Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Application
Uploaded by
Wasim PashaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Application
Uploaded by
Wasim PashaCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Operating System
UNIT 1 OPERATING SYSTEM Structure Page No.
1.0 Introduction 5
1.1 Objectives 6 1.2 Familiarization (I/O Port, Keyboard, Memory) 6
1.2.1 Computer and Motherboard 6
1.2.2 I/O Ports 8
1.2.3 I/O Devices 9
1.2.4 Memory 14
1.3 Windows Operating System 16
1.3.1 Overviews of Windows 16
1.3.2 Windows Installing Procedure 17
1.3.3 Working with XP 25 1.4 Linux Operating System 31
1.4.1 Overview of LUNIX/LINUX Operating System 31
1.4.2 How to install Linux Operating System 32
1.4.3 Linux utilities and Basic Commands 41
1.5 Summary 53 1.6 Answers to Check Your Progress 53
1.0 INTRODUCTION
In this unit, we are going to learn basics of computer. Computer is a machine that performs tasks or
calculations according to a set of instructions, or programs. Compared to those early machines,
today's computers are amazing. Not only are they thousands of times faster, they can fit on your desk,
in your lap, or even in your pocket. Computers work through an interaction of hardware and
software.
Hardware is physical component of a computer system. It is a tiny rectangular chip inside the
computer called the central processing unit (CPU), or microprocessor. It is the "brain" of computer—
the part that translate instructions and performs calculations. Hardware items such as monitor,
keyboard, mouse, printer, and other items are often called hardware devices. Software refers to the
instructions or programs that tell the hardware what to do. The operating system (OS) is system
software that manages computer and the devices connected to it. OS is responsible for management
and coordination of activities and the sharing of the limited resources of computer. The OS acts as a
host for other application software. 6 Lab Course
We will be discussing about two well known operating systems: (a) Windows operating system, and
(b) Linux operating system.
1.1 OBJECTIVES
After going through this unit, you should be able to:
understand about computer and it‘s components;
features of Windows XP;
know the installation procedure of Windows XP;
features of Linux (Fedora);
know the installation procedure of Fedora; and
know the utilities and basic commands of Fedora.
1.2 FAMILIARIZATION WITH I/O PORT, KEYBOARD, MEMORY
Computer plays a key role in how individuals work and how they live. Even the smallest
organizations have computers to help them operate more efficiently, and many individuals use
computers at home for educational, entertainment, and business purposes. Thus you must be familiar
with computers and its components. In the following sub-sections, we will discuss the same and there
is practice session also at the end of this section. Hope you will enjoy this practice session. 1.2.1
Computer and Motherboard Computer : A computer is programmable machine that receives
input, stores, manipulate data, and provides output in a useful format. Computer takes input from
input devices and then compute in CPU and stores in memory and sends output to output devices.
The most common device for input is the keyboard. When you type, you are putting information into
the computer, which is known as input. The most common device for output is the monitor. These
input output devices are connected through I/O Ports. 7 Operating System
Figure 1.1 : Working of Computer A computer system unit contains many parts. As shown in Figure
1.2(a) and Figure 1.2 (b).
Motherboard : The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer. It is also known as the
main board or system board. Typically, the motherboard contains the CPU, BIOS, memory, mass
storage interfaces, serial and parallel ports, expansion slots, and all the controllers required to
control standard peripheral devices, such as the display screen, keyboard, and disk drive.
Collectively, all these chips that reside on the motherboard are known as the motherboard's chipset.
The motherboard can be thought of as the "back bone" of the computer.
Figure 1.2(a) : Overview of Motherboard 8 Lab Course
Figure 1.2 (b) : Detailed Overview of Motherboard CPU : The CPU is the central electronic chip that
contains the processing power of the computer. Today, all CPUs are microprocessors.
1. A microprocessor is a complete computer on a silicon chip.
2. A microprocessor does all of the functions of a computer.
stores data and instructions waiting to be used.
follows changeable instructions.
does input, processing, and output.
Memory : Memory is the part of the computer that temporarily stores applications, documents, and
system operating information. 1.2.2 I/0 Ports In this sub-section, we will study about I/O ports.
Ports and Connectors : A port is a connector located on the motherboard or on a separate adapter.
