Professional Documents
Culture Documents
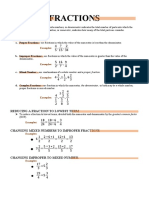
Fractions Decimals and Percentages - Practice Booklet
Uploaded by
Paa JoeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fractions Decimals and Percentages - Practice Booklet
Uploaded by
Paa JoeCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths Revision &
Practice Booklet
Name:
Fractions, Decimals and
Percentages
visit twinkl.com
Maths Revision & Practice Booklet
Revise
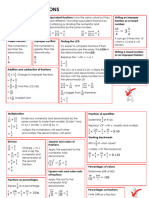
Using Common Factors to Simplify Fractions
Fractions that have the same value but represent this using different denominators and
numerators are equivalent. We can recognise and find equivalent fractions by multiplying or
dividing the numerator and denominator by the same amount. When we simplify a fraction,
we use the highest common factor of the numerator and denominator to reduce the fraction to
the lowest term equivalent fraction (simplest form).
21 Factors of 21: 1 3 7 The highest
36
common factor
Factors of 36: 1 2 3 4 6 9 12 18 36 is 3.
21 ÷ 3 = 7 7
36 ÷ 3 = 12 12
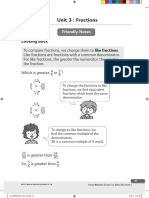
Using Common Multiples to Express Fractions in the Same Denomination
To compare or calculate with
fractions, we often need to give
them a common denominator.
We do this by looking at the
denominators and finding their
lowest common multiple.
3 4 5 × 7 = 35
5 7 35 is the lowest common multiple.
3 3 × 7 = 21 4 4 × 5 = 20
Remember that whatever we do
to the denominator, we have to
5 5 × 7 = 35
7 7 × 5 = 35
do to the numerator.
Page 2 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Maths Revision & Practice Booklet
Comparing and Ordering Fractions, Including Fractions > 1
To compare and order
...look at the 5 2
fractions with the same
denominators…
numerators. 9 > 9
…change the 5 and
3
To compare and order
fractions into
equivalent
9 5
fractions with different ×5 ×9
fractions with the
denominators…
25 27
< 45
lowest common
denominator. 45
2 1
…change the 17 and 13
mixed number
To compare and
order fractions with
into an improper 9 and
4
mixed numbers…
fraction and 7 3
continue
×3 ×7
as needed. 27 < 28
21 21
Add and Subtract Fractions with Different Denominators and Mixed Numbers
When we add and subtract fractions with different
denominators, we need to give them a common
denominator. We use the lowest common multiple
as the common denominator to create equivalent
fractions which we can then add and subtract.
5 2
+
9 3 =
If one of the fractions is a multiple of
5 2 ×3=6
the other, use multiplication to change + ×3=9
the smaller denominator to the same
9 3
denominator as the other fraction.
5 + 6 = 11 =
9 9 9 1 92
Page 3 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Maths Revision & Practice Booklet
8 3
-
9 4 =
If the fractions aren’t multiples of each
8 ×4= 32 3 × 9 = 27
other, use multiplication to change them 9 ×4= 36 4 × 9 = 36
both to the lowest common denominator.
32 - 27 = 5
36 36 36
If the fractions involve adding or subtracting mixed numbers, there are two methods that
can be used:
Add the whole numbers and the Convert the mixed numbers to
fractions separately. improper fractions.
2 35 + 3 14 = 2 56 - 1 15 =
2 + 3 = 5 17 6
- =
85
-
36
=
49
6 5 30 30 30
3 1 12 5 17
+
5 4 = 20 +
20 =
20 49
1 19
30 = 30
17
5+ 20 = 5 17
20
Multiplying Simple Pairs of Proper Fractions, Writing the Answer in its
Simplest Form
Write the whole number 5 4
with a denominator 7 × 1 =
Multiply a Proper
Fraction by a of 1. Multiply the
Whole Number numerators together
20
and multiply the
7 = 2 67
denominators together.
