Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macula e
Uploaded by
Doris ShollaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Macula e
Uploaded by
Doris ShollaCopyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 9/3/2021
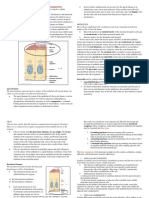
8. VESTIBULE: MACULAE - UTRICLE AND SACCULE
Vestibule | Maculae: Utricle & Saccule Medical Editor: Dr. Sofia Suhada M. Uzir
OUTLINE (A) ANATOMY OF MACULA
The maculae consist of:
I) ANATOMY OF THE INNER EAR o Supporting cells at the bottom
II) MACULA
o Hair cells type I and II
III) UTRICLE
o Vestibular dark cells
IV) SACCULE
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS Functions similar to striae vascularis
VI) REFERENCES Secrete potassium into the endolymph
o Otolithic membrane
I) ANATOMY OF THE INNER EAR Gelatinous membrane rich in
mucopolysaccharides
The inner ear consists of (Figure 1) Contains calcium carbonate crystals called
Cochlea otoconia/otoliths
Vestibule • They have high specific gravity than the
endolymph in the vestibule
(i) Outer bony part
• Hence, they shift a lot due to movements
o Composed of perilymph which is rich in sodium and which include vertical and horizontal linear
low in potassium accelerations and head tilting
Very similar to the composition of cerebrospinal
fluid
(ii) Inner membranous labyrinth
o Inside of the bony labyrinth
o Consist of
Utricle connecting to the semicircular ducts
Saccule connecting to the cochlear duct
o Contains endolymph which is high in potassium and
low in sodium
(iii) Maculae
o Special detector/sensory epithelium inside the inner
membranous labyrinth
Semicircular canals
o Semicircular ducts with the crista ampullaris
Figure 2. Anatomy of macula [Pearson Education]
(B) THE HAIR CELL
(1) Types of hair cells (Figure 3)
(i) Type I
More bulbous towards the basolateral membrane
Have afferent neurons that are more calyx like
(ii) Type II
More cylindrical towards the basolateral membrane
Have afferent neurons that are more boton/bulbous like
(like in the nerve terminal)
Figure 1. Anatomy inner ear [BruceBlaus]
II) MACULA
Situated in the saccule and utricle
Surrounded by endolymph which is rich in potassium
(maintained by the vestibular dark cells) and low in
sodium
Figure 3. Hair cells [K. Sembulingam]
VESTIBULE: MACULAE - UTRICLE AND SACCULE SPECIAL SENSES: Note #8. 1 of 4
III) UTRICLE
(2) Parts of the hair cells Situated on the floor of the utricle is a specialized
The hair cells contain cilia on the apical surface which epithelium called the maculae
consist of o The hair cells (stereocilia) are pointing upwards
o Kinocilium The utricle responds to different types of
A true cilium equilibriums/movements such as:
The longest cilium
o Stereocilia (1) Linear acceleration in the horizontal axis
Microvilli Generally, during a constant acceleration, action
It is connected to the peripheral processes of the potentials stay constant
vestibular ganglia Example:
o The central processes goes into the central nervous o With the head in stationary position→ otoconia aren’t
system moving → the action potential stays constant
o Vestibular ganglion is also known as Scarpa’s ganglia If the otoconia pulls the otolithic membrane forward →
stereocilia beat towards the kinocilium → potassium
Remember: channel opens and potassium and calcium enter the cell
The cochlea contains the spiral ganglia → increase the action potential sent down to the axons
by the structure → the cell is stimulated
Example:
(3) Mechanism of action of the hair cells (Figure 3)
o Stopping the car suddenly with the head moving
Movements of the head either by head tilting and forward → high amount of action potential sent
horizontal and vertical linear accelerations may either down to the axons by the structure
cause stereocilia to
(i) Beat towards the kinocilium
This stretches the tips length → opens up the channels →
potassium and calcium ions move into the cells →
accumulate inside the cell → the cell becomes positive →
causes the cell to depolarize → calcium helps in fusing
the synaptic protein between the vesicle and the cell