This we will discuss in following sub section. As shown in figure 1.2 an internal view of some of the
I/O ports. On the back of computers are several I/O (or Input/output) ports. Above, on the very top
are two PS/2 ports, normally used for mouse and keyboard connections. Below that are the USB, (or
Universal Serial Bus), ports. Below those are two serial ports beside a long parallel port that is often
used to connect to a printer. On the bottom right is a game port for joysticks or other game
controllers. On the bottom left is a microphone hook up, a speaker hook up, and an additional hook
up for another sound input device like a musical keyboard. 9 Operating System
Figure 1. 3. I/O Port I/O Output Devices
ports are there to
connect to I/O
devices. There are
various I/O devices
which are discussed in
the next subsection:
1.2.3 I/O Devices Few
I/O devices are given
Table 1.1. Table 1.1 :
I/O Devices Input
Devices
Mouse Monitor
Joystick LCD
Scanner Printer
Light Pen Plotter
You might also like
- Operating System Basics: Hardware, OS, Windows & LinuxDocument51 pagesOperating System Basics: Hardware, OS, Windows & LinuxNikitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 Computer CmponentsDocument12 pagesLesson 02 Computer CmponentsDBZ sTAR100% (1)
- Computer HardwareDocument90 pagesComputer HardwareKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 MaterialDocument168 pagesUNIT 1 MaterialSancarapu NagarajuNo ratings yet
- 12 5 2023 ClassDocument8 pages12 5 2023 Classbokuwaaho9904No ratings yet
- Intro Module 1 20170101Document18 pagesIntro Module 1 20170101AshlynNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Document32 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)poo235No ratings yet
- T Is A Computer Harware Softwares Fundamentals and PartsDocument21 pagesT Is A Computer Harware Softwares Fundamentals and Partslhieeyhan77No ratings yet
- CM Lab ManualDocument111 pagesCM Lab ManualkamalsmanekNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument9 pagesComputer Organizationstfu.dNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER APPLICATION I - Lesson 3Document11 pagesCOMPUTER APPLICATION I - Lesson 3Hack FinNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IT - 5Document51 pagesAssignment - IT - 5AanchalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document48 pagesUnit 1Sancarapu NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Computer essentials explainedDocument8 pagesComputer essentials explainedShaima AbdulazimNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Introducing Hardware)Document4 pagesChapter One (Introducing Hardware)Siti Fatimah ZulkipliNo ratings yet
- CIT 001 _ Fundamentals of Computer SystemDocument293 pagesCIT 001 _ Fundamentals of Computer SystememailforroughasvrsunoffNo ratings yet
- CIT-001 Full BookDocument293 pagesCIT-001 Full BookLearningScienceNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Main Components of a Personal ComputerDocument30 pagesIntroduction to the Main Components of a Personal Computersachin mrcoolNo ratings yet
- Basic concepts of computers explainedDocument32 pagesBasic concepts of computers explainedabhi_txt90No ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Hardware and Software ComponentsDocument14 pagesIntroduction to Computer Hardware and Software ComponentsAchsah S. ThomasNo ratings yet
- MS Office 2007 - NotesDocument89 pagesMS Office 2007 - NotesmanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure and Functions of a ComputerDocument12 pagesBasic Structure and Functions of a ComputerPRITAM BASUNo ratings yet
- HARDWARE AND NETWORKING PresentationDocument26 pagesHARDWARE AND NETWORKING PresentationhybinjosephNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and NetworkDocument51 pagesComputer Hardware and Networkprashantkumarmuz2004No ratings yet
- Fundamentals (Final1)Document34 pagesFundamentals (Final1)Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- FCPIT Practical FileDocument78 pagesFCPIT Practical Filekaushal2442100% (1)
- Comfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsDocument199 pagesComfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsRhdheh BdhehenNo ratings yet
- Computer Appreciation: Designed by Legitimate ICTDocument16 pagesComputer Appreciation: Designed by Legitimate ICTMiracle UchechukwuNo ratings yet
- 7 - 8 CSS - WK 4-5 Computer System - Jesucrtina NimenzoDocument8 pages7 - 8 CSS - WK 4-5 Computer System - Jesucrtina NimenzoEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure of Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument16 pagesBasic Structure of Computer Hardware and SoftwareEASSA0% (1)
- Software: IT WorkshopDocument12 pagesSoftware: IT WorkshopAnjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Concept of ComputerDocument47 pagesConcept of ComputerAbdullah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Overview of A Computer System.Document32 pagesOverview of A Computer System.grenamoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.1 in ICTDocument3 pagesActivity 2.1 in ICTLedor NapadlabNo ratings yet
- LAB 01-Introduction To Computers-1-7Document7 pagesLAB 01-Introduction To Computers-1-7Mallika Dog54No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Computer Perter NortonDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Computer Perter NortonBilal Hassan0% (1)
- MODULE 1: Parts and Functions of Computers Basic Parts of ComputerDocument31 pagesMODULE 1: Parts and Functions of Computers Basic Parts of ComputerSophia Shannon D. DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer and Computer TroubleshootingDocument15 pagesBasics of Computer and Computer Troubleshootingchibssa alemayehuNo ratings yet
