Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shreya Poster May21 JTS - Shreya Sriram
Uploaded by
nurjOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shreya Poster May21 JTS - Shreya Sriram
Uploaded by
nurjCopyright:
Available Formats
Spontaneous Auditory Neuron Activity
Shreya Sriram ,
1 George Ordiway 1 & Jason Tait Sanchez1,2,3
1Roxelyn and Richard Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders, 2Knowles Hearing Research Center, 3Department of Neurobiology, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL. USA
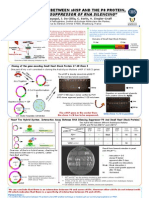
Abstract NMc sEPSCs AMPA-R Mediated sEPSCs
Synaptic connections between neurons is typically established through AMPA-R & GABAA-R AMPA-R Mediated GABAA-R Mediated AMPA-R Mediated AMPA-R Blocker Washout
spontaneous activity in vertebrates. Spontaneous activity is the occurrence of A Mediated sEPSCs B sEPSCs C sEPSCs A sEPSCs B (+CNQX) C (-CNQX)
neuronal events – such as intrinsic action potentials (APs) or postsynaptic
currents – in the absence of external stimuli. Generally, when a neuron is
isolated in a brainstem slice, spontaneous activity is not seen because
physiological conditions are not applicable. However, we have previously
reported spontaneous intrinsic AP activity in a subgroup of neurons in the
avian auditory brainstem (termed NMc). The goal of this project aimed to +PTX & AP-V +CNQX & AP-V +PTX & AP-V +PTX & AP-V +PTX & AP-V
characterize spontaneous synaptic activity of NMc neurons. We identified 0
spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) that were mediated
by ionotropic AMPA receptors (AMPA-Rs) and GABAA receptors (GABAA-Rs).
D D
Amplitude (pA)
Background
sEPSC Frequency (#)
A B
Figure 4: AMPA-R mediated sEPSCs from a NMc neuron. Example traces acquired before (A),
during (B), and after (C) bath application of CNQX (AMPA-R blocker). (B) Average amplitude before
and after AMPA-R blocker. Error bars = standard error of the mean.
GABAA-R Mediated sEPSCs
E
GABAA-R Mediated GABAA-R Blocker Washout
A B C
sEPSC Amplitude (pA)
sEPSCs (+PTX) (-PTX)
C Glutamate GABA
+CNQX & AP-V +CNQX & AP-V +CNQX & AP-V
Glu Glu Glu Glu GABA GABA
Amplitude (pA)
AMPA NMDA GABAA Figure 2. Spontaneous EPSCs from NMc neurons. (A) Example traces of sEPSCs without blocking
AMPA-Rs and GABAA-Rs. (B) AMPA-R mediated sEPSCs or (C) GABAA-R mediated sEPSCs. Violin
Receptor Receptor Receptor plots comparing sEPSCs frequency (D) or sEPSCs amplitude (E) during the three conditions .
sEPSCs Correlations
Figure 1. Structure and function of NMc neurons. (A) NMc neurons receive multiple synaptic
inputs onto their dendrites and soma, unlike traditional adendritic NM neurons which receive 1-2
A B
sEPSC Amplitude (pA)
sEPSC Frequency (#)
large Endbulb of Held synapses. (B) NMc neurons are more excitable, have a lower threshold for AP Figure 5: GABAA-R mediated sEPSCs from a NMc neuron. Example traces acquired before (A),
firing and are more depolarized compared to traditional NM neurons. (C) Schematic of the during (B), and after (C) bath application of PTX (GABAA-R blocker). (B) Average amplitude before and
neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA, and the postsynaptic receptors they bind to. Figure 1 (A & after GABAA-R blocker. Error bars = standard error of the mean.
B) adopted from Hong and Sanchez (2018), Journal of Experimental Neuroscience.
Conclusions
Method
1. sEPSCs of NMc neurons are mediated by AMPA-Rs and GABAA-Rs.
