Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Acids, Esters, and Detergents Explained
Uploaded by
Cornflakes ToastedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Acids, Esters, and Detergents Explained
Uploaded by
Cornflakes ToastedCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Acids
Friday, September 23, 2022 7:13 PM
The homologous series of alkanoic acids has the general formula CnH2n+1COOH. Can be
represented as RCOOH as the COOH group is the active group and R is the rest of the molecule
which is generally unreactive.
Naturally found in:
• Vinegar - ethanoic acid
• Stinging needles and ant stings - methanoic acid
• Rancid butter - butanoic acid
• Citrus fruits - citric acid
• Milk - lactic acid
Preparation of Organic Acids
Oxidising alcohols will form the corresponding organic acid. E.g., ethanoic acid can be
prepared by boiling ethanol with potassium chromate(VI)
The product mixture is fractionally distilled to give pure organic acid
Organic Acids And Esters Page 1
Properties of Alkanoic Acids
Saturday, September 24, 2022 12:22 PM
Physical Properties
Organic acids are covalent compounds with a polar OH bond. The OH bond is even greater
than that of an alcohol because of the extra oxygen in the (O=C-O-H) bond. This oxygen is
highly electronegative and increases the pull of electrons away from the H in the OH group.
Organic acids only exist in liquid and solid forms and usually have higher boiling points than
their corresponding alcohols. E.g. the boiling point of ethanoic acid is 118° C compared to
ethanol's which is 87°C.
The increased polarity makes organic acids extremely soluble in water
Chemical Reactions
Organic acids are weak, and so only partially dissociate when dissolved in water to give free H+
ions.
This also makes them weak electrolytes.
They react like typical acids. They react with:
• Reactive Metals to give salt and H2 gas
• Carbonates and Hydrogen Carbonates to give salt, water and carbon dioxide
• Bases to produce salt and water
Anhydrous/dry organic acids give the following reactions
• Combustion in air or oxygen to give carbon dioxide and water
• Condensation or esterification
Organic acids combine with alcohols in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Water is removed (condensation) and compounds called esters are produced. The H2SO4
acts as a dehydrating agent and a catalyst.
Organic Acids And Esters Page 2
acts as a dehydrating agent and a catalyst.
Organic Acids And Esters Page 3
Esters
Saturday, September 24, 2022 3:20 PM
Esters are formed when alcohols and acids react
Naming Esters
When drawing esters, the acid part comes first, then the alcohol part.
When naming the compound, the alcohol part comes first, followed by the acid part. The
alcohol is named as a branch on the acid.
Larger samples of esters can be prepared by boiling a mixture of alcohol, anhydrous acid and
concentrated H2SO4 under reflux.
This allows continuous boiling without loss of volume to vapourisation.
The product is added to water. The ester floats on the surface and can be separated by
separating funnel.
Organic Acids And Esters Page 4
Properties of Esters
Saturday, September 24, 2022 3:41 PM
Physical Properties
-Esters are covalent, non-polar molecules held together by weak van-der-waals forces. The
strength of the force depends on the size of the molecule.
They are insoluble in water
Short chained organic acids (C1 - C6) produce esters which are oily, pleasant smelling liquids.
They are naturally found in fruits and flowers and are used in perfumes and flavourings.
Long chained organic acids produce esters commonly referred to as fats and oils. They are
greasy, scentless solids and liquids.
Fats and Oils
These are esters formed by the condensation of organic acids with a large hydrocarbon tail
and the tri-alcohol glycerol
Long chained organic acids:
C18H37COOH - stearic acid
C11H23COOH - lauric acid
C15H31COOH - palmitic acid
All of these organic acids can simply be represented as
Glycerol condenses with 3 fatty acid molecules to produce a fat molecule, a tri-ester
Organic Acids And Esters Page 5
Reactions of Esters
The functional group is the ester bond
Esters can undergo hydrolysis (the breakdown of the molecule by the addition of water).
There are 2 types of hydrolysis:
• Acid Hydrolysis - Boiling of the ester with dilute acid (HCl or H2SO4). This gives an organic
acid and alcohol
• Alkaline Hydrolysis - Boiling with aqueous alkali (NaOH or KOH). Yields the salt of the acid
and an alcohol.
As with inorganic salts, the salt formed has totally different properties from the acid. This
reaction is the basis of soap making or saponification.
