Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCSE Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Sonia ClaraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
Sonia ClaraCopyright:
Available Formats
www.mymathscloud.
com © MyMathsCloud
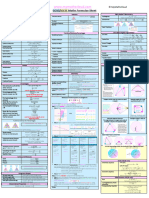
GCSE/iGCSE Maths Formulae Sheet
2D Shapes Statistics Right Angled Trigonometry
! Frequency Density 67/85/-.9
Frequency density = .4,** :)(+; Pythagoras !! + # ! = % !
Area of Triangle x base x height if given hyp⟹subtract, if finding hyp⟹add
"
SOHCAHTOA "## &'( "##
Area of Parallelogram base x height sin * ° =
$%#
, c,- *° =
$%#
, 0!1 *° =
&'(
Pie chart .,+/<379 67/85/-.9
Area of Rectangle !×# Angle= +3+,4
× 360
Area of Trapezoid ! Cumulative frequency This is a running total of the frequencies
× (sum of parallel sides) x height Box Plot
"
Circumference & Area: % = 2(), + = () " Exact Trig Values
Circle
Length of an arc #
× 2()
$%&
Area of a Sector # Fractions/Decimals/Percentages Non Right-Angled Trigonometry
× () " & - /
$%& Sine Rule
Simplifying Fractions Step 1: Find a factor of both numbers i.e. a number that fits in both Finding a side: = =
3D Shapes the numerator AND denominator )*+,
123 ,
)*+.
123 .
)*+0
123 0
Cuboid Surface area 34 = 2#% + 2#7 + 2%7
Step 2: Say how many times for each Finding an angle: = =
Step 3: Check whether you can do steps 1 and 2 again. & - /
where x, y , z are side lengths
Fraction Of Amount
!
of amount Cosine Rule Finding a side: !! = #! + % ! − 2#% cos <
"
Cuboid Volume 8 = #%7 -!6/ !4&!
Step 1: Divide amount by b Finding an angle: < = cos 45 = >
where x, y , z are side lengths Step 2: Multiply answer found by T !-/
Cylinder Surface Area 34 = 29:ℎ + 29: # Improper to Mixed Step 1: Divide the numerator by the denominator. Area of Triangle 1
Step 2: Write down the whole number a !#-@1A
Note: Curved part: 2πrh 2
Step 3: Put the remainder in the numerator. The new denominator & - /
Cylinder Volume 8 = 9: #ℎ remains the same as that of the original improper fraction. Sine Rule Finding a side: = =
)*+, )*+. )*+0
Cone Surface Area 34 = 9:? + 9: # Mixed to Improper Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the fraction’s denominator & - /
Note: Curved part: 9:?, ? is slant length Step 2: Add that to the numerator Finding an angle: = =
)*+, )*+. )*+0
Step 3: Then write the result on the top of the original denominator
Cone Volume 1 Functions
8 = 9: #ℎ + JKL − Fractions Need a common denominator (the smallest number that that both
3 the numerator and denominator fit into) Inverse Replace !(#) with %, swap # & %, solve for %
Sphere Surface Area 34 = 49: # × Fractions Don’t need common denominator.
Note: Hemisphere 39: # Can cancel diagonally or vertically, not horizontally. Composite !((#) means plug ((#) into !(#)
Sphere Volume 4 ÷ Fractions Don’t need a common denominator.
C = 9: $ “Keep change flip” Transformations a=vertical stretch sf ), b=horizontal stretch sf "
!
3
# Decimal to Fraction Write over 10,100,1000 etc depending on how many places after )!(*# + ,) + -
Note: Hemisphere= $ 9: $ the decimal and simplify. c=translation c units x direction, d=translation d
“anything in a bracket affects units in y direction
Prism Volume 8 =Area of cross section x height Decimal to Percent Multiply by 100
!
