Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medications
Medications
Uploaded by
Nashrah Husna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesMedications
Medications
Uploaded by
Nashrah HusnaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
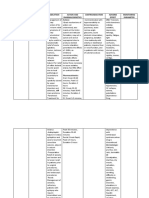
Meds Function and remarks To treat (disease)
Steroids - Stop itch scratch cycle - Itchiness
(Topical, oral) - Psoriasis
Moisturisers - Humectants: attract and bind - Dry skin (ichthyosis)
water from the deeper
epidermis and the
environment to the stratum
corneum.
- Occlusives: Form a barrier to
prevent transepidermal water
loss
- Emollients: Restore the
intercellular lipid bilayer
(vaseline)
Antifungal antiseptics - Two groups: - Skin diseases esp
- Dyes with weak activity: fungal infection like
Gentian violet, Castellani’s Tinea corporis
paint
- 2% selenium sulphide and
20% sodium thiosulphate
Topical antifungals - Skin diseases esp
- Amorolfine fungal infection like
- Cyclopiroxola Tinea corporis/pedis
mine
- Tolfnate
Keratolytics - Remove stratum corneum
- Salicylic acid - E.g: Salicylic acid (+benzoic
acid)
Oral therapy for skin - Fungal infections of scalp,
diseases nails, palms, soles
- Griseofulvin - Terbinafine: Inhibits action of
- Ketoconazole squalene epoxidase leading
- Itraconazole to membrane disruption and
- Fluconazole cell death, against
- Terbinafine dermatophytes
- Itracon-azole: Inhibit
cytochrome P-450 dependent
demethylation, impaired in
the presence of
phenobarbitone
- Griseofulvin: Inhibit cell
division and nucleic acid
synthesis in fungi,
contraindicated during
pregnancy and liver disease.
Analgesics - Relieve of pain without - Any
- NSAIDS impairment of conciousness
- Opioids
- Paracetamol
- Tricyclic
antidepressant
s
- Antiepileptics
- Ketamine
- Lignocaine
Opiates
- Alkaloids like:
- Morphine
- Codeine
Synthetic opioids
- Heroine
- Pethidine
- Pentazocine
- Buprenorphine
- Methadone
Endogenous opioids - Mu (Endorphins):
- Enkephalins Supraspinal and spinal
- Endorphins analgesia, sedation, inhibition
- Dynorphins of respiration, slows GIT
transit, modulation of
hormone and
neurotransmitter release
- Delta (Enkephalins):
Supraspinal and spinal
analgesia, modulation of
neurotransmitter and
hormone
- Kappa (Dynorphins):
Supraspinal and spinal
analgesia, psychotomimetic
effects; slowed GIT transit.
Opioids (based on - Agonist: Function:
actions of opioids Strong: Morphine, Pethidine, - Close voltage gated
receptors) Methadone Ca2+ on presynaptic
Moderate: Codeine nerve terminals and
Weak: Tramadol decrease
- Mixed agonist-antagonist: neurotransmitters
Buprenorphine, Pentazocine release
- Antagonist: Naloxone, - Hyperpolarize and
Naltrexone thus inhibit
postsynaptic neurons
by opening K+ and
decrease response
- Pharmacological
actions: sedation
kappa, miosis kappa
mu, emesis, histamine
release, hypotension
and bradycardia, GIT,
biliary tract, Urinary
bladder and ureter,
Neuroendocrine,
Immune system
Anaesthesia - Premedication - Contraction pain
- Regional analgesics
(Epidural)
Codeine - Use superceded by - Cough
dextromerthophan which is a
synthetic cough depressant
Loperamide - Does not cross CNS - Acute diarrhea
Diphenoxylate and - To reduce abuse - Acute diarrhea
Atropine
Intravenous Morphine - Anxiolytic - Acute pulmonary
- Vasodilatory- Reduce preload oedema
and afterload
- Depressant actions enhanced
by phenothiazines,
monoamine oxidase inhibitors
(MAO), TCA
Oral Methadone - Longer duration than - Opioid dependance
