Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Starter Columbia
Uploaded by
Vu TuongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Starter Columbia
Uploaded by
Vu TuongCopyright:
Available Formats
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.
01
General Information
General Information The brush rigging has four one-piece brushes. The
commutator end cap can be removed to inspect the
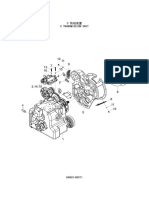
The Delco Remy starter ( Fig. 1) is located at the brushes. The bushing lubrication is provided in each
sintered bronze bushing by an oil-saturated wick. Oil
hand side of the vehicle. can be added to each wick by removing an oil reser-
voir cup, which is accessible on the outside of the
NOTE: The 42–MT series starters have a drive motor.
housing that can be rotated for different mount- Under normal operating conditions, no maintenance
ing positions. On vehicles with the Detroit Diesel will be required between engine overhaul periods. At
Series 55 engine, the starter is installed on the the time of engine overhaul, replace the starter with
right-hand side. a remanufactured starter.
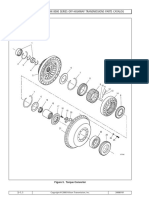
1
2
4 12 3
5 4
11
6
7
10 8
8 9 9
01/07/2000 f150992
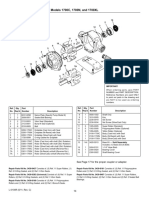
1. Solenoid 5. Drive Housing 9. O-Ring
2. Return Spring and Boot 6. Bronze Bushing 10. Thermostat (450 series only)
3. Shift Mechanism 7. Positive Engagement Drive 11. End Cap
4. Oil Wick 8. Armature Bushing
Fig. 1, 42-MT Starter Motor Components
The starter has a shift lever and solenoid plunger For the basic cranking circuit wiring, see Fig. 2.
that are totally enclosed to protect them from expo-
sure to dirt, icing conditions, and splash. The starter
is equipped with a starter drive, solenoid, and a
Principles of Operation
positive-engagement mechanism that prevents the
Turning the ignition switch to the START position
starter motor from rotating unless the pinion gear is
engaged with the ring gear teeth. The pinion gear is closes the magnetic switch contacts, connecting the
battery to the starter solenoid. As a result, the
mounted on a roller bearing one-way clutch, that al-
plunger and the shift lever move, causing the pinion
lows the pinion to spin when the engine has started.
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 050/1
15.01 Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series
General Information
G
M
B
S
2
15A
+ 15C
1 3
9 15B
14
16
10
52
AA6 4
8
7
6 5 15A
15 15K
07/16/98 f150543a
NOTE: Wire 16 connects to the alternator.
1. Battery 4. Frontwall Connector (pin E1) 7. 10-Amp Circuit Breaker
2. Cranking Motor (top view) 5. Splice Connector 8. Cab/Frontwall Power Stud
3. Magnetic Switch 6. Ignition Switch 9. Engine Power Stud
Fig. 2, Cranking Circuit Wiring
bad connections cause slow cranking speeds that
of the stroke, the solenoid main contacts close and will overheat and damage the starter motor.
the motor cranks the engine. If the pinion fails to en-
The 42–MT 450 series starter is equipped with a
gage the ring gear teeth, the solenoid contacts will
thermal overcrank protection circuit. If overheating
not close the circuit to the motor. The switch must be
occurs, a thermostat opens and stops the current to
released and again moved to the START position to
the magnetic switch, protecting the cranking motor.
attempt another start.
After the motor cools, usually in 1 to 6 minutes, the
When the engine starts, the pinion overruns, protect- thermostat will close and then a new start attempt
ing the armature from excessive speed. When the can be made.
ignition switch is returned to the normal RUN posi-
tion, the solenoid spring returns the plunger and the
pinion disengages from the ring gear.
Never crank the motor longer than 30 seconds at a
time. Stop and allow the motor to cool for at least 2
minutes before cranking again. Weak batteries or
050/2 Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
Starter Removal and Installation
Removal Installation
Before removing the starter from the vehicle for re- 1. Insert the starter nose housing through the
pair, perform the checks in Troubleshooting, 300.
1. Turn off all electrical loads such as lights, igni- 2. Install the three starter mounting bolts and lock-
tion, and accessories. washers. Refer to the fastener and torque values
2. Disconnect the battery negative cable(s). table in .
3. Disconnect the electrical leads attached to the NOTE: Torque values differ according to type of
starter. Mark the terminals and wires for ease of engine installed.
installation. 3. Connect the wires to the starter as previously
NOTE: It may be difficult to gain access to the marked. Tighten the nuts 16 to 30 lbf·in (180 to
starter mounting bolts. For ease of removal, 340 N·cm).
straddle the front axle with your arms extended 4. Spray any exposed terminal connectors with di-
around the leaf springs and use a long socket electric red enamel. See Table 1.
extension.