# and does the opposite” !(−#)=reflcn in %, axis − !(#)=reflcn in # axis
Pyramid Volume 8 = $ × *)EF ):F) × ℎ Fraction to Decimal Write as an equivalent fraction over 10,100,1000 etc and then easy
to divide by this number
Circle Theorems
Indices OR
Use short division if can’t write as an equivalent fraction
Multiplication * & × * - = * &6- Fraction to Percent Turn into a decimal and then just a decimal to percent question i.e. Angle at the centre is double the angle at the circumference
(* & )- = * &- multiply decimal found by 100
Percent to Decimal Divide by 100
(%* & U - )' = % ' * &' U -'
Percent to Fraction Write over 100 and simplify
Division *&
* & ÷ * - = - = * &4- Geometry
*
Negative Powers 1 Straight Line Equation • Slope intercept % = M# + ,
* 4+ = +
* • General )# + *% + - = 0
Fractions ; 4+ %# ; + ;# To get this form we put all the terms from form 1 on one side
=%> = # and =%> = # and multiply all terms by the denominators to get rid of the
; %
+ fractions (if we have them) Angles subtended in the same Angle in a semicircle is a
Fractional Powers $ +
!> = W √!Y Straight Line Gradient/Slope slope =
>!?>% > ?>
OR @%?@! segment by a chord are equal right angle
@!?@%
Percentages Between 2 Points % !
In English this formula just says: subtract the y coordinates and
(#! , %! ), (## , %#) divide by the answer we get by subtracting the U coordinates. It
One amount as a % of the ! as a percentage of " doesn’t matter which way round we subtract, just so long as we
!
other amount × 100
keep the same direction
(wants answer as a %) " Coordinates of midpoint of 2 midpoint = Z
@%&@! >%&>!
, # [
#
Look for the words as a percent of points T#! , %! U , (## , %# ) In English this formula just says: Add the U coordinates and divide
?2@@A9A3BA
Percentage gain/loss × 100 by 2 (i.e. find the average) and add the V coordinates and divide by
C92D237E 2 (i.e. find the average)
(wants answer as a %) Look for the words percentage Distance Between 2 Points distance = ](## − #! )# + (%# − %!)#
gain/loss/increase/decrease (#! , %! ) , (## , %#)
Find percentage of an % Methods to find the equation of a straight line
× amount Tangents which meet at a point are equal Opposite angles of a cyclic
amount 100
D2FA3 7GCH3I in length quadrilateral add to BCD°
Given % of an amount, %
find the full amount &'' We use the letter M to represent slope and , to represent % intercept. If we can find the
gradient M and % intercept , then we are done.
Increasing/decreasing by amount-1 ±
%
/ Step 1: Find the gradient M using one of the following 5 ways
5KK
a% + if increase • Way 1: If given a graph ⟹ pick any 2 points on the graph and use AEF
ABCD
− if decrease
LGCH3I
Reverse percentage %
5±&''
+ if increase ⟹
− if decrease Watch out: All points need
Look for the words originally, at the to be on the circumference!
beginning, before… Alternate segment theorem: A tangent meets a radius at
Pyramid Method For Percentages: The angle between a tangent and a side of ED°
a triangle is equal to the opposite angle
• Way 2: If given a graph ⟹ pick any 2 points on the graph and use the slope formula
Pink horizontal line means divide (÷)
blue line means multiply (×) ⟹ The graph on the left has the following coordinates
• any pair of coordinates.
