Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cannizzaro Reaction: Lab. of Organic Chemistry Second Stage
Uploaded by
san shibuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cannizzaro Reaction: Lab. of Organic Chemistry Second Stage
Uploaded by
san shibuCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab.
of Organic Chemistry
Second Stage
Cannizzaro Reaction
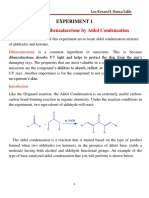
The Cannizzaro reaction is when a non-enolizable aldehyde
reacts with itself in a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide
(NaOH), to form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. A non-
enolizable aldehyde is one that has no alpha hydrogens available
for the aldehyde to form an enol. This reaction is a redox reaction
in which two molecules of an aldehyde are reacted to produce a
primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid using a hydroxide base.
Both alcohols and organic acids are well known for their
biological actions.
1- Antibacterial properties.
2- Preservatives for food.
3- pharmaceutical local application as antiseptics.
Benzyl alcohol has some local anesthetic properties, it is useful
as antipruritic and is the reason for its inclusion in some dental
remedies and injectibles in pharmaceutical preparations
intended for local application, benzyl alcohol has been used up to
10 % in ointments as antipruretic and to prevent secondary
infections.
In injectibles, it is included in many painful IM injectibles, both
as a preservative and as a local anesthetic.
Benzyl alcohol can be prepared by the hydrolysis of benzyl
chloride with sodium hydroxide.
On the other hand, benzoic acid is used as a food preservative
as a free acid, or in the form of sodium salt, also used externally
in form of lotions, ointments, mouth washes, etc.
Benzoic can be prepared by the oxidation of toluene using
oxidizing agent.
Lab. of Organic Chemistry
Second Stage
However, both benzoic acid and benzyl alcohol can be prepared
in laboratory by cannizaro reaction by the action of sodium or
potassium hydroxide on benzaldehyde.
Aim of experiment
Synthesis of benzoic acid and benzyl alcohol.
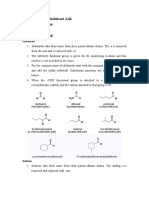
Examples for some compounds to interact by cannizaro
reaction:
Properties of benzyl alcohol
1- Colorless to very fine yellow (due to oxidation) oily liquid.
2- Immiscible with water, miscible with organic solvents like
ether.
3- Boiling point is 204-207 ºC.
Properties of benzoic acid
1- White crystalline plates or needles.
Lab. of Organic Chemistry
Second Stage
2- Sparingly soluble in water, soluble in hot boiled water.
3- Volatile with steam (so can be purified by Steam
distillation ).
4- Reacts with sod. bicarbonate to give CO2 gas.
5- Melting point is 121-123 ºC.
You might also like
- Cannizaro ReactionDocument13 pagesCannizaro Reactionhussein alnasryNo ratings yet
- Ionic Liquids in Biotransformations and Organocatalysis: Solvents and BeyondFrom EverandIonic Liquids in Biotransformations and Organocatalysis: Solvents and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Experiment 123456 1 PDFDocument18 pagesExperiment 123456 1 PDFHardi Ahmed100% (1)
- Expt 6 - 10Document10 pagesExpt 6 - 10shania adanglaNo ratings yet
- Study Material of Synthetic DetergentDocument12 pagesStudy Material of Synthetic DetergentSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Activity No 5 Reading Materials For Properties of Carboxyly Acid and EstersDocument4 pagesActivity No 5 Reading Materials For Properties of Carboxyly Acid and EstersGrace FulguirinasNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones by Group 6 - 20230920 - 072912 - 0000Document18 pagesAldehydes and Ketones by Group 6 - 20230920 - 072912 - 0000ۦۦ CristineNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesJobel De Pedro100% (4)
- Reacciones de Ácidos Carboxílicos Y Sus Derivados: Theoretical FrameworkDocument6 pagesReacciones de Ácidos Carboxílicos Y Sus Derivados: Theoretical FrameworkMaríaNo ratings yet
- Report Sheet No. 7Document7 pagesReport Sheet No. 7Kimberly AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- I. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesI. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidLaily SafitriNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Exp 9Document13 pagesFormal Report Exp 9Rianne SolivenNo ratings yet
- PBCHEMFILEDocument15 pagesPBCHEMFILEShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Uses of The CompoundsDocument10 pagesUses of The CompoundsXin PurpleNo ratings yet
- CHEM Lesson Note 1 G-8Document4 pagesCHEM Lesson Note 1 G-8Baha RNo ratings yet