Multiply the numerators 3 3
together and multiply 5 × 8 =
Multiply Proper
the denominators
Fractions Together
together. Simplify the 9
answer if needed.
= 40
Page 4 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Maths Revision & Practice Booklet
Dividing Proper Fractions by Whole Numbers
Multiplication and division are
inverse operations of each other.
÷ 5 is the same as × 1
1 5
7 5
9 ÷ 6 =
8 ÷ 4 =
7 1 5 1
9 × 6 = 8 × 4 =
7×1 7 5×1 5
9×6 = 54 8×4 = 32
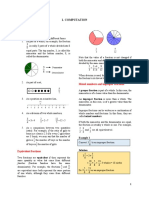
Calculating Decimal Equivalents of Fractions
Every proper fraction has a decimal number equivalent, which we can calculate by dividing
the numerator by the denominator.
Common decimal equivalents of fractions can be learnt as facts:
Fraction
1 1 1 1
2 4 10 5
Decimal 0.5 0.25 0.1 0.2
We can calculate the decimal equivalents of trickier
fractions using written methods of division.
Sometimes, a decimal equivalent will be a long number.
In these cases, you can round the decimal to one or two
decimal places.
0 5 7 1 4 = 0.57 rounded to
7
4 two decimal places.
7 =
7 4 0 0 0
4 5 1
Page 5 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Maths Revision & Practice Booklet
Identify the Value of Each Digit in Numbers to Three Decimal Places
In order to be able to read, write and calculate with decimal numbers, we need to understand
the place value of each digit after the decimal point.
As the place value position moves right of the decimal point, the digits become ten times smaller.
ones tenths hundredths thousandths
1 1 1
10 100 1000
Recall and Use Equivalences between Simple Fractions,
Decimals and Percentages
Fractions, decimals and percentages are equivalent ways of expressing the same proportion.
Fraction Percentage Decimal
1 50% 0.5
2
1 25% 0.25
4
3 75% 0.75
4
1 20% 0.2
5
1
10% 0.1
10
To calculate trickier equivalents, we can use the rules in this diagram to help us:
Percentage to Fraction 3 Fraction to Decimal
Write the percentage as a fraction 5 Divide the numerator by
with a denominator of 100 and Fraction the denominator.
then simplify. 3
60 6 3 5 = 3 ÷ 5 = 0.6
100 = 10 = 5
60% 0.6
Percentage Decimal
Decimal to Percentage
Multiply the decimal by 100
and add the % sign.
0.6 × 100 = 60%
Page 6 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Practise
Supercharge your powers by
answering these questions.
1. Put these fractions in order of size, starting with the smallest.
3 1 7 2 1 mark
4 6 12 3
smallest greatest
2. The numbers in this sequence increase by the same amount each time.
Write the missing numbers. 1 mark
1 1 37 1 12
14
3. In each box, circle the number that is greater.
1 mark
1 3
5 1.55 1 2
3 1.8
1 100
9
1.9 1107 1.67
4. Write the missing fraction in this calculation.
1 mark
1 + 1 + =1
5 3
total for
this page
Page 7 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Practise
5. Write the missing numbers in these equivalent fractions.
4 = 12 = 1 mark
5 90
6. Circle the improper fraction that is equivalent to 4 79
1 mark
40 41 42 43 44
9 9 9 9 9
7. Tick the calculation that is the best estimate.
411 1 15 1 56
1 mark
- +
12
4 - 1 + 2 5-2+2
5-1+2 4-1+1
8. I spent £1.40 on a drink and £1.70 on a sandwich. I have three fifths of my
money left. How much money did I have to start with? 2 marks
Show
your
method
total for
this page
Page 8 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Practise
9. Yesterday, I read 3
7 of my book. Today, I read the remaining 152 pages to
finish the book. How many pages are there in my book? 2 marks
Show
your
method
pages
10. One fruit smoothie contains 23 of a carton of orange juice. I make 7
smoothies. Calculate, as a mixed number, how much orange juice I use 2 marks
altogether.