morphine - Relieves withdrawal
- Withdrawal symptoms are symptoms
milder - Block euphoric effects
- Miu receptor agonist of heroine and
- Long duration morphine
- Bound in the extravascular
compartment and slowly
released
- Can produce physical
dependence and milder
withdrawal
Heroine - Highly effective for severe - Severe pain
pain
- Metabolized by glucuronide
conjugation to
morphine-6-glucuronide and
excreted by kidney
- Less emetic compared to
morphine but same
respiratory depressant effects
- Strong agonist at V opioid
receptor
Fentanyl - Pure mu receptor agonist - Analgesia during
- Extremely potent surgery
- Sufentanil> Fentanyl> - Neurolepanalgesia
Alfentanil - Enhancement of
- High lipid solubility analgesia
- May cause rigidity, require
mechanical ventilation
- Minimal CVD effects, does
not release histamine
Pethidine - Binds to mu opioid receptor - For acute eps of
(Meperidine) - Demethylated to norpethidine moderate to severe
in the liver and excreted in pain
urine - Not for chronic pain
- Antimuscarinic action like dry - Used during labor
mouth/blurring of vision
- Contraindicated in the
presence of underlying
tachycardia
Codeine - A prodrug: can covert to - Oral analgesic for mild
morphine types of pain
- More readily absorbed by - Headache
mouth than morphine - Backache
- Has marked antitussive
activity
- Has respiratory depressant
activity
- Significant constipation
- Little/no euphoria
Dextromethorphan - Anti tussive @ brain stem and - Neuropathic pain
medulla
- Less constipation compared
to codeine
Tramadol - Better side profile than - Moderate to severe
morphine pain
- No respiratory depression - Safe for breastfeeding
- May caue convulsions mothers
- Avoid in taking MAO - Postoperative pain
inhibitors
Loperamide - Miu receptor agonist - Treatment of
- No analgesic activity neuropathic pain
- Control diarrhea by inhibit - Diarrhea
peristalsis
Buprenorphine - Long DOA and difficult to be
reversed by naloxone
- More potent than morphine
Pentozocine - Produce less euphoria - Same as morphine
Opioid antagonists - Reverse effect of agonist - Precipitate the
quickly if opioids are taken symptoms of opiate
withdrawal
- Treatment of
respiratory
depressants, on baby,
detect opioid
addiction, opioid
detox, decrease
alcohol craving
NSAIDS - Inhibit COX enzymes - Joint disorder with
- COX-1: Produce inflammatory
physiologically important PGs presentations
- COX-2: Mediate inflammatory - Arthritis
and pain, induced by
cytokines
- Short term
- Acute and chronic
inflammatory conditions
- Do not produce sedation and
have very low addiction rate
-
Low dose aspirin - Prevention of CVS events
Ibuprofen - Closing patent ductus - PDA
Indomethacin arteriosus in preterm infants - Indomethacin or
before birth etoricoxib: Ankylosing
spondylitis
Glucocorticoids - Decrese inflammation
- Slow disease progression
- Short term treatment of acute
RA flare
- Glucocorticoids and
mineralocorticoids
DMARDS (Disease - Suppress an overactive
Modifying immune system
Anti-Rheumatic - Delay disease progression
Drugs) - Preserve joint integrity
- Decrease systemic
complications
Methotrexate - First line DMARDS treatment - Rheumatoid Arthritis
Allopurinol - Decrease high blood uric acid - Gout
- Used in long term treatment
for gout
Colchicine - Combat pain and - Gout
inflammation due to gout
causes
- Acute an short-term treatment
● Opioids adverse effects: DESIGNER (dry mouth, euphoria, sedation, itch, GI tone
constipation, nausea and vomiting, eyes constriction and respiratory depression.
