Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Lecture-10 (A. K. Patkar) - Converted-Compressed
Uploaded by
Chaudhary chinki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesThe ion exchange process uses ion exchange resins to produce very low hardness water suitable for use in high-pressure boilers. Cation exchange resins contain acidic groups that can exchange hydrogen ions for cations in water like calcium and sodium. Anion exchange resins contain basic groups that can exchange hydroxide ions for anions in water like chloride and sulfate. The process involves loading ions from water onto the resin and then regenerating the resin by eluting ions from it using an acid or base solution.
Original Description:
Water
Original Title
Water Lecture-10 (A. K. Patkar)-converted-compressed
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe ion exchange process uses ion exchange resins to produce very low hardness water suitable for use in high-pressure boilers. Cation exchange resins contain acidic groups that can exchange hydrogen ions for cations in water like calcium and sodium. Anion exchange resins contain basic groups that can exchange hydroxide ions for anions in water like chloride and sulfate. The process involves loading ions from water onto the resin and then regenerating the resin by eluting ions from it using an acid or base solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesWater Lecture-10 (A. K. Patkar) - Converted-Compressed
Uploaded by
Chaudhary chinkiThe ion exchange process uses ion exchange resins to produce very low hardness water suitable for use in high-pressure boilers. Cation exchange resins contain acidic groups that can exchange hydrogen ions for cations in water like calcium and sodium. Anion exchange resins contain basic groups that can exchange hydroxide ions for anions in water like chloride and sulfate. The process involves loading ions from water onto the resin and then regenerating the resin by eluting ions from it using an acid or base solution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
ION EXCHANGE PROCESS
(DE-IONIZATION OR DE-MINERALIZATION)
Mr. Audumbar Patkar
It produces water of very low hardness (~2ppm). So it is very good for treating
water for use in high-pressure boilers.
The process can be used to soften highly acidic or alkaline water.
Ion-exchange resins are insoluble, cross-linked; long chain
organic polymers with a microporous structure and the functional
groups attached to the chains are responsible for the ion-
exchanging properties.
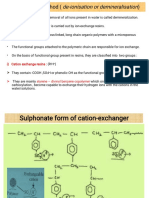
Cation exchange resins are mainly styrene-divinyl
benzene copolymers, which on sulphonation or
carboxylation, becomes capable of exchange
their hydrogen ions with the cations in the water
These resins contain acidic functional groups
(-COOH, -SO3H etc.) which are capable of
exchanging their H+ ions with other cations, which
comes in their contact.
Anion exchange resins are styrene-divinyl
benzene which contain amino or quaternary
ammonium or quaternary phosphonium groups
as an internal part of the resin matrix.
These, after treatment with dil. NaOH solution,
become capable to exchange their OH- ions
with anions in water.
These resins contain basic functional groups
(-NH2=NH2 as hydrochlorides) which are
capable of exchanging their anions with other
anions, which comes in their contact.
RH+ R’OH-
RNa+ + H+ RH+ + Na+
R2Ca2+ + 2H+ 2RH+ + Ca2+
(Exhausted resin) (Acid solution) (Regenerated resin) (washing)
R’Cl- + OH- R’OH- + Cl-
R’2SO42- + 2OH- 2R’OH- + SO42-
(Exhausted resin) (Base solution) (Regenerated resin) (washing)
In next lecture: Potable water standard as per BIS
For your doubts and suggestions: patkaraudumbar@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/appchemistry
RH+ + Na+ RNa+ + H+
2RH+ + Ca2+ R2Ca2+ + 2H+
2RH+ + Mg2+ R2Mg2+ + 2H+
(Fix bed of resin) (ions in water) (Fix bed of resin) (water)
R’OH- + Cl- R’Cl- + OH-
2R’OH- + SO42- R’2SO42- + 2OH-
2R’OH- + CO32- R’2CO32- + 2OH-
(Fix bed of resin) (ions in water) (Fix bed of resin) (water)
You might also like
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Aquatrac5 enDocument4 pagesAquatrac5 enTRIMECHNo ratings yet
- Softening Methods4Document3 pagesSoftening Methods4Tejas YadavNo ratings yet
- HYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mind MapDocument18 pagesHYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mind MapTanay1 MitraNo ratings yet