membrane → fusion release neurotransmitters out by
exocytosis, these include aspartate and glutamate → will
increase the action potentials
(ii) Beat away from the kinocilium
The tips length relaxes→ closes the channels → no
potassium and calcium ions will move into the cells → the Figure 5. Linear acceleration on the horizontal axis
cell becomes slightly negative/hyperpolarize → fusion of [Oregon State University]
the vesicle with the cell membrane will not take place →
no neurotransmitters will be released → there will be no
If the otoconia pulls the otolithic membrane backwards
the action potentials
→ stereocilia moves away from the kinocilium →
decrease the amount of action potential sent down
Example:
o Accelerate the car suddenly with the head moves
backwards → otoconia pulls the otolithic membrane
backwards → stereocilia moves away from the
kinocilium → little or no action potential will be sent
down the axons
Note:
Not all the hair cells will be stimulated at the same time. It
Figure 4. Mechanism of action of hair cells [Britannica]
depends on the direction of which the stereocilia are moving
o Moving towards the kinocilium stimulate the hair cells
o Hence, depending on the direction of movement, some
of the stereocilia might move towards the kinocilium but
some might not
(2) Head tilt
Tilting the head to the sides/nodding will stimulate the
stereocilia
When the head moves sideways, the otoconia pulls the
otolithic membrane → stereocilia moves towards the
kinocilium → the action potential increase
When the head moves back to the middle the otoconia
pulls the otolithic membrane in the opposite direction →
stereocilia moves away from the kinocilium → the action
potential decrease
2 of 4 SPECIAL SENSES: Note #8. VESTIBULE: MACULAE - UTRICLE AND SACCULE
IV) SACCULE
Situated on the wall of the saccule is the sensory
epithelium called the maculae
o The hair cells (stereocilia) are pointing outwards
(Figure 5)
The saccule responds to:
(1) Vertical linear acceleration
Accelerating upwards move stereocilia down, and
decelerating downwards move the stereocilia up
Example:
o Standing in the elevator and it suddenly goes up →
the gravitational forces will pull the otoconia down →
the otolithic membrane moves downward → if the
stereocilia beats toward the kinocilium → the action
potential will increase
o Standing in the elevator and it suddenly goes down →
due to the drag forces, the otoconia will move upward
and pulls the otolithic membrane with it → if the
stereocilia beats away from the kinocilium → the
action potential will decrease
(2) Low frequency vibrations
Not as important as the response to the vertical linear
acceleration
Figure 6. The saccule which is stimulated when tilting the head
[Health Jade]
VESTIBULE: MACULAE - UTRICLE AND SACCULE SPECIAL SENSES: Note #8. 3 of 4
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS Which sensory receptor is most sensitive to
angular acceleration?
Otoliths are normally located in: a. Crista
a. The ampulla of semicircular canal b. Utricle
b. The utricle c. Saccule
c. The modiolus d. Organ of Corti
d. The cochlea
Vestibular apparatus: CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
a. Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth
b. May help in initiating the voluntary movements VI) REFERENCES
c. Contains receptors concerned with regulation of ● Sembulingam K , Sembulingam Prema; Essentials of
body posture and equilibrium Physiology for Dental Students. Hair Cells [digital image] 2016.
https://www.jaypeedigital.com/book/9789385999468/chapter/ch104
d. Has no role in perception of acceleration ● Blausen.com staff (2014). Medical gallery of Blausen Medical
2014. Anatomy of Inner Ear [digital image]
Vestibular apparatus: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inner_ear#/media/File:Blausen_0329_E
arAnatomy_InternalEar.png
a. Consists of semicircular canals only
● Encyclopaedia Britannica Inc,. Mechanism of Actions of Hair
b. Contains two types of sensory organs, crista and Cells [digital image] 1997.