Whole-cell voltage clamp recordings were obtained from domesticated
C
sEPSC Frequency (#)
chickens at embryonic (E) days E19-E21. Spontaneous postsynaptic
2. Frequency and amplitude of sEPSCs were not correlated with low voltage
excitatory currents (sEPSCs) were recorded by voltage clamping neurons
activated potassium currents (LVAK+), suggesting that spontaneous
near their resting membrane potential (-60 mV) for 2 minutes. Synaptic
synaptic activity is not related to intrinsic excitability.
transmission through AMPA-Rs and GABAA-Rs were blocked depending on
which synaptic currents were isolated and studied. sEPSC properties were
3. sEPSC frequency and amplitude were correlated, suggesting that more
recorded and analyzed before, during, and after bath application of CNQX
synaptic events have larger average amplitudes.
(AMPA-R blocker), or PTX (GABAA-R blocker). NMDA-Rs were blocked with sEPSC Amplitude (pA)
AP-V to isolate the other currents. Data reported are from 19 NMc neurons.
Figure 3. Correlations of sEPSC frequency, amplitude and low voltage activated potassium 4. Spontaneous AMPA and GABA neurotransmission suggests that NMc
Funding: NIH, NIDCD R01 DC017167 & R03 DC013841 (JTS) current (LVAK+). The relationship of sEPSC frequency (A) and amplitude (B) as a function of LVAK+ synaptic inputs are complex and specialized.
School of Communication and The Knowles Hearing Research Center, Northwestern University was not significant. (C) The relationship between sEPSC frequency and amplitude was significant.
You might also like
- Print Vol 18Document122 pagesPrint Vol 18nurjNo ratings yet
- Fake Love Need Not Apply by Chantal HeideDocument111 pagesFake Love Need Not Apply by Chantal HeideMigena DanushiNo ratings yet
- DCN Design Solution For TATA Optical NetworkDocument19 pagesDCN Design Solution For TATA Optical NetworkAnkur ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPaper Chromatography Lab ReportGeraldineMay50% (2)
- Amyloid Plaque and Neurofibrillary Tangle Formation in Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument2 pagesAmyloid Plaque and Neurofibrillary Tangle Formation in Alzheimer's DiseaseMelanieNo ratings yet
- Https - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 15 Fly Alzh Ref m096 Eng 00 Alzheimers PW Handout DigitalDocument2 pagesHttps - Learn - Cellsignal.com - Hubfs - Pdfs - 15 Fly Alzh Ref m096 Eng 00 Alzheimers PW Handout DigitaltamaraNo ratings yet
- Synaptic Amplification in Motoneurons Computational and Mechanistic ImplicationsDocument3 pagesSynaptic Amplification in Motoneurons Computational and Mechanistic ImplicationsdagushNo ratings yet
- Poster Complet v2Document1 pagePoster Complet v2SANVITTAYAGUL PronsagornNo ratings yet
- Forming The Rna Strand: Chapter 12 BiochemistryDocument4 pagesForming The Rna Strand: Chapter 12 BiochemistrySerin Puji AstutiNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Noise Energy To Electrical Energy Via Acoustic Metamaterial Coupled Quarter Wavelength Resonator May 2022Document4 pagesConversion of Noise Energy To Electrical Energy Via Acoustic Metamaterial Coupled Quarter Wavelength Resonator May 2022Angelica Auguis CañeteNo ratings yet
- 3A Aiški BiosintezėDocument1 page3A Aiški BiosintezėMonika LožytėNo ratings yet
- NullDocument1 pageNullapi-16525854No ratings yet
- Nuclear Receptors: G-Protein CoupledDocument2 pagesNuclear Receptors: G-Protein CoupledJordan DouglasNo ratings yet