● Opioids withdrawal symptoms: WITHDRAWAL (withdrawal, irritability/insomnia,
tremors/tachycardia, hypertension, diarrhea, rhinorrhea, anxiety/arthralgia/myalgia,
weight loss, abdominal cramps, lacrimation(cries))
You might also like
- Comprehensive Pharmacology SummaryDocument25 pagesComprehensive Pharmacology Summarysubash p100% (1)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableDocument2 pagesCholinergic Pharmacology - Drug TableFNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Cinva Ram Compressed Earth Block Press Plans PDFDocument3 pagesCinva Ram Compressed Earth Block Press Plans PDFChiku Amani Chikoti0% (1)
- Veterinary CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesVeterinary CNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse Effect Monitoring ParameterDocument5 pagesDrug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse Effect Monitoring ParameteryssatNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Geometrical Form Analysis in Islamic Architecture 3Document28 pagesPositive and Negative Geometrical Form Analysis in Islamic Architecture 3VANSH JAGGINo ratings yet
- Spotlight On First Phonics 5 FlashcardsDocument87 pagesSpotlight On First Phonics 5 Flashcardsdaemonkn100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BDocument30 pagesDrug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BCess Lagera Ybanez0% (1)
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- DexamethasoneDocument3 pagesDexamethasoneGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Percy Greg - Across The ZodiacDocument595 pagesPercy Greg - Across The ZodiacCem AvciNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reviewer 001Document7 pagesPharmacology Reviewer 001Kath MartinezNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Nano Robots in Bio TechnologyDocument13 pagesNano Robots in Bio Technologyralz_indiaNo ratings yet
- Elliptical Head Design ToolDocument1 pageElliptical Head Design Toolnaveen_86No ratings yet
- 6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyDocument2 pages6 MAGNESIUM SULFATE Drug StudyGwyn Rosales100% (2)
- ACS NZ Stamp Catalogue 2018Document136 pagesACS NZ Stamp Catalogue 2018Auckland City Stamps100% (18)
- Medications TackledDocument3 pagesMedications TackledAl-Khan HadjailNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsLaureece Salm ApduhanNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Pharmacology: Mary Whyte Marshall, MSN, RN, BCDocument58 pagesNCLEX Pharmacology: Mary Whyte Marshall, MSN, RN, BCPeiling LiangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology, II SemDocument186 pagesPharmacology, II SemSheba RoymonNo ratings yet
- Respratory Drugs I-IIDocument10 pagesRespratory Drugs I-IITyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- Pharma Midterm CNS and ANS Drugs ReviewerDocument9 pagesPharma Midterm CNS and ANS Drugs ReviewerChesca LayosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Histamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCDocument57 pagesHistamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCFaisal 'arifNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument3 pagesCholinergic Antagonistszkhan260No ratings yet
- Pharmacology in NursingDocument1 pagePharmacology in NursingJessa Mae Barquilla100% (1)
- Pharmacology Must KnowsDocument7 pagesPharmacology Must KnowsventicompilationNo ratings yet
- 12-PH-Analgesic and NSAIDDocument22 pages12-PH-Analgesic and NSAIDRisang Nur WigunaNo ratings yet
- AdrenomimimeticsDocument40 pagesAdrenomimimeticshealer sruthyNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DrugDocument10 pagesPsychiatric DrugKollebeng Pangda PasiwatNo ratings yet
- Characteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseDocument4 pagesCharacteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseShafiqah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Year Ii Pharmacology Drugs ListDocument21 pagesYear Ii Pharmacology Drugs ListsaifuddinNo ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reviewer Module 1Document10 pagesPharmacology Reviewer Module 1Krizia mae LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory DrugsDocument16 pagesNon Steroidal Anti Inflammatory DrugsAaditya TrivediNo ratings yet
- Right-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichDocument47 pagesRight-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug Studyginosan100% (1)