macula that discharges impulses along the 8th and https://www.britannica.com/science/macula
9th cranial nerves ● Oregnon State University. The Vestibular System. Linear
acceleration of horizontal axis [digital image]
c. Located inside the petrous portion of temporal bone https://open.oregonstate.education/aandp/chapter/15-4-equilibrium/
d. Can discharge impulses that affect muscle tone in ● Pearsons Education 2012. Anatomy of macculea [digital image]
distal muscles of the limbs only https://slideplayer.com/slide/8429493/
● Health Jade. The saccule [digital image]
https://healthjade.net/vestibular-system/
The semi-circular canals: ● CNS mcq exam [quiz]
a. 3 pairs on each side http://www1.mans.edu.eg/facmed/dept/physiology/pdf/cns%202nd%
20term.pdf
b. Detect the angular acceleration
c. Contains fluid rich in Na+ ions
d. Its receptors show depolarization when Na+ influx in
the apical border of its hair cells
The hair cells in the vestibular receptors organs:
a. Only stimulated during acceleration
b. Show hyper-polarization when stereocilia deviated
towards kinocilium
c. Show depolarization when stereocilia deviated
towards kinocilium
d. Show depolarization when stereocilia deviated away
kinocilium
Endolymph:
a. It is found within the membranous labyrinth
b. Has a K+ concentration closes to that of the extra-
cellular fluid
c. Is electrically negative with respect to the perilymph.
d. Inertia has no role in the stimulation of receptors in
the semicircular canals during rotation
All of the following statements about the vestibular
apparatus is true except:
a. It consists of semicircular canals and two small sacs,
utricle and saccule
b. The semicircular canals contain sensory organs
called crista
c. The utricle and saccule are concerned with
perception of linear acceleration
d. Concerned with regulation of muscle tone during
performance of fine skilled movement
The central connection of the vestibular apparatus
includes all of the following except:
a. Cerebellum
b. Reticular formation
c. Medial longitudinal bundle on both sides
d. Limbic cortex
Linear acceleration is transduced in the:
a. Cupula
b. Cristae
c. Maculae
d. Organ of Corti
e. Scarpa's ganglion
4 of 4 SPECIAL SENSES: Note #8. VESTIBULE: MACULAE - UTRICLE AND SACCULE
You might also like
- International Review of General and Experimental Zoology: Volume 3From EverandInternational Review of General and Experimental Zoology: Volume 3William J. L. FeltsNo ratings yet
- 428 - Eyes-Ears-Nose-Throat Physiology) Cochlea - Spiral Organ of CortiDocument4 pages428 - Eyes-Ears-Nose-Throat Physiology) Cochlea - Spiral Organ of CortiSairamNo ratings yet
- Khan 2013Document7 pagesKhan 2013Juan VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The EarDocument10 pagesHistology of The EarmohamadNo ratings yet
- Anatomyofthevestibularsystem Areview PDFDocument8 pagesAnatomyofthevestibularsystem Areview PDFJacqueline Rebolledo BravoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanasssadulllahNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2.4 TissuesDocument46 pagesUNIT 2.4 TissuesrazaliafifaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Inner EAR: Dr. As Maan Assisstant Professor Department of EntDocument38 pagesAnatomy of Inner EAR: Dr. As Maan Assisstant Professor Department of EntPrabaa Kharan0% (1)
- 24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)Document24 pages24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- L2.1 - Simple Epithelium, 2march 2022Document32 pagesL2.1 - Simple Epithelium, 2march 2022TalarNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Part 4 FinalDocument23 pagesCell Biology Part 4 FinalVittal Athul RNo ratings yet
- Review: Mechanotransduction by Hair Cells: Models, Molecules, and MechanismsDocument12 pagesReview: Mechanotransduction by Hair Cells: Models, Molecules, and MechanismsMaria AnggieNo ratings yet
- TOB 2.1Document32 pagesTOB 2.1LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- ZOOLEC (Tissues Table)Document6 pagesZOOLEC (Tissues Table)JOHN ANDREW EVIANo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument4 pagesCilia and FlagellaAnurag chavan100% (1)
- The Physiology of The Senses: Lecture 10 - BalanceDocument13 pagesThe Physiology of The Senses: Lecture 10 - BalanceBrain AngganaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Biology Practical Record Writing 2022-23 - Part 3Document54 pagesClass Xi Biology Practical Record Writing 2022-23 - Part 3Om SolankiNo ratings yet