- Euroline Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Antigen Profi Les: Examples of Antigen CombinationsDocument1 pageEuroline Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Antigen Profi Les: Examples of Antigen CombinationsNéfer TitiNo ratings yet
- A Common Neural Circuit Mechanism For Internally GDocument14 pagesA Common Neural Circuit Mechanism For Internally GArie AnggaNo ratings yet
- Serotonin and Its Role in PsychiatryDocument46 pagesSerotonin and Its Role in PsychiatryAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Print PDFDocument11 pagesPrint PDFFe CasarolliNo ratings yet
- Euroline Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Antigen Profi Les: Examples of Antigen CombinationsDocument1 pageEuroline Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Antigen Profi Les: Examples of Antigen CombinationsRiskullah MakmurNo ratings yet
- 2006-Slicer and The ArgonautesDocument8 pages2006-Slicer and The ArgonautesJorge Hantar Touma LazoNo ratings yet
- ABI Prism 7000 Sequence Detection System User Guide - 2Document74 pagesABI Prism 7000 Sequence Detection System User Guide - 2Aqwin PolosoroNo ratings yet
- Transmitter PropertiesDocument1 pageTransmitter PropertiesNaveed PashaNo ratings yet
- Gamma Radiation: Types Radiation Produced by Radioactive DecayDocument2 pagesGamma Radiation: Types Radiation Produced by Radioactive DecaykingstonNo ratings yet
- Sistem Saraf Otononm: Afrisusnawati RaufDocument44 pagesSistem Saraf Otononm: Afrisusnawati Raufsuci amirNo ratings yet
- RNa Pol & PromotersDocument12 pagesRNa Pol & Promotersfazila zahoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Assignment 4Document2 pagesChapter 1 Assignment 4nabihazonabNo ratings yet
- Ficsher 2Document15 pagesFicsher 2ryan.chow.95No ratings yet
- B22 Neural Mechanisms of Learning & MemoryDocument21 pagesB22 Neural Mechanisms of Learning & MemoryNilanjana Chatterjee ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Cell Edge User Discussion: PerformanceDocument10 pagesCell Edge User Discussion: PerformanceBagoes SidhartaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Do RNA Na CélulaDocument45 pagesAtlas Do RNA Na Célulailc67123No ratings yet
- The Scientist - Winter 2023Document92 pagesThe Scientist - Winter 2023Martha LopushynskaNo ratings yet
- NT Release PPCNS 2023Document16 pagesNT Release PPCNS 2023Yasmin Sophia MNo ratings yet
- Filters in RadiographyDocument1 pageFilters in RadiographykingstonNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation Review Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesTranscription and Translation Review Lesson PlanjaneyzhouNo ratings yet
- Brochure CS 2500Document4 pagesBrochure CS 2500SuciNo ratings yet
- NHB SuppoDocument11 pagesNHB SuppoAna-Roberta NitaNo ratings yet
- Cells MMDocument1 pageCells MMShahzad KhurramNo ratings yet
- Formation of Initiation Complex: Po Ly-A Ly - ADocument1 pageFormation of Initiation Complex: Po Ly-A Ly - Areno rajagukgukNo ratings yet
- First Time User Guide To PN Junction V1.31: Network For Computational Nanotechnology (NCN)Document16 pagesFirst Time User Guide To PN Junction V1.31: Network For Computational Nanotechnology (NCN)G.R.Mahendrababau AP - ECE departmentNo ratings yet
- First Time User Guide To PN Junction V1.31: Network For Computational Nanotechnology (NCN)Document16 pagesFirst Time User Guide To PN Junction V1.31: Network For Computational Nanotechnology (NCN)Amey JadhavNo ratings yet
- 1986-Pacific-Sierra-Accurate Laboratory Boresight Alignment of Transmitter Receiver Optical AxesDocument8 pages1986-Pacific-Sierra-Accurate Laboratory Boresight Alignment of Transmitter Receiver Optical AxesLK DAINo ratings yet
