Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 - Biochemistry-1 (Carbohydrate)
Uploaded by
Rose KasidiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 - Biochemistry-1 (Carbohydrate)
Uploaded by
Rose KasidiCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio-chemistry
(Carbohydrates)
Carbohydrates
They may be defined as polyhydroxyaldehydes or ketones or compounds which produce them
on hydrolysis.
They are the most abundant dietary source of energy (4 Cal/gm) for all organisms
Stereoisomerism
Stereoisomers are the compounds that have the same structural formulae but differ in
their spatial configuration.
A carbon is said to be asymmetric when it is attached to four different atoms or groups.
The number of asymmetric carbon atoms (n) determines the possible isomers of a given
compound which is equal to 2n. Glucose contains 4 asymmetric carbons, and thus has
16 isomers.
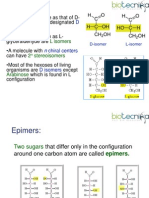
Epimer
If two monosaccharides differ from each other in their configuration around a single specific
carbon (other than anomeric) atom are referred to as epimers to each orher.
Enantiomers
They are a special type of stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other. The two
members are designated as D- and L-sugars.
Diastereomers
The term diastereomers is used to represent the stereoisomers that are not mirror images of
one another
Anomers 1
The and cyclic forms of D-glucose are known as anomers.
Pharmagpat.com | Contanct no: +91-8128156200, +91-8401457975
Email Id: pharmagpat@yahoo.com
Bio-chemistry
(Carbohydrates)
Monosaccharides Biological Function
Trioses
Glyceraldehyde Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is an intermediate in glycolysis.
Dihydroxyacetone Its 1-phosphate is an intermediate in glycolysis.
Tetroses
D-Erythrose Its 4-phosphate is intermediate in carbohydrate metabolism(HMP
shunt pathway)
Pentoses
D-Ribose For the structure of RNA and nucleotide coenzyme (ATP NAD+,
NADP+)
D-Deoxyribose For the structure of DNA
D-Ribulose It is an important metabolite in Hexose monophosphate shunt.
Involved in the function of glycoproteins
D-Xylose
Excreted in urine in essential pentosuria
L-Xylulose
As a constituent of lyxoflavin of heart muscle
D-Lyxose
Hexoses
D-Glucose The ‘sugar fuel of life’
D-Galactose Converted to glucose failure leads to galactosemia
For the structure of polysaccharides
D-Mannose 2
Its phosphates are intermediate of glycolysis
D-Fructose
Pharmagpat.com | Contanct no: +91-8128156200, +91-8401457975
Email Id: pharmagpat@yahoo.com
Bio-chemistry
(Carbohydrates)
Heptoses
Its 7-phosphate is an intermediate in Hexose monophosphate shunt
D-Sedoheptulose and in photosynthesis
Disaccharides Biological Function
Sucrose Most commonly used table sugar supplying calories
Exclusive carbohydrate source to breast feed infants. Lactose
Lactose deficiency leads to diarrhoea and flatulence
Maltose An important intermediate in digestion of starch
Maltose is composed of two -D-glucose units held together by (1 -- 4) glycosidic bond.
Isomaltose, the glucose units are held together by (1 -- 6) glycosidic linkage.
Sucrose is made up of -D-glucose and -D-fructose. The two monosaccharide are held
together by a glycosidic bond (1 -- 2), between C 1 of -glucose and C2 of -fructose.
Lactose is composed of -D-galactose and -D-glucose held together by (1 -- 4) glycosidic
bond.
Polysaccharides
1. Homopolysaccharides which on hydrolysis yield only a singlet type of
monosaccharide
Starch consists of two polysaccharide components-water soluble amylose and a water
insoluble amylopectin.
3
Amylose is a long unbranched chain in which D-glucose units held by (1 -- 4) glycosidic
linkages.
Pharmagpat.com | Contanct no: +91-8128156200, +91-8401457975
Email Id: pharmagpat@yahoo.com
Bio-chemistry
(Carbohydrates)
Amylopectin on the other hand is a branched chain with (1 – 6) glycosidic bonds at the
branching points
Inulin is a polymer of fructose i.e., fructosan. It is used for assessing kidney function through
measurement of glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Glycogen consists of glucose repeating unit glycogen joined together by (1 -- 4) glycosidic
bonds, and (1 -- 6) glycosidic bonds at branching points.
2. Heteropolysaccharides on hydrolysis yield a mixture of a few monosaccharaides
or their derivatives.
Glycosaminoglycan Composition Function(s)
Hyaluronic acid D-Glucuronic acid , Serves as a lubricanat and
N-acetylglucosamine shock absorber. Promotes
wound healing.
Chondroitin sulfate D-Glucuronic acid, Helps to maintain the
N-acetylgalactosamine 4- structure and shape of soft
sulfate tissues.
Heparin D-Glucuronate 2-sulfate, Acts as an anticoagulant.
N-sulfoglucosamine 6-sulfate
Dermatan sulfate L-lduronic acid, Maintains the shape of
N-acetylgalactosamine 4- tissues.
sulfate
Keratan sulfate D-Galactose, Keeps cornea transparent.
