Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry
Uploaded by
Faizah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesThe document discusses the composition and structure of the atmosphere and issues related to air pollution. It notes that the atmosphere is made up of several layers and is composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen. It also mentions several problems with air quality including global warming, acid rain, and ozone depletion caused by pollution from industry, transportation and other human activities. The rise of carbon dioxide in the air from burning fossil fuels is discussed as a contributor to global warming. The greenhouse effect and common greenhouse gases are described along with their role in increasing temperatures globally.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the composition and structure of the atmosphere and issues related to air pollution. It notes that the atmosphere is made up of several layers and is composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen. It also mentions several problems with air quality including global warming, acid rain, and ozone depletion caused by pollution from industry, transportation and other human activities. The rise of carbon dioxide in the air from burning fossil fuels is discussed as a contributor to global warming. The greenhouse effect and common greenhouse gases are described along with their role in increasing temperatures globally.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesChemistry
Uploaded by
FaizahThe document discusses the composition and structure of the atmosphere and issues related to air pollution. It notes that the atmosphere is made up of several layers and is composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen. It also mentions several problems with air quality including global warming, acid rain, and ozone depletion caused by pollution from industry, transportation and other human activities. The rise of carbon dioxide in the air from burning fossil fuels is discussed as a contributor to global warming. The greenhouse effect and common greenhouse gases are described along with their role in increasing temperatures globally.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Chapter (7)
Air
The air is industrialization and transportation, polluted with some harmful
gases.
The growing problems of acid rain, some harmful gases, global warming and
ozone depletion.
Polluted air cause irritation to serious diseases.
Cultural heritage sites suffered enormous damage due to acid rain.
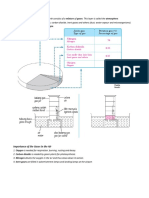
(a) The Structure of the Atmosphere
Air about 8 ~ 10 km thick called the atmosphere.
Atmosphere is divided into five layers:
1) Troposphere
2) Stratosphere
3) Mesosphere
4) Thermosphere
The gases are held in an envelope by earth’s gravity.
Troposphere has about 75% nearest to earth. All living thing and all human
activity occur in it.
Stratosphere, ozone layer, shields living creatures from deadly ultraviolet
radiation.
Mesosphere, atmosphere reaches into space becomes extremely thin beyond
ozone layer.
Thermosphere, in the earth’s atmosphere directly above the mesosphere.
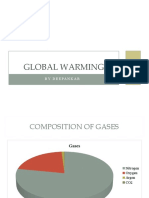
(b) Composition of Air
Mixture of several gases.
Main gases are nitrogen and oxygen.
Carbon dioxide and the noble gases are present in smaller amounts.
A mixture, composition varies from time to time and from place to place.
Air contains
a) 78% (nitrogen)
b) 21% (oxygen)
c) 0.03% (carbon dioxide)
d) 0.97% (noble gases)
Carbon dioxide rise, when we burn more and more fossil fuels (coals, oil and
gas).
In air, almost 0% in a desert, about 5% in a tropical.
Gases in air are colorless and odorless.
We depend on oxygen. Plants depend on carbon dioxide.
Without nitrogen in air, fuels would burn too fast.
Oxygen is slightly soluble in water and reacts with many other substances.
Three important reactions involving oxygen
1. Combustion
2. Respiration
3. Rusting
Energy respiration keeps us warm, hundreds different reactions to go on in
our bodies.
Carbon dioxide in the air, important to all living things.
Green plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, produce glucose
(carbohydrate) and oxygen. Plants use carbon dioxide and release oxygen into
the air.
(d) Air Pollution and Common Air Pollution
Air pollution is caused by soil particles (called particulates) and poisonous
gases in the air. These substances are called air pollutants.
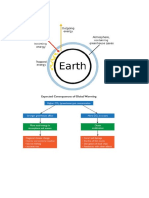
(e) Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect
Earth’s surface warmed by radiation from the sum.
Sunlight, earth’s surface warms and surface release heat in the form of infrared
radiation.
Carbon dioxide and other gases caused global warming. Air trap’s radiation
and prevent escaping into space.
Amount of carbon dioxide and heat-trapping gases, the larger is amount of heat
trapped and warmer the earth becomes.
The average temperature of the Earth increases leading to global warming.
Greenhouse gases, without we would freeze to death at night, the sun is not
shining.
The level of greenhouse gases, so high, is causing global warming.
Greenhouse gases (GHGs)
1) Water vapour
2) Carbon dioxide
3) Methane
4) Nitrous oxide
5) Ozone
Man-made
1) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
2) Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
3) Perfluorocarbons (FPFCs)
4) Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6)
Burning fossil fuels and farm-lands, excessive use of fertilizers’ increases the
amount of greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases increasing, flooding, drought, cyclone, forest fire, landslide,
heat wave, etc.
Melting of glaciers and Artic ice will increase sea levels resulting in many coast
communities being flooded and no longer habitable.
(f) How Acid Rain is Produced
One major environmental effect of air pollutants cause acid rain.
