Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Free Temwala Ad10k Stetm Free 100%
Uploaded by
wifik31459Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Free Temwala Ad10k Stetm Free 100%
Uploaded by
wifik31459Copyright:
Available Formats
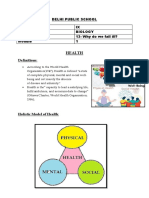
What Is Health?
In simple terms, Health can be defined as being free from all diseases and
infections. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), health is not only
the absence of disease or illness. It is a state of an active and energetic
condition, including physical, mental, and social well-being. A balanced diet and
regular exercise play an important role in maintaining the good health of an
individual. There are many factors which affect health, such as:
Poorly balanced diet
Genetic disorders
Stress and anxiety
Infection from pathogens
Intake of unhealthy and unhygienic food
Lack of exercise and other physical activities
To maintain good health, an individual should include a healthy and balanced diet
and maintain personal hygiene along with regular exercise and other physical
activities. Everyone should be aware of the different types of diseases and their
effects.
Read More: Important Questions for Class 12 Chapter 8: Human Health and Diseases
What Are Diseases?
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting a healthy living organism. It is
broadly divided into infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious diseases- These diseases are caused by the pathogens, such as bacteria,
viruses, fungi, and parasites and can be easily transmitted from one person to
another; hence it is also known as a contagious or communicable disease. Common
Cold, Tuberculosis, flu, ringworm, and malaria are some examples of infectious
diseases.
Non-infectious diseases- Diseases which cannot be transmitted from one person to
another are called non-infectious disease, it is also known as non-communicable
disease. These diseases can be either caused by genetic disorders, unhealthy diets,
lack of physical activity and a few environmental factors.
Some Common Diseases in Humans
A pathogenic bacterium known as Salmonella typhi is known to cause typhoid in
humans. This fever can be confirmed by the Widal test.
Pneumonia is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Hemophilus influenza.
Rhinovirus, a group of viruses, is known to cause one of the most infectious
ailments in humans, cold.
Plasmodium, a small protozoan, causes malaria. Another protozoan, Entamoeba
histolytica, causes amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery).
Ascaris(an intestinal parasite) causes ascariasis.
Wuchererta, the filarial worm, causes filariasis or elephantiasis.
Immunity
Immunity is defined as the ability of the body to protect, defend and fight against
invading pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and other foreign bodies and toxic
substances. There are two types of immunity.
Innate immunity – non-specific defence type of immunity present at the time of
birth achieved by the provision of 4 barrier types – the physical barrier,
physiological barrier, cellular barrier, and cytokine barrier.
Acquired immunity – pathogen-specific immunity that is characterized by memory.
Active and Passive Immunity
Active immunity is where the host produces antibodies in the form of dead or living
microbes when it is exposed to antigens. It is a slow process, taking time to
provide its full effective response. Passive immunity, on the other hand, is the
immunity where ready-made antibodies are given directly to protect the body against
any foreign agents.
AIDS
Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome is caused by HIV(Human Immunodeficiency Virus),
a member of the retrovirus group.
It is generally transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person, blood
transfusion with contaminated blood and its products, through the share of infected
needles, from the infected mother to her child through the placenta. ELISA(Enzyme-
linked immunosorbent assay) is the diagnostic test for AIDS.
You might also like
- Lyme Disease Booklet1 PDFDocument42 pagesLyme Disease Booklet1 PDFBetty100% (1)
- Vaccine free Healthy in a Viral Epidemic How to Prevent Virus Infections Vaccine-Free with Three Effective Antiviral StrategiesFrom EverandVaccine free Healthy in a Viral Epidemic How to Prevent Virus Infections Vaccine-Free with Three Effective Antiviral StrategiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Pass Program ClueDocument851 pagesPass Program Clueshafat001100% (2)
- Nishi's QB - PhathoDocument42 pagesNishi's QB - PhathofrabziNo ratings yet
- Insertion and Removal of Intrauterine Devices-AAFPDocument8 pagesInsertion and Removal of Intrauterine Devices-AAFPnouval_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology Exam Questions and AnswersDocument107 pagesEpidemiology Exam Questions and Answersdimitrios82% (34)
- 474-1 Intro and History of MicrobiologyDocument46 pages474-1 Intro and History of MicrobiologybenjamingNo ratings yet