Approved Dielectric Red Enamel
4. Remove the mounting bolts and lockwashers
(Fig. 1) that attach the starter to the engine. Re- Protectant Material Approved Brands
move the starter. MMM 1602 IVI–Spray Sealer,
Spray-On Application Red Electric Grade; order from
the PDC
Glyptal 1201EW– Low VOC,
Red; order at
Brush-On Application
www.glyptal.com or 1-800-
GLP-1201
Table 1, Approved Dielectric Red Enamel
5. Connect the battery negative cable(s).
03/23/2001 f150115a
1. Starter Mounting Bolts (with lockwashers)
Fig. 1, Starter Installation
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 100/1
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
Ignition Switch Removal and Installation
Removal
1. Disconnect the batteries.
2. Reach in underneath the switch housing and re-
move the ignition switch from the rubber grom-
met. It is not necessary to remove the switch
housing.
3. Remove the electrical connector from the rear of
the switch.
Installation
1. Connect the electrical connector to the ignition
switch.
the switch points inboard, towards the steering
wheel.
3. Connect the batteries.
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 110/1
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Problem—Starter Cranks Slowly Or Not At All
Problem—Starter Cranks Slowly Or Not
At All
Possible Cause Remedy
The batteries are undercharged. Do a load test on the batteries. See Section 54.02, Subject 140, for
instructions. Charge or replace batteries as needed.
If the batteries were discharged, check the alternator voltage and output. See
the troubleshooting subject in the appropriate alternator section in Group 15
for instructions.
The battery cables do not deliver sufficient Check the available cranking voltage. Go to "Available Cranking Voltage Test"
voltage to the starter. for instructions.
The starter solenoid circuit is broken. Check the starter solenoid circuit. Go to "Starter Solenoid Circuit Test" for
instructions. Make repairs as needed. Start the engine to verify the repair.
The control circuit is broken. Check the starter wiring. Go to "Starter Wiring Test" for instructions. Make
repairs as needed. Start the engine to verify the repair.
The magnetic switch is broken. Replace the magnetic switch. Go to Section 54.03, Subject 100, for
replacement instructions.
The starter ring gear or pinion gear is Visually check the ring and pinion gears. Go to "Ring and Pinion Gear Test"
damaged. for instructions.
The starter does not stay engaged. Go to "Cold Weather Starting Test" for instructions.
The starter is damaged. Replace the starter.
There is a mechanical problem in the
See Group 01 or the engine manufacturer’s manuals.
engine.
The drive belt is loose. Check the drive belt. See the drive belt subject in the appropriate engine
section in Group 01 for instructions. If necessary, tighten to the
Start the engine and check the alternator voltage and output. See the
troubleshooting subject in the appropriate alternator section in Group 15 for
instructions.
The drive belt is damaged or missing. Check the drive pulleys for locked bearings. Repair or replace any damaged
components. Replace the drive belt and start the engine.
Check the alternator voltage and output. See the troubleshooting subject in
the appropriate alternator section in Group 15 for instructions.
Troubleshooting Chart Available Cranking Voltage
Problem—Starter Spins, But Does Not Crank
Test
For troubleshooting instructions, see Fig. 1. BATTERY CABLE TEST
Problem—Starter Makes Clicking Noise, But Does 1. Connect the positive lead of a carbon pile tester
Not Crank (Or Cranks Intermittently) to the starter solenoid B (battery) terminal. Con-
For troubleshooting instructions, see Fig. 1. nect the negative lead of the carbon pile to the
starter G (ground) terminal. See Fig. 2.
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 300/1
15.01 Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series
Troubleshooting
Connect voltmeter
More than 6.0 V from solenoid "S" 6.0 V or less
terminal to ground.
Engage start switch.
Symptoms continue
Remove starter. Check & repair
Visually check pinion. Milled pinion magnetic switch
circuit.
OK
OK
Repair or replace starter.
(Do not install)
Repair verified.
Milled teeth
Visually check ring gear.
OK
Replace ring gear and check
flange to flywheel dimension.
Reinstall starter and
perform "Cranking
Circuit Test." Defective
Replace starter and verify repair.
