Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kaplan Anatomy
Uploaded by
Beto RendonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kaplan Anatomy
Uploaded by
Beto RendonCopyright:
Available Formats
Visi t w w w . a f r a t a f r e e h .
co m f o r m o r e
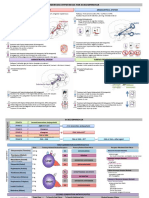
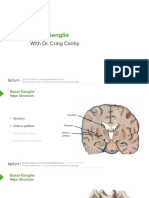
Chapter 7 l Basal Ganglia
Cortex
Note
Both basal ganglia pathways utilize
Glutamate 2 GABA neurons in series, and a
Indirect
Input center “disinhibition.”
Globus pallidus GABA/Enkephalin Striatum
external segment (acetylcholine)
GABA/
Dopamine Note
Direct Substance P Dopamine drives the direct pathway;
GABA
Substantia nigra acetylcholine (ACh) drives the indirect
pars compacta pathway.
Subthalamic Globus pallidus Substantia nigra
nucleus Glutamate internal segment pars reticulata
Sostanen migra
:
Output center GABA
⑯
Thalamus Ventral anterior/
ventral lateral Dopamine
thalamic nuclei
/ I S
Clear arrows: excitatory Supplementary
Shaded arrows: inhibitory motor area Dir D 28
*S
G:
↳s E
Figure III-7-2. BasalIII-7-2.
Figure Ganglia Pathways
b ⑯
Via Dirc ta
↑
Indirectl
Dopamine and cholinergic effects /planca to I no plancabol
In addition to the GABA neurons, 2 other sources of chemically significant neu-
rons enhance the effects of the direct or indirect pathways.
Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra in the midbrain project to the
striatum. The effect of dopamine excites or drives the direct pathway, increasing
cortical excitation. Dopamine excites the direct pathway through D1 receptors
and inhibits the indirect pathway through D2 receptors.
Cholinergic neurons found within the striatum have the opposite effect. Acetyl-
choline (Ach) drives the indirect pathway, decreasing cortical excitation.
88
319
You might also like
- Vesicular and Cell Membrane Transporters.: Atpase From InsideDocument5 pagesVesicular and Cell Membrane Transporters.: Atpase From InsidejttodayNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument24 pagesBasal Gangliabrittany AcheampongNo ratings yet
- Neurontransmitters Chart-1Document3 pagesNeurontransmitters Chart-1kedawNo ratings yet
- Neuro Block 2 - Part 1 (Edit)Document13 pagesNeuro Block 2 - Part 1 (Edit)Miguel MansillaNo ratings yet
- ZilniceDocument23 pagesZilnice5cm46hysvxNo ratings yet
- Parkinson Disease: DR Selly Marisdina, SP.SDocument39 pagesParkinson Disease: DR Selly Marisdina, SP.Sanggun rahmania100% (1)
- Poor Unfortunate Souls: From THE LITTLE MERMAID (2023)Document4 pagesPoor Unfortunate Souls: From THE LITTLE MERMAID (2023)Edward ThrumNo ratings yet
- 2019 Pain and OpioidsDocument38 pages2019 Pain and Opioidsgowod86101No ratings yet
- By Dr. AlabastroDocument9 pagesBy Dr. Alabastro2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugskv 14No ratings yet
- Pregnenolone Trial in Autism-A Neurosteroid Approach 2016Document23 pagesPregnenolone Trial in Autism-A Neurosteroid Approach 2016redmi karimNo ratings yet
- NHB SuppoDocument11 pagesNHB SuppoAna-Roberta NitaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SampleDocument3 pagesPharmacology SampleGeeta AdhikariNo ratings yet
- 2018 Structure of A Human Synaptic GABAa Receptor - CompressedDocument22 pages2018 Structure of A Human Synaptic GABAa Receptor - CompressedVitoria LimaNo ratings yet
- Https - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 16 Fly DLB 00061 Eng Notch PW Handout SMDocument2 pagesHttps - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 16 Fly DLB 00061 Eng Notch PW Handout SMtamaraNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HypothesisDocument2 pagesDopamine HypothesisBo123456100% (3)
- PD Topic OutlineDocument3 pagesPD Topic OutlineEUNICE CORILLONo ratings yet
- NEUROLOGIDocument8 pagesNEUROLOGINasrudin EfendiNo ratings yet
- Indra Penglihatan FixDocument8 pagesIndra Penglihatan FixRimayaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Epilepsy: Nandit P BDocument53 pagesPharmacotherapy of Epilepsy: Nandit P BNandit BanawalikarNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument5 pagesBasal Gangliai gede ricky jaya purnawarmanNo ratings yet
- CVS Drugs NotesDocument13 pagesCVS Drugs NotesTara LeungNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatments For Neurodegeneration: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesDrug Treatments For Neurodegeneration: ObjectivesNur FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Major Brain Regions and Their Major Interconnections (김Document2 pagesMajor Brain Regions and Their Major Interconnections (김신윤상0% (1)
- Movement Disorder TreatmentsDocument3 pagesMovement Disorder TreatmentsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Bio ZDocument1 pageBio ZsaharNo ratings yet
- Notch SignalingDocument2 pagesNotch SignalingMelanieNo ratings yet
- Tripartite SynapseDocument1 pageTripartite SynapseYusuf JunetNo ratings yet