- Chang Chap 4Document72 pagesChang Chap 4MR no oneNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Water Treatment Plant: M/S Jindal Power Limited (4X250 MW) Opjstpp, Tamnar, RaigarhDocument41 pagesLecture On Water Treatment Plant: M/S Jindal Power Limited (4X250 MW) Opjstpp, Tamnar, RaigarhPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Carbon Carbon Dioxide Carbon Carbon Dioxide: MG MGDocument3 pagesCarbon Carbon Dioxide Carbon Carbon Dioxide: MG MGDSE No WorriesNo ratings yet
- 3 Dec - Science - Imp Concept - 1511844465Document20 pages3 Dec - Science - Imp Concept - 1511844465Syed nameerNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument22 pagesHydrogenKeerthana MNo ratings yet
- 10 FEB HydrogenDocument27 pages10 FEB Hydrogensachin anuseNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ResinDocument7 pagesIon Exchange ResinAnup Bajracharya75% (4)
- Penukar Ion-08 PDFDocument40 pagesPenukar Ion-08 PDFdani darmawanNo ratings yet
- Portable Exchange Deionization BasicsDocument99 pagesPortable Exchange Deionization BasicsJonas RiveraNo ratings yet
- EXP 12 - RedoxDocument5 pagesEXP 12 - RedoxilknurNo ratings yet
- 10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must DoDocument63 pages10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must Doanshu26stNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Da1Document6 pagesChemistry Da1Vijayaraj MNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen in 1 Shot - Class Notes - JEEDocument22 pagesHydrogen in 1 Shot - Class Notes - JEESaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Methods of Purification: The Process of Ion-ExchangeDocument13 pagesMethods of Purification: The Process of Ion-ExchangebilalNo ratings yet
- 25 HydrogenDocument53 pages25 HydrogenAbdul MateenNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument48 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionDavid MaranzhyanNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ProcessDocument10 pagesIon Exchange Process056 Jatin GavelNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ResinsDocument8 pagesIon Exchange ResinsabdulanisNo ratings yet
- Basic Ion Exchange ProcessesDocument12 pagesBasic Ion Exchange ProcessesMd Suzon MahmudNo ratings yet
- Penukar Ion 07Document35 pagesPenukar Ion 07Farhan DermawanNo ratings yet
- The Major Classes of Chemical ReactionsDocument47 pagesThe Major Classes of Chemical ReactionsJoe NasalitaNo ratings yet
- Laporan KPiDocument18 pagesLaporan KPimiaw713No ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ResinsDocument5 pagesIon Exchange ResinsAJITHNo ratings yet
- 3Document66 pages3Nikhil AroraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Ion ExchangeDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Ion ExchangeGOWTHAM GUPTHANo ratings yet
- Oxides, Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesOxides, Acids, Bases and Salts12&13 SciencesNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 2Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 2jw wNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper 1Document14 pagesReactions of Copper 1jw wNo ratings yet
- Softening MethodsDocument7 pagesSoftening MethodsPranay ChandrikapureNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument40 pagesDM PlantArunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Process ConfigDocument30 pagesIon Exchange Process Confignermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Method (De-Ionisation or Demineralisation) : I) Cation Exchange ResinsDocument10 pagesIon Exchange Method (De-Ionisation or Demineralisation) : I) Cation Exchange ResinsRaunit VermaNo ratings yet
- Caco Mgco MG (OH)Document28 pagesCaco Mgco MG (OH)Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.soap 1Document35 pages1.soap 1taghrid itaniNo ratings yet
- Dardel InfoDocument7 pagesDardel InfoajwebNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument37 pagesWater TreatmentAMAL MATHEWNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Reactions and SolutionsDocument12 pagesAqueous Reactions and SolutionsDavid Jonathan Polo100% (1)
- Hydrogen - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesHydrogen - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2024manishnwdsharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Ion Exchange ProcessesDocument9 pagesBasic Ion Exchange ProcessesSAYEDNo ratings yet
- Chem Mod 6 #2Document77 pagesChem Mod 6 #2hruthika.schoolNo ratings yet
- Chem 125 07.10.2019Document9 pagesChem 125 07.10.2019nilofar jawadiNo ratings yet
- ION EXCHANGEjashDocument9 pagesION EXCHANGEjashJash SapariyaNo ratings yet
- 1 IER FundamentalsDocument54 pages1 IER FundamentalsAdam FendrychNo ratings yet
- HYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE MindmapDocument15 pagesHYDROGEN - Class Notes - JEE Mindmapadsaditya24No ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Acids, Bases and Salts: PropertiesDocument2 pagesChapter-2 Acids, Bases and Salts: PropertiesAkASHNo ratings yet
- Softening FinalDocument23 pagesSoftening FinalSonali Jahagirdar100% (1)
- WRD Ot Chemical Clarification Metals Precipitation 445210 7Document38 pagesWRD Ot Chemical Clarification Metals Precipitation 445210 7Fadella VilutamaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its Compounds: Short Answer QuestionsDocument5 pagesHydrogen and Its Compounds: Short Answer QuestionsGagan NdNo ratings yet
- Part IV Acids and Bases NotesDocument45 pagesPart IV Acids and Bases NotesHon KwanNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ResinsDocument7 pagesIon Exchange ResinsVirgilMaroNo ratings yet
- Ion ExchangeDocument4 pagesIon ExchangeslchemNo ratings yet
- The Aqueous Phase ReactionDocument16 pagesThe Aqueous Phase ReactionRSL100% (1)
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument64 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionSoul Relaxation LabNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Past PapersDocument13 pagesGroup 2 Past PapersShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument12 pagesUnit 2 - Basic Mechanical Engineering - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inPubgNo ratings yet
- PerkinElmer Turbomatrix Headspace & Headspace Trap SpecificationsDocument4 pagesPerkinElmer Turbomatrix Headspace & Headspace Trap SpecificationsAri NurrochimNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Hydraulic RoughnessDocument5 pagesFactors Influencing Hydraulic RoughnessFaruk AtalarNo ratings yet
- Torsionally Stressed CylinderDocument9 pagesTorsionally Stressed CylinderCharyNo ratings yet
- Cet SumsDocument6 pagesCet SumsPradeep SutharNo ratings yet
- 2001 Hoenig - Sample - Prep - Preparation Steps in Environmental Trace Element Analysis Talanta - 2001Document18 pages2001 Hoenig - Sample - Prep - Preparation Steps in Environmental Trace Element Analysis Talanta - 2001ctimanaNo ratings yet
- On The Importance of Antifouling Coatings Regarding Ship Resistance and PoweringDocument14 pagesOn The Importance of Antifouling Coatings Regarding Ship Resistance and PoweringMadan Pal SainiNo ratings yet
- Sae J1453 OrfsDocument7 pagesSae J1453 Orfslink2u_007No ratings yet
- Flow MetersDocument21 pagesFlow MetersEverlynn Joy JosephNo ratings yet
- Recovery Boiler Water Treatment: January 2007Document44 pagesRecovery Boiler Water Treatment: January 2007thiagoNo ratings yet
- OlinDocument16 pagesOlinA AhmedNo ratings yet
- SOP 75v4 Specific-Gravity FinalDocument22 pagesSOP 75v4 Specific-Gravity FinalAldwiNo ratings yet
- Heat Diffusion EquationDocument7 pagesHeat Diffusion EquationGaye KanaltıNo ratings yet
- Kamalkant Chem For All BBSR 1Document4 pagesKamalkant Chem For All BBSR 1kamalkantmbbsNo ratings yet
- Dual Film RT Article PDFDocument7 pagesDual Film RT Article PDFRaja Muaz Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, (GIKI) Faculty of Engineering Sciences (FES)Document3 pagesGhulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, (GIKI) Faculty of Engineering Sciences (FES)bilal khanNo ratings yet
- AP Review CH 12Document6 pagesAP Review CH 12ygtefferaNo ratings yet
- GeodrenPEIT TDSDocument1 pageGeodrenPEIT TDSYYOUNOS_MANo ratings yet
- 6226 en 1Document28 pages6226 en 1adelabdelaal100% (1)
- Safety Coordinator Msds Training ProgramDocument48 pagesSafety Coordinator Msds Training Programapi-266263464No ratings yet
- Modified SYLLABUS PDFDocument9 pagesModified SYLLABUS PDFSHRIKANTNo ratings yet
- H1000e K FJDocument8 pagesH1000e K FJSyarif HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Minerals - SilicatesDocument2 pagesMinerals - SilicateshNo ratings yet
- SPE 189134 Economic Optimization of Water and Gas Shut Off Treatment in Oil WellsDocument16 pagesSPE 189134 Economic Optimization of Water and Gas Shut Off Treatment in Oil WellsEdgar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and PrteinDocument33 pagesAmino Acids and PrteinJohny VillanuevaNo ratings yet
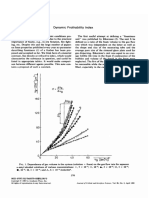
- Dynamic Frothability IndexDocument3 pagesDynamic Frothability IndexjvchiqueNo ratings yet
- Key Points: B B B X XDocument5 pagesKey Points: B B B X XSIDDHANT KATARIANo ratings yet
- Discovery of Gamma-Rays: Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument3 pagesDiscovery of Gamma-Rays: Electromagnetic SpectrumJOHN K KOCHUMMENNo ratings yet