Pick Told parallel to another
Let’s choose line ⟹
(−3,5) and (3,3)
Cross off what you want and do the resulting operation (multiplication or division)
Note: we use the pyramid on the right if increasing/decreasing by an amount
Simple Interest %
amount + =amount × × time>
5KK
(interest on initial amount) %
Interest = amount × × time Extra helpful facts to remember
5KK
Note: Make sure t and % are same unit of time • Way 3: If given another line parallel to ⟹ locate M for this line and use same slope
' = )* − , ' =*+) ' = −* + . ' = −) + /* ' = ) − .*
Compound Interest (interest N O 0 = 22 − 1 0 =2+2 0 =2+2 Need to re-order Need to re-order
FV = PV=1 + > this first since it is this first
added also earns interest) 5KK We can spot this This means the This means the not in the form 0 =
FV=future value, PV=present value straight away
gradient = 2
same as
0 = 12 + 2
same as
0 = −12 + 4
52 + 6
0 = 32 − 2
0 = −42 + 2
0=time, \= interest rate gradient = −4
gradient = 1 gradient = −1 gradient = 3
Quadratics '+* =. ' − )* = 8 )* + .' = 8 8* − )' = 9 * + )' + 8 = :
We need to use We need to use We need to use We need to use We need to use
Quadratic Function: Solutions 4-±√-!4R&/ For two intersecting chords, the products of their diagonals are equal
*= , !≠0 algebra to re- algebra to re- algebra to re- algebra to re- algebra to re-
to ]^P + _^ + ` = D !& arrange arrange arrange
40 = −22 + 5
arrange
−20 = −52 + 7
arrange
!# = %F !(! + #) = %(% + F)
0 = −2 + 4 0 = 22 + 5 20 = −2 − 5
−22 + 5 −52 + 7
Completing The Square - ! -! 0= 0=
! =* ± > +%− This means the 4 −2
0=
−2 − 5
]^P ± _^ + ` = D !& R& same as gradient = 2 We can split this up
in order to separate
We can split this up
in order to separate
2
We can split this up
Max/Min Value -! 0 = −12 + 4 the gradient and 0 the gradient and 0 in order to separate
% − intercept intercept the gradient and 0
R& gradient = −1 intercept
2 5 5 7
Compound Measures 0=− 2+
4 4
0= 2−
2 2 1
0=− 2−
5
2 2
Speed ()*+,-./ We can simplify the #
speed= +)1/ fraction
gradient = "
!
gradient = − "
1,** 1 5
Density density= 23451/ 0=− 2+
2 4 Series (iGCSE only)
Pressure 637./
pressure= ,7/,
!
gradient = − " Arithmetic sequence: IJK term:
• Way 4: If given another line old perpendicular to ⟹ locate M for this line and don’t u3 = a + (n − 1)d
use the same slope but instead ”flip the fraction and change the sign” (this I just the sum of n terms
Pink horizontal line means divide (÷) n 1
Green vertical line means multiply (×) fact that perpendicular slopes multiply to make −1. S3 = [2a + (n − 1)d] = (! + P)
o
#
If a line has slope 2 Wnote: this means the same as $b then a perpendicular slope is − #
$
2 2
o
#
If a line has slope − % then a perpendicular slope is #
% ! =first term, d= common diff, P=last term
cross off what you want and do the resulting operation (multiplication or division) $ Geometric sequence: u3 = ar 345
o If a line has slope % then a perpendicular slope is −3
Congruent Shapes • Way 5: If given 2 points ⟹ use formula
>!?>%
S3 =
7(549")
=
7(9"45)
,r≠1
@!?@% 549 945
SSS (side side side) Three sides of each triangle equal where ! =first term, r= common ratio
Step 2: Find the _ intercept ` using one of the following 2 ways
SAS (side angle side) Two sides and included angle equal • reading it off the graph (if given the graph this is where the graph crosses the % axis Differentiation (iGCSE only)
AAS (angle angle side) Two angles and corresponding side equal • plugging the point given (#, %) into the equation (replace # with the # value and %
RHS (right hypotenuse leg) Contains right angle and hypotenuse and with the % value).
