Professional Documents
Culture Documents
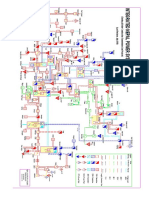
SCMPE Chapter 2 Mind Map
Uploaded by
govarthan1976Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCMPE Chapter 2 Mind Map
Uploaded by
govarthan1976Copyright:
Available Formats
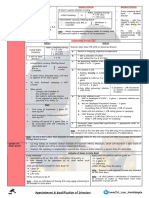
Meaning and Basic
Chapter 2 - Modern Business Enviorment Cost of Quality
Supply Chain - All activities
associated with flow &
transformation of goods from
upply Chain Management -
S
Management of all activities
associated with flow &
s per SCM, each of the above
A
activities are integrated & inter-
related to each other.
t is a continuous effort where
I
commitment is required from top
to bottom
Objective of SCM is to meet
customer demand in cost
effective manner
raw material stage to end user. transformation of goods from
Raw Material stage to end
user
ost of Good Quality/
C Cost of Bad Quality/ Optimal COQ Types of Supply Chain
Cost of Conformance/ Cost of Non-
Push Model Pull Model
Cost of Control Conformance /Cost of Financial Prospective Non Financial Prospective
Failure of Control
Stock is produced on the basis Stock is produced on the basis
Testing & Inspection, Audit here Combined Cost is
W Where Cost of Bad Quality is
of estimated demand of actual demand
of Material etc. minimum. [Short-Term] minimum, as it results in
Internal Failure Cost External Failure Cost
increased customer How relationship with suppliers
Equipment Accuracy satisfaction & are
checks Scrap, Waste Repairs & Servicing sales. [Long-Term] developed & maintained?
Prevention Cost Appraisal Cost Incurred During Production Process/Field Testing Sources
ework/Repair/
R Warranty Claims
No. of Suppliers
Rectification/ Retesting
Product Acceptance Cost, Quality, Time
Returns, Recalls Supplier Relationship Management
Quality Planning Testing Incurred After Production Partnership with suppliers
Downgrading
but Before Delivery Complaints, Litigation
Quality / Design Review Procedure Verification Benefits
Downtime Cost
Quality / Staff Training Service of Quality Control Incurred after the product is
Rejection Support / Customer Care Upstream Supply Chain
Consultant delivered due to quality Ensures quality & innovation
Centre Cost Management
Quality Circles failure.
Contribution Loss Enhances reliability in delivery
upplier Review /
S
Incurred Before Production
Screening / Evaluation E-Procurement is an electronic
Product Liability
Insurance method which
Planned Preventive Use of Information Technology
imposes speed & efficiency of
Maintenance
Expediting procurement.
Design / Process Re-
engineering Types of Supply Chain E-Sourcing: Electronic method E-Purchasing: Product E-Payment: Electronic
Management for finding Selection & Invoicing &
new suppliers Ordering Online Electronic Fund Transfer
Includes many components from
definition of services to Analysis of customers & their
termination of agreement. behaviour
Customer Relationship Customer Account Profitability
Service Level Agreements
Plan – Establish Objectives / Management
ustomer
C
n agreement between
A Legally binding formal or
Develop Action
upply Chain
S Downstream Supply Chain
Customer Lifetime Value
Lifetime Value PDCA CYCLE FOR Management
Management
customer & service provider. informal contract. Do - Implement Customer Selection, Extension
CONTINUOUS
Check - Measure IMPROVEMENT Use of Information Technology
Net Present Value of projected
cash flows from a lifetime of Act – Take corrective action
customer relationship. To collect orders To record sales [Use of E-POS]
European Model used to achieve Adopt new philosophy
Inbound Logistics
Sustainable Excellence
Create consistency of purpose
towards improvement Operations
Purpose
Porter’s Primary Activities
Institute Training on Job Outbound Logistics
Vision Module 1 : Direction in Value Chain
Institute Education & Self- Marketing & Sales
Strategy
Improvement
Service
Engaging Stakeholders set of 3 Modules 1. EFQM Excellence Model
Module 2 : Execution Institute Leadership
hilosophy for developing &
p Supply Chain Management