- CALIBRATE IMSE Answer Key by Sir CarlDocument5 pagesCALIBRATE IMSE Answer Key by Sir CarlMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Rabies Control Program by DohDocument11 pagesRabies Control Program by DohSabrina Porquiado Magañan SNNo ratings yet
- Best - Dysbioprotocols 10Document12 pagesBest - Dysbioprotocols 10MavisNo ratings yet
- Fighting the Virus: How to Boost Your Immune Response and Fight Viruses and Bacteria Naturally: Essential Spices and Herbs, #14From EverandFighting the Virus: How to Boost Your Immune Response and Fight Viruses and Bacteria Naturally: Essential Spices and Herbs, #14No ratings yet
- BETEL (Piper Betle) LEAVES EXTRACT AS ANTIBACTERIAL DISINFECTANT SPRAYDocument56 pagesBETEL (Piper Betle) LEAVES EXTRACT AS ANTIBACTERIAL DISINFECTANT SPRAYAbigail MonisNo ratings yet
- 12 Bio Notes 100% FreeDocument2 pages12 Bio Notes 100% Freewifik31459No ratings yet
- Class 9 - How Do We Fall Ill - ScienceDocument9 pagesClass 9 - How Do We Fall Ill - Scienceamir anwarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Revision NotesDocument48 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Revision Notesdevesh saiNo ratings yet
- Ce Elect 1 Sanitary Engineering Disease and ImmunityDocument12 pagesCe Elect 1 Sanitary Engineering Disease and ImmunityRiJade Bibiano100% (3)
- Question Answers Ch-13Document4 pagesQuestion Answers Ch-13AnamikaNo ratings yet
- GR - 9 - Revision Notes - Why We Do Fall IllDocument9 pagesGR - 9 - Revision Notes - Why We Do Fall IllAditi KumariNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus) : Kelompok: 1.desy Puspitasari 2.indah Sari 3.reni Hayati A. 4.roro Asih SDocument15 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus) : Kelompok: 1.desy Puspitasari 2.indah Sari 3.reni Hayati A. 4.roro Asih SRoro AshNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Presentación de Microsoft PowerPointDocument7 pagesNuevo Presentación de Microsoft PowerPointXiao LiuNo ratings yet
- Human Health and Diseases by Ahmed OmaarDocument3 pagesHuman Health and Diseases by Ahmed OmaarAhmed OmaarNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall IllDocument15 pagesWhy Do We Fall IllShiv ShivaNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Class IX Subject Biology 13-Why Do We Fall Ill? 1Document6 pagesDelhi Public School Class IX Subject Biology 13-Why Do We Fall Ill? 1Shreyashkar JhaNo ratings yet
- Health and DiseaseDocument3 pagesHealth and DiseaseMehbub LaskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Why Do We Fall Ill: 1. Health and Its FailureDocument3 pagesChapter 13 - Why Do We Fall Ill: 1. Health and Its FailureSahil Gupta100% (1)
- Human Health and Disease-1Document53 pagesHuman Health and Disease-1Aman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Human Health and DiseasesDocument18 pagesNotes On Human Health and Diseasesraushankumar05072No ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument10 pagesHealth Educationrjay pascualNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument10 pagesHealthAthul ShajiNo ratings yet
- Health & Disease Unit IV Part IDocument42 pagesHealth & Disease Unit IV Part Irajx2shekharNo ratings yet
- Health: Why Do We Fall IllDocument5 pagesHealth: Why Do We Fall IllPapu BapiNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument10 pagesInfectious DiseasesAgnes Marie RendonNo ratings yet
- 13 QN ANSWRS Why Do We Fall IllDocument3 pages13 QN ANSWRS Why Do We Fall IllceoNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument54 pagesHuman Health and Diseaseayushtak001No ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument59 pagesHuman Health and Diseasesaryan aggarwal100% (1)
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument54 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseTirth TupeNo ratings yet
- Pa3 Set 2exam Paper Set 2.Document4 pagesPa3 Set 2exam Paper Set 2.Harsh vardhan singh XI-DNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument31 pagesPath o PhysiologyjayamohanNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH 13 Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Th Science: Topics in The ChapterDocument7 pagesNotes of CH 13 Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Th Science: Topics in The ChaptermallikaNo ratings yet
- VaccineDocument2 pagesVaccinedarshan baskarNo ratings yet
- Health and Its FailureDocument10 pagesHealth and Its FailureAmit KasniaNo ratings yet
- Notes Why Do We FallDocument4 pagesNotes Why Do We FallRohit JainNo ratings yet
- CH 13 - Why Do Fall Ill - SA Type 2Document7 pagesCH 13 - Why Do Fall Ill - SA Type 2vishnu babuNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseasesDocument10 pagesHuman Health and Diseasesmiranpathan2424No ratings yet
- Antibiotics, Vaccines and Diseases-1Document38 pagesAntibiotics, Vaccines and Diseases-1Siraj Jan SoomroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01: Modern Technologies That Help in The Control of DiseasesDocument17 pagesLesson 01: Modern Technologies That Help in The Control of Diseasesjayar0824No ratings yet