02/18/97 f040314
Fig. 1, Milled Pinion Symptoms
IMPORTANT: Connect the voltmeter to the 5. Turn on the carbon pile again and adjust it to a
starter B terminal, not to the carbon pile clamp. 500-amp load, as before. Read and record the
voltage (V2) on the voltmeter. Turn off the carbon
2. Set a digital voltmeter on the low scale (2V, 3V, pile.
or 4V, depending on type of meter) and connect
the positive lead to the battery positive (+) termi- NOTE: Ignore the minus (–) sign.
nal. Connect the negative lead to the starter B
6. Add the positive (V1) and the negative (V2) volt-
terminal. age loss readings together. If the total voltage
3. Turn on the carbon pile and adjust it to a 500- loss is 0.5 volt or less, the battery cables are
amp load. Read and record the voltage (V1) on OK.
the voltmeter. Turn off the carbon pile.
Add the positive (V1) and the negative (V2) volt-
4. Now connect the digital voltmeter (still set on the age loss readings together. If the total voltage
low scale) to the battery negative (–) terminal loss is more than 0.5 volt, repair or replace as
and the starter G (ground) terminal. necessary.
IMPORTANT: Connect the voltmeter to the
starter G terminal, not to the carbon pile clamp.
300/2 Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
Troubleshooting
3. If the starter still does not crank, go to "Ring and
Pinion Gear Test."
4
3
Starter Solenoid Circuit Test
2
B The starter solenoid circuit includes the starter sole-
1
noid, cranking motor, magnetic switch, and ignition
S
switch. It is part of the cranking circuit. See Fig. 3.
G If there is excessive voltage loss in the starter sole-
5 at all, or it may drop out too soon when battery volt-
age goes down. Do the following test to check for
6 excessive voltage loss in the starter solenoid circuit.
1. Disconnect, at the solenoid, the lead from the
magnetic switch to the S terminal on the starter
solenoid.
09/10/96 f150600
2. Use a small clamp or 8-gauge jumper wire to
1. Voltmeter (recording V2, negative side voltage
loss)
connect this lead to the positive lead of a carbon
2. Starter Solenoid pile tester. Connect the negative lead of the car-
3. Voltmeter (recording V1, positive side voltage loss) bon pile to the starter G (ground) terminal. See
4. Battery Fig. 4.
5. Carbon Pile
6. Starter
3. Set a digital voltmeter on the 20V scale and con-
nect the positive lead to the starter B (battery)
Fig. 2, Battery Cable Test terminal. Connect the negative lead to the mag-
netic switch lead to which the carbon pile is al-
7. Disconnect the carbon pile and the voltmeter. ready connected.
Reconnect the magnetic switch to the starter S
terminal. 4. Read and record (as V3) the battery voltage
shown on the meter, about 12.6V.
INTERCONNECTING CABLE TEST NOTE: This step requires two persons.
5. Have one person turn the ignition switch to the
person cranks the engine, the second person START position while the other person listens for
uses a voltmeter to measure the voltage across the clicking sound of the magnetic switch closing.
the starter solenoid B (battery) and starter G Read the voltage on the voltmeter. It should read
(ground) terminals. very low voltage, less than 0.1V.
2. If the voltage is 9.0 volts or less while cranking, IMPORTANT: If the magnetic switch does not
check the battery interconnecting cables.
close, do the "Magnetic Switch Circuit Test." For
2.1 While cranking, measure the voltage instructions, see Section 54.03, Troubleshoot-
across each battery. ing, 300.
2.2 If the difference between any two batter- 6. Check the starter solenoid circuit voltage loss.
ies in the same battery box is more than
0.5 volt, check and replace the intercon- 6.1 Turn the ignition key to the START posi-
necting cables as required. tion; then turn on the carbon pile and ad-
just it to a 100-amp load.
2.3 If any cable or connection feels warm to
the touch, check and replace the inter- 6.2 Now read and record (as V4) the voltage
connecting cables as required. on the voltmeter. Turn off the carbon pile.
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 300/3
15.01 Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series
Troubleshooting
G
M
B
S
2
15A
+ 15C
1 3
9 15B
14
16
10
52
AA6 4
8
7
6 5 15A
15 15K
07/16/98 f150543a
NOTE: Wire 16 connects to the alternator.
1. Battery 4. Frontwall Connector (Pin E1) 7. 10-Amp Circuit Breaker
2. Cranking Motor (top view) 5. Splice Connector 8. Cab/Frontwall Power Stud
3. Magnetic Switch 6. Ignition Switch 9. Engine Power Stud
Fig. 3, Cranking Circuit Wiring
6.3 If the voltage drop (V4–V3) is 1.0V or IMPORTANT: It is difficult to gain access to the
less, the starter solenoid circuit is OK. Do starter S terminal. Avoid touching the starter B
the "Magnetic Switch Circuit Test." For terminal at the same time as the S terminal, as
instructions, see Section 54.03, Trouble- this can cause an electric shock.
shooting, 300.