Rule * + ⟹ 1* +45
Remember: Constants go to 0
another side equal '%
Make sure the slope M from step 1 is plugged in and solve/re-arrange for , using Turning/Stationary Points Solve =0
RHS (right hypotenuse leg) Contains right angle and hypotenuse and algebra. Make sure you plug in the correct point that the line passes through, not ';
(Max/Min)
another side equal just any point. Proving whether Max/Min Use knowledge of shape of graph
Direct/Indirect Proportion U is … proportional to * Circles (# − ))# + (% − *)# = : # +* ! happy face min
S centre (), *), radius :
Directly: U = b* , Inversely: U = −* ! sad face max
; <
+* max on left, min on right
<
−* min on left, max on right
You might also like
- GCSE Formula SheetDocument1 pageGCSE Formula Sheetaadilmiah2019No ratings yet
- GCSE Formula SheetDocument1 pageGCSE Formula SheetSara AyaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Formula SheetDocument1 pageGCSE Formula SheetShahzeb AliNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Formula SheetDocument1 pageAP Calculus AB Formula SheetArad zeinaliNo ratings yet
- Dzexams 3am Mathematiques 334343Document3 pagesDzexams 3am Mathematiques 334343bennacer.mansourNo ratings yet
- Deflection of Beams NotesDocument21 pagesDeflection of Beams Notes周暐凱No ratings yet
- LMFI - LAB 2 - Numero de Reynolds PDFDocument5 pagesLMFI - LAB 2 - Numero de Reynolds PDFMaximiliano Verdugo OrdenesNo ratings yet
- Globalization: A Threat to Cultural Diversity in Southern Ethiopia?From EverandGlobalization: A Threat to Cultural Diversity in Southern Ethiopia?No ratings yet
- A Level Formula SheetDocument1 pageA Level Formula SheetstudierNo ratings yet
- Urdu Se English Seekhen PDFDocument27 pagesUrdu Se English Seekhen PDFMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- 03 PDFDocument6 pages03 PDFMaroua ElbrazziNo ratings yet
- AASHTO LRFD 2014 BridgeDesignSpecifications 7th Ed (US)Document1 pageAASHTO LRFD 2014 BridgeDesignSpecifications 7th Ed (US)dickyNo ratings yet
- Matrices Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesMatrices Cheat Sheetganeshykr100% (6)
- 02Document15 pages02Franc ChedjouNo ratings yet
- Matematicas Empresariales Temario Apuntes Temas 1 5Document77 pagesMatematicas Empresariales Temario Apuntes Temas 1 5JermenNo ratings yet
- Manual Estruturas Mistas 2 1 3Document16 pagesManual Estruturas Mistas 2 1 3Ana Carolina MaiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture25 FilledinDocument3 pagesLecture25 FilledinyonathanNo ratings yet
- Insize Promotion Prices Applicable From 1st Jan, 21 To 30th Apr, 21Document48 pagesInsize Promotion Prices Applicable From 1st Jan, 21 To 30th Apr, 21Vijayakumar Hadron MechNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Rules Chart - 230407 - 124119Document2 pagesDifferentiation Rules Chart - 230407 - 124119Sara AyaNo ratings yet
- Ce Document Est Mis À Disposition Selon Les Termes de La Licence Creative Commons "Attribution - Partage Dans Les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International". HTTPS://WWW - Immae.eu/coursDocument10 pagesCe Document Est Mis À Disposition Selon Les Termes de La Licence Creative Commons "Attribution - Partage Dans Les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International". HTTPS://WWW - Immae.eu/coursEnidroun OutNo ratings yet
- Aalborg Universitet: Wasilewski, J. Wiechowski, Wojciech Tomasz Bak, Claus LethDocument8 pagesAalborg Universitet: Wasilewski, J. Wiechowski, Wojciech Tomasz Bak, Claus LethAwan Uji KrismantoNo ratings yet
- Ce Document Est Mis À Disposition Selon Les Termes de La Licence Creative Commons "Attribution - Partage Dans Les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International". HTTPS://WWW - Immae.eu/coursDocument8 pagesCe Document Est Mis À Disposition Selon Les Termes de La Licence Creative Commons "Attribution - Partage Dans Les Mêmes Conditions 4.0 International". HTTPS://WWW - Immae.eu/coursfatima zaharNo ratings yet
- 10CalcSQLI 6upDocument9 pages10CalcSQLI 6upM UllerNo ratings yet