Rain water, naturally slightly acidic (pH of about 5.7).
Carbon dioxide in the air dissolves in rain water, form carbonic acid.
Oxides of Sulphur and nitrogen released industrial waste into atmosphere.,
dissolve in water, becomes more acidic.
Coal-burning power plants and engines fueled by oil or petrol release gases,
can form acid rain, falls far from its source.
Rain water with a pH less than 5 is called acid rain, negative effects.
You might also like
- Katakamuna: The World You See Is Just The Tip of The IcebergDocument8 pagesKatakamuna: The World You See Is Just The Tip of The IcebergThomas100% (1)
- Apes U2 Outline BiodiversityDocument2 pagesApes U2 Outline Biodiversityapi-352694884No ratings yet
- EVAC MSP VII C User ManualDocument67 pagesEVAC MSP VII C User ManualAaron Tearle100% (1)
- Unlock The AWL Sublist 1Document75 pagesUnlock The AWL Sublist 1Шунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument33 pagesClimate ChangeKhiZra ShahZad100% (2)
- Earths AtmosphereDocument26 pagesEarths AtmosphereJaicel Claudette100% (1)
- Environmental ChemistryDocument40 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryharryNo ratings yet
- NicheMetabarcoding StudentWS CLDocument4 pagesNicheMetabarcoding StudentWS CLEshan Farooque75% (4)
- 6.0 Elements of Urban Design & Image of The CityDocument9 pages6.0 Elements of Urban Design & Image of The CityAngel CabreraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry Class-XiDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry Class-XiSatyaSaraswatNo ratings yet
- Pochampally Process Design SheetsDocument2 pagesPochampally Process Design Sheetskiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- BiPV Best Practice Guidelines PDFDocument61 pagesBiPV Best Practice Guidelines PDFsdo6289 AtpadiNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument28 pagesGreen House EffectVyshnavi P VNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument30 pagesGreenhouse EffectFernan SibugNo ratings yet
- RA L9 Global Warming 9Document29 pagesRA L9 Global Warming 9md.daud.ul.islamNo ratings yet
- The EarthDocument3 pagesThe EarthloheesNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry NotesharishNo ratings yet
- Assignment II PAT353Document5 pagesAssignment II PAT353fanhaoheNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry - Shobhit Nirwan PDFDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry - Shobhit Nirwan PDFVarun MadaanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry PDFDocument12 pagesChemistry Notes Class 11 Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry PDFAbbaas AlifNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Sources & EffectsDocument43 pagesAir Pollution Sources & EffectsPraba PrabhatNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument74 pagesAir PollutionSaneet AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & Ozone LayerDocument12 pagesGlobal Warming & Ozone LayerWayne JohannesNo ratings yet
- Ncert 12Document16 pagesNcert 12haarika1006No ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument11 pagesEnvironmental PollutionrupeshNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectsDocument8 pagesGreen House Effectssme chemistryNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry CetDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry CetSumit PatilNo ratings yet
- GRP5 Chemistry of The Atmosphere Kulang NG Dalawang Topics Sorry PoDocument10 pagesGRP5 Chemistry of The Atmosphere Kulang NG Dalawang Topics Sorry PoJersey Mae PerlasNo ratings yet
- Env. IssuesDocument8 pagesEnv. Issuesyadavsuyash007No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7rajana ramliNo ratings yet
- Name:: Syed Mubashir Ali ShahDocument12 pagesName:: Syed Mubashir Ali ShahSyed Mubashir Ali H ShahNo ratings yet
- General Science - Environmental Science CSS PakistanDocument22 pagesGeneral Science - Environmental Science CSS PakistanNearpeer0% (1)
- Chapter Iv - Envt'l Issues MST 21Document53 pagesChapter Iv - Envt'l Issues MST 21del143masNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Air and AtmosphereDocument4 pagesClass 7 Air and AtmosphereBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document15 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentphanhaibangNo ratings yet
- Notes and Answerkey ofDocument190 pagesNotes and Answerkey ofBernát GulyásNo ratings yet
- Env - Sci Assg. 4Document9 pagesEnv - Sci Assg. 4Rohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument33 pagesAir PollutionKapil BudasanaNo ratings yet
- Globle WarmingDocument87 pagesGloble WarmingVijay Maurya100% (1)
- GWCC-Complete NotesDocument59 pagesGWCC-Complete Notesvandanagowda12No ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument19 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryNeeraj RathiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4&5Document18 pagesChemistry Unit 4&5Tadele tesfayeNo ratings yet
- I Would Like To Express My Special Thanks of Gratitude To My Teacher MrsDocument19 pagesI Would Like To Express My Special Thanks of Gratitude To My Teacher MrsShalini ParthipanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (Pollution) Part 1Document53 pagesUnit 2 (Pollution) Part 1kumar.abhinav1015No ratings yet