- Drug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Handout 2563 OpioidsDocument84 pagesHandout 2563 OpioidsPiya TangNo ratings yet
- Ings Pre MedsDocument1 pageIngs Pre MedsIngrid LarobisNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyVenus April LimonNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Pcol 1 Prefinals Part 1 PDFDocument9 pagesPcol 1 Prefinals Part 1 PDFJillian Mae DacerNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSalbutamol - Drug Studygervisrael.gonzales.twphosiNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument29 pagesPsychotropic DrugsBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Substance Hallucinogens and Dissociatives - CompressedDocument39 pagesPsychotropic Substance Hallucinogens and Dissociatives - CompressedshuyuichewNo ratings yet
- Cancer BruhDocument1 pageCancer Bruhcc22No ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument10 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordstrawberryNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-PtsdDocument4 pagesDrug Study-PtsdWILMARIE SAPANTANo ratings yet
- 7endocrine DrugsDocument2 pages7endocrine DrugsSOFIA ALYSSA MARIE ABUDENo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Agents: VbanetDocument26 pagesAnesthetic Agents: Vbanetdona0010100% (1)
- Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAdrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System Adrenergic Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Pharma DrugsssDocument8 pagesPharma DrugsssClairie Jhane ClaorNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Moldova Moldova: Republica RepublicDocument12 pagesMoldova Moldova: Republica RepublicdianazolotcovNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English Key Reading&Writing1Document8 pagesCambridge English Key Reading&Writing1Anne KellyNo ratings yet
- Corporation LimitsDocument141 pagesCorporation LimitsPavan KarnamNo ratings yet
- Age of The EarthDocument20 pagesAge of The EarthApril Rose AyubanNo ratings yet
- The Physical Theory of Neutron Chain Reactors - Semantic ScholarDocument3 pagesThe Physical Theory of Neutron Chain Reactors - Semantic Scholar张坚No ratings yet
- Maths 041 Set 3 2022 - 23)Document9 pagesMaths 041 Set 3 2022 - 23)owenknight3456No ratings yet
- M3.1 - Philippine'S Integrating Sustainability With Other CountriesDocument2 pagesM3.1 - Philippine'S Integrating Sustainability With Other CountriesBlythe LeyvaNo ratings yet
- VinylFrog E-Catalog 2023Document15 pagesVinylFrog E-Catalog 2023svtechnologsNo ratings yet
- The Frustrating NoDocument11 pagesThe Frustrating NoLu LarNo ratings yet
- Armavia Flight 967 AccidentDocument3 pagesArmavia Flight 967 AccidenttherosantibadNo ratings yet
- Escalante - On The 32nd Anniversary of Martial RuleDocument4 pagesEscalante - On The 32nd Anniversary of Martial RuleJack SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Metric Spaces - Sergey MozgovoyDocument41 pagesLecture Notes: Metric Spaces - Sergey MozgovoyNúñezNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Developing Vertex Form of A QuadraticDocument7 pagesGuided Notes Developing Vertex Form of A Quadraticapi-554203344No ratings yet
- Teks Lagu NatalDocument4 pagesTeks Lagu NatalTina HerreraNo ratings yet
- The Love of God TENORDocument4 pagesThe Love of God TENORDorothy Ann SombilunaNo ratings yet
- 106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-21-32-Ch3Document12 pages106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-21-32-Ch3Thooi Joo WongNo ratings yet
- Efsa - Tolerable Upper Intake LevelsDocument482 pagesEfsa - Tolerable Upper Intake LevelsdrantistNo ratings yet
- Science Class 9 Notes SoundDocument1 pageScience Class 9 Notes SoundPriyaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- Tongue TwistersDocument19 pagesTongue TwistersarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Under The Ocean: Uno Zwei Tutu:: WWW - Uno - ZweiDocument10 pagesUnder The Ocean: Uno Zwei Tutu:: WWW - Uno - ZweiSilvana Valenzuela AranedaNo ratings yet
- Stm32 Usb C PD Solutions PresentationDocument34 pagesStm32 Usb C PD Solutions Presentationnisaken634No ratings yet
- Constant-Coefficient Linear Differential Equations: Math 240 - Calculus IIIDocument21 pagesConstant-Coefficient Linear Differential Equations: Math 240 - Calculus IIIdillawer ali naqiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Refrigeration &gas LawsDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Refrigeration &gas LawshoahongtrangNo ratings yet