N-acetylglucosamine 6-
sulfate
Pharmagpat.com | Contanct no: +91-8128156200, +91-8401457975
Email Id: pharmagpat@yahoo.com
You might also like
- Modulator: Dr. P.B.Desai HOD, Dept of Biochemistry. Presenter: DR Vijayetha S. KagwadDocument68 pagesModulator: Dr. P.B.Desai HOD, Dept of Biochemistry. Presenter: DR Vijayetha S. KagwadvijayethaNo ratings yet
- Occurence, Structure and Fuctions of MaonosaccharidesDocument10 pagesOccurence, Structure and Fuctions of MaonosaccharidesgayathriNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Structure, Classification and FunctionsDocument70 pagesCarbohydrates: Structure, Classification and FunctionsShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short CourseDocument31 pagesBiochemistry: A Short CourseEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Karbohidrat (Ertemuan 2-1Document38 pagesKarbohidrat (Ertemuan 2-1dobleelNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument15 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistryshuklaaryan1806No ratings yet
- 03 CarbohydrateDocument45 pages03 CarbohydrateManojitNo ratings yet
- BBC1 K14 K15 KarbohidratDocument31 pagesBBC1 K14 K15 Karbohidratbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate - Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate - Lecture NotesKate Taylor100% (1)
- Biographic of YogiDocument22 pagesBiographic of YogiKaveen VijayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument57 pagesChemistry of Carbohydratesdrpnnreddy100% (1)
- Biochemistry I (SGS 236)Document33 pagesBiochemistry I (SGS 236)Mustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydrateDocument14 pagesCarbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydratesukNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Classification and StructuresDocument54 pagesCarbohydrate Classification and StructuresAymen AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument39 pagesCarbohydratesWardah AliNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument21 pagesCARBOHYDRATESLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Part IDocument32 pagesCarbohydrate Part IHamza QaziNo ratings yet
- 251120190carbohydrates (2) 2019Document26 pages251120190carbohydrates (2) 2019slmen1269No ratings yet
- حل كتاب القسم كامل bio 102Document46 pagesحل كتاب القسم كامل bio 102Naba KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Monosaccharide DerivativesDocument8 pagesLesson 8. Monosaccharide DerivativesPrincess-Nadeera Sangkula PungutanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate & Its ClassificationDocument11 pagesCarbohydrate & Its ClassificationZoya SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates 2Document131 pagesChemistry of Carbohydrates 2Sawera RaheemNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument10 pagesBiomoleculeststylizeNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument12 pagesOutputMarielle VentulaNo ratings yet
- Essential Fatty Acids & Eicosanoids: Dr. Sandeep Agrawal MD DNBDocument34 pagesEssential Fatty Acids & Eicosanoids: Dr. Sandeep Agrawal MD DNBMohan bhargavNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument18 pagesChemapi-709918261No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDocument53 pagesCarbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesHarrish SandeevNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Biochemistry of TransportDocument21 pagesBiochemistry - Biochemistry of TransportAndreaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 LipidDocument10 pagesChapter 08 Lipid楊畯凱No ratings yet
- BTBC209IU Biochemistry 1: International UniversityDocument33 pagesBTBC209IU Biochemistry 1: International UniversityLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - CarbohydratesDocument76 pagesModule 6 - CarbohydratesPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and Derivatives: Structures, Functions and ExamplesDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates and Derivatives: Structures, Functions and ExamplesNabeela NargisNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bio ChemistryDocument9 pagesClinical Bio ChemistrylegendofrohithNo ratings yet
- PolysachharidesDocument24 pagesPolysachharidesshizarahimNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES: STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND FUNCTIONSDocument25 pagesCARBOHYDRATES: STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND FUNCTIONSYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 4: Lipid ChemistryDocument19 pagesLecture No. 4: Lipid ChemistrySafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Biochemistry: Classification of LipidDocument5 pagesWeek 7 Biochemistry: Classification of LipidRiza Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharides: Types and FunctionsDocument21 pagesPolysaccharides: Types and FunctionsCemal SarwarNo ratings yet
- SugarDocument30 pagesSugarmamuuramadanNo ratings yet
- Carbs 2Document6 pagesCarbs 2Biang AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Question Bank With Solution Biochemistry PDFDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank With Solution Biochemistry PDFKiran SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BiochemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 2 BiochemistrySireNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Carbohydrates Spring 24Document25 pagesLecture 6-Carbohydrates Spring 24ziadwageh74No ratings yet
