants.
30) Venus is a terrestrial planet but has far more carbon dioxide in its atmosphere then Earth.
What major effect do you think this has on the planet & it’s environmental conditions?
31) Does the moon produce, absorb, reflect, or refract light? What is the difference between
reflection and refraction?
32) What galaxy do we live in? How many constellations in our galaxy? How many galaxies are
there in the universe?
33) Explain what happens to both pitch and sound waves as a police car approaches you and as it
moves away from you. What is this referred to as?
34) List three physiological changes that occur to an astronaut who spends prolonged amounts of
time in space.
35) Why is it important to maintain carbon dioxide and oxygen concentrations at a constant level
in the cabin of any manned spacecraft?
36) What are the three components of a rocket? Which component is different between a rocket
use in war (ballistic missile) and a rocket used to launch a satellite?
37) List three ways that humans have benefited from satellites.
38) Satellite TV users shouldn’t have to ever reposition their dish. This is because the satellite it is
receiving information from is in a ______________ orbit. Describe what this means.
39) What advantages does the Hubble telescope have over ground based telescopes? (
40) What is the difference between a refracting telescope and a reflecting telescope? Which was
used first and which is more powerful?
41) What is space junk and how is it dangerous?
42) List two political, ethical, and environmental considerations for space exploration.
43) What is the difference between altitude and azimuth when describing a star’s position?
Explain how they would be different for somebody in northern BC and somebody in southern
Ontario.
44) Sketch a diagram showing the life cycle of a sun-like star and a massive star.
Ecole McTavish Bishop, Mahdi, Staples Science 9
You might also like
- Dwnload Full Life Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Life Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions Manual PDFbeliefknackq3zcb100% (9)
- Life Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesLife Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions Manualnotablesteppedp609kw96% (27)
- Life Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesLife Span Human Development 9th Edition Sigelman Solutions ManualJessicaPorteraiydm100% (16)
- 50 Marks QPDocument3 pages50 Marks QPPrasanna SankheNo ratings yet
- Topic ReviewDocument4 pagesTopic ReviewNatnael WeldehawariatNo ratings yet
- A Brief Survey of LifeDocument8 pagesA Brief Survey of LifeAlex YoonNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 1 I Ntroduction: Themes in The Study of LifeDocument40 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 1 I Ntroduction: Themes in The Study of Lifemanilyn_cute888No ratings yet
- Ecology Unit Study Guide AP BiologyDocument3 pagesEcology Unit Study Guide AP Biologytanu96tpNo ratings yet
- Evo Eco NotesDocument6 pagesEvo Eco NotesREDDEN GAMBOANo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mcas Review Question SetDocument13 pagesGrade 8 Mcas Review Question Setapi-294483847No ratings yet
- ISC Bio Section ADocument4 pagesISC Bio Section Ashravs77No ratings yet
- Final Study Guide LS 1Document7 pagesFinal Study Guide LS 1lilazbakr3636No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecology The Economy of Nature 8th Edition Rick Relyea Robert e RicklefsDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Ecology The Economy of Nature 8th Edition Rick Relyea Robert e RicklefsJohn Rigby100% (31)
- Final Exam Review Ayearof7 Grade ScienceDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Review Ayearof7 Grade Scienceapi-302537188No ratings yet
- The Smallest Structural and Functional Unit in A Multicellular Organism Is ADocument7 pagesThe Smallest Structural and Functional Unit in A Multicellular Organism Is AKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Biology Revision GuideDocument9 pagesYr10 Biology Revision Guideanas.amr.abdullahNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit #7 - Evolution, Natural Selection, and SpeciationDocument3 pagesBiology Unit #7 - Evolution, Natural Selection, and SpeciationLisa LeviNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam Practice Questions-Rachel SchlosserDocument8 pagesBiology Exam Practice Questions-Rachel SchlosseroboglerNo ratings yet
- Module 17 Evolution and Its Social RepercussionsDocument11 pagesModule 17 Evolution and Its Social RepercussionsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 100 Past QuestionsDocument37 pages100 Past QuestionsNasif Basher0% (1)