Show
your
method
cartons
11. In this circle, 1
4
3 are shaded.
and 16
What fraction of the whole circle is not shaded? 2 marks
Show
your
method
total for
this page
Page 9 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Practise
12. What fraction of this diagram is shaded?
2 marks
1
? 8 2
3
Show
your
method
2 marks
13. I make a model out of 25 cubes.
What percentage of the cubes in the model are blue?
Show
your
method
total for
this page
Page 10 of 11 visit twinkl.com
Practise
14. I have £380. I spend 18% of my money on a new bike.
How much money do I spend on my new bike? 2 marks
Show
your
method
total for
this page
Self-Assessment
Colour in the superhero strength-o-meter to show how you feel
about each of these statements:
I can use common factors to simplify fractions and use common
multiples to express fractions in the same denomination.
I can compare and order fractions, including fractions > 1.
I can add and subtract fractions with different denominators and
mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions.
I can multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the
answer in its simplest form.
I can divide proper fractions by whole numbers.
I associate a fraction with division and calculate decimal
fraction equivalents.
I can recall and use equivalences between simple fractions,
decimals and percentages.
Page 11 of 11 visit twinkl.com
You might also like
- Activity Week 9Document15 pagesActivity Week 9rhiana encinasNo ratings yet
- Comparing and ordering fractions with common denominatorsDocument19 pagesComparing and ordering fractions with common denominatorsMichael John LerumNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument13 pagesMathsRangeNo ratings yet
- Fractions and Decimals NotesDocument5 pagesFractions and Decimals NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Comparing and Ordering Fractions Power PointDocument20 pagesComparing and Ordering Fractions Power PointTeacher JAY-AR LAGMANNo ratings yet
- Common FractionsDocument3 pagesCommon Fractionsnjaphasenamile80No ratings yet
- Business Math Lesson GuideDocument9 pagesBusiness Math Lesson GuideKaye VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Ordering FractionsDocument20 pagesComparing and Ordering FractionsanjNo ratings yet
- Grade 7Document51 pagesGrade 7Han-z Caganan DanielNo ratings yet
- Representing Fractions in Different FormsDocument6 pagesRepresenting Fractions in Different Formsreeta ramNo ratings yet
- t2 M 4551 Year 6 Maths Vocabulary Word Mats - Ver - 2Document17 pagest2 M 4551 Year 6 Maths Vocabulary Word Mats - Ver - 2kubashaniNo ratings yet
- Find + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Document3 pagesFind + 5: Business Math Example: 3 8 5 9 6Pherngy CadanoNo ratings yet
- 2 FractionDocument16 pages2 FractionSubrataThakuraNo ratings yet
- Addition, Subtraction of Rational Fraction SIM PDFDocument13 pagesAddition, Subtraction of Rational Fraction SIM PDFGladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- 60a2c5803a0b0-Grade 6 Unit 9 (Part 2) 5Document2 pages60a2c5803a0b0-Grade 6 Unit 9 (Part 2) 5Erandi Kusala AmarasiriNo ratings yet
- w06 HDTBasMathDocument3 pagesw06 HDTBasMathKhaeroni KhaeroniNo ratings yet
- RX MX5 Ny 0 B Ljyr 02Document11 pagesRX MX5 Ny 0 B Ljyr 02Aftab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Nmat QuantitativeDocument24 pagesNmat QuantitativeCathreen Agatha Fule100% (1)
- Maths For Healthcare Professionals: Fractions Decimals Ratio Percentages BMI Averages Unit ConversionDocument51 pagesMaths For Healthcare Professionals: Fractions Decimals Ratio Percentages BMI Averages Unit ConversionUrwa ImanNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Let Review Part 2Document15 pagesGen Math Let Review Part 2Joshua MarianoNo ratings yet