Creating Sustainable Value
strengthening management Drive out fear Process
Stakeholder Perceptions Module 3 : Results system
Move towards single supplier for eeming 14 Point for
D
Analysing Result Radar y developing Quality
b any one item Process Improvement 1. Plan / Production Planning 2. Procure 3. Make 4. Deliver / Logistics
Management Principles Eliminate Slogans Integrated System of Planning
Result Approach Deploy Assess Refine and Control by Management
for achieving excellence in Develop a plan to address aw Material is procured /
R Manufacture the product eliver the product
D
Remove Workmen Barriers
requirement of customer purchased from supplier in this required by customer manufactured for customer
2. Singapore BE Framework Business Excellence everything that an o Meet customer Expectation
T
and Organizational Objectives step
Transformation is everyone’s Job
Leadership
Model organisation does & also to roduction must be planned
P As per Demand & Taste of logistics – Inbound Logistics &
sustain it. By Continuous Improvement in based on Actual or Estimated Keep good relations with supplier customer Outbound Logistics
Strategy
Some Business Excellence
Cease dependence on Inspection
TQM Quality Demand to ensure timely delivery &
Tools Shareholders better quality xcellent system must be in
e
Eliminate Management by
Customers Holistic tool which creates Objectives With the Aim of Achieving Zero place to ensure movement of
Employees Select quality suppliers materials & goods is uninterrupted
3. Baldrige Criteria for value for all Defect in Quality
Measurement, Analysis & Breakdown barriers between
Performance stakeholders & not just Customers
Knowledge Management department TQM is an Investment Rather
Excellence owners than Cost In-house Logistics : Trained
Workforce Society
Improve Constantly & Forever
Without additional Expenditure Third Party Logistics : Tie up
Operations Improve Product mix
Supplier Relationship
Results t is a contractual agreement
I Introduce Employee Development Information flow Demand Management Management Cash Flow
where supplier agrees to supply programme
4. Japan Quality Award Model to customer with no guarantee ey Processes
K
of receiving payment, but
Ways in which Investment in SCM Business
Empowering Empolyee
5. Australian BE Framework payment of supply is based upon in TQM can be made Model
benefits that emerge to Improve Top Management Capacity & Skills Management Customer Relationship Service Delivery Management
customer. Comittment Management
It is a risky stance to supplier, Monitering Performance
Benefits of SCM
as he may walk away with
nothing but if benefits to Ensuring Customer Satisfaction
customer are substantial, he can Minimise Waste Reduce Supply Chain Cost Better Customer Service Better Delivery Optimum Inventory Generating Capability & Becoming Improves Supplier Relationship Ease & Transparency
get larger Commitment
Meaning Future Ready
return.
Culture
Gain Sharing Agreement Gain/Benefit is not necessarily
Continuous Improvement
financial.
Six C's of TQM
REASONS FOR FAILURE Co-Operation
win-win situation both supplier &
customer Customer Focus
Unstructured terms of agreement There should be pre-defined Control
formula for sharing of
Error in Implementation benefits & period thereof.
ad relationship between
B
Supplier & Customer Outsourcing
Cost Saving Loss of Confidentiality
t is also referred as
I Advantages Investment Saving Disadvantages Risk of losing sensitive data How to address the above issues
‘Contracting Out’ in Outsourcing
Business Flexibility Quality Problems
shifting of Tasks/ Processes/ Develop a Code of Conduct Set up an Audit Team Give list of outsourcing entities
Jobs on website
You might also like
- Hmcost3e SM Ch11Document45 pagesHmcost3e SM Ch11Sushant KarnikNo ratings yet
- Suspect/Counterfeit Items Resource HandbookDocument94 pagesSuspect/Counterfeit Items Resource HandbookmelisbbNo ratings yet