- Parade Through The KingdomsDocument19 pagesParade Through The KingdomsjamesjuiceNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Heredity And Genetics - A Study Of The Modern Biological Laws And Theories Relating To Animal And Plant BreedingFrom EverandAn Introduction To Heredity And Genetics - A Study Of The Modern Biological Laws And Theories Relating To Animal And Plant BreedingNo ratings yet
- Exam Review - Jan 2012Document3 pagesExam Review - Jan 2012Ms Ratna Lestyana DewiNo ratings yet
- Guided Reading Notes on Biology Chapters 1 and 50-55Document14 pagesGuided Reading Notes on Biology Chapters 1 and 50-55Biftu BussaNo ratings yet
- Biology Methods and General Paper: B. Sc. Degree Examinations 2010Document4 pagesBiology Methods and General Paper: B. Sc. Degree Examinations 2010gggtdyfhuuoNo ratings yet
- Els Q2 Module 10Document8 pagesEls Q2 Module 10Princess JunioNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microbiome Science: How Microbes Shape Animal BiologyFrom EverandFundamentals of Microbiome Science: How Microbes Shape Animal BiologyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Bacteria Study GuIdeDocument2 pagesBacteria Study GuIdeemilyfalck17No ratings yet
- Evolving Ecosystems - Inheritance and Selection in - 231022 - 213309Document10 pagesEvolving Ecosystems - Inheritance and Selection in - 231022 - 213309Ali Ruíz CoronelNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Guide to Infectious Diseases: Understanding the Biologic Classes of Pathogenic OrganismsFrom EverandTaxonomic Guide to Infectious Diseases: Understanding the Biologic Classes of Pathogenic OrganismsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Study QuestionsDocument2 pagesStudy QuestionsShuPingLockNo ratings yet
- CM1 - Bacteria and Archaea WorksheetDocument12 pagesCM1 - Bacteria and Archaea WorksheetRebecca DaouNo ratings yet
- Activities in Eco 2Document3 pagesActivities in Eco 2Makulit C AkoNo ratings yet
- Evolution Test Review KeyDocument5 pagesEvolution Test Review Keyapi-242868690No ratings yet
- The Dynamics of Arthopod Predator-Prey Systems. (MPB-13), Volume 13From EverandThe Dynamics of Arthopod Predator-Prey Systems. (MPB-13), Volume 13No ratings yet
- Quiz QuestionsDocument63 pagesQuiz QuestionsJesseBautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Study Guideapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Caste and Ecology in the Social Insects. (MPB-12), Volume 12From EverandCaste and Ecology in the Social Insects. (MPB-12), Volume 12Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Test Bank For Social Psychology The Science of Everyday Life First EditionDocument4 pagesTest Bank For Social Psychology The Science of Everyday Life First EditionMary Smith100% (28)
- Chapter 1 Assessments and QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Assessments and QuestionsAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Biolgoy 11 2012Document4 pagesBiolgoy 11 2012Hamza Aturus100% (2)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Genetics 8th Edition by KlugDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Genetics 8th Edition by Klugminhkhoit8cua3No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Social Psychology The Science of Everyday Life First EditionDocument4 pagesTest Bank For Social Psychology The Science of Everyday Life First EditionAmber Gault100% (28)
- Classification and Evolution Review Sheet: Accelerated BiologyDocument5 pagesClassification and Evolution Review Sheet: Accelerated Biologyapi-241650818No ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument32 pages3rd Quarter ReviewerLyane Faye TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Biology Final Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagesBiology Final Exam Study Guideapi-236677776No ratings yet
- Science 8 Q4 Episode 7 SLMDocument4 pagesScience 8 Q4 Episode 7 SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Unit ReviewDocument3 pagesSemester 1 Unit ReviewEthan MedleyNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology The Essentials 3rd EditionDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Biology The Essentials 3rd EditionKristi Markus100% (34)
- Gen Bio 2 Mod3doneDocument45 pagesGen Bio 2 Mod3doneNikki AlquinoNo ratings yet
- Test-2 Characteristics and Classification of Organisms (KEY)Document4 pagesTest-2 Characteristics and Classification of Organisms (KEY)Ali AzlanNo ratings yet
- Biology Eoc Study GuideDocument6 pagesBiology Eoc Study Guideapi-350761092No ratings yet