- 306 Cannizzaro ReactionDocument9 pages306 Cannizzaro Reactionayesha sanaNo ratings yet
- 2-28!3!14 Oxidation ReductionDocument11 pages2-28!3!14 Oxidation ReductionNadine Harajli HamzehNo ratings yet
- تقرير 1Document6 pagesتقرير 1Sajjad FalahNo ratings yet
- Rohan Roy - pt314 - 3rdsemDocument13 pagesRohan Roy - pt314 - 3rdsem53 Rohan RoyNo ratings yet
- Properties:: Carbonic Acid, (HDocument4 pagesProperties:: Carbonic Acid, (HPRAGYA S BABU AIMLNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Organic Chemistry - Organic Acids and EstersDocument8 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Organic Chemistry - Organic Acids and EstersCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CNC XDocument8 pagesCNC Xvandanachaudhary075No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument5 pagesAldehydes and KetonesFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 AlcoholDocument11 pagesLab 3 AlcoholalihusseinNo ratings yet
- Experiment-4 Group-8Document5 pagesExperiment-4 Group-8ROSE ANN JAWADNo ratings yet
- Assignment DPS CHEM Notes-2 Class-X 0110Document3 pagesAssignment DPS CHEM Notes-2 Class-X 0110bunny reedNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Benzoic Acid From BenzamideDocument18 pagesPresentation of Benzoic Acid From BenzamideFazal rahimNo ratings yet
- Review On Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone From Benzaldehyde by Claisen-Schmidt Reaction and Their Biological ActivitiesDocument9 pagesReview On Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone From Benzaldehyde by Claisen-Schmidt Reaction and Their Biological Activitieskgothatso maleteNo ratings yet
- Name: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik ID: 1913442004: AldehydeDocument6 pagesName: Andi Ria Indahsari Asik ID: 1913442004: AldehydeAndi RiaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Phenols FinalDocument45 pagesAlcohols and Phenols Finalmalikchandkhokhar2211No ratings yet
- Chem 3Document4 pagesChem 3Cristyl Vismanos GastaNo ratings yet
- Production and Synthesis of Antiseptics and DisinfectantDocument12 pagesProduction and Synthesis of Antiseptics and DisinfectantDicksonNo ratings yet
- Cannizarorxn 120207190937 Phpapp01Document71 pagesCannizarorxn 120207190937 Phpapp01Adrian PINo ratings yet
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-NaphtholDocument4 pagesSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-NaphtholEdric RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1Document93 pagesAldehydes Ketones & Carboxylic Acids 1jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- Benz AldehydeDocument1 pageBenz AldehydeWisuda ArafatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry ProjectAhmed fatahNo ratings yet
- Chem Mod 6 #2Document77 pagesChem Mod 6 #2hruthika.schoolNo ratings yet
- Fused Heterocycles With One Heteroatoms: by - Vishal Singh Solanki A.P. at Ideal Institute, Posheri, Wada, Palghar, M.HDocument70 pagesFused Heterocycles With One Heteroatoms: by - Vishal Singh Solanki A.P. at Ideal Institute, Posheri, Wada, Palghar, M.Hshardul bugadiNo ratings yet
- 3 Ethoxy 4 HydroxybenzaldehydeDocument2 pages3 Ethoxy 4 HydroxybenzaldehydemeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- Chem LabDocument15 pagesChem LabSimon AguatisNo ratings yet
- GEMs ID90Document8 pagesGEMs ID90Andre PNo ratings yet
- Benzyl Alcohol PropertiesDocument3 pagesBenzyl Alcohol PropertiesmeimeiliuNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetoneDocument18 pagesAldehydes and KetoneAli AlisonNo ratings yet
- Procedure Act 1Document15 pagesProcedure Act 1Rhealyn LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Laboratory ReportDocument9 pagesExperiment 9 Laboratory ReportjuneNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Peroxide: - Dr. David G. WilliamsDocument15 pagesHydrogen Peroxide: - Dr. David G. WilliamsAfina ShsNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 Date: Preperation of Benzaldehyde Phenyl Hydrazone From Phenyl Hydrazine AIMDocument24 pagesExperiment No.1 Date: Preperation of Benzaldehyde Phenyl Hydrazone From Phenyl Hydrazine AIMVarun Dev KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 9-Article Text-29-1-10-20201106Document4 pages9-Article Text-29-1-10-20201106Nico KudadiriNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Lab19.16.13Document8 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab19.16.13neuronerd67% (3)
- Lecture 8 Benzoic AcidDocument6 pagesLecture 8 Benzoic AcidIgnacio Real BuffelliNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 12: Preparation of Precipitated Sulfur USPDocument7 pagesExperiment No. 12: Preparation of Precipitated Sulfur USPAlessandra Joy M. RoceroNo ratings yet