2. Connect this lead to the positive lead of a carbon
If the voltage drop (V4–V3) is more than pile tester. Connect the negative lead of the car-
1.0V, the voltage loss is excessive. Go to bon pile to the starter G (ground) terminal (leave
"Starter Wiring Test." as in "Starter Solenoid Circuit Test").
3. Set a digital voltmeter on the low scale and con-
Starter Wiring Test nect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the
starter solenoid B (battery) terminal. Connect the
1. Disconnect the lead from the magnetic switch to negative lead of the voltmeter to the large termi-
the S terminal on the starter solenoid (leave as nal of the magnetic switch that is connected to
in "Starter Solenoid Circuit Test"). the starter B terminal (circuit 15B). See Fig. 5. If
any voltage shows, reconnect to the other large
terminal.
300/4 Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
Troubleshooting
rect terminal. Low resistance indicates that the
connections are correct.
1 4. Have a second person start the engine momen-
tarily.
2 IMPORTANT: If the magnetic switch does not
close, do the "Magnetic Switch Circuit Test." For
4 3
B instructions, see Section 54.03, Troubleshoot-
5 ing, 300.
5.1 Turn the ignition key to the START posi-
tion, then turn on the carbon pile and ad-
just it to a 100-amp load.
G 5.2 Now read and record the voltage (V5) on
the voltmeter. Turn off the carbon pile.
6 6. Now connect the positive lead of the digital volt-
01/15/97 f150550a meter (still set on the low scale) to the magnetic
1. Ignition switch 4. Digital Voltmeter switch lead which is already connected to the
2. Magnetic Switch 5. Starter Solenoid carbon pile (as in "Starter Solenoid Circuit Test").
3. Carbon Pile 6. Cranking Motor Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to the
Fig. 4, Starter Solenoid Circuit Test other large terminal on the magnetic switch (cir-
cuit 15C). See Fig. 6.
1
2
1
3 3
B 2
4 B
4
S
S
5
5
G
G
08/27/96 f150547
08/27/96 f150548
1. Digital Voltmeter 4. Starter Solenoid
2. Magnetic Switch 5. Cranking Motor 1. Magnetic Switch 4. Starter Solenoid
3. Carbon Pile 2. Carbon Pile 5. Cranking Motor
3. Digital Voltmeter
Fig. 5, Starter Wiring Test, First Wire Voltage Loss (V5)
Fig. 6, Starter Wiring Test, Second Wire Voltage Loss
NOTE: If desired, do a continuity check on the (V6)
circuit to be sure that it is connected to the cor-
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 300/5
15.01 Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series
Troubleshooting
7. Have a second person start the engine momen- 3. If the engine still does not crank properly after
tarily. replacing the starter, look for a mechanical prob-
lem in the engine. For instructions, see
8. Check the second wire voltage loss (V6).
Group 01 or the engine manufacturer’s manuals.
NOTE: Ignore the minus (–) sign.
8.1 Turn the ignition key to the START posi- Cold Weather Voltage Test
tion, then turn on the carbon pile and
again adjust it to a 100-amp load. In cold weather, the starter may fail to engage, even
though it performed well at higher temperatures. Do
8.2 Now read and record the voltage (V6) on the following test to check for cold weather voltage
the voltmeter. Turn off the carbon pile. loss in the cranking circuit.
8.3 Add the two voltages (V5 and V6) to- 1. With the ignition switch on, clamp a heavy bat-
gether to get the total wire voltage loss. If tery jumper cable between the two large studs
the total wire voltage loss adds up to 0.8 on the magnetic switch. Remove the jumper im-
volt or less, the wiring is OK. Replace the mediately to stop the engine from cranking.
magnetic switch. For instructions, see
Section 54.03, Subject 100. 2. If the engine starts with the jumper in place, do
the "Starter Wiring Test." Repair/replace the wir-
If the total wire voltage loss adds up to ing connections, terminals, and/or magnetic
more than 0.8 volt, check the wire con- switch as necessary.
nections for tightness and the terminals
for corrosion. Repair or replace as neces- 3. If the engine now starts properly, check the
sary. starter mounting bolts for tightness and do the
"Alternator Wiring Test." See the troubleshooting
9. Disconnect the carbon pile and the voltmeter. subject in the appropriate alternator section in
Reconnect the magnetic switch to the starter S Group 15 for instructions.
terminal.
4. If the engine still does not start properly, go to
10. Check all wiring and connections and repair or "Available Cranking Voltage Test."
replace as needed. For instructions on wire re-
pair, see Section 54.00, Subject 100.
