Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecological Imbalance Part I
Uploaded by
bikramsubedi485Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecological Imbalance Part I
Uploaded by
bikramsubedi485Copyright:
Available Formats
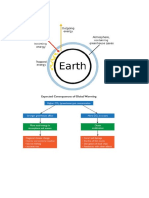
Ecological Imbalance and its Consequences
The ecological condition of the earth is deteriorating due to technological and industrial advancement as well as population
explosion. Balance ecological condition of the earth is degraded by the human activities, like:
Increase in population.
Excessive & unplanned Urbanization.
Industrialization.
Demand of increased population forced to use more natural resources.
Use of pesticides, chemical fertilizers.
Deforestation, mining, disposal of waste materials etc.
Common Ecological imbalances are: Green House Effect, Ozone layer depletion, Acid rain, Ecological invation etc.
1. Green House Effect
It is the warming effect found in atmosphere by allowing solar radiations to pass in, but preventing long wave heat radiations to
pass out, due to the envelop of gases like CO, CO2 , SO2 etc which surround the earth’s atmosphere causing rise in
temperature. This retention of heat energy by the earth due to the presence of gases like CO 2, CO, SO2, and CH4 etc is known
as green house effect or atmospheric effect. When the normal CO2 level increases significantly due to the various human
activities, CO2 gas form a thick layer in the atmosphere which permits the radiation in to the earth but checks radiation of the
heat from the earth surface to the space, as a result the temperature of the earth surface increases this phenomenon is called
global warming. Besides these gases nitrogen dioxide, methane, chlorofloro-carbons (CFCs) are also responsible for heating
the earth.
Causes of green house effect:
Various human activities are responsible for the green house effect which brings about the increase in the global temperature,
called “Global Warming” which may brings different hazards to the entire ecosystem. . Common causes of this effect are:
Production of more CO2 during fuel burning.
Increase in human population and deforestation, increases the level of CO 2 in atmosphere.
Production of air pollutants like, CO2, CO , SO2, nitrogen dioxide, methane, chlorofloro carbons (CFCs) during fuel
burning.
Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels releases more CO2 etc.
Consequences of green house effect:
Global warming
Rise of temperature leads to increase the sea level due to the melting of polar snow
Snow melting in the mountain may cause flood during monsoon.
Hurricanes and cyclones near by the ocean.
High temperature more evaporation from farm so decrease the productivity of land.
Monsoon may even stop or rainfall may alter.
Production of food will be reduced
Desert area will be increased etc.
Control of green house effect
Plantation and conservation of natural resources.
Alternate source of energy should be used
Fuel having low amount of sulphur content should be used.
Wise and economic use of fossil fuels etc.
2. Depletion of Ozone (O3) layer
It is the process of destruction or using up of ozone (O3) in the stratosphere by different pollutants making the ozone
layer thinner. Ozone is a natural gas of the earth’s atmosphere. Ozone gas is formed from the oxygen which is available in the
atmosphere freely. Ozone layer is present in the stratosphere which absorbed UV radiation of the sun. This layer forms a
protective covering around the earth atmosphere. It presence the UV rays present in the solar radiation from reaching our
atmosphere which save us from the extremely damaging effect of ultra violet rays, which may cause various skin diseases
including skin cancer.
It has been reported that Ozone layer is getting thinner and thinner .Such thinner layer of ozone may not be sufficient to control
the Ultra Violet rays.
Causes of Ozone layer depletion
In the atmosphere the Chlorofluorocarbon (CFCs) is broken down due to the action of intense UV radiation of sun to
liberate chloride molecules and each chloride molecules react with 1000atoms of Ozone in chain, converting in to Oxygen. In
this process the chlorine atom again destroy another molecule of Ozone.
Chlorofluorocarbon (CFCs) and Nitrogen oxide produces during the use of high technology, which are stable and non-
reactive in nature.
Air pollution which are produced by the combustion fossil fuels, air craft, industries, satellites , nitrogen fertilizers etc
Volcanic eruption.
Burning of large forest and savannahs.
Fuel used in jet planes
Awareness program, literacy program,
Strong laws and their implementation, etc.
Consequences of Ozone layer depletion.
Change in environment
Cause skin cancer and blindness.
Reduce the productivity of crops
Destruction of aquatic life
May cause different kinds of plant and animal disease.