Organic Acids And Esters Page 6
Detergents
Saturday, September 24, 2022 5:11 PM
Detergents improve the cleaning power of water
There are two types:
• Soaps
Made by the process of saponification in which fats and oils are hydrolysed by boiling
with concentrated NaOH
Fat / Oil + NaOH -> sodium salt of organic acid (soap) + Glycerol
A soap is the salt of a long chained organic acid.
• Soapless Detergents
Made by reacting hydrocarbons from petroleum with concentrated sulphuric acid. The
product is neutralised with NaOH to form a salt with a long hydrocarbon chain. E.g.
C18H29OSO3Na.
Detergents are composed of 2 parts: a polar head, and a long, non-polar, hydrocarbon tail.
Detergents do 2 things:
• It forms and interface between water and the fabric to improve wetting ability of the
water
• The non-polar tail dissolves in the dirt, and polar head dissolves in the water. The soap
particles are able to surround an lift the dirt off the fabric.
Organic Acids And Esters Page 7
Organic Acids And Esters Page 8
You might also like
- Neural Networks From Scratch in PythonDocument658 pagesNeural Networks From Scratch in PythonZé Felipe100% (2)
- Lab Report SoapDocument15 pagesLab Report Soapanon_327056880100% (3)
- Functional Groups - Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Learning Question: How Do Functional Groups Affect TheDocument20 pagesFunctional Groups - Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Learning Question: How Do Functional Groups Affect TheemanNo ratings yet
- Esters75275254 131207020139 Phpapp02Document19 pagesEsters75275254 131207020139 Phpapp02Mujthaba AdmaniNo ratings yet
- GO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidDocument18 pagesGO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic AcidcikaifaNo ratings yet
- Ethanoic Acid ChemDocument14 pagesEthanoic Acid ChemjasmynefNo ratings yet
- Assignment DPS CHEM Notes-2 Class-X 0110Document3 pagesAssignment DPS CHEM Notes-2 Class-X 0110bunny reedNo ratings yet
- Soaps & Detergents: Cleansing Agents for Daily LifeDocument13 pagesSoaps & Detergents: Cleansing Agents for Daily Lifejia_yuan938459No ratings yet
- Soaps and Detergents: A ComparisonDocument26 pagesSoaps and Detergents: A ComparisonIka BakarNo ratings yet
- 2019 Ch104 Organic AcidsDocument111 pages2019 Ch104 Organic Acidsgenesis gengerNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study of Structure, Properties & ReactionsDocument42 pagesOrganic Chemistry Study of Structure, Properties & ReactionsAlisha KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Note (SPM)Document10 pagesChemistry Note (SPM)Jakob VooNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab (Soaps)Document19 pagesChem Lab (Soaps)Amiro Iqbal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- SoapsDocument20 pagesSoapsSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- 4.1.3 Carboxylic Acids & EstersDocument5 pages4.1.3 Carboxylic Acids & EstersFin BrickmanNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of SoapDocument34 pagesSynthesis of SoapAlex Atienza100% (1)
- Chemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsDocument7 pagesChemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsAnonymous HLkNDToNo ratings yet
- Detergent (Group 1,2)Document29 pagesDetergent (Group 1,2)Sourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Report Sheet No. 7Document7 pagesReport Sheet No. 7Kimberly AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 8.30 Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pages8.30 Carboxylic AcidslovejoyNo ratings yet
- I. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesI. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidLaily SafitriNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Naming of EstersDocument6 pagesFunctional Groups: Naming of EsterspappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chemistry: Chemical For ConsumerDocument16 pagesForm 5 Chemistry: Chemical For Consumernaqiu96No ratings yet
- Tyndale-Biscoe and Mallinson Society: Senior DepartmentDocument11 pagesTyndale-Biscoe and Mallinson Society: Senior DepartmentAlima IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemical For ConsumersDocument17 pagesChemical For ConsumersBjergsenNo ratings yet
- Esters - Properties, Preparation and ReactionsDocument4 pagesEsters - Properties, Preparation and ReactionsSurendra RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives ExplainedDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Derivatives ExplainedÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Compare Properties of Homemade Soap and DetergentsDocument16 pagesCompare Properties of Homemade Soap and DetergentsNurul AinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Laboratory-1 (CHE F312) Lab Report Engineering Chemistry Lab E-6 SaponificationDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering Laboratory-1 (CHE F312) Lab Report Engineering Chemistry Lab E-6 SaponificationHritik LalNo ratings yet