- Lecture Research BiochemDocument16 pagesLecture Research BiochemDianne MaeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - CarbohydratesDocument30 pagesLesson 2 - CarbohydratesWycliffe AsmanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesCarbohydratesgifty NambeyeNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesCarbohydratesAtul KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Carbohydrates: Ι H -C-Oh Ι Ι ΙDocument4 pagesTypes of Carbohydrates: Ι H -C-Oh Ι Ι ΙTinder KamdevNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Polysaccharides ActivityDocument3 pagesBiochemistry - Polysaccharides ActivityAllen Paul CoveroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Lipids, Derived & Complex Lipids: - Structure - FunctionsDocument75 pagesBiochemistry: Lipids, Derived & Complex Lipids: - Structure - FunctionsDwi Itu IinNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESChristine Kylene AycardoNo ratings yet
- HARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificanceDocument4 pagesHARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificancedandiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Structure, Classification and FunctionsDocument13 pagesCarbohydrates: Structure, Classification and FunctionsLouis TNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Part 2Document48 pagesCarbohydrates Part 2biotecnika_testNo ratings yet
- 20210416 สารเคมีในเซลล์ของสิ่งมีชีวิต SARANYA_Document50 pages20210416 สารเคมีในเซลล์ของสิ่งมีชีวิต SARANYA_Panyapat SrisawatNo ratings yet
- Importance of Starch and Glycogen in PolysaccharidesDocument15 pagesImportance of Starch and Glycogen in PolysaccharidesNivashini VindhyaNo ratings yet
- DIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATESDocument45 pagesDIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATESEkber IsmayilovNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates and LipidsCarlene OretaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Movement of Beta-Lain Pigment in Beetroot CellsDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Movement of Beta-Lain Pigment in Beetroot Cellszarahirani25% (4)
- C612Document5 pagesC612dinhtung2210100% (1)
- World Bank ReportDocument14 pagesWorld Bank Reportaditya_erankiNo ratings yet
- RMD - Lightmix Modular CE IVD Assay BrochureDocument4 pagesRMD - Lightmix Modular CE IVD Assay BrochureDummy Tester JrNo ratings yet
- Candidates applied for Medical Officer post on contract basisDocument11 pagesCandidates applied for Medical Officer post on contract basiszephyrNo ratings yet
- Sakshijain75.Final ProDocument46 pagesSakshijain75.Final ProOm AherNo ratings yet
- The Role of Technology in AgricultureDocument35 pagesThe Role of Technology in AgricultureDivyesh ThumarNo ratings yet
- Main Receiving Station PDFDocument8 pagesMain Receiving Station PDFPrakash Kumar0% (1)
- 2020 End Year 6 PenulisanDocument8 pages2020 End Year 6 PenulisanZulhillmi ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Lubricants: Chapter - 5 Lubricants and LubricationDocument5 pagesLubricants: Chapter - 5 Lubricants and LubricationMalaika AzeemNo ratings yet
- Fosfomycin: Review and Use Criteria BackgroundDocument12 pagesFosfomycin: Review and Use Criteria BackgroundAbu Azzam Al-Hadi100% (1)
- RESOLUTION 2022-08 Denial of Setback VarianceDocument5 pagesRESOLUTION 2022-08 Denial of Setback VarianceMatt McKinneyNo ratings yet
- 02 - Purulent Inflammatory DiseaseDocument60 pages02 - Purulent Inflammatory Diseaseshekhawatyuvraj051No ratings yet
- Analysis of Drinking Water Quality Parameters (A Case Study of Hanumangarh Town)Document8 pagesAnalysis of Drinking Water Quality Parameters (A Case Study of Hanumangarh Town)Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Economic Case for Immobilizing EnzymesDocument25 pagesEconomic Case for Immobilizing EnzymesNikki ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Herbal MedicineDocument38 pagesHerbal MedicineBurei KouNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 - 2.4 - Consolidated Assessments (Photosynthesis)Document8 pagesBio 2 - 2.4 - Consolidated Assessments (Photosynthesis)Lena ManibaNo ratings yet
- Tap ChangerDocument5 pagesTap ChangerRavindra AngalNo ratings yet
- Separation Processes Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument14 pagesSeparation Processes Lecture 1 Introductionabood assrfndyNo ratings yet
- NAVAL Hot Tapping Tool User GuideDocument19 pagesNAVAL Hot Tapping Tool User GuidemarconelucenapereiraNo ratings yet
- Fuente As-IDocument4 pagesFuente As-IadalaviNo ratings yet
- Concrete's enormous role in world's longest sea bridgeDocument3 pagesConcrete's enormous role in world's longest sea bridgeRafiath SiraNo ratings yet
- NBME 22 OfflineDocument200 pagesNBME 22 OfflineGautham Kanagala86% (14)
- Presley v. Lockwood: Respondent's Trial BriefDocument37 pagesPresley v. Lockwood: Respondent's Trial BriefTony Ortega100% (2)
- Megawin: Numerical Over Current & Earth Fault RelayDocument16 pagesMegawin: Numerical Over Current & Earth Fault Relaynaran19794735100% (5)
- Pursuing a Career in CosmetologyDocument3 pagesPursuing a Career in CosmetologyMaria CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Checklist PDFDocument84 pagesChecklist PDFJeremiah Miko LepasanaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Henkel Benchmarking (Solutions)Document10 pages03 - Henkel Benchmarking (Solutions)/jncjdncjdnNo ratings yet
- Nihms 223615 PDFDocument15 pagesNihms 223615 PDFElay PedrosoNo ratings yet
- SanCoP7 AgendaDocument2 pagesSanCoP7 AgendaNicolaGreeneNo ratings yet