Decreases the rate of photosynthesis due to the reduction of chlorophyll etc
Control of Ozone layer depletion
To control the ozone layer depletion global effort is essential.
Use of CFCs should be minimized by alternative chemical.
Awareness program, literacy program,
Strong laws and their implementation, etc.
3. Acid rain (Black rain)
The process of deposition of acid, gases (SO2, NO2) from the atmosphere on land in the form of precipitation or rain is
known as Acid rain. During this process acidic gas mix with water vapors and forms the respective acids like H 2SO4 and
HNO3. Actually presence of acid in rain water is called acid rain. Some pollutants like aluminum, cadmium, lead, zinc and
arsenic oxide of sulphur and nitrogen leads to the formation of acid which cause the acid rain. The P H of normal rain is 5.6, if
the PH of rain water is lesser then 5.6 then the rain is called acid rain. Acid rain caused due to the presence of carbonic acid
formed by the reaction of free CO2 with water. The acid rain consists of PH of 4 to 4.5 due to additional acids in rain water.
Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen do not remain in gases state for a long time, so they react with water vapors to form acids and
these acids comes down as rain on the earth surface , called acid rain or black rain.
Causes of Acid rain
Industrialization.
Presence of pollutants like oxide of sulpher, carbon and nitrogen with different metals.
Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and hydro carbons.
Nitrogen oxides are produced as nitrogen and oxygen combine in the internal combustion engines and released in
vehicle exhaust gases.
Industries and power plants emit large quantities of SO2 and Nitrogen oxides in to atmosphere etc.
Consequences of Acid rain
Acid rain destroys the crops, forests.
It corrodes the manmade and natural monuments, statue, buildings, bridges, etc
It increases the acidity of soil.
It is the cause of pollution.
Due to acid rain soil quality is degraded so productivity could decline.
Microorganisms (many bacteria and blue green algae) are also killed due to acid rain.
Even it kills aquatic animals and plants found in aquatic habitat etc.
Control of Acid Rain
Use of fossil fuel should be minimized by using alternate source of energy like solar energy, electricity, bio-gases etc
Catalytic converter should be used in automobiles.
Sulphur free fossil fuel should be used.
Awareness program, literacy program,
Strong laws and their implementation etc.
4. Biological invasion (Ecological invasion)
The sudden spread and establishment of new species accidentally in the new area which was not previously recorded
is known as invasion. The invasive species may grow in, spread and ecologically alter the existing community.
Biological invasions by animals, plants, pathogens or vectors are one of the greatest environmental and economic
challenges along with habitat destruction. Biological invasions are a major force of change which affect many
dimensions of life on earth. It is the leading cause of biodiversity loss in local and global level. Biological invasion is
equally seen in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem.
The characteristics of invasive species are:
1. They grow fast and they can reproduce rapidly.
2. Dispersal ability is very high.
3. They exhibit phenotype plasticity (the ability to alter growth form to suit current conditions).
4. Invasive species have high degree of ecological tolerance.
5. They are considered as generalist in food consumption habit.
Causes of biological invasion
1. Changes in habitat suitability: can provide new opportunities for colonization. For example, the grasses recover
and colonize quickly in fi re burned areas. Consequently, one colonist can open large areas of suitable habitat for
another.
2. Climate change: can also lead to colonization of new species by facilitating dispersal.
3. Genetic adaptation: The onset of rapid spatial spread is sometimes also attributed to genetic adaptation to the
new environment. Genetic effects play important role in acquiring adaptational features.
4. Dominant nature: of invasive species tend to become one of the dominant species easily in the system.
Patterns or mechanisms of biological invasion
Arrival, establishment, spread and impact are the four major steps of mechanism in invasion
1. Arrival: It is the process by which individuals are transported to new areas outside of their native range. Rising
levels of world trade and travel have resulted in an ever increasing arrival of alien species, however, most of them
have failed to establish.
2. Establishment: It occurs when populations grow to sufficient levels. The establishment phase thus represents a
critical period. Founder populations typically are small and consequently are at great risk of death. Generally, the
smaller the founder population, the less likely is establishment.
3. Spread of a non-indigenous organism: It is a process by which the new species expands in new habitat. It
causes economic harm and become invasive.