- Process MappingDocument1 pageProcess MappingG Sathesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 10 Pages Directors' Summary - by CA Harsh GuptaDocument10 pages10 Pages Directors' Summary - by CA Harsh Guptagovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Bobcat - 325 - 328Document1 pageBobcat - 325 - 328Laboratorio IP50% (2)
- E-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureDocument29 pagesE-Commerce Client Server ArchitecturewalterpeterscottNo ratings yet
- Strategic Change ManagStrategic Change Management Solutionement SolutionDocument13 pagesStrategic Change ManagStrategic Change Management Solutionement SolutionFarah TahirNo ratings yet
- ASCP Fundamentals Student Guide Vol 1 PDFDocument450 pagesASCP Fundamentals Student Guide Vol 1 PDFLaxminarayana100% (1)
- BobcatDocument1 pageBobcatGregorNo ratings yet
- Managing The Global Supply ChainDocument15 pagesManaging The Global Supply ChainsubhojsNo ratings yet
- Notes:: CheniereDocument1 pageNotes:: CheniereMonse LNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 7 ElevenDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 7 ElevenSyed Noman100% (1)
- ANSR Corporate Innovation ReportDocument60 pagesANSR Corporate Innovation ReportVarsha BNo ratings yet
- Samsung Supply Chain ManagementDocument3 pagesSamsung Supply Chain ManagementHarold Dela Fuente100% (1)
- Case Analysis Embraer FinalDocument17 pagesCase Analysis Embraer Finalfossaceca67% (3)
- 11 Schematic Diagrams: 11-1 Power - Sound Schematic DiagramDocument10 pages11 Schematic Diagrams: 11-1 Power - Sound Schematic DiagramGeovanny SanJuanNo ratings yet
- CBI Channels Segments Europe Fresh Fruit Vegetables 2014Document9 pagesCBI Channels Segments Europe Fresh Fruit Vegetables 2014mitcanNo ratings yet
- Pug Hateg - ItDocument1 pagePug Hateg - Itachiser100% (1)
- SPUPL - Kadapa - APDocument1 pageSPUPL - Kadapa - APNeeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Logistic Application Legacy ListDocument5 pagesLogistic Application Legacy ListjunemrsNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Routing Switch 2500 Series Quick Install Guide: Powering UpDocument1 pageEthernet Routing Switch 2500 Series Quick Install Guide: Powering UpTárcio LunaNo ratings yet
- Denali NPPDocument1 pageDenali NPPapi-19487128No ratings yet
- Denali Park98Document1 pageDenali Park98Jose Manuel Garcia ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Planta General ESC 1.20: Icetex Mocoa - PutumayoDocument1 pagePlanta General ESC 1.20: Icetex Mocoa - PutumayoMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- Electrical System C32 Generator Set With EMCP3: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic SymbolsDocument4 pagesElectrical System C32 Generator Set With EMCP3: Harness and Wire Electrical Schematic Symbolsyasser eljabaliNo ratings yet
- Endblock Rebar DetailDocument1 pageEndblock Rebar DetailBogdanPaiusNo ratings yet
- Invest in Malaysia's Capital of Creation: CyberjayaDocument2 pagesInvest in Malaysia's Capital of Creation: CyberjayaFaiz SarminNo ratings yet
- 2019 Roadway Improvement ProgramDocument1 page2019 Roadway Improvement ProgramFOX59/CBS4No ratings yet
- Grid 2076 ChartDocument2 pagesGrid 2076 ChartPujan Amit GurungNo ratings yet
- Quality Control: Elevation FrontDocument5 pagesQuality Control: Elevation FrontAria NickbakhtNo ratings yet
- Villa Madrid: Veintiuno de AbrilDocument1 pageVilla Madrid: Veintiuno de AbrilMel RiszeNo ratings yet
- District 7Document1 pageDistrict 7augustapressNo ratings yet
- Sir Duke - BassDocument6 pagesSir Duke - Bassjackypoose76 bocNo ratings yet
- System Map PDFDocument3 pagesSystem Map PDFJ JaldinNo ratings yet
- Enlace Cable Peru - Entel-ModelDocument1 pageEnlace Cable Peru - Entel-ModelHubert Reynaldo Chang EscalanteNo ratings yet
- (Column Size) : (Grey Mat Tile Finish)Document1 page(Column Size) : (Grey Mat Tile Finish)Prdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Marlow Series 580: In-Line Mounted Centrifugal PumpDocument32 pagesMarlow Series 580: In-Line Mounted Centrifugal PumpCarlosama MarioNo ratings yet