Magnetic Switch Circuit Test
For the "Magnetic Switch Circuit Test," see Sec-
tion 54.03, Troubleshooting, 300.
Ring and Pinion Gear Test
person bars the engine over, the second person
starter pinion gear visually (check all the teeth in
both gears).
2. If the pinion teeth are damaged, replace the
starter. If the ring gear teeth are damaged, re-
place the ring gear.
NOTE: For ring gear replacement procedures,
see the engine manufacturer’s manuals.
300/6 Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
For a cranking circuit wiring diagram, see Fig. 1.
For a schematic of the engine starting circuit wiring
harness, see Fig. 2.
G
M
B
S
2
15A
+ 15C
1 3
9 15B
14
16
10
52
AA6 4
8
7
6 5 15A
15 15K
07/16/98 f150543a
NOTE: Wire 16 connects to the alternator.
1. Battery 4. Frontwall Connector (pin E1) 7. 10-Amp Circuit Breaker
2. Cranking Motor (top view) 5. Splice Connector 8. Cab/Frontwall Power Stud
3. Magnetic Switch 6. Ignition Switch 9. Engine Power Stud
Fig. 1, Cranking Circuit Wiring
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 400/1
15.01 Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series
120 120B
2
1
30G
3
30
15B
15
C
5
16
11
GND 15C
A
15
6
16 B
10
GNDA
8
9
11/22/95 f150552
1. Transmission Temperature Gauge Sensor Harness 6. To Starter Solenoid "S" Terminal
Connector 7. To Starter Solenoid "B" Terminal
2. To Back-Up Light Switch 8. To Starter "G" Terminal
3. Frontwall Harness Connector 9. To A/C Compressor Clutch
4. To Magnetic Switch 10. To Alternator Output Terminal
5. To Battery Cable Power Terminal 11. To Alternator Ground Terminal
Fig. 2, Engine Charging Circuit Wiring Harness
Fastener Torque Values
Torque Value
Fastener Description Size
lbf·ft (N·m) lbf·in (N·cm)
Nose Housing Bolts 5/16–18 13–17 (18–23) —
Frame Capscrews (grade 8) 1/4–28 — 144–192 (1620–2160)
Solenoid Mounting Bolts (grade 8) 1/4–20 — 150–200 (1700–2260)
Copper Terminals 1/2–13 20–25 (27–34) —
Solenoid Side Terminals 10–32 — 16–30 (180–340)
Brush Screw 8–32 — 18–24 (200–280)
400/2 Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000
Starter, Delco Remy 42MT Series 15.01
Fastener Torque Values
Torque Value
Fastener Description Size
lbf·ft (N·m) lbf·in (N·cm)
Frame Plug 1-3/8–18 — 48–72 (540–820)
Detroit Diesel (steel housing) 5/8–16 137–147 (186–199) —
Detroit Diesel (aluminum housing) 5/8–16 85–95 (115–129) —
Caterpillar (steel or aluminum housing) 5/8–16 130–170 (176–230) —
Cummins (steel or aluminum housing) 5/8–16 130–170 (176–230) —
Table 1, Fastener Torque Values
Columbia Workshop Manual, Supplement 0, April 2000 400/3
You might also like
- Hino Freno de Ahogo 1Document4 pagesHino Freno de Ahogo 1Yeam_90No ratings yet
- Tomos4 Operating Manual PDFDocument15 pagesTomos4 Operating Manual PDFEmir Jordamović100% (1)
- TLB2 4WD 4WS (47865813)Document14 pagesTLB2 4WD 4WS (47865813)pitbullNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts List: AXLE 28.36M REF. 138094Document10 pagesSpare Parts List: AXLE 28.36M REF. 138094Inacio MiraNo ratings yet
- Repair Parts Sheet RC-1006 AND RC-10010: L981 Rev. D 10/08 For Date Codes Beginning With The Letter "C" CautionDocument2 pagesRepair Parts Sheet RC-1006 AND RC-10010: L981 Rev. D 10/08 For Date Codes Beginning With The Letter "C" CautionWin Min TunNo ratings yet
- Parts Bulletin: PT TVS Motor Company Indonesia 2011, All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesParts Bulletin: PT TVS Motor Company Indonesia 2011, All Rights ReservedRama ChandranNo ratings yet
- Allison MT (B) 640, 643, 650, 653 Series On-Highway Transmissions Parts CatalogDocument3 pagesAllison MT (B) 640, 643, 650, 653 Series On-Highway Transmissions Parts CatalogMarcos LunaNo ratings yet
- DV15 (T) (Ti) (Tis)Document101 pagesDV15 (T) (Ti) (Tis)irwan yuniardi100% (2)