4. Impact stage: It is the result of invasive species spread over the area.
Impacts of biological invasion
Global threats to local ecosystems.
Native species become vulnerable soon.
Reduce the agricultural production.
Changes the soil quality.
Loss of local business.
Mitigation measures
A. Early identification and their mitigation before establishment in large area.
i. Strict cargo inspection and quarantine is the best method to stop biological invasions.
ii. This includes correct identification of species and destruction of species in any developmental stages.
iii. It is very important to stop their any types of reproduction.
B. Mitigating the impacts after establishment.
i. Making them to slow propagate.
ii. Reestablishing the native species.
iii. Invasivorism: by increasing invasive species eating or destroying in order to control, reduce, or eliminate
their populations. Like, Beetles and few fungus may help to eradicate them.
In Nepal, there are 179 alien plant species have established their self-replacing population (i.e naturalized), and
among them 26 species, mostly native of tropical Americas, has been reported to be invasive with negative impacts
on environment including agriculture production.
Few examples of invasive plant species,
P
o
s
i
t
i
v
e
impact of biological invasion: Some invasive species have the potential to provide a suitable habitat or food source
for other organisms. In areas where a native has become extinct or reached a point the invasive species can help in
restoration process till.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You might also like
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentkunkulol100% (1)
- PYP Planner - Sharing The PlanetDocument4 pagesPYP Planner - Sharing The Planetdanny96% (28)
- Environmental Laws in Malaysia - Bukit Merah Case StudyDocument65 pagesEnvironmental Laws in Malaysia - Bukit Merah Case StudyMohamadDanielBinYaacobNo ratings yet
- Flood Management Master Plan For Metro Manila and Surrounding AreasDocument21 pagesFlood Management Master Plan For Metro Manila and Surrounding AreasArangkada Philippines100% (1)
- Biology FolioDocument12 pagesBiology Foliomuhd khobirNo ratings yet
- Env - Sci Assg. 4Document9 pagesEnv - Sci Assg. 4Rohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Human Impact On EcosystemDocument22 pagesHuman Impact On Ecosystemjeremy yanNo ratings yet
- Environment Protection and Business ObligationsDocument13 pagesEnvironment Protection and Business ObligationsRaj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- A Level Environmental Management NotesDocument26 pagesA Level Environmental Management Notescharumbirakimtontapiwa751No ratings yet
- Global Warming & Ozone LayerDocument12 pagesGlobal Warming & Ozone LayerWayne JohannesNo ratings yet
- Folio Biology: Endangered EcosystemDocument23 pagesFolio Biology: Endangered Ecosystemsabrina_shaharNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument3 pagesPollutionMe anNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Climate Change (The Science of Climate Change)Document30 pagesIntroduction To Climate Change (The Science of Climate Change)enoch taclanNo ratings yet
- Geomedicine AssignmentDocument14 pagesGeomedicine AssignmentCaleb Momanyi OmbatiNo ratings yet
- Q1. Resettlement and Rehabilitation: Q2. Global Warming ? Explain in BriefDocument39 pagesQ1. Resettlement and Rehabilitation: Q2. Global Warming ? Explain in BriefDivyam BhushanNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGlobal WarmingkuramasanadaNo ratings yet
- Bio DiversityDocument9 pagesBio DiversityJawwadNo ratings yet
- Name: Aina Najwa Binti Amir Class: 4 RossaDocument15 pagesName: Aina Najwa Binti Amir Class: 4 RossaAina NajwaNo ratings yet
- Geography Environmental ManagementDocument24 pagesGeography Environmental ManagementMirriamNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project of Biology 1 VRSDocument14 pagesInvestigatory Project of Biology 1 VRSAina shivhareNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 9-Endangered Ecosystem Power PointDocument65 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 9-Endangered Ecosystem Power PointDelima Adan100% (1)
- Asssesment Sheet (Autorecovered)Document22 pagesAsssesment Sheet (Autorecovered)ABHISHEK RAWATNo ratings yet