- ANCA PosterDocument1 pageANCA PostervemalNo ratings yet
- RNA-seq Bioinformatics: Format and QC of Short ReadsDocument37 pagesRNA-seq Bioinformatics: Format and QC of Short ReadsManovriti ThakurNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument12 pagesBiomoleculesPRADEEP CNo ratings yet
- Synapses: Department of Mathematical SciencesDocument7 pagesSynapses: Department of Mathematical SciencesilincaNo ratings yet
- Peg 4Document1 pagePeg 4api-197110397No ratings yet
- Technological Advances in Synthetic Biology: Subhayu BasuDocument33 pagesTechnological Advances in Synthetic Biology: Subhayu Basuapi-26720455No ratings yet
- Major Brain Regions and Their Major Interconnections (김Document2 pagesMajor Brain Regions and Their Major Interconnections (김신윤상0% (1)
- Experiment 1 InstructionsDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 InstructionsWhitney BlanchatNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi SSPDocument108 pagesFisiologi SSPhusna aninda farahitaNo ratings yet
- By Dr. AlabastroDocument9 pagesBy Dr. Alabastro2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Echo Reference Card 2011Document2 pagesEcho Reference Card 2011Aleksandar MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- CNS Drugs PharmacologyDocument8 pagesCNS Drugs PharmacologyAenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0306452214009932 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0306452214009932 MainRubén Alcalá ArgüellesNo ratings yet
- Cmi Biacoret200 Getting StartedDocument8 pagesCmi Biacoret200 Getting StartedÖzge ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Caffeine Has A Dual Influence On NMDA Receptor-Mediated Glutamatergic Transmission at The HippocampusDocument16 pagesCaffeine Has A Dual Influence On NMDA Receptor-Mediated Glutamatergic Transmission at The HippocampusSolisNo ratings yet
- 24 Short - Term - Depression - TC FFI - Optional PDFDocument9 pages24 Short - Term - Depression - TC FFI - Optional PDFThe Panda EntertainerNo ratings yet
- Radio TV Experimenter 1965-02-03Document132 pagesRadio TV Experimenter 1965-02-03mplennaNo ratings yet
- 9.K. Hepatite - HIVDocument9 pages9.K. Hepatite - HIVAna MîndrilăNo ratings yet
- DNA TechnologyDocument28 pagesDNA TechnologyJohn NinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TranscriptionDocument2 pagesChapter 3 TranscriptionYuume YuuNo ratings yet
- SM Slides 2upDocument63 pagesSM Slides 2upSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Transmitted Intensity and Linear Attenuation CoefficientDocument3 pagesTransmitted Intensity and Linear Attenuation CoefficientkingstonNo ratings yet
- Power and Disempowerment_Zhang DaniDocument13 pagesPower and Disempowerment_Zhang DaninurjNo ratings yet
- The Rhetoric of Enslavement_ Humanity, Gender, And Recognition in Frankenstein (APA) - Eleen WaffnerDocument14 pagesThe Rhetoric of Enslavement_ Humanity, Gender, And Recognition in Frankenstein (APA) - Eleen WaffnernurjNo ratings yet
- Results Descriptive StatisticsDocument14 pagesResults Descriptive StatisticsnurjNo ratings yet
- Kings, Queens, and Kermit - Lydia WeirDocument7 pagesKings, Queens, and Kermit - Lydia WeirnurjNo ratings yet
- The Rhetoric of Enslavement: Humanity, Gender, and Recognition in Frankenstein (APA) - Eleen WaffnerDocument15 pagesThe Rhetoric of Enslavement: Humanity, Gender, and Recognition in Frankenstein (APA) - Eleen WaffnernurjNo ratings yet