- TTLA0651Document384 pagesTTLA0651Rafał DworakNo ratings yet
- Ohlins SU148Document7 pagesOhlins SU148r41nd0gNo ratings yet
- 400 ClutchesDocument21 pages400 ClutchesMrAlbert2009No ratings yet
- Toyota x888 RM Section 2 3Document190 pagesToyota x888 RM Section 2 3ssinokrotNo ratings yet
- Bcf42ht MaruyamaDocument16 pagesBcf42ht Maruyamasneider182No ratings yet
- Models: J08C-TP and J08C-TRDocument16 pagesModels: J08C-TP and J08C-TRnguyen phuong nhaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo MBDocument146 pagesCatalogo MBLeopoldo WilleNo ratings yet
- LX279 With 48C Deck: Lawn Tractor 48" Convertible DeckDocument1 pageLX279 With 48C Deck: Lawn Tractor 48" Convertible DeckManuel Fernandez Mora0% (1)
- 769 03191Document32 pages769 03191asiyaNo ratings yet
- 10 8974 CompassR Volute Replacement IandODocument6 pages10 8974 CompassR Volute Replacement IandOGOWTHAMNo ratings yet
- KG MaintSheet 3120 3320 3520 3720Document2 pagesKG MaintSheet 3120 3320 3520 3720raymundo velasquezNo ratings yet
- 7575 DI Arjun International 4WD 2WD Parts Catalogue17 PDFDocument246 pages7575 DI Arjun International 4WD 2WD Parts Catalogue17 PDFSamsher AliNo ratings yet
- Timming Injector Perkins 4000Document7 pagesTimming Injector Perkins 4000Anonymous V9fdC6100% (5)
- KIP 3100 Parts Manual Ver 2 0Document111 pagesKIP 3100 Parts Manual Ver 2 0Antonio DominguezNo ratings yet
- DIESEL ENGINE ISUZU 4JG2 Service ManualDocument48 pagesDIESEL ENGINE ISUZU 4JG2 Service ManualArmando Orta90% (10)
- Clutch Hino 2.5Document4 pagesClutch Hino 2.5Yeam_90No ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument12 pagesSteering Systemluis tocoraNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 5.01 Issue C: Wet Alarm Valve Model B, D, EDocument1 pageData Sheet 5.01 Issue C: Wet Alarm Valve Model B, D, EpitigoiNo ratings yet
- Lonking CDM860 Wheel Loader Parts Catalogue PDFDocument175 pagesLonking CDM860 Wheel Loader Parts Catalogue PDFFedi SNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Power Train System: Group 1 Structure and OperationDocument18 pagesSection 3 Power Train System: Group 1 Structure and OperationAndré TarginoNo ratings yet
- Throttle Body Explanation and CalibrationDocument2 pagesThrottle Body Explanation and CalibrationReynaldo FloresNo ratings yet
- Valve Clearances & Cylinder NumberingDocument5 pagesValve Clearances & Cylinder NumberingsxturboNo ratings yet
- Visi N: Mantis Stereo Viewing System Operating Instructions and Service ManualDocument27 pagesVisi N: Mantis Stereo Viewing System Operating Instructions and Service ManualpetrocelliNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Power Train SystemDocument21 pagesSection 3 Power Train SystemErik Borras EstradaNo ratings yet
- Hino Freno de Ahogo 3Document4 pagesHino Freno de Ahogo 3Yeam_90No ratings yet
- Repair Parts Sheet Hydraulic Cylinders RD-166 and RD-1610Document4 pagesRepair Parts Sheet Hydraulic Cylinders RD-166 and RD-1610Umar YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Allison 8000 Series Off-Highway Transmissions Parts CatalogDocument5 pagesAllison 8000 Series Off-Highway Transmissions Parts CatalogMETİN100% (1)
- Allison MT (B) 640, 643, 650, 653 Series On-Highway Transmissions Parts CatalogDocument6 pagesAllison MT (B) 640, 643, 650, 653 Series On-Highway Transmissions Parts CatalogMarcos LunaNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Power Train System: Group 1 Structure and OperationDocument20 pagesSection 3 Power Train System: Group 1 Structure and OperationAndré TarginoNo ratings yet
- Mastil Drive UnitDocument16 pagesMastil Drive Unitluis tocoraNo ratings yet
- Mech Systems 1Document106 pagesMech Systems 1Hanuma Reddy100% (1)
- CB-225D Hydraulic Schematic Vibratory CompactorsDocument2 pagesCB-225D Hydraulic Schematic Vibratory Compactorsjohn miguelNo ratings yet