- Kitab لباب الحديث FullDocument182 pagesKitab لباب الحديث FullAwi OzyNo ratings yet
- HPHT Part 1 IntroductionDocument13 pagesHPHT Part 1 IntroductionCarlos A.No ratings yet
- 15H - Second and Higher DerivativesDocument1 page15H - Second and Higher Derivativesanon_140351515No ratings yet
- WWW Mzos HRDocument2 pagesWWW Mzos HRIvona ŠupićNo ratings yet
- 01Document11 pages01Franc ChedjouNo ratings yet
- 29 ServicescitizenshipandthecountryoforiginprincipleDocument24 pages29 ServicescitizenshipandthecountryoforiginprincipleRevekka TheodorouNo ratings yet
- B+ S/ (+RTDocument1 pageB+ S/ (+RTjeremy876No ratings yet
- April PDFDocument2 pagesApril PDFMSalleh MFNo ratings yet
- Downloadggrenew - Ashx 3Document1 pageDownloadggrenew - Ashx 3talengsak srisatchathornNo ratings yet
- Sound & Mach1Document3 pagesSound & Mach1Abhiyan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Button Attaching Juki mb1800BDocument6 pagesButton Attaching Juki mb1800BSayantan RahaNo ratings yet
- Unit - V Game Theory 4 SideDocument2 pagesUnit - V Game Theory 4 Sidelingeshfortnite9990No ratings yet
- COSCOTDocument9 pagesCOSCOTSuresh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous 2Document20 pagesMiscellaneous 2Gayle MirandaNo ratings yet
- Double Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorDocument4 pagesDouble Angle Identities Worksheet With Graphysc CalculatorErin PhillipsNo ratings yet
- 11 1Document24 pages11 1Selma SenioritaNo ratings yet
- 11Document24 pages11Akram SaidiaNo ratings yet
- Chapitre VI Introduction Aux Ecoulements Turbulents PDFDocument6 pagesChapitre VI Introduction Aux Ecoulements Turbulents PDFHillo MessenNo ratings yet
- בטון 2 עבודה 5Document1 pageבטון 2 עבודה 5loai tumaNo ratings yet
- 7 & C D E D, & Fgeeh Fif - ' Jeek DFLG MeeeDocument6 pages7 & C D E D, & Fgeeh Fif - ' Jeek DFLG Meeefercabr9354No ratings yet
- 2009 Asian Test Symposium 2009 Asian Test Symposium 2009 Asian Test SymposiumDocument2 pages2009 Asian Test Symposium 2009 Asian Test Symposium 2009 Asian Test SymposiumrjnmsdNo ratings yet
- ElectroDocument17 pagesElectroerroumaissae elyoufiNo ratings yet
- Welding Selection ChartDocument1 pageWelding Selection ChartAbhinit KumarNo ratings yet
- AVON E-BroschüreDocument1 pageAVON E-BroschüreDUSKYNo ratings yet
- Math 2ge19 2trim3Document2 pagesMath 2ge19 2trim3Ghiles OularbieNo ratings yet
- Planos ElectricasDocument3 pagesPlanos ElectricasR J Bejarano FernandezNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog - Tools - Contacts - Twin Wire End Ferrules With Plastic Collar - Conductor Nom. Cross-Section 4.0mm - Packed Loose in Polythene BagDocument1 pageProduct Catalog - Tools - Contacts - Twin Wire End Ferrules With Plastic Collar - Conductor Nom. Cross-Section 4.0mm - Packed Loose in Polythene BagGabriel Rodriguez GigireyNo ratings yet
- Ste Ta PavaiDocument19 pagesSte Ta PavaiSubrahmanyam PendyalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document1 pageChapter 10halharbi0568No ratings yet
- Worked Examples of Gradient Evaluation: Note Immediately That Is A Vector Field!Document1 pageWorked Examples of Gradient Evaluation: Note Immediately That Is A Vector Field!IITD MEMNo ratings yet
- Dive Planning WorksheetDocument4 pagesDive Planning Worksheetunderwater_archaeology100% (7)
- GP11 General Procedure For Pre-Production-Prototype Parts PDFDocument12 pagesGP11 General Procedure For Pre-Production-Prototype Parts PDFmpedraza-1No ratings yet
- Viewcontent CgiDocument14 pagesViewcontent CgiThe English TeacherNo ratings yet
- Three Approaches From Europe: Waldorf, Montessori, and Reggio EmiliaDocument14 pagesThree Approaches From Europe: Waldorf, Montessori, and Reggio EmiliaThe English TeacherNo ratings yet
- FUSE GGDocument1 pageFUSE GGmuhamad.badar9285No ratings yet