- ENT Specialist 2Document44 pagesENT Specialist 2Shirley MulongoNo ratings yet
- Human EarDocument22 pagesHuman Earbodkheomkar.299No ratings yet
- 100 - Neurology Physiology) Descending Tracts OverviewDocument3 pages100 - Neurology Physiology) Descending Tracts OverviewOsman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Vestibular System: Sensing Head MovementsDocument14 pagesThe Vestibular System: Sensing Head MovementsEslam ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes on Epithelial Tissue CharacteristicsDocument1 pageHistology Notes on Epithelial Tissue CharacteristicsJustine May S. ColicoNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Sciences NuggetsDocument126 pagesAnatomic Sciences NuggetsjankiNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Function and Anatomy RatnaDocument36 pagesVestibular Function and Anatomy RatnaRatna WindyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Inner Ear PresentationDocument61 pagesInner Ear PresentationKarishma MishraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument27 pagesAnatomy of EarKhush BakhtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 EarsDocument60 pagesChapter 15 EarsSrihari SriramNo ratings yet
- L 10 BalanceDocument11 pagesL 10 BalanceMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQDocument36 pagesEnt MCQDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cells and Tissues NotesDocument33 pagesAnaphy Cells and Tissues NotesshannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument23 pagesCombine PDFsigninNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue L 1Document35 pagesAnimal Tissue L 1Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Types Simple Epithelia: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesTypes Simple Epithelia: ObjectivesSheba Victoria RabagoNo ratings yet
- Histo 2 PDFDocument13 pagesHisto 2 PDFabdulrazaqNo ratings yet
- The Sense of BalanceDocument13 pagesThe Sense of BalanceDwiki HartantoNo ratings yet
- Cilia, Ciliary MovementDocument11 pagesCilia, Ciliary MovementMariana CarneiroNo ratings yet
- Human Histology 5.2 NeuroepitheliumDocument4 pagesHuman Histology 5.2 NeuroepitheliumBlubby BleuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document2 pagesExercise 1Sheba Victoria RabagoNo ratings yet
- Histology QuestionDocument4 pagesHistology QuestionLeng BunthaiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Tissue - Part 1Document5 pagesAnaphy - Tissue - Part 1Aileen DemaguilaNo ratings yet
- LOCOMOTION IN ParamoeciumDocument4 pagesLOCOMOTION IN Paramoeciummanojitchatterjee2007No ratings yet
- PChapter 5 Epithelial Tissue PDFDocument4 pagesPChapter 5 Epithelial Tissue PDFRuel MateoNo ratings yet
- Iris and Ciliary BodyDocument46 pagesIris and Ciliary BodyPremaaloshineeThanabalNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan THTDocument9 pagesPemeriksaan THTAtikah MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Histology: First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022Document22 pagesHistology: First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022Fea Kristine PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Epithelium and Connective Tissue Lecture SummaryDocument4 pagesEpithelium and Connective Tissue Lecture SummaryDan ChoiNo ratings yet
- Bone and Bone FormationDocument8 pagesBone and Bone FormationAnuj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial cell polarity and surface modificationsDocument4 pagesEpithelial cell polarity and surface modificationsAlyssa AlferezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Cell and Tissues) (No)Document34 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (Cell and Tissues) (No)shannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- 2ND Year Histology QUICK RECAPDocument12 pages2ND Year Histology QUICK RECAPMarya Safdar100% (2)
- Anatomy of Inner Ear and Neural PathwaysDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Inner Ear and Neural PathwaysVineet ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesEmbryology of The Respiratory SystemASIIMWE WINNIE CATHERINENo ratings yet
- 2-Inner Ear AnatomyDocument14 pages2-Inner Ear AnatomyM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Unit IV For StdsDocument52 pagesSpecial Senses Unit IV For StdsanwarNo ratings yet
- The Inner Ear - Bony Labyrinth - Membranous Labryinth - TeachMeAnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Inner Ear - Bony Labyrinth - Membranous Labryinth - TeachMeAnatomywzt2001No ratings yet