- Power Take-Off On Engines: Issue 2Document16 pagesPower Take-Off On Engines: Issue 2ruanNo ratings yet
- Hyosung Aquila 250GV - Manual de Despiece - InglesDocument123 pagesHyosung Aquila 250GV - Manual de Despiece - Inglesjjq100% (1)
- Disassembly, Inspection and Repair: Solenoid Hold-In TestDocument7 pagesDisassembly, Inspection and Repair: Solenoid Hold-In TestWylk BeserraNo ratings yet
- JO Prel 40-50 RemoteDocument28 pagesJO Prel 40-50 RemoteŞener ÖZSOYNo ratings yet
- Carraro Tlb1 Up Parts CatalogDocument15 pagesCarraro Tlb1 Up Parts CatalogЮрий100% (1)
- Formacion Motores KubotaDocument14 pagesFormacion Motores KubotaTerah PioNo ratings yet
- 99790-87100-02 - Know Your Lift TruckDocument48 pages99790-87100-02 - Know Your Lift TruckBARRENECHEA DELGADO ISAACNo ratings yet
- BRAKE SYSTEM HyundaiDocument6 pagesBRAKE SYSTEM HyundaiAfshin GhafooriNo ratings yet
- b50d Mki EngineDocument24 pagesb50d Mki EngineMIANo ratings yet
- L1204C Plus - Section 4 - PowertrainDocument60 pagesL1204C Plus - Section 4 - PowertrainPeetNo ratings yet
- Service Manual SM01 - 081 - 036.00: Gear Pump/Motor, Recondition WarningDocument4 pagesService Manual SM01 - 081 - 036.00: Gear Pump/Motor, Recondition WarningJorge YuniorNo ratings yet
- GX325 With 54C Deck: Garden Tractor 54" Convertible DeckDocument1 pageGX325 With 54C Deck: Garden Tractor 54" Convertible Deckramel5217780No ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue Kubota Z482 PDFDocument50 pagesParts Catalogue Kubota Z482 PDFRantoniaina100% (2)
- 1700 Roller Pump Parts BreakdownDocument1 page1700 Roller Pump Parts Breakdownrndslickbar 2021No ratings yet
- C G48U3-80011 Transmission UnitDocument16 pagesC G48U3-80011 Transmission UnitJOAO BIANCHININo ratings yet
- M8.8 1161 001Document4 pagesM8.8 1161 001Jimmy HernandezNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Kohller 18HP SV540 HUSI2009 - AAaa - SV540-0024Document11 pagesCatalogo Kohller 18HP SV540 HUSI2009 - AAaa - SV540-0024Jhonatan ComakNo ratings yet
- To Protect Your Warranty, Use Only ENERPAC Hydraulic Fluid.: FTR-Series Foundation Tensioners, RoundDocument8 pagesTo Protect Your Warranty, Use Only ENERPAC Hydraulic Fluid.: FTR-Series Foundation Tensioners, RoundVitaliiNo ratings yet
- Ford Manual for Owners and Operators of Ford Cars and Trucks (1919)From EverandFord Manual for Owners and Operators of Ford Cars and Trucks (1919)No ratings yet
- Agc 4 Data Sheet 4921240400 UkDocument32 pagesAgc 4 Data Sheet 4921240400 UkLOI HONo ratings yet
- TH TNDocument16 pagesTH TNVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Um en Gaiconfig User Guide 107326 en 06Document94 pagesUm en Gaiconfig User Guide 107326 en 06fiera669No ratings yet
- Digital Voltage Regulator: Installation and MaintenanceDocument112 pagesDigital Voltage Regulator: Installation and MaintenanceVu TuongNo ratings yet
- TDS 16V4000M63LDocument2 pagesTDS 16V4000M63LVu Tuong100% (1)
- Cloning Programming : Controller MenuDocument2 pagesCloning Programming : Controller MenuVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Practical IssuesDocument3 pagesPractical IssuesVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Can Tran: H.NguyenDocument11 pagesCan Tran: H.NguyenVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Can Tran: H.NguyenDocument11 pagesCan Tran: H.NguyenVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Can Tran: H.NguyenDocument11 pagesCan Tran: H.NguyenVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Can Tran: T.NguyenDocument5 pagesCan Tran: T.NguyenVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Agc-4 MK Ii: Operator'S ManualDocument24 pagesAgc-4 MK Ii: Operator'S ManualVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Hameln Eugen - Reintjes - Strasse 7 WWW - Reintjes-Gears - de D-31785Document17 pagesHameln Eugen - Reintjes - Strasse 7 WWW - Reintjes-Gears - de D-31785Vu TuongNo ratings yet