- Cidade Maravilhosa - Sax Alto (Eb)Document1 pageCidade Maravilhosa - Sax Alto (Eb)Clodoaldo bezerra da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Property Lines Are Compiled by Adjusting The Property Lines ToDocument1 pageProperty Lines Are Compiled by Adjusting The Property Lines ToM-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Creating HTML Reports in PowershellDocument1 pageCreating HTML Reports in PowershellAjay Kumar DwivediNo ratings yet
- GP Racing UK - April 2024Document108 pagesGP Racing UK - April 2024Victor UwpNo ratings yet
- Yauli TiclioDocument1 pageYauli TiclioJhon James Rojas CarhuamacaNo ratings yet
- Extension of Southern Expressway Project - Section 1 11+500 To 15+900 SectionDocument1 pageExtension of Southern Expressway Project - Section 1 11+500 To 15+900 SectionsathiyanNo ratings yet
- Cancontrol List 2022-07-27 enDocument115 pagesCancontrol List 2022-07-27 enAndrés Felipe Matamala QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Fuses - SM6 - Shneider ElectricDocument1 pageFuses - SM6 - Shneider ElectricBernat ItayNo ratings yet
- Hps141c EeDocument1 pageHps141c Eeapi-3709639No ratings yet
- Fajr Film FestivalDocument1 pageFajr Film Festivalhossien zargarNo ratings yet
- Brighton Citycentre Walking Map2017Document1 pageBrighton Citycentre Walking Map2017LucNo ratings yet
- Atr SPLL (Max) El DWG It L30 6059 PDFDocument1 pageAtr SPLL (Max) El DWG It L30 6059 PDFHirushan MenukaNo ratings yet
- Peta Jalur MudikDocument2 pagesPeta Jalur MudikHeri susantoNo ratings yet
- Millfields MapDocument1 pageMillfields MapLevon VincentNo ratings yet
- Gerudo Valley: Arr. L. BluntDocument3 pagesGerudo Valley: Arr. L. BluntXd JakeNo ratings yet
- As App Vs Rev Foot1675404512947Document2 pagesAs App Vs Rev Foot1675404512947Fadi AlatrashNo ratings yet
- Supatá-ALC-ALT 1-COMBINADO-Versión 1 AutoCAD-Presentación5Document1 pageSupatá-ALC-ALT 1-COMBINADO-Versión 1 AutoCAD-Presentación5Andres Bonilla RNo ratings yet
- Pablo Fernando Ramirez TesissDocument1 pagePablo Fernando Ramirez TesissAngel MedinaNo ratings yet
- METRO System Sistema de METRODocument2 pagesMETRO System Sistema de METROImrich FarkašNo ratings yet
- PORSICASOplano ModelDocument1 pagePORSICASOplano ModelYordi Baca HerreraNo ratings yet
- Franklin Architectural PlanDocument6 pagesFranklin Architectural PlanTim Foldy-PortoNo ratings yet
- Hasil Seleksi Kompetensi p3k Sesi Ke-1 12-10-2021Document6 pagesHasil Seleksi Kompetensi p3k Sesi Ke-1 12-10-2021Ulfia NurchamamiNo ratings yet
- SCALE 1: 400: Denah Rencana Ac Lantai 3 Perancangan Bangunan Mixed Use (Shopping Mall, Hotel, Office)Document1 pageSCALE 1: 400: Denah Rencana Ac Lantai 3 Perancangan Bangunan Mixed Use (Shopping Mall, Hotel, Office)najiha salsabilaNo ratings yet
- SCALE 1: 400: Denah Rencana Ac Lantai 4 Perancangan Bangunan Mixed Use (Shopping Mall, Hotel, Office)Document1 pageSCALE 1: 400: Denah Rencana Ac Lantai 4 Perancangan Bangunan Mixed Use (Shopping Mall, Hotel, Office)najiha salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Retail Lower Ground Floor Layout .Document1 pageRetail Lower Ground Floor Layout .Aayat ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Excel Construction Project Management Templates Construction Documentation Tracker TemplateDocument1 pageExcel Construction Project Management Templates Construction Documentation Tracker TemplateaaNo ratings yet
- Mexico Site Devt Plan A1Document1 pageMexico Site Devt Plan A1Bray CastroNo ratings yet
- DVDHM3200 EeDocument3 pagesDVDHM3200 EeDjonathan Xavier WencionekNo ratings yet
- Slides 10Document33 pagesSlides 10aaroncete14No ratings yet
- Nte GR D: E-Bel2-56.2-3Document1 pageNte GR D: E-Bel2-56.2-3Prashant SanapNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC IT Historian PresDocument59 pagesSIMATIC IT Historian PresDo Van TuNo ratings yet
- PmlaDocument3 pagesPmlagovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Test 3Document8 pagesTest 3govarthan1976No ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument12 pagesStandard Costinggovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Scmpe RTP M23Document36 pagesScmpe RTP M23govarthan1976No ratings yet