- QUANTITATIVE METHOD LECTURE 1: BASICSDocument22 pagesQUANTITATIVE METHOD LECTURE 1: BASICSGia Huy LạiNo ratings yet
- Aljon Math Module 1 q1Document13 pagesAljon Math Module 1 q1Eliseo Acedo PamaNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Ordering Fractions (Unlike Denominators) Whole Lesson 2Document11 pagesComparing and Ordering Fractions (Unlike Denominators) Whole Lesson 2UMAH DEVI M CHANDARNo ratings yet
- 7 - Quiz 1 - Mathematics - FractionsDocument1 page7 - Quiz 1 - Mathematics - FractionsDigilib Cambridge TazkiaNo ratings yet
- MA4 9NA (Indices)Document8 pagesMA4 9NA (Indices)E GlassNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Comparing FractionsDocument2 pages1.4 Comparing FractionswainejamesmoteNo ratings yet
- Types of Fractions: 4 5 7 15 2 34Document4 pagesTypes of Fractions: 4 5 7 15 2 34Kathleen AnnNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1-ActivityDocument24 pagesLESSON 1-Activityarjay matanguihanNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Maths Assessment FractionsDocument11 pagesYear 5 Maths Assessment Fractionstlhalatsigao57No ratings yet
- Add and Subtract Fractions (40 chDocument5 pagesAdd and Subtract Fractions (40 chA DNo ratings yet
- Don Carlos Polytechnic College College of Teacher EducationDocument14 pagesDon Carlos Polytechnic College College of Teacher EducationChen MaglunsodNo ratings yet
- 3 LessonDocument10 pages3 LessonAmit Gaurav100% (1)
- MATHEMATICS REVIEWERDocument17 pagesMATHEMATICS REVIEWERsheena diazNo ratings yet
- Math 4Document12 pagesMath 4jonesmanNo ratings yet
- Converting A Mixed Number To An Improper FractionDocument3 pagesConverting A Mixed Number To An Improper FractionMathnasium of BentonvilleNo ratings yet
- PutationDocument6 pagesPutationJnr DogheadNo ratings yet
- Fraction Lesson PowerpointDocument9 pagesFraction Lesson Powerpointapi-445198464No ratings yet
- Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers GuideDocument7 pagesDividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers GuideArgell GamboaNo ratings yet
- The Fraction Cheat Sheet Math 8Document1 pageThe Fraction Cheat Sheet Math 8txcrudeNo ratings yet
- HL MathsDocument425 pagesHL MathsBalageeon100% (1)
- MATH REVIEWER For 4th GradersDocument3 pagesMATH REVIEWER For 4th GradersJul RoseNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions PowerPointDocument20 pagesAdding and Subtracting Fractions PowerPointJenilyn EspejoNo ratings yet
- Fractions Comp Packet RevisedDocument20 pagesFractions Comp Packet Revisedapi-235199292No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Basic College Mathematics 8Th Edition by Tobey Slater Blair and Crawford Isbn 0134178998 9780134178998 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Basic College Mathematics 8Th Edition by Tobey Slater Blair and Crawford Isbn 0134178998 9780134178998 Full Chapter PDFernesto.medina346100% (12)
- Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers: Find - , Expressing The Answer in Simplest FormDocument3 pagesAdding and Subtracting Rational Numbers: Find - , Expressing The Answer in Simplest FormStanleyNo ratings yet
- Sweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay Cp. No. 09109436343Document6 pagesSweet & Karen Review and Tutorial Center No. 82 Zone 1, Estancia Malinao, Albay Cp. No. 09109436343Dominic CareoNo ratings yet
- Finding Prime Factors: Intermediate and Necessary Concept To Learn Before You Further Explore FractionsDocument14 pagesFinding Prime Factors: Intermediate and Necessary Concept To Learn Before You Further Explore FractionsMarisa VetterNo ratings yet