- Can Tran: T.NguyenDocument5 pagesCan Tran: T.NguyenVu TuongNo ratings yet
- Deif AGC 200Document29 pagesDeif AGC 200Girva GirdanNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica Us MotorsDocument14 pagesFicha Técnica Us MotorsKeren ArteagaNo ratings yet
- 561 Live Work - A Management PerspectiveDocument97 pages561 Live Work - A Management Perspectiveasi midobarNo ratings yet
- Vscan UM GM092102 5 00 PDFDocument211 pagesVscan UM GM092102 5 00 PDFAzzam SaputroNo ratings yet
- Application Engineering Bulletin: Electronic Throttle Control Specifications Automotive Industrial G-DriveDocument3 pagesApplication Engineering Bulletin: Electronic Throttle Control Specifications Automotive Industrial G-DriveMiguel Angel Cortes PrietoNo ratings yet
- Danaher Motion - Kollmorgen AKM Series DatasheetDocument46 pagesDanaher Motion - Kollmorgen AKM Series Datasheetcristian2340No ratings yet
- Presentation On WattDocument12 pagesPresentation On WattShambhukumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Myrius Nextgen Main BrochureDocument92 pagesMyrius Nextgen Main BrochureAkashNo ratings yet
- Safety Guidelines For Direct DrivesDocument9 pagesSafety Guidelines For Direct DrivesJOseNo ratings yet
- AQ 102 Manual EN1.2Document44 pagesAQ 102 Manual EN1.2Alexandre MorenoNo ratings yet
- LCOE Calculator 1Document44 pagesLCOE Calculator 1Jorge Isaac Flores SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Chap 2 PSA IIDocument48 pages2023 Chap 2 PSA IIShokry AhmedNo ratings yet
- CLAP SWITCH ValidationboardDocument5 pagesCLAP SWITCH ValidationboardVeronica GavanNo ratings yet
- Testing ROCOF Based On New IEC Standard An enDocument22 pagesTesting ROCOF Based On New IEC Standard An enFredrikNo ratings yet
- ADR155Document176 pagesADR155Abdou taksi lmakhfiNo ratings yet
- BASLER - Instruction Manual For Ground Fault Relay Be1-64FDocument27 pagesBASLER - Instruction Manual For Ground Fault Relay Be1-64Fcarloviggiano4_26961100% (1)
- Lab 1 Basic Logis GatesDocument11 pagesLab 1 Basic Logis GatesHazeem JokeNo ratings yet
- Active Bass Boost FilterDocument1 pageActive Bass Boost FilterJosé RazoNo ratings yet
- EC I, Nba 1Document4 pagesEC I, Nba 1Sudha PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- PC160 Merik Home Access Home DepotDocument8 pagesPC160 Merik Home Access Home DepotIsaac SantoyNo ratings yet
- Cacat Yang Umum Terdapat Pada PipaDocument10 pagesCacat Yang Umum Terdapat Pada PipaAntrasit CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Electrical SafetyDocument74 pagesCh1 - Electrical SafetySayed ShafeiNo ratings yet
- Deep Sea Electronics PLC: Dse9Xx, Dse91Xx, Dse92Xx & Dse94Xx Series Battery Charger Operator ManualDocument70 pagesDeep Sea Electronics PLC: Dse9Xx, Dse91Xx, Dse92Xx & Dse94Xx Series Battery Charger Operator ManualYahya El SadanyNo ratings yet
- Electrical - Electrical Engineering Pocketbook Handbook - Koffler - 1993Document49 pagesElectrical - Electrical Engineering Pocketbook Handbook - Koffler - 1993Rotax_KidNo ratings yet
- Report Creativity and Innovation UTHM Pair AssignmentDocument33 pagesReport Creativity and Innovation UTHM Pair AssignmentInahMisumi67% (6)
- SLV-N650 N750 SMDocument2 pagesSLV-N650 N750 SMEmerson ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Customer Benefits: MV Air-Insulated Switchgear RangeDocument8 pagesCustomer Benefits: MV Air-Insulated Switchgear RangewillvinNo ratings yet
- Kte-750 ManualDocument15 pagesKte-750 ManualFernando GuatemalanNo ratings yet
- DRACO ZULO LED Floodlight Colour Series (RGB)Document2 pagesDRACO ZULO LED Floodlight Colour Series (RGB)Ptt EngineeringNo ratings yet
- QuickdrawDocument32 pagesQuickdrawNoe JimenezNo ratings yet