- Deep Brain Stimulation of The Lateral Habenula To Treat Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia - Irene QuanDocument12 pagesDeep Brain Stimulation of The Lateral Habenula To Treat Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia - Irene QuannurjNo ratings yet
- Assessing Blockchain Potential in Healthcare Project Management Through The Colony Dapp - Blockchain Research GroupDocument20 pagesAssessing Blockchain Potential in Healthcare Project Management Through The Colony Dapp - Blockchain Research GroupnurjNo ratings yet
- A Pipeline Flows Both Ways: Contradictions of An Activist Trajectory - Lucy LondonDocument16 pagesA Pipeline Flows Both Ways: Contradictions of An Activist Trajectory - Lucy LondonnurjNo ratings yet
- Apadula Consubstantiation Paper - Emily ApadulaDocument26 pagesApadula Consubstantiation Paper - Emily ApadulanurjNo ratings yet
- NDUFS4, Mir-27b and Cardiac Hypertrophy - Norma MarshallDocument19 pagesNDUFS4, Mir-27b and Cardiac Hypertrophy - Norma MarshallnurjNo ratings yet
- Oliveira Fernanda NURJ Condensed - Fernanda OliveiraDocument12 pagesOliveira Fernanda NURJ Condensed - Fernanda OliveiranurjNo ratings yet
- The Revolutionary Potential of Independent Video Games - Delaney McCallumDocument45 pagesThe Revolutionary Potential of Independent Video Games - Delaney McCallumnurjNo ratings yet
- Rubin Anna NURJ Condensed - Anna RubinDocument19 pagesRubin Anna NURJ Condensed - Anna RubinnurjNo ratings yet
- Khraisheh Kayan NURJ CondensedDocument22 pagesKhraisheh Kayan NURJ CondensednurjNo ratings yet
- Condensed Thesis - Brian VogelDocument15 pagesCondensed Thesis - Brian VogelnurjNo ratings yet
- Kubis - Kendall - NURJ - Food As Power, Growing As ResistanceDocument12 pagesKubis - Kendall - NURJ - Food As Power, Growing As ResistancenurjNo ratings yet
- Jacob WiesenthalDocument13 pagesJacob WiesenthalnurjNo ratings yet
- Esperne James NURJ Essay RAND - James EsperneDocument8 pagesEsperne James NURJ Essay RAND - James EspernenurjNo ratings yet
- Erdman-Luntz Sierra NURJ Essay Medical Non-Compliance A Structural Issue - Sierra Erdman-LuntzDocument9 pagesErdman-Luntz Sierra NURJ Essay Medical Non-Compliance A Structural Issue - Sierra Erdman-LuntznurjNo ratings yet
- Yale X Nurj OnlineDocument48 pagesYale X Nurj OnlinenurjNo ratings yet
- Harita Duggirala Expo Poster 2 Template .PPTX (1) - Harita DuggiralaDocument1 pageHarita Duggirala Expo Poster 2 Template .PPTX (1) - Harita DuggiralanurjNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of U.S Elections - Emma MansellDocument12 pagesMathematical Modeling of U.S Elections - Emma MansellnurjNo ratings yet
- Irish Language Revitalization in The Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland - Shannon LallyDocument1 pageIrish Language Revitalization in The Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland - Shannon LallynurjNo ratings yet
- EmilyShteynbergExpoPoster - Emily ShteynbergDocument1 pageEmilyShteynbergExpoPoster - Emily ShteynbergnurjNo ratings yet
- DMC PPT - Inaara GangjiDocument26 pagesDMC PPT - Inaara GangjinurjNo ratings yet
- ML Undergraduate Research Symposium Presentation - Madison LuceDocument1 pageML Undergraduate Research Symposium Presentation - Madison LucenurjNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Gap Processing by English Speakers (1) - Abigail ZuercherDocument12 pagesParasitic Gap Processing by English Speakers (1) - Abigail ZuerchernurjNo ratings yet
- Radical Caring Oral Presentation - Chloe WongDocument17 pagesRadical Caring Oral Presentation - Chloe WongnurjNo ratings yet