- Night Scan Powerlite ECDDocument2 pagesNight Scan Powerlite ECDSUNIL MISHRANo ratings yet
- Neural Structures Involved in The Control of MovementDocument68 pagesNeural Structures Involved in The Control of MovementSAYAN NAGNo ratings yet
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1Document42 pagesNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1pp100% (1)
- Pharmacology Final Drug TablesDocument388 pagesPharmacology Final Drug TablesTJNo ratings yet
- Shreya Poster May21 JTS - Shreya SriramDocument1 pageShreya Poster May21 JTS - Shreya SriramnurjNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmissionDocument66 pagesNeurotransmissionSheik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument1 pageChemotherapy Drugsmp658t952dNo ratings yet
- NeigeDocument26 pagesNeigeAchmad Nur AffendickNo ratings yet
- Guide For Nuclide ChartDocument2 pagesGuide For Nuclide ChartRufino RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PriseChargeTherapEpilepsie Navarro 2015Document43 pagesPriseChargeTherapEpilepsie Navarro 2015Aya KheNo ratings yet
- Biological Activities of Piri-Piri: (Cyperus Articulatus)Document3 pagesBiological Activities of Piri-Piri: (Cyperus Articulatus)zsebpapNo ratings yet
- Indian Rivers SystemDocument10 pagesIndian Rivers SystemMeena VipinNo ratings yet
- Part One: Overture and Pageantry : TenderlyDocument6 pagesPart One: Overture and Pageantry : TenderlyEneas Augusto100% (1)
- The Great Sea The Great Sea: The Legend of Zelda: The Wind WakerDocument2 pagesThe Great Sea The Great Sea: The Legend of Zelda: The Wind WakerGabriel VizcainoNo ratings yet
- 2-EAS Presentation Sideney Alkemist LabsDocument33 pages2-EAS Presentation Sideney Alkemist LabsFernando PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Notch Signaling - Cell Signaling TechnologyDocument3 pagesNotch Signaling - Cell Signaling Technologyasadbiotech4No ratings yet
- Gateway - Arima W350DI PDFDocument44 pagesGateway - Arima W350DI PDFJose BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chandini Rao Moderator: Dr. Princy PallattyDocument52 pagesDr. Chandini Rao Moderator: Dr. Princy PallattySaqib ChandNo ratings yet
- GRAPHDocument11 pagesGRAPHAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Sym&Parasym DrugsDocument2 pagesMind Map Sym&Parasym Drugsjitpinun.sNo ratings yet
- Phantom Selections - Barker - BassesDocument4 pagesPhantom Selections - Barker - BassescatherinedonaldNo ratings yet
- Gaba Receptors: Subtypes, Regional Distribution, and FunctionDocument5 pagesGaba Receptors: Subtypes, Regional Distribution, and FunctionKresna WicaksanaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medication ChartDocument2 pagesRespiratory Medication Chartchandangm56No ratings yet
- Slides 14 BasalGanglia BrainAndNervousSystemDocument18 pagesSlides 14 BasalGanglia BrainAndNervousSystemNicole YatawaraNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument53 pagesAnxiolyticsHenock AsfawNo ratings yet
- Ganglios BasaleDocument3 pagesGanglios BasaleCarlos BuitragoNo ratings yet
- GABA cAMPDocument71 pagesGABA cAMPsuweino_harunNo ratings yet
- All Trouble Shoot Rev3Document22 pagesAll Trouble Shoot Rev3Claudio PereiraNo ratings yet
- DG85 Ti06Document2 pagesDG85 Ti06Metalurgica VISILUNo ratings yet
- Adrenal CortexDocument8 pagesAdrenal CortexEdward Xiam100% (1)
- Neuro Basal GangliaDocument14 pagesNeuro Basal GangliaFu Xiao ShanNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument13 pagesBasal GangliaVivek PNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument51 pagesCerebellumLiya ThaaraNo ratings yet
- DistoniaDocument23 pagesDistoniaOsvaldo CortésNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Basal Ganglia: James Knierim, Ph.D. Department of Neuroscience The Johns Hopkins UniversityDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Basal Ganglia: James Knierim, Ph.D. Department of Neuroscience The Johns Hopkins Universityayumi himuraNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument41 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemhijrah nafeerNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument11 pagesBasal GangliaSTEVEN OKURUTNo ratings yet
- 2018 DystoniaDocument23 pages2018 DystoniaTony NgNo ratings yet
- Https Emedicine - Medscape.com Article 1831191-PrintDocument59 pagesHttps Emedicine - Medscape.com Article 1831191-PrintNoviatiPrayangsariNo ratings yet
- Basalganglia 160304172613 PDFDocument49 pagesBasalganglia 160304172613 PDFamna rashidNo ratings yet
- Frenkel Exercise Protocol For Patient With Parkinsons DiseaseDocument39 pagesFrenkel Exercise Protocol For Patient With Parkinsons DiseaseHumaira Rahman0% (1)
- Pocket Neurology (Pocket Notebook Series) (PDFDrive)Document659 pagesPocket Neurology (Pocket Notebook Series) (PDFDrive)Kirstine Gail Zingalawa-EfacNo ratings yet