- Carbon & Its Compounds - pdf-28Document5 pagesCarbon & Its Compounds - pdf-28WARRIORS100% (1)
- 1.soap and Detergent Making Through History-DeSKTOP-JP1D0AVDocument6 pages1.soap and Detergent Making Through History-DeSKTOP-JP1D0AVtaghrid itaniNo ratings yet
- Module Carbon CompoundsDocument23 pagesModule Carbon CompoundspkrajenpillaiNo ratings yet
- LayoutDocument55 pagesLayoutHenok Moges KassahunNo ratings yet
- Soap ReportDocument16 pagesSoap ReportAddison JuttieNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids:: Properties of Carboxyic AcidsDocument3 pagesCarboxylic Acids:: Properties of Carboxyic AcidsMuhammadShabbirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F5 Chapter 2Document42 pagesChemistry F5 Chapter 2Norhafiza HasimuddinNo ratings yet
- Acid Theory Changes Over TimeDocument9 pagesAcid Theory Changes Over TimeAlan SongNo ratings yet
- ESTERSDocument36 pagesESTERSAbdihakemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Yang Ini)Document45 pagesChemistry (Yang Ini)Nabil MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument100 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsmrpulkit20No ratings yet
- Ester Nomenclature, Properties, Reactions and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesEster Nomenclature, Properties, Reactions and ApplicationsHuntal NapitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 NoteDocument19 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 NoteshashababygewlNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersDocument12 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 5 Chemical For ConsumersOrkid Fazz89% (9)
- Chemistry Easy ScienceDocument12 pagesChemistry Easy ScienceIman SyakirahNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument32 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsTusharr sgrNo ratings yet
- Notes On AlcoholsDocument3 pagesNotes On AlcoholsAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- L I P I D SDocument42 pagesL I P I D SCindy FelixNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Uitm. Soap Preparation. Comparison Soap and Detergent Properties.Document16 pagesLab 6 Uitm. Soap Preparation. Comparison Soap and Detergent Properties.niniwani59No ratings yet
- Week 7 (B) ChemistryDocument3 pagesWeek 7 (B) ChemistryBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Components of Food: Chemistry Project 2005-2006Document69 pagesComponents of Food: Chemistry Project 2005-2006Ann Deocampo DuayNo ratings yet
- SOAPS and DetergentsDocument66 pagesSOAPS and DetergentsMkhalilizul SiHamba CintaIlahi100% (1)
- Soap and DetergentsDocument18 pagesSoap and DetergentsYarIxx NikIcNo ratings yet
- Acids bases and salts class 10 notesDocument8 pagesAcids bases and salts class 10 notesashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Indicators GuideDocument13 pagesAcids, Bases and Indicators GuideJoshenderNo ratings yet
- Soaps and Detergents: A Concise GuideDocument18 pagesSoaps and Detergents: A Concise GuideVince BagguatanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment 9 Acyl Compounds: Soaps and Detergents I. ObjectivesJobel De Pedro100% (4)
- Soap and Detergent 2Document37 pagesSoap and Detergent 2Erviani RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Reacciones de Ácidos Carboxílicos Y Sus Derivados: Theoretical FrameworkDocument6 pagesReacciones de Ácidos Carboxílicos Y Sus Derivados: Theoretical FrameworkMaríaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesCSEC Chemistry - ElectrochemistryCornflakes Toasted100% (1)
- StatisticsDocument9 pagesStatisticsCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Acids, Bases and SaltsCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
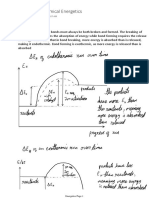
- Chemical Energetics: Energy Changes in ReactionsDocument5 pagesChemical Energetics: Energy Changes in ReactionsCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics - The AtomDocument5 pagesCSEC Physics - The AtomCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics - MagnetismDocument5 pagesCSEC Physics - MagnetismCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Csec Quadratic Add Math QuestionsDocument2 pagesCsec Quadratic Add Math QuestionsCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Control Strategies For Physically Simulated Characters Performing Two Player Competitive SportsDocument11 pagesControl Strategies For Physically Simulated Characters Performing Two Player Competitive SportsRafael TavaresNo ratings yet