- It 1-5Document108 pagesIt 1-5Shruthi DyavegowdaNo ratings yet
- BSA 1 TrainingDocument305 pagesBSA 1 TrainingSrinidhi RaoNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading NotesDocument101 pages1st Grading NotesSophia Shannon D. DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computers and Programming Lesson 1Document31 pagesIntroduction to Computers and Programming Lesson 1Krizaleih QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Lasu CSC 111 Notes - 1Document25 pagesLasu CSC 111 Notes - 1Oluwatoyin TobiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document36 pagesModule 1Ankit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bab IiiDocument84 pagesBab Iiifajarbanurea3No ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument13 pagesComputer Applications.sujatha100% (1)
- FCPC NotesDocument147 pagesFCPC Notesspeed_a5987100% (1)
- A Digital Computer System (DCS) : HardwareDocument36 pagesA Digital Computer System (DCS) : HardwareMădălin NiculescuNo ratings yet
- Hardware ComponentsDocument13 pagesHardware ComponentsMega PuspiytaNo ratings yet
- 1 Computers FundamentalsDocument13 pages1 Computers Fundamentalsdevil's doubleNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Digital DevicesDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Digital DevicesGovardhanan RayanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Meeting 2: Following Question 1 - 3Document4 pagesExercise Meeting 2: Following Question 1 - 3Rafael BilliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hardware and Software Lecture Note - 1Document36 pagesIntroduction To Hardware and Software Lecture Note - 1ernestafriyie04No ratings yet
- Icf 7 Module Second QuarterDocument24 pagesIcf 7 Module Second QuarterKazandra Cassidy Garcia100% (1)
- Part 1 Computer Software Application ModuleDocument56 pagesPart 1 Computer Software Application ModuleJenny Mae OrillaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Programming Module 1ADocument27 pagesIntro To Programming Module 1AChristian KingawNo ratings yet
- How computer software helps run hardware componentsDocument6 pagesHow computer software helps run hardware componentsRavi Mohan BhattNo ratings yet
- Byte 1979 08Document268 pagesByte 1979 08Viliux Y (viliux80)No ratings yet
- CS 2006 (Coa) - CS - End - May - 2023Document14 pagesCS 2006 (Coa) - CS - End - May - 2023223UTKARSH TRIVEDINo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organization Presented by Mr.P.Prashan T Ap/AimlDocument365 pagesComputer Architecture and Organization Presented by Mr.P.Prashan T Ap/AimlPrashant PiseNo ratings yet
- Mpi V Sem It Guess Paper SolutionsDocument52 pagesMpi V Sem It Guess Paper Solutionshofehag577No ratings yet
- MsinfologDocument274 pagesMsinfologLep LepNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers and ApplicationsDocument228 pagesMicrocontrollers and ApplicationsGovinda Prasad AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Et 3491 Unit-1 Part 1Document107 pagesEt 3491 Unit-1 Part 1anbarasudhandapani100% (1)
- Os Chapter 12Document11 pagesOs Chapter 12varnits30No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document283 pagesChapter 3Biruk DawitNo ratings yet
- FMM Unit-1Document28 pagesFMM Unit-1CS ENo ratings yet
- Programming Manual: Programmable ControllerDocument257 pagesProgramming Manual: Programmable ControllerCRISENTENANo ratings yet
- F MC-16LX MB90385 Series Hardware Manual: 16-Bit MicrocontrollerDocument652 pagesF MC-16LX MB90385 Series Hardware Manual: 16-Bit MicrocontrollerAndrew IvanovNo ratings yet
- Sys InfoDocument232 pagesSys InfoИван СтояновNo ratings yet
- 0049 (Ec 506)Document2 pages0049 (Ec 506)DiyaNo ratings yet
- UPD78F9116A NECElectronicsDocument263 pagesUPD78F9116A NECElectronicsO6U Pharmacy RecordingsNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument28 pagesUntitled Documentrobymuiruri42No ratings yet
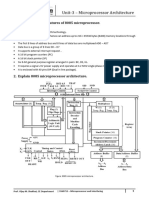
- Microprocessor and Its Applications - Bridge Cource MaterialDocument15 pagesMicroprocessor and Its Applications - Bridge Cource Materialsanchiga nandhiniNo ratings yet
- CSE312 Sınav Öncesi TekrarDocument27 pagesCSE312 Sınav Öncesi TekraraktarmamailimNo ratings yet
- Terms ICT 1Document27 pagesTerms ICT 1Quỳnh Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CS401 Solved Subjective Final Term by JunaidDocument25 pagesCS401 Solved Subjective Final Term by Junaidasimtoqeer458No ratings yet
- 100 Embedded Interview QuestionsDocument107 pages100 Embedded Interview Questionsakshantz ekkaNo ratings yet
- Memory-Mapped I ODocument5 pagesMemory-Mapped I O翁銘禧No ratings yet
- An 0819Document6 pagesAn 0819Nandish HsNo ratings yet
- MPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-3 13052022115048AMDocument15 pagesMPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-3 13052022115048AMmailsender787No ratings yet
- Es 301 - MpiDocument1 pageEs 301 - MpiISHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Module VDocument41 pagesModule VAryan JainNo ratings yet
- CH07 Input OutputDocument36 pagesCH07 Input OutputNguyen Phuc Nam Giang (K18 HL)No ratings yet
- Orin-TRM DP10508002v1.1pDocument8,752 pagesOrin-TRM DP10508002v1.1pĐồng RyanNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting: Self Diagnosis FunctionDocument28 pagesTrouble Shooting: Self Diagnosis FunctionamadhamballyNo ratings yet
- Advance Microprocessor HandoutDocument87 pagesAdvance Microprocessor HandoutytbarekukNo ratings yet