- Asssesment Sheet (Autorecovered)Document22 pagesAsssesment Sheet (Autorecovered)ABHISHEK RAWATNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Engineering Air PollutionDocument21 pagesBasic Civil Engineering Air Pollutionrajat4kokaneNo ratings yet
- Evs Module 7Document8 pagesEvs Module 7shifa10abhpemsNo ratings yet
- Envt Unit 1Document75 pagesEnvt Unit 1Divya GoelNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument8 pagesGlobal WarmingsamanNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Affect The EnvironmentDocument3 pagesHow Do Humans Affect The EnvironmentmynameNo ratings yet
- Brown Modern Nature Presentation (1) - CompressedDocument32 pagesBrown Modern Nature Presentation (1) - CompressedRhodjane Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: PollutionDocument5 pagesLiterature Review: PollutionAirul IszwanNo ratings yet
- Env. Control & Energy in Buildings Report 1 Environmental Problems Oct (2021)Document10 pagesEnv. Control & Energy in Buildings Report 1 Environmental Problems Oct (2021)Hesham Ibrahim ElzorekyNo ratings yet
- Env. IssuesDocument8 pagesEnv. Issuesyadavsuyash007No ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument31 pagesUnit 3 NotesappachudNo ratings yet
- 36 ch16 PDFDocument6 pages36 ch16 PDFMallikarjuna MuthyaluNo ratings yet
- Effect On EnvironmentDocument4 pagesEffect On EnvironmentOluwabusolami AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Effect On EnvironmentDocument4 pagesEffect On EnvironmentOluwabusolami AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EcosystemDocument20 pagesModule 1 Ecosystemab cdNo ratings yet
- 9: Endangered Ecosystem: Biology AssignmentDocument33 pages9: Endangered Ecosystem: Biology AssignmentHayat HayatiNo ratings yet
- Biology Folio KSSM 2022 T5Document12 pagesBiology Folio KSSM 2022 T5LEE YEN NI MoeNo ratings yet
- Impact of Industrialization & Modernization On EnvironmentDocument98 pagesImpact of Industrialization & Modernization On EnvironmentYogesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Apuntes ImpactosDocument4 pagesApuntes ImpactosNerea Solier romeroNo ratings yet
- Environmental IssuesDocument23 pagesEnvironmental IssuesAneen ZamanNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Atmospheric Pollution: StructureDocument18 pagesUnit 10 Atmospheric Pollution: Structuretarakesh17No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingDocument11 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingA Aldika Farlis50% (2)
- The Reasons Why This Paperwork Is Being Done Is Due To Several Objectivs As Stated BelowDocument13 pagesThe Reasons Why This Paperwork Is Being Done Is Due To Several Objectivs As Stated Belowna816722No ratings yet
- Ecochallenge Presentation Group 1Document24 pagesEcochallenge Presentation Group 1Husni Mohd RadziNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument5 pagesBiodiversityTeng Foo LimNo ratings yet
- Environmental Concerns Renewable Energy Resources Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Concerns Renewable Energy Resources Climate ChangeAisha RgNo ratings yet
- Populations Can Be of The Same Size, But They May Have Different Densities. When We Consider The Number of IndividualsDocument3 pagesPopulations Can Be of The Same Size, But They May Have Different Densities. When We Consider The Number of IndividualsEmely CulveraNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Environmental Awareness: Study Guide For Module No. 14Document3 pagesClimate Change and Environmental Awareness: Study Guide For Module No. 14Maylene CalicdanNo ratings yet
- Biologycha P9: Endangere D: EcosytemDocument15 pagesBiologycha P9: Endangere D: EcosytemLynn OoiNo ratings yet
- Folio Biology Form 4Document31 pagesFolio Biology Form 4Amin Rosnan0% (1)
- 9.1 Human Activities That Endangered An Ecosystem Pollution: DeforestationDocument10 pages9.1 Human Activities That Endangered An Ecosystem Pollution: DeforestationsyahmisyahmiNo ratings yet
- Environment and DevelopmentDocument84 pagesEnvironment and DevelopmentSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- DESERTIFICATIONDocument8 pagesDESERTIFICATIONWhiskey /No ratings yet
- Endangered Ecosystem: MRSM MersingDocument9 pagesEndangered Ecosystem: MRSM MersingHaninii Suhaila HKNo ratings yet