- Fraction Multiplication and Division With Mental Math - World Mental CalculationDocument8 pagesFraction Multiplication and Division With Mental Math - World Mental CalculationRojo VoavyNo ratings yet
- M3 - Operations Based On FractionsDocument10 pagesM3 - Operations Based On Fractionscandybot98No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Fractions: Looking BackDocument6 pagesUnit 3: Fractions: Looking BackMohammad Musa AbidNo ratings yet
- Divisibility Rule ExtensionDocument3 pagesDivisibility Rule ExtensionamorNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions Different DenominatorsDocument16 pagesAdding and Subtracting Fractions Different DenominatorsmomoNo ratings yet
- 1 Operations On FractionsDocument31 pages1 Operations On FractionsRosda BundaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Student TextbookDocument50 pagesChapter 8 Student TextbookrmicallefNo ratings yet
- Factorizing by Taking GCFDocument16 pagesFactorizing by Taking GCFabdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document2 pagesChapter 9api-247228121No ratings yet
- Algebra IDocument240 pagesAlgebra IMahobe100% (2)
- T Par 1647428183 World Geography Escape Room Game Ver 4Document15 pagesT Par 1647428183 World Geography Escape Room Game Ver 4Paa JoeNo ratings yet
- Credit Analyst ReviewDocument4 pagesCredit Analyst ReviewPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- A Better Way To Cut CostsDocument4 pagesA Better Way To Cut CostsPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Fsi Anticipating Bank Customer Needs PWCDocument12 pagesFsi Anticipating Bank Customer Needs PWCPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- ADB Bank Ghana PLCDocument1 pageADB Bank Ghana PLCPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Fiction Reading Revision MatDocument2 pagesFiction Reading Revision MatPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- 5-For-5 Reading Test 5 QuestionsDocument1 page5-For-5 Reading Test 5 QuestionsPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Y5 Arithmetic Full Test 9 PDFDocument12 pagesY5 Arithmetic Full Test 9 PDFfatimahNo ratings yet
- Year 6-Term-2-Reading-Assessment-Reading-Booklet-FictionDocument3 pagesYear 6-Term-2-Reading-Assessment-Reading-Booklet-FictionPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- CA t2 M 1126 Grade 4 Multiplication and Division Term 2 Test English Canadian Ver 1Document8 pagesCA t2 M 1126 Grade 4 Multiplication and Division Term 2 Test English Canadian Ver 1Paa JoeNo ratings yet
- Official SSAT Lower Level Practice Test 2 v1 QuestionsDocument30 pagesOfficial SSAT Lower Level Practice Test 2 v1 QuestionsPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Year 6-Term-2-Reading-Assessment-Mark-Scheme-Non-FictionDocument4 pagesYear 6-Term-2-Reading-Assessment-Mark-Scheme-Non-FictionPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- 5-For-5 Reading Test 5 AnswersDocument1 page5-For-5 Reading Test 5 AnswersPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Au t2 e 2166 The Spotty Octopus Writing Sample - Ver - 2Document1 pageAu t2 e 2166 The Spotty Octopus Writing Sample - Ver - 2Paa JoeNo ratings yet
- UNESCODocument70 pagesUNESCOPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Article Writing PowerPointDocument9 pagesArticle Writing PowerPointPaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Figure1 Statement of Financial PerformanceDocument1 pageFigure1 Statement of Financial PerformancePaa JoeNo ratings yet
- Au t2 e 846 Year 5 Narrative Writing Quotthe Creature and The Haunted Housequot Writing Activity Sheet Ver 2Document4 pagesAu t2 e 846 Year 5 Narrative Writing Quotthe Creature and The Haunted Housequot Writing Activity Sheet Ver 2Paa JoeNo ratings yet
- Python Essentials 1Document128 pagesPython Essentials 14139 NIVEDHA S50% (2)