- Question On Hardware - Software-Storage 4it01 PDFDocument28 pagesQuestion On Hardware - Software-Storage 4it01 PDFAsif Zubayer PalakNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management in Indonesia: Important Issues to Know before Establishing a Subsidiary in IndonesiaFrom EverandHuman Resource Management in Indonesia: Important Issues to Know before Establishing a Subsidiary in IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - IRN Fab Transfer PCN NoticeDocument22 pagesMicrosoft Word - IRN Fab Transfer PCN NoticeJadilson PradoNo ratings yet
- ScilabDocument4 pagesScilabAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNo ratings yet
- Visedo FPC-2016Document13 pagesVisedo FPC-2016Probonogoya Erawan SastroredjoNo ratings yet
- Ansible Automation SA Technical Deck Q2FY19Document43 pagesAnsible Automation SA Technical Deck Q2FY19daniel_vp21No ratings yet
- 1 Name of Work:-Improvement of Epum Road (Northern Side) Connecting With Imphal-Saikul Road I/c Pucca DrainDocument1 page1 Name of Work:-Improvement of Epum Road (Northern Side) Connecting With Imphal-Saikul Road I/c Pucca DrainHemam PrasantaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument8 pagesPDFDocNo ratings yet
- Mercedes (DTC) 976990001963 20220615144147Document3 pagesMercedes (DTC) 976990001963 20220615144147YB MOTOR Nissan - Datsun SpecialistNo ratings yet
- Ultimate GuideDocument33 pagesUltimate GuidemrosamusicNo ratings yet
- PalmistryDocument116 pagesPalmistrymarinoyogaNo ratings yet
- Sindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionDocument192 pagesSindarin-English Dictionary - 2nd EditionNea Tan100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document82 pagesChapter 2Kavitha Selvaraj50% (2)
- With EU Stage V Engine Installed: 200 HP (149 KW) / 2,200 RPMDocument4 pagesWith EU Stage V Engine Installed: 200 HP (149 KW) / 2,200 RPMSara Sarmiento EcheverryNo ratings yet
- 100 Yer PM PPM 0605Document40 pages100 Yer PM PPM 0605biplabpal2009No ratings yet
- Novel Image Enhancement Technique Using CLAHE and Wavelet TransformsDocument5 pagesNovel Image Enhancement Technique Using CLAHE and Wavelet TransformsInnovative Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Food - Forage - Potential - and - Carrying - Capacity - Rusa Kemampo - MedKonDocument9 pagesFood - Forage - Potential - and - Carrying - Capacity - Rusa Kemampo - MedKonRotten AnarchistNo ratings yet
- Arc 2019-2020Document95 pagesArc 2019-2020AEN HTM DD1 HTM DD1No ratings yet
- The Failed Rotator CuffDocument307 pagesThe Failed Rotator Cufforthofitness2017No ratings yet
- Adminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDocument3 pagesAdminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDenise CastroNo ratings yet
- Working at Heights GuidelineDocument15 pagesWorking at Heights Guidelinechanks498No ratings yet
- TR189 Kathuria PDFDocument168 pagesTR189 Kathuria PDFuqiNo ratings yet
- EASA - Design OrganisationsDocument30 pagesEASA - Design Organisationsyingqi.yangNo ratings yet
- Macleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusDocument2 pagesMacleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusSIMONE BLAIRNo ratings yet
- HardikDocument21 pagesHardikGohil HardikNo ratings yet
- Phineas Gage: From The Passage of An Iron Rod Through The Head"Document1 pagePhineas Gage: From The Passage of An Iron Rod Through The Head"GlupiaSprawaNo ratings yet
- VAM Must Sumitomo 1209 PDFDocument4 pagesVAM Must Sumitomo 1209 PDFnwohapeterNo ratings yet
- Taper Lock BushesDocument4 pagesTaper Lock BushesGopi NathNo ratings yet
- High Performance Dialysis GuideDocument28 pagesHigh Performance Dialysis GuideRoxana ElenaNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones Postoperatorias en Esofagectomía Por Cáncer. Evaluación de 215 Casos Según Definiciones Del Grupo de Consenso InternacionalDocument7 pagesComplicaciones Postoperatorias en Esofagectomía Por Cáncer. Evaluación de 215 Casos Según Definiciones Del Grupo de Consenso InternacionalPaulo RoseroNo ratings yet
- Magneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionDocument18 pagesMagneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- From Science To God by Peter RussellDocument6 pagesFrom Science To God by Peter RussellFilho adulto pais alcolatrasNo ratings yet