- English Task Details:: Michael 191424015 1A-TkpbDocument3 pagesEnglish Task Details:: Michael 191424015 1A-TkpbKael SimbNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Human Activities That Endanger An EcosystemDocument7 pages9.1 Human Activities That Endanger An EcosystemMuhamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document14 pagesUnit 6Kandukuri Varun VenkyNo ratings yet
- Suggest Ways To Minimize Human Impact On The Environment: S8Lt-Ivj-25Document44 pagesSuggest Ways To Minimize Human Impact On The Environment: S8Lt-Ivj-25Joseph Gabriel Genuino CruzNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyMuhamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution:-: Serious Environmental ProblemDocument11 pagesAir Pollution:-: Serious Environmental ProblemAbhipsa BisiNo ratings yet
- NSTP Week 10 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesNSTP Week 10 Lesson PlanGian Jane QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Ecological Design, A New Critique PDFDocument12 pagesEcological Design, A New Critique PDFNaninho Do Maldonado ANo ratings yet
- CSR PlanDocument22 pagesCSR PlanDanisha RogersNo ratings yet
- Q#2 SolutionDocument5 pagesQ#2 SolutionJemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Mata Pelajaran: Bahasa Inggris Kelas/Jurusan: Xi / Mipa & Ips Answer The Following Questions With The Correct Answers!Document1 pageMata Pelajaran: Bahasa Inggris Kelas/Jurusan: Xi / Mipa & Ips Answer The Following Questions With The Correct Answers!Seprianus AndriNo ratings yet
- An Ecological Network For Large Carnivores As A Key Tool For Protecting Landscape Connectivity in The CarpathiansDocument15 pagesAn Ecological Network For Large Carnivores As A Key Tool For Protecting Landscape Connectivity in The CarpathiansNorberto MuzzachiodiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness Module 2Document9 pagesDisaster Readiness Module 2Marvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Fisherfolks On Climate Change Awareness and Adaptation in Lake Sampaloc of San Pablo City, Laguna, PhilippinesDocument8 pagesKnowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Fisherfolks On Climate Change Awareness and Adaptation in Lake Sampaloc of San Pablo City, Laguna, PhilippinesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Outstanding Universal Value: Puerto-Princesa Subterranean River National ParkDocument3 pagesOutstanding Universal Value: Puerto-Princesa Subterranean River National ParkI'm a Smart CatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Narmada Bachao Andolan v. Union of IndiaDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 - Narmada Bachao Andolan v. Union of IndiaAnshul RanjanNo ratings yet
- Biosphere ReservesDocument28 pagesBiosphere Reservesjaya priyankaNo ratings yet
- 01 Air Pollution Lesson PresentationDocument17 pages01 Air Pollution Lesson PresentationNADA MohammadNo ratings yet
- Glaciers Melting A Serious Threat To The Mountain Community of Gilgit BaltistanDocument2 pagesGlaciers Melting A Serious Threat To The Mountain Community of Gilgit Baltistansadam khanNo ratings yet
- Stetson SpeechDocument3 pagesStetson Speechjosiah9_5No ratings yet
- Impact DDocument302 pagesImpact Dhehehe685No ratings yet
- Resilient Parks Resilient City - Park People 1.compressedDocument14 pagesResilient Parks Resilient City - Park People 1.compressedMaria StoicaNo ratings yet
- Risk and Crisis Management PDFDocument1 pageRisk and Crisis Management PDFMohamad FirdausNo ratings yet
- Solid and Hazardous Waste NotesDocument5 pagesSolid and Hazardous Waste Notesapi-242064664No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SST3005Document32 pagesLecture 4 SST3005Sleeping BeautyNo ratings yet
- Minute March 2, 2023Document8 pagesMinute March 2, 2023Dianita ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Peaky HackerNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Scope & SequenceDocument2 pagesScience 5 Scope & SequenceAljeanNo ratings yet
- Soal Tryout UTBK 2023Document5 pagesSoal Tryout UTBK 2023Adnan KadarusmanNo ratings yet
- LandslidesDocument16 pagesLandslidesk2v1n567% (3)
- 00 - Contents Everyday Science MCQsDocument5 pages00 - Contents Everyday Science MCQsmimtiazshahid100% (1)
- Andrews 2004Document18 pagesAndrews 2004Sara Julliane Ribeiro AssunçãoNo ratings yet
- Ways of Knowing Natural EnvironmentsDocument14 pagesWays of Knowing Natural Environmentsapi-248891002No ratings yet