- Air Pollution, 2019 IIDocument18 pagesAir Pollution, 2019 IIPubg BoyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - (Philoid IN) PDFDocument18 pagesUnit 1 - (Philoid IN) PDFKawshik RayNo ratings yet
- Envt Unit 1Document75 pagesEnvt Unit 1Divya GoelNo ratings yet
- Wasifa Project Natural ResourcesDocument16 pagesWasifa Project Natural ResourcesSamiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Aecc 13Document52 pagesAecc 13Sachin PatelNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument11 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument5 pagesGlobal WarmingDeepankar Singh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument16 pagesAir PollutionJessicaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Complete Environmental ChemistryDocument134 pagesClass 11 Complete Environmental ChemistryAditya BindalNo ratings yet
- Ecological Imbalance Part IDocument4 pagesEcological Imbalance Part Ibikramsubedi485No ratings yet
- The Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesThe Greenhouse EffectDayanaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection ActDocument15 pagesConsumer Protection ActanjankumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-14 Day-1Document16 pagesUNIT-14 Day-1kailash sharmaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument8 pagesGlobal WarmingsamanNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument6 pagesGreen House EffectVir PatelNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Causes Effects and Control of AirDocument21 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Causes Effects and Control of AirAli SaniNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Global Warming, Acid Rain, Ozone Layer Depletion, Nuclear Accident, HolocaustDocument29 pagesClimate Change: Global Warming, Acid Rain, Ozone Layer Depletion, Nuclear Accident, HolocaustAllen Rey TicarNo ratings yet
- CARBON COMPOUNDS: Pollution Aspects: Received Date: Jan. 2020 Revised: April 2020 Accepted: June 2020Document9 pagesCARBON COMPOUNDS: Pollution Aspects: Received Date: Jan. 2020 Revised: April 2020 Accepted: June 2020Vaibhav SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Island Costal Protection Zone 2011: Assignment 7 Dr. Puneet SharmaDocument5 pagesIsland Costal Protection Zone 2011: Assignment 7 Dr. Puneet SharmaShreya GoyalNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For The Preparation of The Ground For Installation of Right of Way Fence at Marshy AreasDocument3 pagesMethod Statement For The Preparation of The Ground For Installation of Right of Way Fence at Marshy AreasKasun UdaraNo ratings yet
- CAL FIRE - Caldor Fire Updates - Sept. 5, 2021 AMDocument7 pagesCAL FIRE - Caldor Fire Updates - Sept. 5, 2021 AMKUNR Reno Public RadioNo ratings yet
- According To 2021-22 Syllabus: Icse XDocument23 pagesAccording To 2021-22 Syllabus: Icse X39-Varshit TandekarNo ratings yet
- Occurrence of Microplastic Fragments in The PasigDocument9 pagesOccurrence of Microplastic Fragments in The PasigRowena LupacNo ratings yet
- Speakers and Panelists: Distinguished Speaker Ms Grace FuDocument10 pagesSpeakers and Panelists: Distinguished Speaker Ms Grace FulucasNo ratings yet
- Speaking SkillsDocument2 pagesSpeaking SkillsttvhtttttxcailayNo ratings yet
- Environment-Comp KS3 DONEDocument4 pagesEnvironment-Comp KS3 DONEitsmortal742No ratings yet
- Ostrom. 1993. Design Principles in Irrigation SystemsDocument6 pagesOstrom. 1993. Design Principles in Irrigation Systemsacharya.venishaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Module NSTP 1 REVISED MINIMUM 2021Document12 pagesUNIT 4 Module NSTP 1 REVISED MINIMUM 2021Justine Ryan L. MalgapoNo ratings yet
- 5-Yokdil2 2021Document27 pages5-Yokdil2 2021FurkanNo ratings yet
- SDS PVC PrimerDocument2 pagesSDS PVC PrimerAhmad AnthonyNo ratings yet
- 8342 27041 1 EdDocument8 pages8342 27041 1 Ednur fadilahNo ratings yet
- 1.4 SustainabilityDocument40 pages1.4 Sustainabilityrania khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Forest and Ecosystem Conservation in The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Forest and Ecosystem Conservation in The PhilippinesMae SabuelvaNo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 608 - Articles - 250165 - Submission - Proof - 250165 7156 597857 1 10 20230628Document17 pagesAjol File Journals - 608 - Articles - 250165 - Submission - Proof - 250165 7156 597857 1 10 20230628Nathalie Jewel MarcialNo ratings yet
- Trial SPM Questions 2020 (Paper 2) Chapters Section A Section B Section CDocument2 pagesTrial SPM Questions 2020 (Paper 2) Chapters Section A Section B Section Chuda186No ratings yet
- Module 2: Laboratory Chemical Safety and Spill ResponseDocument13 pagesModule 2: Laboratory Chemical Safety and Spill Responseghada gattouchNo ratings yet
- Note MakingDocument6 pagesNote MakingBhavyaNo ratings yet
- Lahore College For Women University: Geography AssignmentDocument8 pagesLahore College For Women University: Geography AssignmentAzka AsimNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Eng - 3dayDocument116 pagesModule 1 - Eng - 3dayJoseph P. CagconNo ratings yet
- Geography & DemographicsDocument14 pagesGeography & DemographicsErika PastranaNo ratings yet