Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Summary
Chemistry Summary
Uploaded by
Adele Smyth HarrisCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Summary
Chemistry Summary
Uploaded by
Adele Smyth HarrisCopyright:
Available Formats
Essential Anatomy & Physiology
Chemistry Summary
Atoms are the smallest and simplest units of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction.
Atoms consist of protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral) and electrons (negatively
charged).
Atoms combine to form a molecule.
Molecules containing atoms of only one kind are called elements.
Molecules containing atoms of different kinds are called compounds.
Organic compounds contain carbon. The four main groups are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
and nucleic acids.
Water is the most abundant inorganic compound.
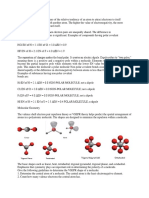
Atoms can bond with each other by accepting, giving up or sharing electrons.
Atoms with either a negative or positive charge are called ions.
Ionic bonds are formed when atoms either accept or give up an electron(s).
Covalent bonds are created when atoms share one, two or three pairs of electrons.
Hydrogen bonds are formed by electrostatic forces between molecules.
When inorganic compounds dissolve in water their atoms dissociate. This process is called
ionization.
Acids dissociate to form an excess of positively charged hydrogen ions and therefore create
an acidic solution.
Bases dissociate to form an excess of negatively charged hydroxide ions and therefore create
an alkaline solution.
Salts dissociate to form neither hydrogen ions nor hydroxide ions.
Acidity/alkalinity is measured on the pH scale.
pH0 represents the extreme of acidity.
pH14 represents the extreme of alkalinity.
The pH of pure water is 7.
Copyright © 2022 Essential Training Solutions Ltd
You might also like
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- CH 02 Outline and Summary NotesDocument8 pagesCH 02 Outline and Summary NotesDaniel PerezNo ratings yet
- Ejara Zge4301 M2act1Document4 pagesEjara Zge4301 M2act1JAMAICA EJARANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes and WorksheetsDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Notes and WorksheetsConner ChingNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman 032191855X 9780321918550Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman 032191855X 9780321918550kimberlyandersonypjkomeifs100% (24)
- Solution Manual For Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4Th Edition Bauman 032191855X 9780321918550 Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesSolution Manual For Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4Th Edition Bauman 032191855X 9780321918550 Full Chapter PDFherbert.lopez868100% (15)
- Lecture 2Document9 pagesLecture 2hfzyahmd613No ratings yet
- 09/098 Bio NotesDocument3 pages09/098 Bio NotesNaomi SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Basic ChemistryClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesPhysical Science 2nd QuarterAngelica C. BramajeNo ratings yet
- EfB 2 - The Chemistry of LifeDocument11 pagesEfB 2 - The Chemistry of LifeOkti An Naafi'uNo ratings yet
- Science Notes q2Document8 pagesScience Notes q2itohtomoka017No ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Review: Earth and Space ScienceDocument48 pagesBasic Chemistry Review: Earth and Space SciencefluronineNo ratings yet
- Advbio CH 2 Student Notes 13-14Document4 pagesAdvbio CH 2 Student Notes 13-14Mary MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GlossaryDocument7 pagesChemistry GlossarygialuanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ch. 2 NotesDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Ch. 2 Notesanthony.brown2No ratings yet
- Review - Expt. 1 - Ionic - Molecular CompoundsDocument1 pageReview - Expt. 1 - Ionic - Molecular CompoundsKaren Joy MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- A. Chemical Composition of The BodyDocument15 pagesA. Chemical Composition of The BodyShumail JANNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manual PDFvespersroyalist.mjdj100% (5)
- GagoDocument5 pagesGagoJon JoeruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 WorkbookDocument12 pagesChapter 2 WorkbookChantelle LemieuxNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument40 pagesAtoms and MoleculesJeemCarloFagelaPulaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabDocument1 pageProperties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabKevonSingh1No ratings yet
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life 1Document4 pagesChemistry of Life 1batuhanNo ratings yet
- BIO-103 Section 5 Chemistry of Life: Date: 23 Feb 2021 Preyanka - Nath@northsouth - EduDocument29 pagesBIO-103 Section 5 Chemistry of Life: Date: 23 Feb 2021 Preyanka - Nath@northsouth - EduSamiun Mazumder ChayanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael WindelspechtDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspechtoverspinmeetklac40100% (48)
- Full Download Solution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht PDF Full Chaptergabertconsomme.gygy100% (18)
- Basics of InorganicDocument2 pagesBasics of Inorganicsaqibkhanhanfi5070No ratings yet
- Appendix E - Polarity WorksheetDocument3 pagesAppendix E - Polarity WorksheetshafferjfNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument8 pagesThe Chemistry of LifeAda Gay Olandia Serencio0% (1)
- Chapter2Atoms, Molecules, & LifeDocument18 pagesChapter2Atoms, Molecules, & LifeJohn Carlo AwarayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter2Atoms, Molecules, & LifeDocument18 pagesChapter2Atoms, Molecules, & LifeJohn Carlo AwarayanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesMd TaaseenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document53 pagesLecture 2Hà Nguyễn Thị ViệtNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Chemistry NotesDocument19 pagesBonding in Chemistry Notesteacher_555No ratings yet
- AP Biology Midterm Study GuideDocument3 pagesAP Biology Midterm Study GuideCleopatra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of LifeDocument4 pagesChemicals of LifeZoeNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 Chemistry of LifeDocument5 pagesQuiz 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 Chemistry of LifenadiaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document23 pagesActivity 1KassyKasNo ratings yet
- 940 Elements Compounds MixturesDocument33 pages940 Elements Compounds MixturesEllen Grace Aguirre TobezaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Review (Students)Document16 pagesBasic Chemistry Review (Students)AnilovRozovaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manualinkleunsevensymdy100% (41)
- 2 1 OverviewDocument34 pages2 1 Overviewapi-262378640No ratings yet
- Full Download Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterglumpyperuke.zb26k100% (15)
- Lecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023Document48 pagesLecture 1 - Basic Chemistry, Carbon, Macromolecules 2023PPNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Chemistry Unit 1 by Sir Mehmood AhmedDocument43 pagesBasic Concepts in Chemistry Unit 1 by Sir Mehmood AhmedKhurram Paul100% (2)
- Introduction To Biochemistry FinalDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry FinalOpoka John ModiNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 2Document4 pagesAP Biology Outline - Chapter 2Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Bonding Grade 9Document12 pagesCoordinate Bonding Grade 9Vipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry VocabularyDocument3 pagesChemistry VocabularybluepixarlampNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Chemical Elements Water 22-23Document42 pages1.1. Chemical Elements Water 22-23Guillem DehesaNo ratings yet
- Presentation C.elementsDocument17 pagesPresentation C.elementsEsterkaKraljikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic ChemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Basic ChemistryHannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- General Concepts of BasesDocument2 pagesGeneral Concepts of BasesMargaretNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts: Elements, Atoms, Isotopes Etc. Chemical Formulas, Chemical Bonds Solutions, Concentrations, PHDocument120 pagesKey Concepts: Elements, Atoms, Isotopes Etc. Chemical Formulas, Chemical Bonds Solutions, Concentrations, PHKrap AynosNo ratings yet
- BIOL100, Prof Adrienne Alaie: Fall 2010Document118 pagesBIOL100, Prof Adrienne Alaie: Fall 2010Barukh B. Rohde0% (1)
- Chemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesChemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionsgibbsNo ratings yet
- Adge G4 ReportDocument50 pagesAdge G4 ReportJayson DoceNo ratings yet