- CPA - A Guide For TeachersDocument162 pagesCPA - A Guide For TeachersXevi Camps PochNo ratings yet
- CC 2017 tn5m Ri Se l01Document6 pagesCC 2017 tn5m Ri Se l01api-2937535880% (1)
- Signed Number RepresentationsDocument18 pagesSigned Number Representationsselvam_08No ratings yet
- Ks3 Maths Dictionary WorksheetsDocument41 pagesKs3 Maths Dictionary WorksheetscarlagimenoNo ratings yet
- FGHJGHJDocument25 pagesFGHJGHJGunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- 5a (Digital System) Number System - Amin - V.studentDocument50 pages5a (Digital System) Number System - Amin - V.studentHilmyZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Keys To The Study of Chemistry: Follow-Up ProblemsDocument28 pagesChapter 1 Keys To The Study of Chemistry: Follow-Up Problems범수No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Number SystemsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 Number SystemsAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Python Programming For BeginnersDocument117 pagesPython Programming For Beginnersjan100% (1)
- Duenorth Academics - Crack The IIM Indore IPM (Integrated Programme in Management) Complete Manual-Pearson (2017) PDFDocument661 pagesDuenorth Academics - Crack The IIM Indore IPM (Integrated Programme in Management) Complete Manual-Pearson (2017) PDFXpertkami83% (6)
- ProgressionDocument26 pagesProgressionHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics DLP Year 6 0000Document12 pagesRPT Mathematics DLP Year 6 0000PAVITHEERA A/P TAMIL SILVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 7 PDFDocument158 pagesMaths Grade 7 PDFAbdirahman100% (3)
- BMAT2112 Business Math Written Work 1Document5 pagesBMAT2112 Business Math Written Work 1Christian Tero0% (2)
- Exercise 1.3: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number SystemDocument7 pagesExercise 1.3: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1-Number SystemArish KhanNo ratings yet
- MELC-Based Syllabus for Senior High School Business MathematicsDocument3 pagesMELC-Based Syllabus for Senior High School Business MathematicsRey Salomon100% (2)
- Rename Decimal Numbers To Fractions Whose Denominators Are Factors of 10 and 100Document25 pagesRename Decimal Numbers To Fractions Whose Denominators Are Factors of 10 and 100MARY VIE CALAONo ratings yet
- Binary Decimal and HexadecimalDocument78 pagesBinary Decimal and HexadecimalThivaNo ratings yet
- 0862 Lower Secondary Mathematics Stage 9 Scheme of Work - tcm143-595645Document121 pages0862 Lower Secondary Mathematics Stage 9 Scheme of Work - tcm143-595645Abel MasitsaNo ratings yet
- Learn PHP Variables & Data TypesDocument4 pagesLearn PHP Variables & Data TypesIliasAhmedNo ratings yet
- Teach Fractions with Candy, Pies, Tortillas and More Fun Food ActivitiesDocument5 pagesTeach Fractions with Candy, Pies, Tortillas and More Fun Food ActivitiesEr Weng TerqNo ratings yet
- IntegersDocument3 pagesIntegersSchool Desk SpaceNo ratings yet
- Rational and irrational numbersDocument16 pagesRational and irrational numbersMia DanielsNo ratings yet
- Emvic Core8 BookDocument655 pagesEmvic Core8 BookAlisha TaylorNo ratings yet
- e-Prac-CAT-01 - TestDocument39 pagese-Prac-CAT-01 - TestMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Conversions: ROM Ercent TO EcimalDocument3 pagesConversions: ROM Ercent TO EcimalDoo RaNo ratings yet
- Error Log For The Official Guide OG 2020Document151 pagesError Log For The Official Guide OG 2020Keren CherskyNo ratings yet
- DS BookDocument375 pagesDS BookSnehasis ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Amzn1 Tortuga 3 T27XTY10ZAVK8MDocument373 pagesAmzn1 Tortuga 3 T27XTY10ZAVK8MMathan LuceroNo ratings yet