- GI HISTOLOGY HIGHLIGHTSDocument9 pagesGI HISTOLOGY HIGHLIGHTSJimell ObradorNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue FunctionsDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue FunctionsNoriel LacsinaNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE OF MEDICINE HISTOLOGY LABORATORY MANUALDocument9 pagesCOLLEGE OF MEDICINE HISTOLOGY LABORATORY MANUALMB MontalboNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals - NotesDocument11 pagesStructural Organization in Animals - NotesAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- 14 Nervous SystemDocument89 pages14 Nervous SystemJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Oral Mech Cranial Nerve Assessment: © 2021 Medical Slps LLCDocument17 pagesOral Mech Cranial Nerve Assessment: © 2021 Medical Slps LLCsahar.sheayto.18No ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous Systemsalmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Implant Supported Fixed ProsthesisDocument32 pagesImplant Supported Fixed ProsthesisShabeel PnNo ratings yet
- Symptom Conductive Hearing Loss.3Document3 pagesSymptom Conductive Hearing Loss.3Muhammad Pringgo ArifiantoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Q&aDocument627 pagesFinal Exam Q&aReut shapiraNo ratings yet
- Curly Kids Guide 11-20 PDFDocument4 pagesCurly Kids Guide 11-20 PDFMorgana MedradoNo ratings yet
- Pulpectomy in Primary TeethDocument28 pagesPulpectomy in Primary TeethLily BrostNo ratings yet
- (Series in Radiology 24) Raad H. Mohiaddin MD, MSC, Donald B. Longmore FRCS, FRCR (Auth.) - MRI Atlas of Normal Anatomy-Springer Netherlands (1992)Document200 pages(Series in Radiology 24) Raad H. Mohiaddin MD, MSC, Donald B. Longmore FRCS, FRCR (Auth.) - MRI Atlas of Normal Anatomy-Springer Netherlands (1992)Tina SNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Part 1Document6 pagesNervous System Part 1rb YangzonNo ratings yet
- A 3D Printed Surgical Analogue To Reduce Donor Tooth Trauma During AutotransplantationDocument8 pagesA 3D Printed Surgical Analogue To Reduce Donor Tooth Trauma During AutotransplantationAdriana BragaNo ratings yet
- Perio RestorativeDocument5 pagesPerio RestorativeErdeli StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Gellis - Self Care Facial Cupping and Gua Sha - Read-OnlyDocument25 pagesGellis - Self Care Facial Cupping and Gua Sha - Read-OnlyLukasNo ratings yet
- DD of TeethDocument53 pagesDD of TeethRanjit DanielNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Premolars1Document54 pagesMaxillary Premolars1Parthvi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Facial ExpressionsDocument16 pagesFacial Expressionsoliver naragNo ratings yet
- KennedyDocument4 pagesKennedyAndraClejaNo ratings yet
- Question Chapter 4 Spinal Cord and Ascending, Descending, and Interegmental TractsDocument17 pagesQuestion Chapter 4 Spinal Cord and Ascending, Descending, and Interegmental TractsTrang BuiNo ratings yet
- Norma FrontalisDocument79 pagesNorma Frontalisrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Third Window Lesions of The Inner Ear Quinton Gopen 9-30-09Document163 pagesThird Window Lesions of The Inner Ear Quinton Gopen 9-30-09Mahmoud Az MostafaNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Functions of the Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Structure and Functions of the Nervous SystemArrianne Sjairra PimentelNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 The Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesActivity 6 The Integumentary SystemEmpleo MaryNo ratings yet
- Understanding Neurological AssessmentDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Neurological AssessmentTcx YivcNo ratings yet
- Neurocranium & ViserocraniumDocument8 pagesNeurocranium & ViserocraniumfmandolangNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy of HumansDocument3 pagesDental Anatomy of HumansDeepak VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaDocument50 pagesCase Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaKaren Bianca Matampale EspinolaNo ratings yet
- By: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiDocument24 pagesBy: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiRakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- CantopexieDocument15 pagesCantopexiemnif arefNo ratings yet
- Slides 22 OrbitalMusclesInnervation HeadNeckAnatomyDocument25 pagesSlides 22 OrbitalMusclesInnervation HeadNeckAnatomyAli AdelNo ratings yet
- 2.extraction 2Document64 pages2.extraction 2Moderator Zhi Ling YauNo ratings yet