- ROOTS OF A QUADRATIC Add Math PDFDocument1 pageROOTS OF A QUADRATIC Add Math PDFCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Control Strategies For Physically Simulated Characters Performing Two Player Competitive SportsDocument11 pagesControl Strategies For Physically Simulated Characters Performing Two Player Competitive SportsRafael TavaresNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism CSEC NotesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism CSEC NotesCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Components and Energy FlowDocument135 pagesEcosystem Components and Energy FlowCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument116 pagesCellsCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Painting of Steelwork Manual Provides GuidanceDocument33 pagesMaintenance Painting of Steelwork Manual Provides GuidancerohanZorbaNo ratings yet
- Connectors Installed On SCL Columns: Technical BulletinDocument1 pageConnectors Installed On SCL Columns: Technical BulletinJorge Enrique MenesesNo ratings yet
- KB310-SSRE Baby Changing Station: Technical Data SheetDocument4 pagesKB310-SSRE Baby Changing Station: Technical Data SheetDavid MoralesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledNUR AMAANY ABDUL NASIRNo ratings yet
- Blasting & Painting Inspection For Onshore and Offshore Fabrication Procedure PSP No. 06Document6 pagesBlasting & Painting Inspection For Onshore and Offshore Fabrication Procedure PSP No. 06AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Workability of ConcreteDocument2 pagesWorkability of ConcreteOmar Al AskandaraniNo ratings yet
- Interpipe CatalogueDocument41 pagesInterpipe CatalogueDpnsHome100% (2)
- Dishwashing Liquid Chemical Formula and Manufacturing ProcessDocument3 pagesDishwashing Liquid Chemical Formula and Manufacturing ProcessLeonilo BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Mastertop 1240 TdsDocument3 pagesMastertop 1240 Tdsdilshad khanNo ratings yet
- Early Works Package - Specification B (Section 317210) - Tunnel Primary Support - Ground ReinforcementDocument3 pagesEarly Works Package - Specification B (Section 317210) - Tunnel Primary Support - Ground ReinforcementZain AbidiNo ratings yet
- Bisco One StepDocument4 pagesBisco One Steptravolta0No ratings yet
- ASTM D 1142 - 95 (Reapproved 2006)Document11 pagesASTM D 1142 - 95 (Reapproved 2006)Julian Felipe Noguera CruzNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument53 pagesReportutkarshNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 4Document28 pagesLecture # 4Usama ShahidNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet TimbercoatDocument2 pagesData Sheet TimbercoatajoilhamNo ratings yet
- HEMPADUR MULTI-STRENGTH 35530 BlackDocument2 pagesHEMPADUR MULTI-STRENGTH 35530 BlackRuby Faith EspinosaNo ratings yet
- JN Series Vertical Shaft Concrete Mixer PDFDocument2 pagesJN Series Vertical Shaft Concrete Mixer PDFHenan NF Mechanical Installation Co., Ltd.No ratings yet
- ASTM E84 - 19b Standard Test Method For Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials PDFDocument6 pagesASTM E84 - 19b Standard Test Method For Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials PDFKishor BaruahNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Heat Resistant Alloy in Process GasDocument16 pagesFailure Analysis of Heat Resistant Alloy in Process GasBubai111No ratings yet
- A11122XG W/B Gloss Coating: Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageA11122XG W/B Gloss Coating: Technical Data SheetYenifer LinaresNo ratings yet
- Silica fume/CHAPTER 1Document45 pagesSilica fume/CHAPTER 1mohanNo ratings yet
- Siemens Acuson X300 Ultrasound Imaging System - Instruction Manual (En)Document5 pagesSiemens Acuson X300 Ultrasound Imaging System - Instruction Manual (En)HOSP. DA RESTAURAÇÃONo ratings yet
- FeC and TTT DiagramsDocument12 pagesFeC and TTT DiagramsMohamed El-WakilNo ratings yet
- Explosive WeldingDocument54 pagesExplosive WeldingNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Cug2050 ThermalbackfillDocument4 pagesCug2050 ThermalbackfillimranNo ratings yet
- Pantile Church Instructions PDF PDFDocument1 pagePantile Church Instructions PDF PDFAlvaro ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Automation Basics - Combustible Gas Detector Sensor Drift - Catalytic VsDocument1 pageAutomation Basics - Combustible Gas Detector Sensor Drift - Catalytic VsHilder Ramirez PuellesNo ratings yet
- Roofing Sheet MetalDocument15 pagesRoofing Sheet MetalKim AnneNo ratings yet
- Metals and How To Weld ThemDocument1 pageMetals and How To Weld ThemJack JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 01 - Transferencia de Masa Por Difusion PDFDocument13 pages01 - Transferencia de Masa Por Difusion PDFNinoska EspinozaNo ratings yet