- Antibiotics For CssDocument38 pagesAntibiotics For CsstayyabsaifNo ratings yet
- (Third Quarter) HEALTHDocument44 pages(Third Quarter) HEALTHMary Rose DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Health PDFDocument25 pagesLesson 4 Health PDFRomeo BalingaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 Why Do We Fall Ill: Notes Class:Ix Biology Page 1 ofDocument8 pagesChapter - 13 Why Do We Fall Ill: Notes Class:Ix Biology Page 1 ofKhatrasNo ratings yet
- Health and HygieneDocument13 pagesHealth and HygieneSonam ParaswaniNo ratings yet
- TP 1Document8 pagesTP 1nitesh tirkeyNo ratings yet
- Class 12Document17 pagesClass 12Jitendra Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- PW DiseaseDocument3 pagesPW DiseaseLaxman ThapaNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Falling IllDocument22 pagesReasons For Falling IllNarayanaNo ratings yet
- Human Health and Disease Part 1 NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Health and Disease Part 1 NotesDeepanshu GaurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pathophysiology Lecture1Document30 pagesIntroduction To Pathophysiology Lecture1infofact849No ratings yet
- Aki Ola Shs Text BookDocument1 pageAki Ola Shs Text BookmargaretboronsumNo ratings yet
- Types of Diseases PDFDocument11 pagesTypes of Diseases PDFCherry CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 14.04.20 IIDocument22 pagesUnit 1 14.04.20 IIDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- IX Bio Ch4 Ill KeylearningsDocument4 pagesIX Bio Ch4 Ill KeylearningsPriya DharshniniNo ratings yet
- NSTP Unit 4Document14 pagesNSTP Unit 4Sophie DatuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: "Why Do We Fall Ill?"Document4 pagesChapter 13: "Why Do We Fall Ill?"Vivek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Identify The Differences Between Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and ParasitesDocument4 pages1.1 Identify The Differences Between Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and ParasitesgemmaNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill PDFDocument3 pages09 Science Notes ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill PDFthiruNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall Ill 2Document3 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill 2Shreyashkar JhaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 1 PDFDocument36 pagesPathophysiology 1 PDFAsifa Bhutto100% (1)
- PPDCDocument13 pagesPPDCGAYATHRI100% (1)
- Journal IcuDocument2 pagesJournal IcuRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PathologyDocument114 pagesMicrobiology Pathologykhaleelkhamjan100% (1)
- Aki & CKDDocument61 pagesAki & CKDChengzhi KhorNo ratings yet
- Biology Pre - Board Class 12Document4 pagesBiology Pre - Board Class 12priyanshuvaibhav1301No ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis: Assessment and CareDocument51 pagesNeonatal Sepsis: Assessment and CareParbatiNo ratings yet
- Fever in Children PDFDocument2 pagesFever in Children PDFDaerobbi NurwansyahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - 13.01.2023Document33 pagesLecture 9 - 13.01.2023Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 and DiabetesDocument3 pagesCOVID 19 and DiabetesAynun JMNo ratings yet
- C+F-Spirometra İnfection in Cats and DogsDocument5 pagesC+F-Spirometra İnfection in Cats and Dogstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Its Haematological Correlates-1Document8 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis and Its Haematological Correlates-1mentari_64No ratings yet
- Asacs - Newsletter - Apr - Jun - 2010 - Final & Rectified On 11-10-10Document24 pagesAsacs - Newsletter - Apr - Jun - 2010 - Final & Rectified On 11-10-10devainetNo ratings yet
- Sharma Et Al 2017Document8 pagesSharma Et Al 2017Kryzn NNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Incident ReportDocument1 pageInfection Control Incident ReportyolandaNo ratings yet
- Free TOEFLPractice TestDocument35 pagesFree TOEFLPractice TestMonkey Monkey100% (1)
- Rapid Plasma Reagin 2020Document6 pagesRapid Plasma Reagin 2020REMAN ALINGASANo ratings yet
- Health Facts Covid 19 Fast Facts About CovidDocument2 pagesHealth Facts Covid 19 Fast Facts About Covidanastacia arceNo ratings yet
- Patho Respiratory - KatherineDocument9 pagesPatho Respiratory - KatherineKayla MayerNo ratings yet
- The Microbial World and YouDocument4 pagesThe Microbial World and Youanum786110No ratings yet
- HCC Surveillance in An Era of BiomarkersDocument48 pagesHCC Surveillance in An Era of BiomarkersRobert G. Gish, MDNo ratings yet
- Pulp Revascularization of A Necrotic Infected Immature Permanent Tooth: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument4 pagesPulp Revascularization of A Necrotic Infected Immature Permanent Tooth: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureRiad BachoNo ratings yet