- SCMPE India Tour Notes by Sankalp Kanstiya @mission - CA - FinalDocument133 pagesSCMPE India Tour Notes by Sankalp Kanstiya @mission - CA - Finalgovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Test 4Document8 pagesTest 4govarthan1976No ratings yet
- ISCA MCQs Chapter - 8 Emerging TechnologiesDocument13 pagesISCA MCQs Chapter - 8 Emerging Technologiesgovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Test 3Document8 pagesTest 3govarthan1976No ratings yet
- Garment Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesGarment Executive Summarygovarthan1976No ratings yet
- National Programme For Organic Production: Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)Document22 pagesNational Programme For Organic Production: Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)govarthan1976No ratings yet
- Flowchart 140522095644 Phpapp02Document41 pagesFlowchart 140522095644 Phpapp02govarthan1976No ratings yet
- 4 Assembly Line BalancingDocument11 pages4 Assembly Line Balancinggovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Greenhouses Bringing Home Profitable Yeilds - 3Document5 pagesGreenhouses Bringing Home Profitable Yeilds - 3govarthan1976No ratings yet
- Greenhouse VegproductionDocument8 pagesGreenhouse Vegproductiongovarthan1976No ratings yet
- Implementing Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Reactive, Cooperative, and Dynamic ModelsDocument22 pagesImplementing Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Reactive, Cooperative, and Dynamic ModelsJuhi BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- C1 IntroductionDocument48 pagesC1 IntroductionaliawawaNo ratings yet
- XIM University: Supply Chain Management (Mba 2021-2022) Mini ProjectsDocument4 pagesXIM University: Supply Chain Management (Mba 2021-2022) Mini ProjectsSupratik BiswalNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Competitive Strategy, Competitive Advantage - Gaining Competitive Advantage Through LogisticsDocument12 pagesLogistics and Competitive Strategy, Competitive Advantage - Gaining Competitive Advantage Through LogisticsHemasri ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Insights 2022Document134 pagesSustainability Insights 2022Evgeny KnyazevNo ratings yet
- Weekly Schedule of MBA 2018 SIVB Week 3Document7 pagesWeekly Schedule of MBA 2018 SIVB Week 3Hassan Amir KhanNo ratings yet
- E-Supply Chains - Virtually Non-Existing: Research NoteDocument8 pagesE-Supply Chains - Virtually Non-Existing: Research NoteSaikumar SelaNo ratings yet
- Part 1-Forecasting PDFDocument15 pagesPart 1-Forecasting PDFJohn TentNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Study of Characteristics and Time Reduction in Reverse Supply Chain Using System DynamicsDocument6 pagesMethodology For Study of Characteristics and Time Reduction in Reverse Supply Chain Using System DynamicsArief RachmanNo ratings yet
- The $100M StoreDocument116 pagesThe $100M StorekkrumiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Business 9609/41Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Business 9609/41Arnold VasheNo ratings yet
- Scormark Premier Corporate Sample ReportDocument62 pagesScormark Premier Corporate Sample ReportNohemi RivasNo ratings yet
- Taiwan and The Fight For DemocracyDocument9 pagesTaiwan and The Fight For DemocracyGiorgi SoseliaNo ratings yet
- Rcoa PDFDocument16 pagesRcoa PDFDelmar FerrerNo ratings yet
- Appendix B - Amaala Supplier Code of Conduct + Acknowledgement FormDocument8 pagesAppendix B - Amaala Supplier Code of Conduct + Acknowledgement FormAhmadNo ratings yet
- UNIT V LogisticsDocument10 pagesUNIT V LogisticsfruitnutsNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument77 pagesPDFriyanNo ratings yet
- Green Strategy For Global Operations and Logistics: Presentation: Group IXDocument8 pagesGreen Strategy For Global Operations and Logistics: Presentation: Group IXprashantNo ratings yet
- Completon Report: Earthquake Emergency Assistance ProjectDocument108 pagesCompleton Report: Earthquake Emergency Assistance ProjectFree ThinkerNo ratings yet