- Thesis Poster - Meghna GaddamDocument1 pageThesis Poster - Meghna GaddamnurjNo ratings yet
- LAW246 Lecture Notes 4Document3 pagesLAW246 Lecture Notes 4Lita ptr projectNo ratings yet
- Texto Medicina English Oficial-1Document58 pagesTexto Medicina English Oficial-1Alvarez WilNo ratings yet
- Tes Formatif Kelas 9Document2 pagesTes Formatif Kelas 9Masdalyla TinendungNo ratings yet
- Igcse 6677Document20 pagesIgcse 6677Mohamed HNo ratings yet
- Evolutionxii 180730153121 PDFDocument45 pagesEvolutionxii 180730153121 PDFrajaprasad2No ratings yet
- TERM2 NON-FICTION COMPREHENSION WORKSHEET (Paper 1)Document4 pagesTERM2 NON-FICTION COMPREHENSION WORKSHEET (Paper 1)ziad ahmedNo ratings yet
- Gardner Psychoanalysis, Science and CommonsenseDocument22 pagesGardner Psychoanalysis, Science and CommonsenseSebastian GardnerNo ratings yet
- CV Charbel Niño El-Hani: EducationDocument44 pagesCV Charbel Niño El-Hani: EducationHira SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4muhammad syamimNo ratings yet
- Basic 1 Exam 1aDocument3 pagesBasic 1 Exam 1aAdriana Yabar CondoriNo ratings yet
- Company Stem Cell Therapy CelligenicsDocument1 pageCompany Stem Cell Therapy Celligenicsadrian kohNo ratings yet
- Gene SilencingDocument22 pagesGene SilencingDebadrita DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Ekstrak Pasak Bumi PD Prokopulasi Mencit PDFDocument7 pagesEkstrak Pasak Bumi PD Prokopulasi Mencit PDFEndang ListianiNo ratings yet
- CRISPR Technology Principles and ProspectivesDocument99 pagesCRISPR Technology Principles and ProspectivesMostafa100% (1)
- Water PractiseDocument14 pagesWater PractiseAfan MirajNo ratings yet
- Space Dungeon Book II Xenozoa and Uncommon TechnologyDocument56 pagesSpace Dungeon Book II Xenozoa and Uncommon TechnologyJosephNo ratings yet
- Biology Genetic Modification EssayDocument4 pagesBiology Genetic Modification EssayPRANZACTION 2.0No ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4Document12 pagesWeek 3 & 4elbaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Plant Science PDFDocument2 pagesHandbook of Plant Science PDFJoshua GrahitaNo ratings yet
- Alvarez Et Al 2010 Kinetic Analysis and Mathematical Modeling of Growth and Lactic Acid Production of Lactobacillus Casei VarDocument9 pagesAlvarez Et Al 2010 Kinetic Analysis and Mathematical Modeling of Growth and Lactic Acid Production of Lactobacillus Casei VarClaudio Alarcón GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Ix - Nso Set - B Ggn-2Document19 pagesIx - Nso Set - B Ggn-2Priyanka NegiNo ratings yet
- 6-Principles of Automated Haematology AnalyzerDocument27 pages6-Principles of Automated Haematology AnalyzerWasana MendisNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 7A English LearnersDocument268 pagesScience Grade 7A English LearnersDedi Tab S2No ratings yet
- S10 Q3 Enhanced Hybrid Module 6 Week 6 FinalDocument15 pagesS10 Q3 Enhanced Hybrid Module 6 Week 6 Finalace fuentesNo ratings yet
- The History of GeneticsDocument13 pagesThe History of GeneticsClaire DonilaNo ratings yet
- Ojps 6 143Document11 pagesOjps 6 143Nikhitha S NairNo ratings yet
- Presentation Schedule (Dr. Getrude Cosmas)Document4 pagesPresentation Schedule (Dr. Getrude Cosmas)PDPPPJ11021 Rahim Bin RahmanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Millet Bran Derived-Bound Polyphenols in LPS-induced HT-29 Cell Signaling PathwayDocument13 pagesAnti-Inflammatory Effects of Millet Bran Derived-Bound Polyphenols in LPS-induced HT-29 Cell Signaling PathwayKito TongHuiNo ratings yet