- I. Themes in The Study of LifeDocument9 pagesI. Themes in The Study of Lifejayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- APES 2009 RKV Chapter 7 Community Ecology Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesAPES 2009 RKV Chapter 7 Community Ecology Review QuestionsAPES2000No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Social Studies Chapter 4 BookletDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Social Studies Chapter 4 BookletZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- 2024 CalenderDocument12 pages2024 CalenderZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math (Unit 1) - Square Roots and Surface AreaDocument24 pagesGrade 9 Math (Unit 1) - Square Roots and Surface AreaZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations Practice 1Document5 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Practice 1Zunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Trans Drivers Guide Cars Light Trucks 2021 01Document128 pagesTrans Drivers Guide Cars Light Trucks 2021 01Sivananda Reddy P100% (1)
- Grade 8 Percent JournalDocument28 pagesGrade 8 Percent JournalZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Eqautions Practise 2Document2 pagesBalancing Chemical Eqautions Practise 2Zunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Scientific Method Study GuideDocument3 pagesGrade 9 - Scientific Method Study GuideZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Ratio JournalDocument45 pagesGrade 8 Ratio JournalZunairah AdnanNo ratings yet
- The Truth About SexDocument4 pagesThe Truth About SexTimothy OdohNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 6 - Reproduction of Non-Vascular PlantsDocument20 pagesModule in Science 6 - Reproduction of Non-Vascular PlantsMAYETTE PAYABANNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed Final - Which Is The Best Way ToDocument10 pagesGen Ed Final - Which Is The Best Way ToJhea LaysonNo ratings yet
- Ejaculation ReportDocument15 pagesEjaculation Reportsolvent967% (3)
- Enerzad - L Arginine & OligospermiaDocument3 pagesEnerzad - L Arginine & OligospermiaOs MohamedNo ratings yet
- Unique Features of Charts of Twins: Krishnamurthy S, IndiaDocument7 pagesUnique Features of Charts of Twins: Krishnamurthy S, IndiaSaptarishisAstrologyNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Semen Analysis: Information For PatientsDocument8 pagesA Guide To Semen Analysis: Information For PatientsgalvigarciaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Foundation Stocks and Breeding MethodsDocument7 pagesSelection of Foundation Stocks and Breeding Methodsdelacruz.nonaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Insemination GuideDocument3 pagesArtificial Insemination Guidesagi muNo ratings yet
- Kinsey & Secular Sex ValuesDocument85 pagesKinsey & Secular Sex ValuesThandolwetu SipuyeNo ratings yet
- What Is Teenage Pregnancy?Document6 pagesWhat Is Teenage Pregnancy?Paul ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - General Properties and Classification of FungiDocument4 pagesLecture 1 - General Properties and Classification of FungiRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Pola Reproduksi Burung Tekukur dan PuterDocument9 pagesPola Reproduksi Burung Tekukur dan PuterCandratama Indar SeptiantoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsDocument19 pagesMeiosis Notes 2018 Fill InsLydia LamNo ratings yet
- 2023 HSC Biology MGDocument19 pages2023 HSC Biology MGazizi5916No ratings yet
- Reproductive System Grade 7Document5 pagesReproductive System Grade 7Valentina NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- AdolescenceDocument40 pagesAdolescenceJhong Xyrus100% (2)
- Kama Sutra Sucks!: The 8 Biggest Mistakes Guys Make in Bed ... and How YOU Can Easily Avoid Them!Document31 pagesKama Sutra Sucks!: The 8 Biggest Mistakes Guys Make in Bed ... and How YOU Can Easily Avoid Them!Samuel Engelen50% (2)
- (10 Marks) : DP BiologyDocument6 pages(10 Marks) : DP BiologyMarianAsuncionNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument494 pagesMicrobiologyAditi ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of The RH LawDocument1 pageSWOT Analysis of The RH LawAsirante LumenNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 2 Grade 8 Quarter 4Document4 pagesSummative Test 2 Grade 8 Quarter 4Anthony IlustreNo ratings yet
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocument5 pagesAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Kinsey Research Summary Updated - August 2012Document5 pagesKinsey Research Summary Updated - August 2012LC WalkerNo ratings yet
- UACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2011 UNEB Marking GuideDocument12 pagesUACE BIOLOGY PAPER 2 2011 UNEB Marking GuideArthurNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis 4BIO9Document31 pagesSpermatogenesis 4BIO9CourtneyNo ratings yet
- MCN JournalDocument5 pagesMCN JournalElleNo ratings yet
- Relocating Marie BonaparteDocument25 pagesRelocating Marie BonaparteΗπειρωτική ΕταιρείαNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- Gender Sensitivity Seminar GuideDocument72 pagesGender Sensitivity Seminar GuideLyrMa NCNo ratings yet