- CHEM35 1 E7 Cannizzaro Reaction PDFDocument4 pagesCHEM35 1 E7 Cannizzaro Reaction PDFSherlHolmesNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesColor Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesRüveyda AkçinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Green Chemistry)Document5 pagesAssignment 1 (Green Chemistry)saurabh.ch2001No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDFDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDFÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Ss2 WK 10 Hydrocarbon and Crude OilDocument8 pagesSs2 WK 10 Hydrocarbon and Crude Oilamakaemilia5No ratings yet
- Project On ChemistryDocument13 pagesProject On ChemistryBadhal PaudelNo ratings yet
- Acid D Bases Work SheetDocument2 pagesAcid D Bases Work Sheetrayyan asadNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document25 pagesSet 3SriramNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Introduction - BiochemistryDocument59 pagesLec 1 - Introduction - BiochemistryKen WalkerNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document51 pagesCH 03Mark BakalanNo ratings yet
- Diskusi 4 (Acids and Bases) - Dito WDocument12 pagesDiskusi 4 (Acids and Bases) - Dito WnoniNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Control Treatment: Answer KeyDocument66 pagesCorrosion Control Treatment: Answer KeyEscobar ValderramaNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry All Formulas From Errorless BookDocument28 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry All Formulas From Errorless Book100 RishabhNo ratings yet
- PF NSO SOF (17 18) Class 10 - SolDocument18 pagesPF NSO SOF (17 18) Class 10 - SolAadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- 101 CHM EqualDocument24 pages101 CHM EqualDave LarryNo ratings yet
- 5424 The Halogeno Morphides and Codides and The Mechanism of The Morphine Apomorphine Transformation3dc4Document16 pages5424 The Halogeno Morphides and Codides and The Mechanism of The Morphine Apomorphine Transformation3dc4Jo JohNo ratings yet
- How To Make RodinalDocument2 pagesHow To Make RodinaltoomuchroseNo ratings yet
- Exp 6.5 Salt Hydrolysis-1Document5 pagesExp 6.5 Salt Hydrolysis-1Michael Toretto100% (1)
- 07 S and P Block Elements Que. Final E 3Document16 pages07 S and P Block Elements Que. Final E 3gnkstarNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Intro To CDocument32 pagesModul 1 Intro To CUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- US7745383Document10 pagesUS7745383Sharda RamberanNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Cheat Sheet InhouseDocument2 pagesEquilibrium Cheat Sheet InhouseShirleyLinNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument48 pagesWaterchad9631No ratings yet
- Y9 Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFDocument17 pagesY9 Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFRamesh Adwani0% (1)
- 8 - Chem - TB Sol - CH 6 Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pages8 - Chem - TB Sol - CH 6 Chemical ReactionsNetra VasoyaNo ratings yet
- Silver Recovery From Synthetic Photographic and Medical X Ray Process EffluentsDocument8 pagesSilver Recovery From Synthetic Photographic and Medical X Ray Process Effluentsاحمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- OXIDES (Metals & Non-Metals)Document4 pagesOXIDES (Metals & Non-Metals)gauri guptaNo ratings yet
- Water: Water (Chemical Formula H O) Is An Inorganic, TransparentDocument43 pagesWater: Water (Chemical Formula H O) Is An Inorganic, TransparentEiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- SLG Chem2 LG 4.9 BuffersDocument6 pagesSLG Chem2 LG 4.9 BuffersIman SontousidadNo ratings yet
- 7th Chemistry DLP Study Package FinalDocument101 pages7th Chemistry DLP Study Package FinalAdityaNo ratings yet
- Topic:-Nomenclature: 1. Give IUPAC Name ofDocument16 pagesTopic:-Nomenclature: 1. Give IUPAC Name ofkannan2030No ratings yet
- Chem Notes 3e MR Machipanda Term 2Document22 pagesChem Notes 3e MR Machipanda Term 2Tendai MugengeNo ratings yet
- CHEM 301 LEC - Analytical Chemistry I LectureDocument5 pagesCHEM 301 LEC - Analytical Chemistry I LectureDaniel TanNo ratings yet
- f1 Chem H-SP 10 QPDocument43 pagesf1 Chem H-SP 10 QPmarcusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ? ? ?? ?? ? Support MaterialDocument400 pagesChemistry ? ? ?? ?? ? Support MaterialAdityaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Conductometric TitrationsDocument20 pagesUnit 4 Conductometric Titrationschandratom100% (1)